AI can make your SEO efforts faster, better, and more fun—if you know how to use it.
Here are 14 practical ways to get faster, more efficient SEO results with help from your robot overlords friends.
To use AI in the best way (and avoid the mistakes many people make), it helps to understand what we mean when we talk about “AI”. Here’s everything you need to know about AI, in under 60 seconds:
- When people talk about “AI” today, they generally mean generative AI: software ****** that can create text or images. ChatGPT is the most popular tool.
- Generative AI works like a super-powerful autocomplete. It has “read” billions of documents and is very good at creating similar documents in response to your prompts.
- Generative AI is very good at summarizing information, short-form writing, and sounding confident. It’s bad at math, consistency, and anything that involves understanding the “bigger picture” (like writing an SEO strategy for your particular company).
- AI generally doesn’t tell you when it’s misunderstood your question, can’t do what you’ve asked, or doesn’t have the right data available—so treat all of its answers with healthy skepticism.
With those ideas lodged in your brain, let’s look at how you can use AI tools for faster, better SEO.
AI is great for brainstorming keyword ideas and helping you to understand precisely what searchers need when they search for a particular keyword.
Suggest seed keywords
“Seed” keywords are words and phrases related to your business that you can use as the starting point for keyword research.
Pick a starting topic and ask AI to suggest related keywords: sub-topics, questions, similar concepts, you name it.

Take your list of ideas, plug them into a keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer, and you can quickly see the estimated traffic potential and Keyword Difficulty for each of these terms:
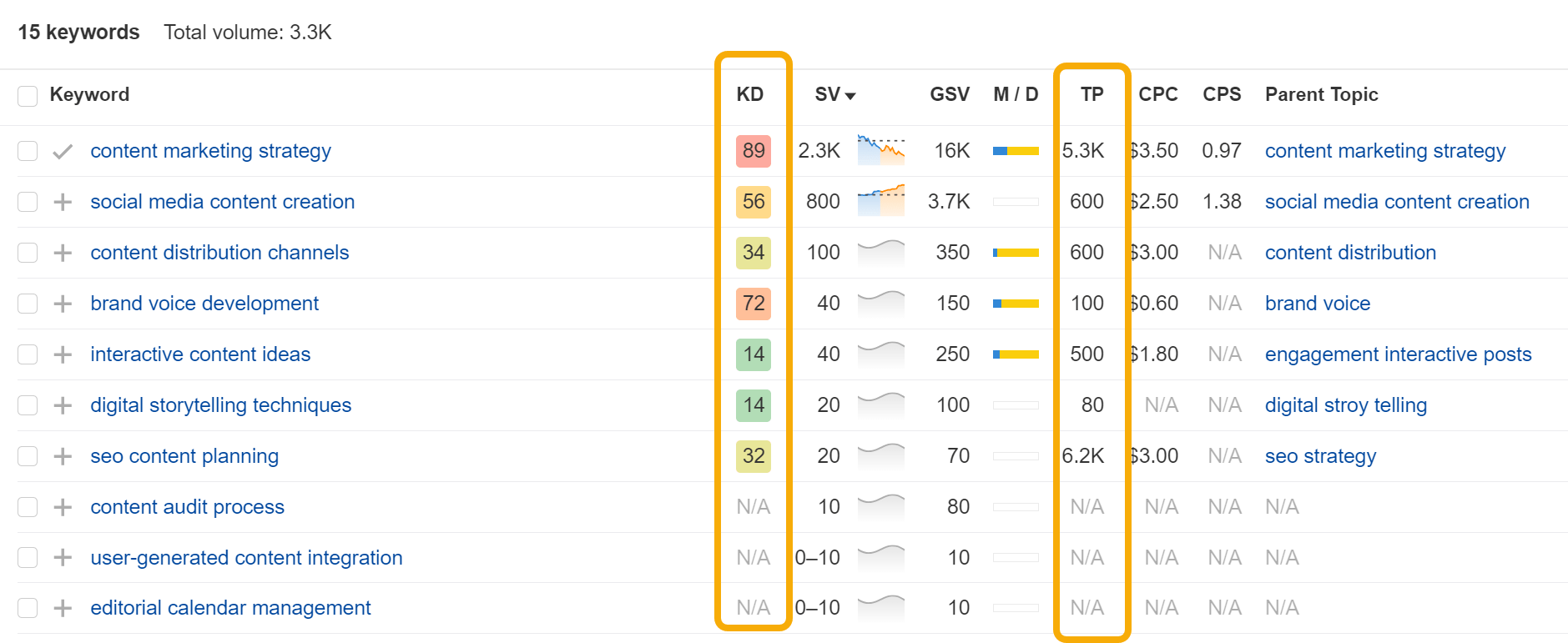
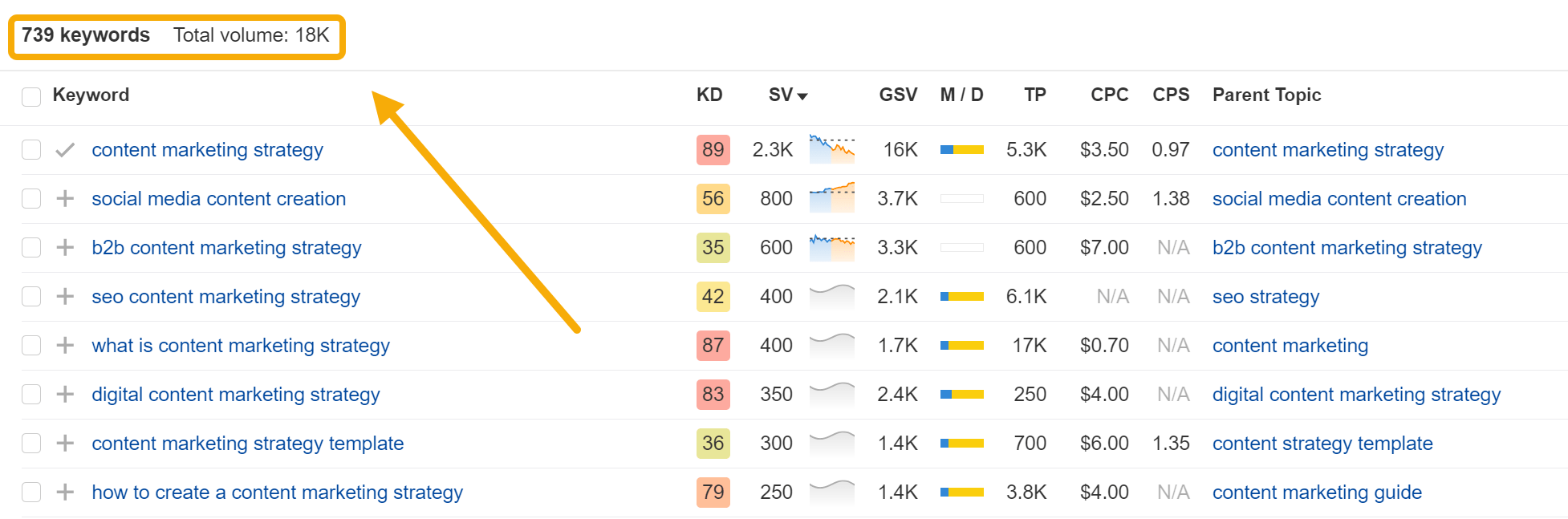
Not all of these seed keywords will have meaningful volume, but that’s okay. Switch to the Matching terms or Related terms tabs, and you’ll see hundreds more related keywords that do:
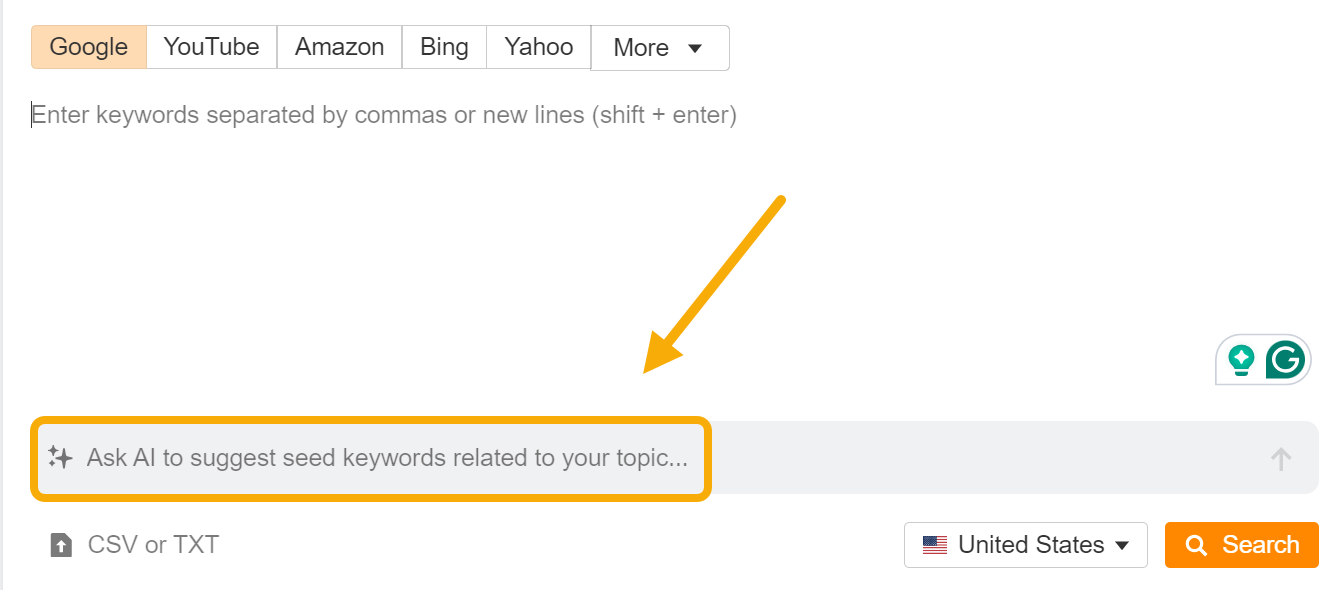
You can even skip the ChatGPT part entirely and use the built-in AI suggestion feature in Keywords Explorer:
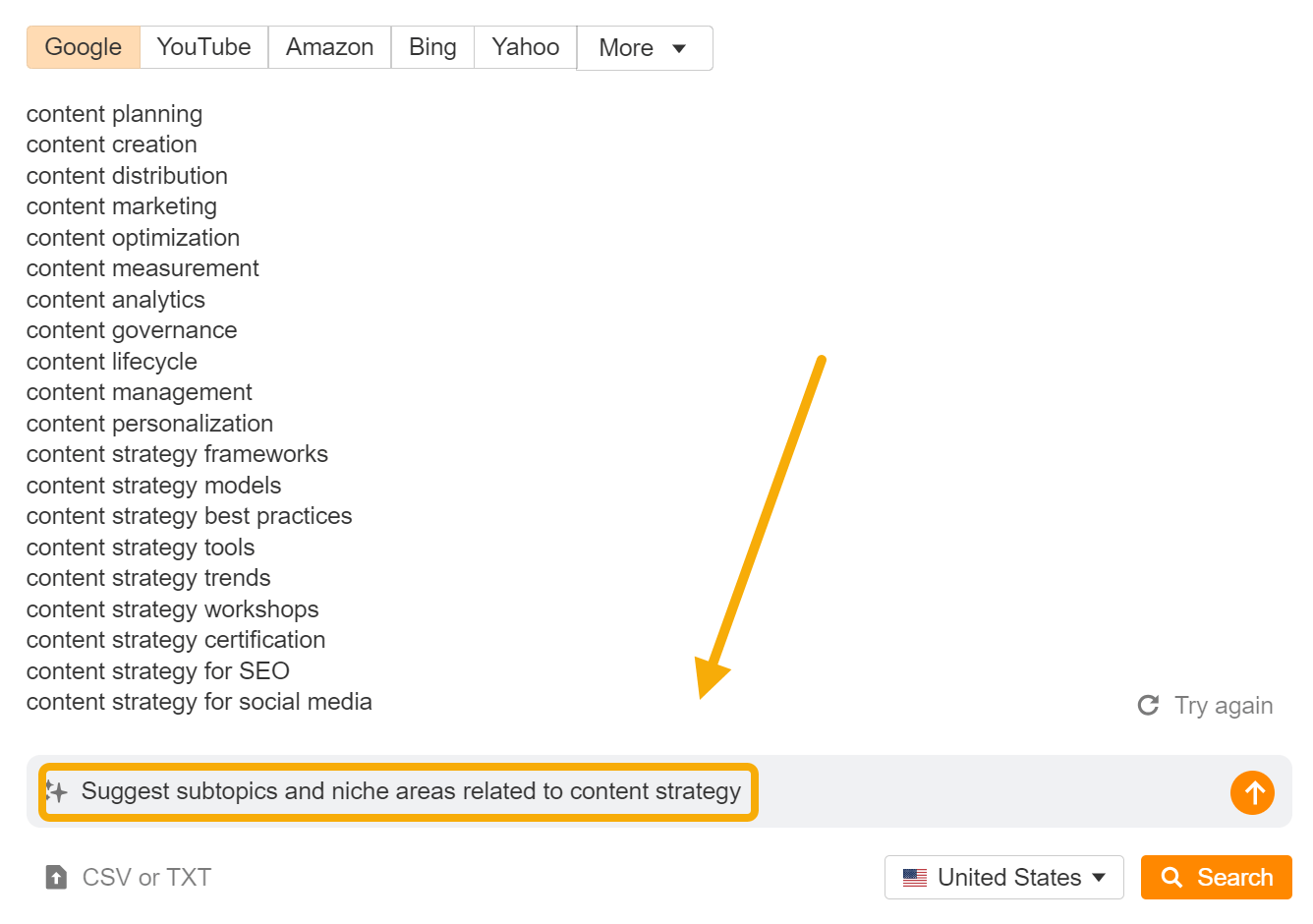
Here, our AI copilot has brainstormed “subtopics and niche areas” related to our core topic, content strategy:
Sidenote.
Don’t trust any volume or difficulty numbers AI gives you. Tools like ChatGPT don’t have access to actual keyword data—but they can hallucinate and make numbers up. If you want real data, you’ll need a keyword research tool like Ahrefs.
Analyze SERP intent
AI can help you understand the different types of search intent present in a particular SERP (search engine results page).
This can be useful for working out which type of content you need to create to match the dominant intent (do searchers want an informational guide, or a free tool?).
In the example below, I copy/pasted page titles from the SERP for the keyword “LLM” and asked ChatGPT to categorize them by the different intent types present:

After a little cajoling and refining, ChatGPT grouped the titles into a few different categories, like definitional (explaining what an LLM is) and comparative (comparing different types of AI ******):

You can take this process to the next level with the Identify intents feature in Ahrefs. For your given keyword, scroll to the SERP overview report, and hit the “Identify intents” button:
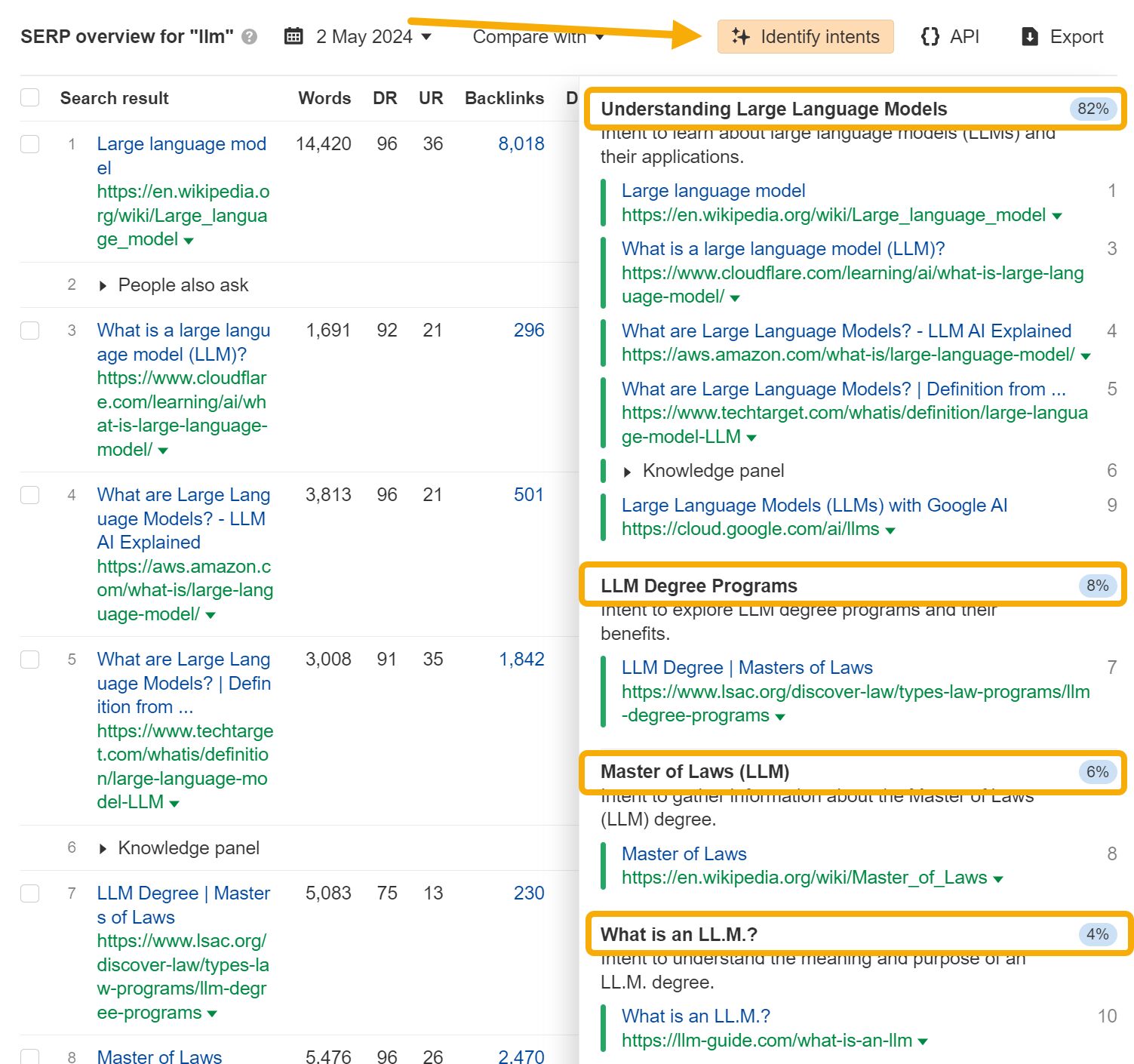
This has the benefit of also showing you the percentage of total estimated traffic each intent receives.
In this example, with 82% of traffic, it makes sense to target the keyword “llm” with a definitional article about LLMs, and ignore the lower traffic intent associated with LLM degree programs.
AI can be used to pump out complete articles, but you’ll get better results—and have less risk of a Google penalty—if you use it like a creative sparring partner for your content creation process.
Brainstorm titles and headers
Titles and headers have a crucial indirect role in SEO by encouraging readers to actually click and read through your content. AI can dramatically speed up the process of brainstorming titles and headers.
Here, I’ve pasted the content of my latest blog post into ChatGPT and asked it to suggest title ideas:

I generally don’t use these ideas verbatim, but ChatGPT regularly generates words or phrases that make their way into my finished titles.
You can also use our free blog post title generator in the same way. Just describe your topic, choose the writing tone, and hit “generate”:

You can modify and create new ideas at the click of a button:

Check grammar
AI is great for checking writing for grammar mistakes. Here, I’ve pasted an article paragraph into our free AI grammar checker…

…and a moment later, AI has flagged two possible issues for me to resolve:

Edit transcripts
Maybe you’ve interviewed an expert and want to add their quotes and experience into your search content. Or maybe your team has created a YouTube video that you’d like to repurpose into a keyword-targeted article.
In either case, you can use AI to tidy up and correctly format transcripts, making it much easier to pull out quotes and ideas.
In this example, I’ve asked ChatGPT to correct a free (and error-prone) transcript from a YouTube video:

And here’s the edited version, complete with correctly capitalized brand names, removed typos, and grammatically correct punctuation:

SEO is a never-ending process, and AI can be a useful tool for speeding up some of the ongoing optimization tasks you’ll need to make to keep your pages ranking.
Add missing topics
One way to improve search content’s performance is to ensure that it includes important information that the searcher needs. Common sense can be a useful guide, asking yourself “which topics am I missing?”—but AI can help automate the process too.
Ahrefs’ new experimental Content Grader tool uses AI to automatically analyze the top-ranking articles for a particular keyword, identify the topics present, and score them according to how well they cover the topic.
Here’s an example for the keyword programmatic seo, comparing the content of my article to the content of other top-ranking pieces. We can immediately see a couple of missing topic areas:
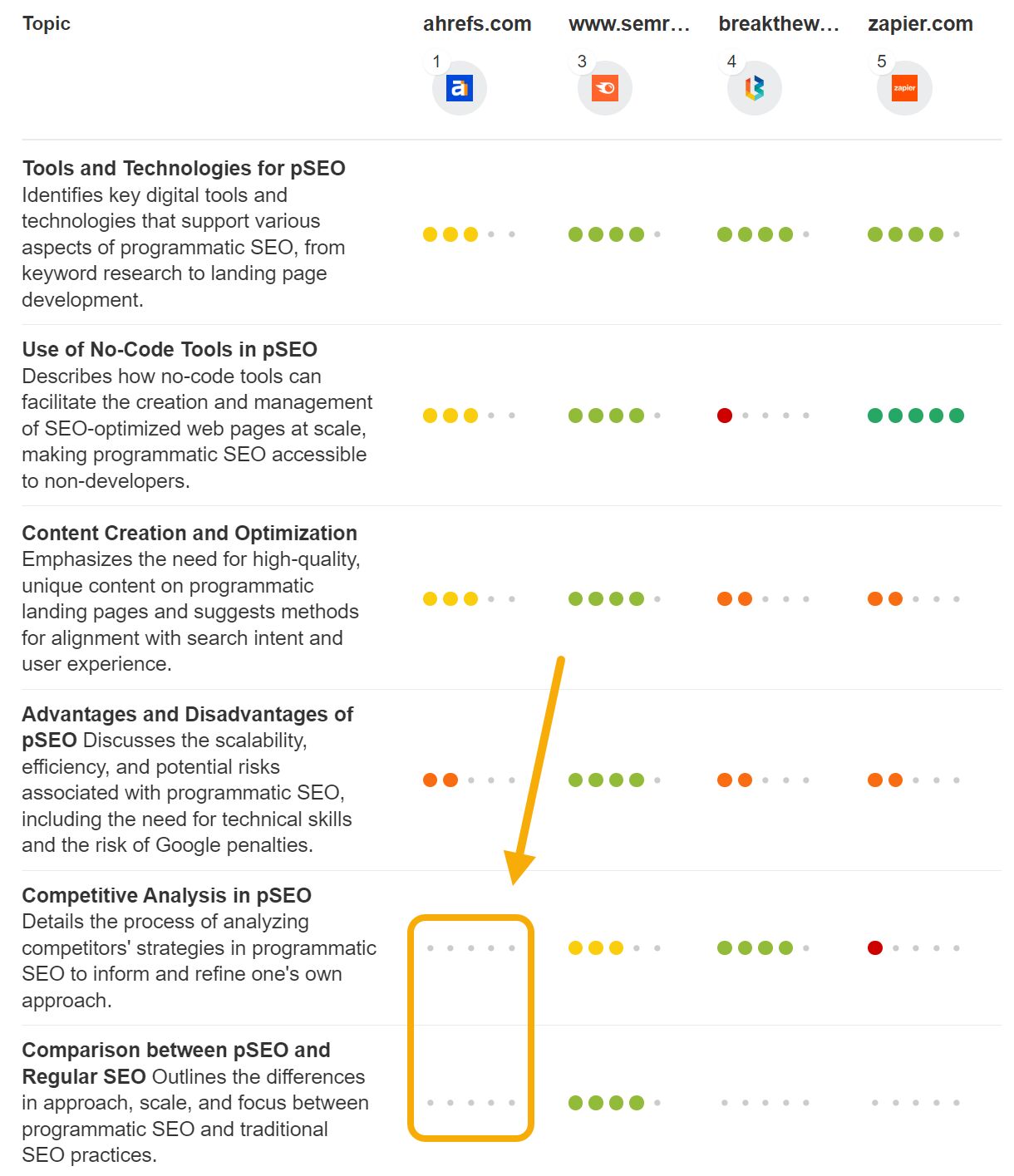
Content Grader can even explain how you should address the topic gap, and share an example from another top-ranking article:

Write meta descriptions
Good meta descriptions encourage searchers to click on your pages, but Google has a tendency to change and rewrite even the most carefully-crafted meta descriptions.
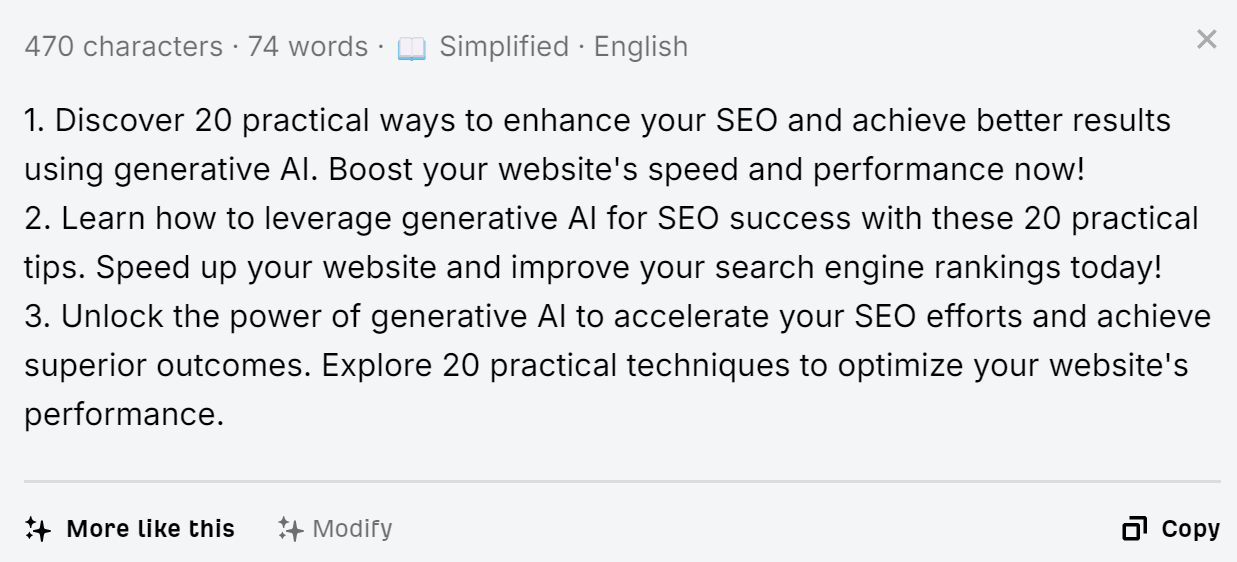
If you want to generate lots of meta descriptions without sinking tons of time into the process, AI is pretty perfect. Here’s our free AI meta description generator: just describe the contents of your page, choose a writing tone and the number of variations you’d like, and hit generate.

And here are the outputs:
Make content more helpful
Aleyda Solis created a custom GPT (a specially trained AI model) that reviews content according to Google’s helpful content guidelines.
While I don’t think it’s a replacement for the skilled judgment of a professional SEO, it can offer a quick, automated way to pinpoint obvious problems with content.
Here I’ve asked it to compare my article on programmatic SEO to a competing article:

It’s easy to mess up certain parts of technical SEO, like schema or hreflang implementation. From my experience, AI is better and more reliable than I am in these areas.
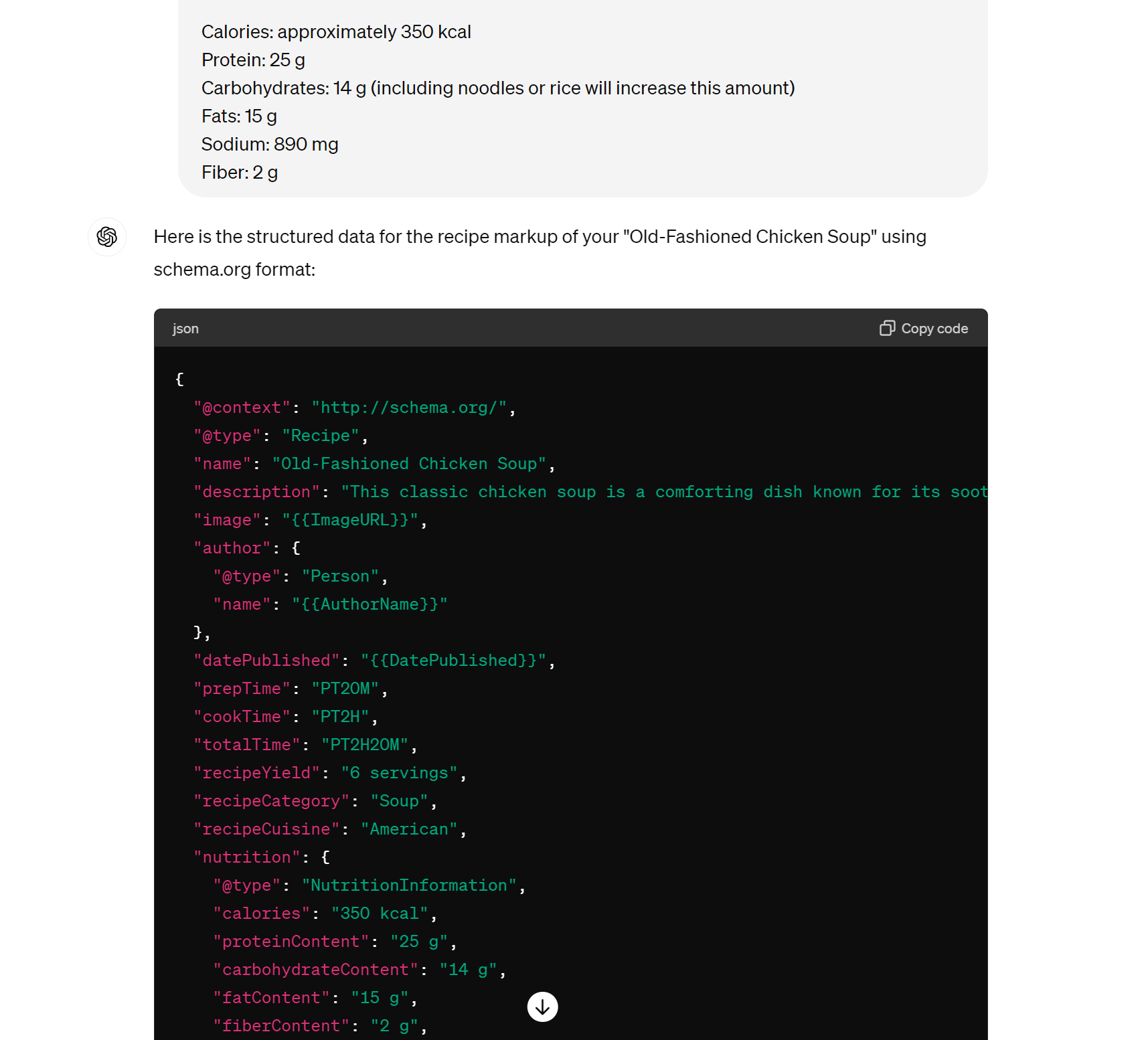
Create schema markup
Here, I’ve asked for recipe schema for a chicken soup recipe. With a couple of tweaks (like adding in the recipe author), I could add this to my page and become eligible for rich results (and most likely more clicks):
Generate hreflang

AI is great at helping with these analytical and reporting tasks, from digging through performance data to see which tactics work, to sharing your findings in easy-to-communicate ways with your company or clients.
Of all the AI/SEO use cases I’ve covered, these are probably my favorite.
Constructing regex queries
Regular expressions (or regex) allow you to search within text and data for patterns that are otherwise difficult to spot. They can be pretty complicated, but AI is extremely good at writing and troubleshooting very complex queries for you.
Here’s ChatGPT helping me extract URLs from a list of email addresses, combining regex queries with a Google Sheets formula:
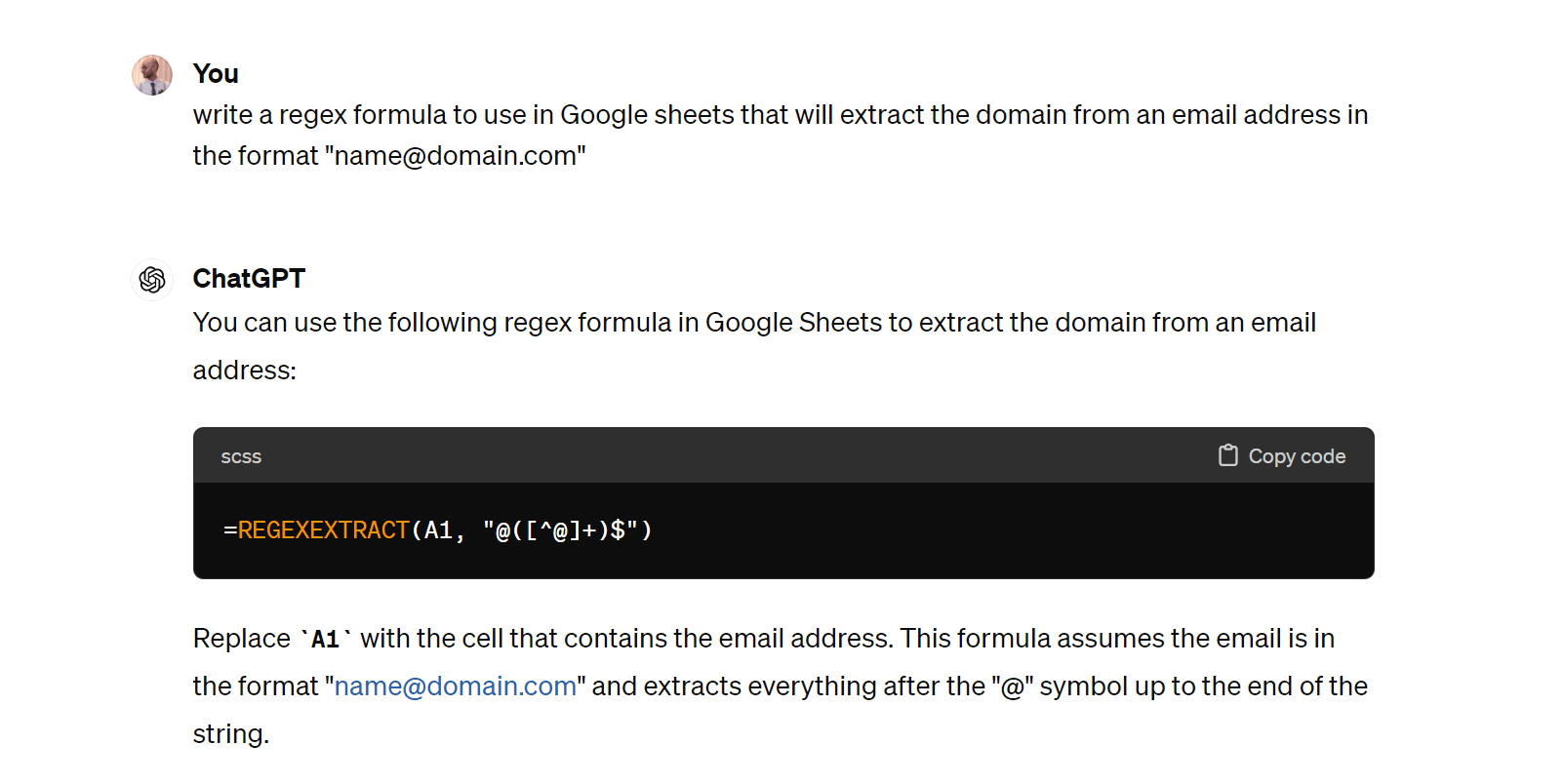
And here it’s helping me filter a spreadsheet of URLs by their crawl depth:
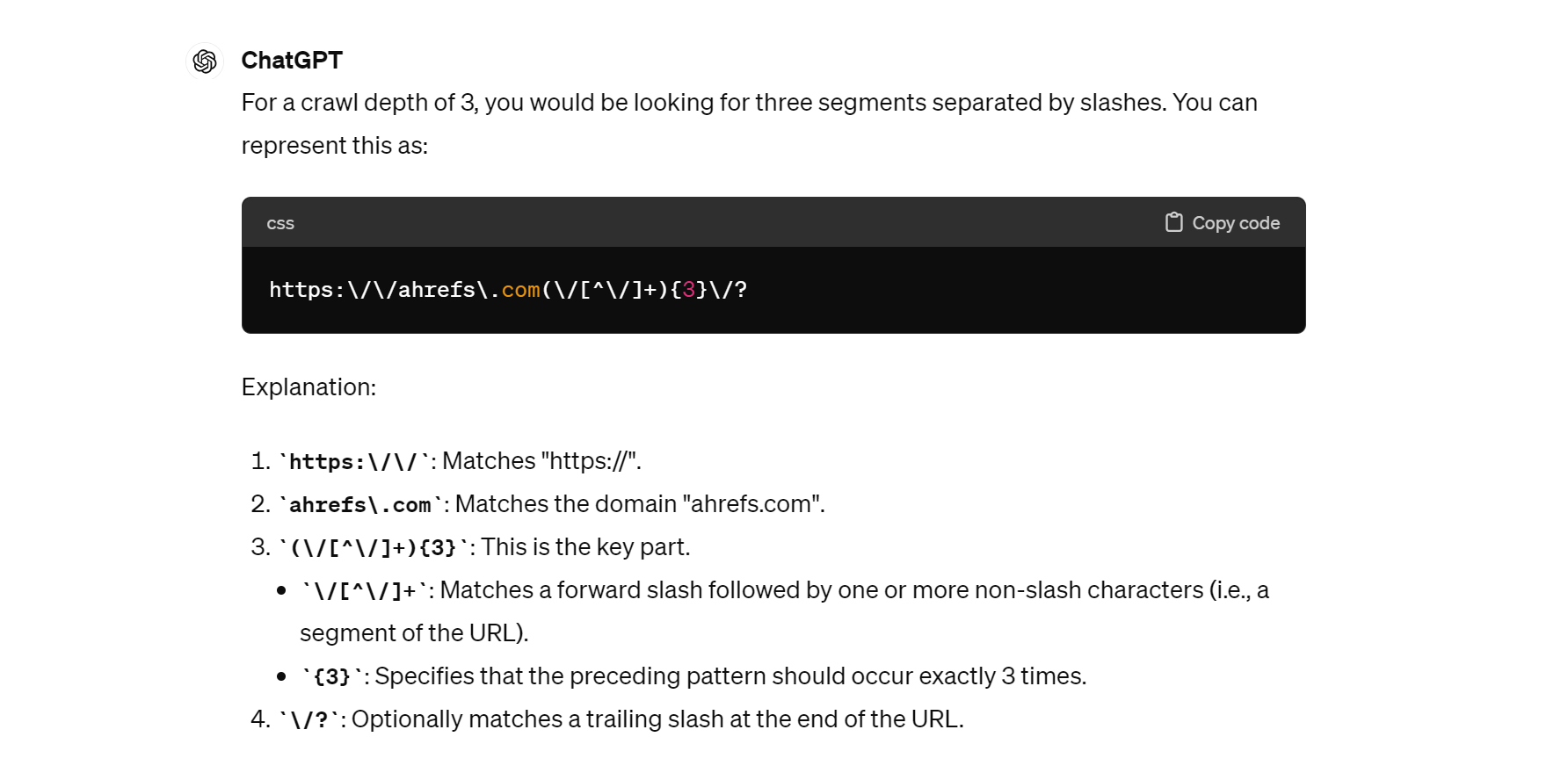
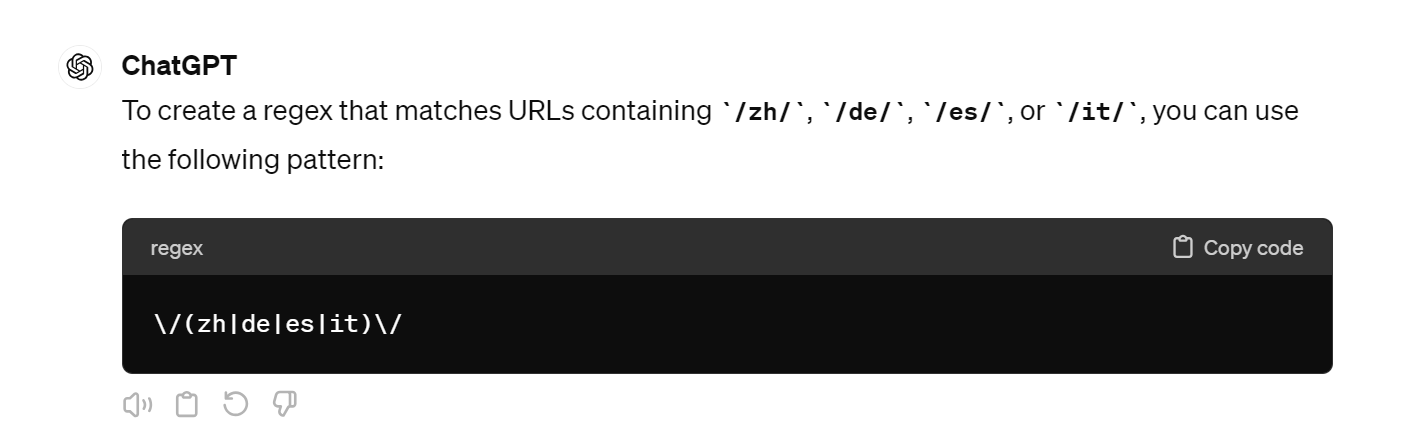
And here it’s written a query to use with Ahrefs Site Audit to help me filter out localized content (pages that have country codes, like /de/ for Germany, somewhere in their URL):
Making Google Sheets formula
SEOs spend a lot of time in spreadsheets, often wrangling lots of data with complicated formulas. ChatGPT can make this process much, much easier.
Here I’ve described the structure of an article reporting spreadsheet to ChatGPT, and asked for a very complicated formula to allow me to filter for certain types of published articles. It doesn’t even break a sweat:

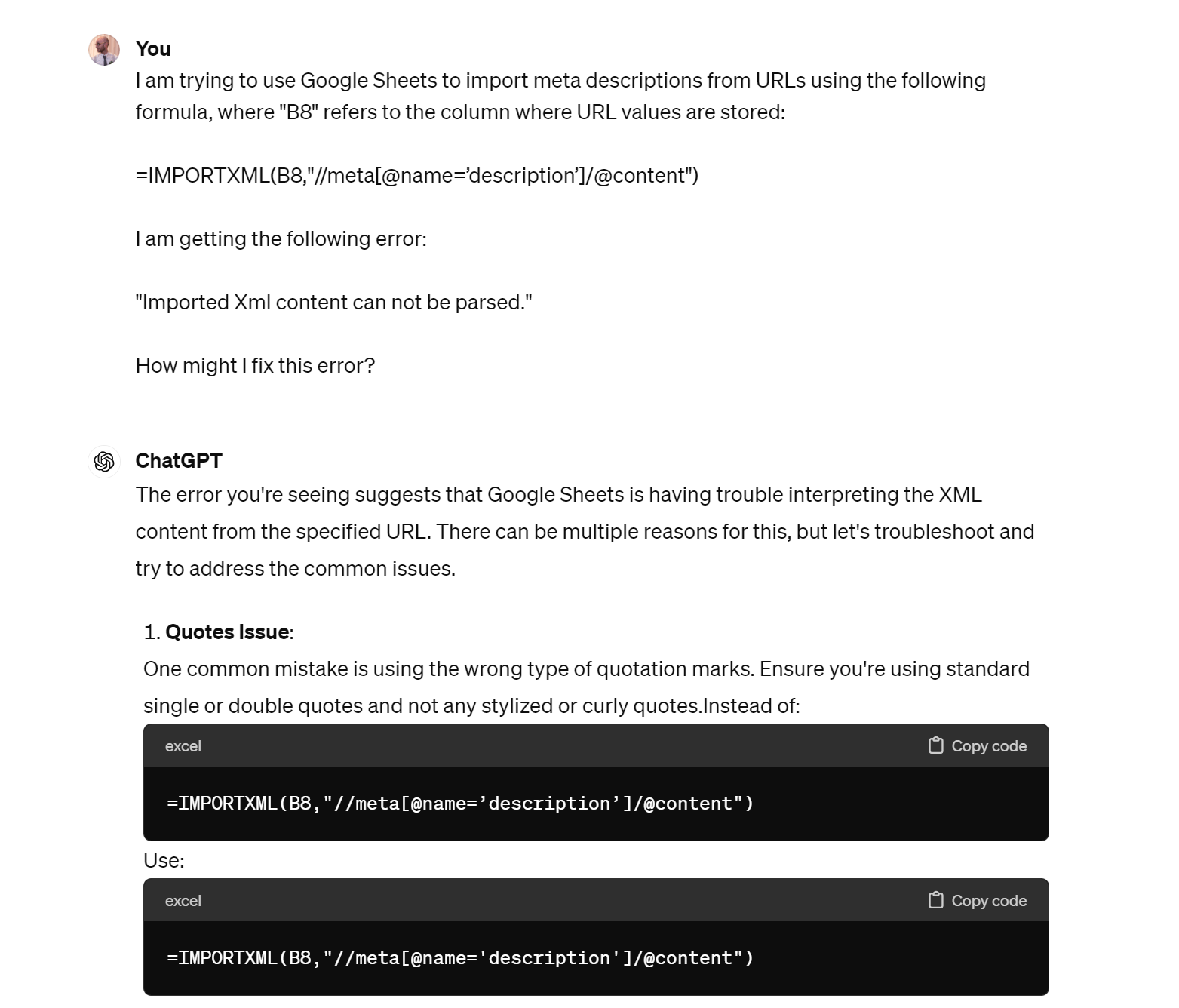
It’s also great for troubleshooting when things go wrong:
Writing Python scripts
Python is a popular language for automating SEO processes. Generative AI is pretty darn handy at writing and troubleshooting Python code, and I’ve used it to help speed up some of my SEO processes.
Here, I asked AI to create a basic web scraper for storing data from a given webpage:

And here I asked for help writing a script to call the Ahrefs API and collect bulk traffic and backlink data for a list of websites:
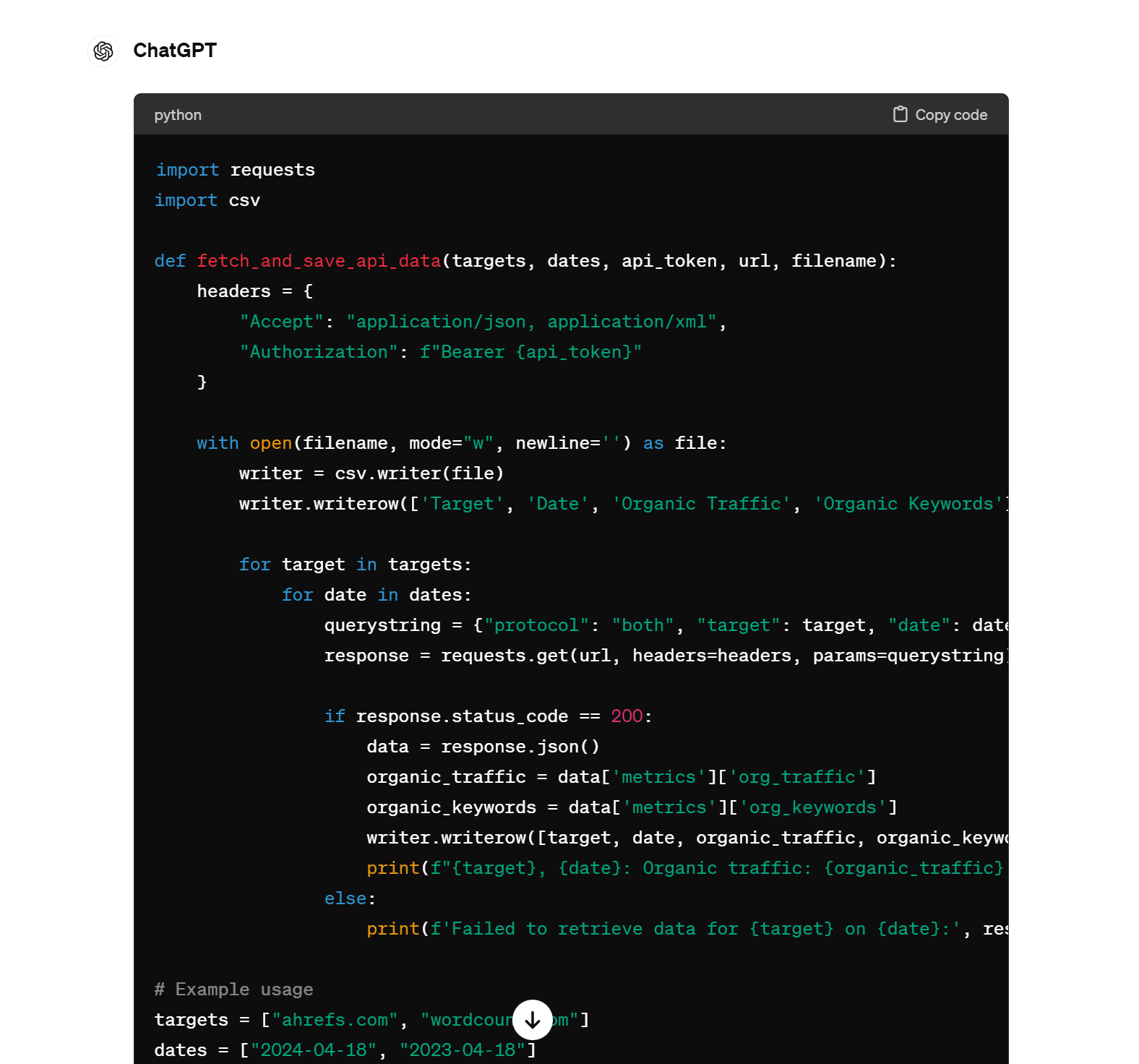
And yes—both of these scripts worked!
Vizualize performance data
All of the visuals in this section were created with ChatGPT, Ahrefs data, and a little know-how.
For longer explanations (and the prompts used to make these visualizations), check out Patrick’s article:
Here’s a graph of organic traffic over time, with traffic anomalies (usually Google updates) highlighted:

Here’s a plot comparing desktop and mobile rankings for a selection of keywords:

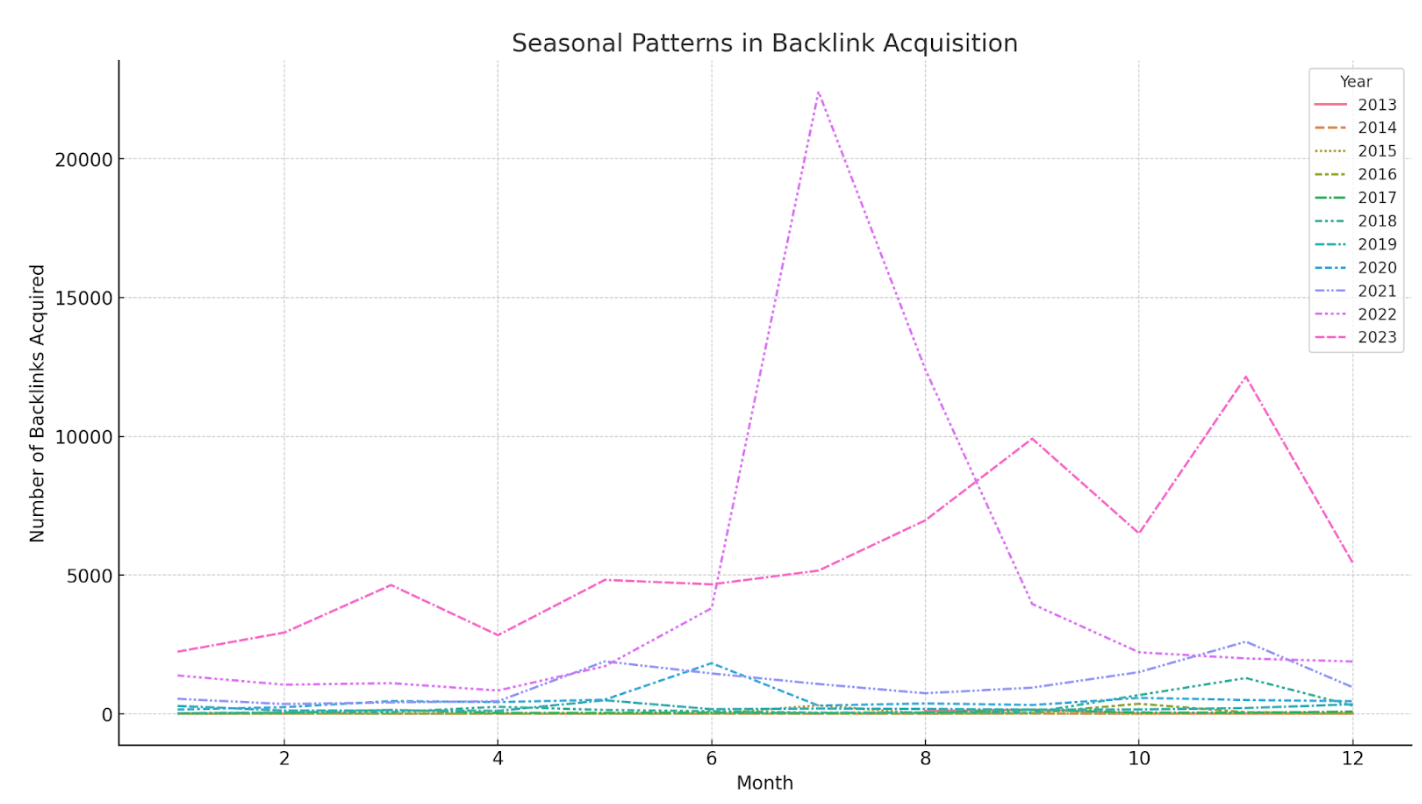
And here’s a chart showing seasonal patterns in backlink acquisition:
AI can help you do SEO, but it’s also changing the industry as a whole. There are lots of myths circulating about the impact of AI. Let’s address the biggest, head-on.
Does Google penalize AI content?
No, not strictly speaking. Google penalizes bad content, and AI makes it easy to make bad content.
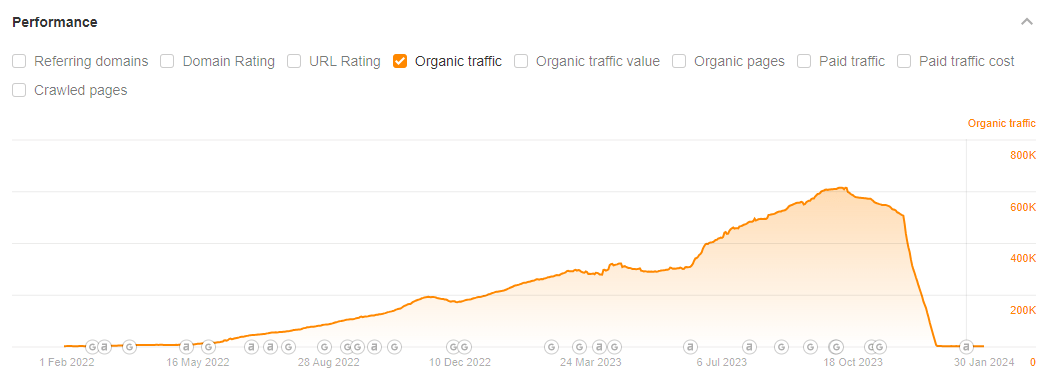
Some companies use AI to dramatically scale and automate their content creation. When this content is thin, there’s a chance that Google will issue a manual spam penalty. In this example, a site used AI to publish 1,800 thin articles and received a penalty, tanking their traffic to virtually zero:
As I’ve written before,
“I don’t think that publishing AI content means an automatic penalty. AI content detectors don’t work, and even if they did, Google is apparently agnostic to AI use—but it is not agnostic to bad content or bad actors. And AI makes it very easy to make bad content.”
It’s a good idea to use AI to improve the efficiency or quality of your content, but not to pump out thin spam content.
Is Google losing market share to AI?
It doesn’t look like it.
Google has always been the main search engine SEOs care about, and in the age of AI… that hasn’t really changed. According to Statcounter, Google’s market share has held relatively steady at a staggering 91%:

But although Google’s dominance over the search market is pretty unchallenged, there are more alternatives than ever. These are useful for seeing where Google might take inspiration and improve its own search experience in the future:
- Competing search engines are offering their own AI features (like Bing or our Yep.com).
- Companies like Perplexity.ai offer an alternative search experience built entirely on AI ******
- Some people are even building their own AI chatbots trained on specific bodies of work—instead of asking Google for health and fitness advice, you could ask a chatbot trained on the Huberman Labs podcast.
Will SGE reduce traffic from certain keywords?
Maybe.
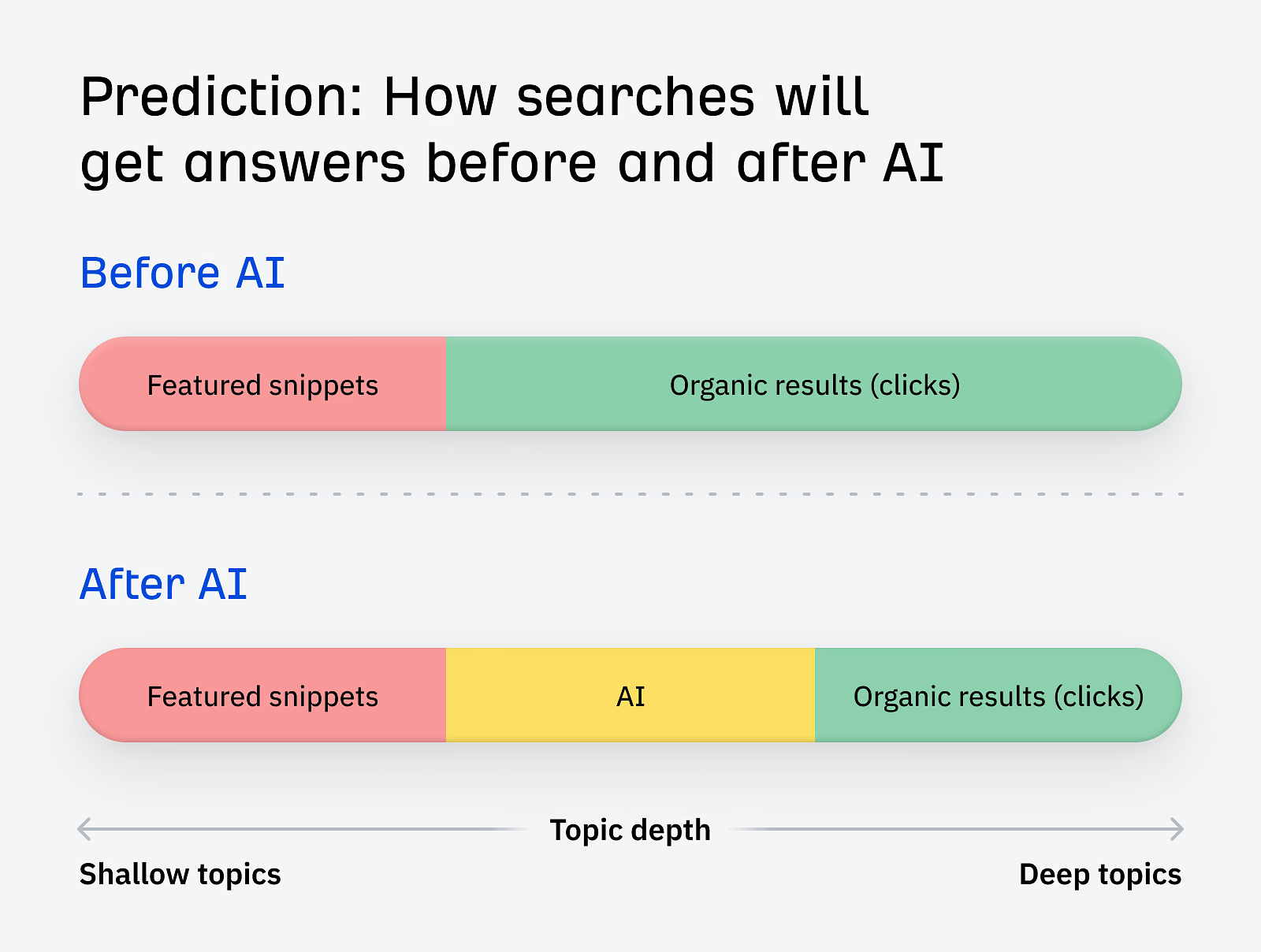
Google has just launched AI Overviews (formerly known as Search Generative Experience, or SGE). AI Overviews seem to work a lot like featured snippets: they try to answer the searcher’s query directly, right there in the SERP, without the need to click on another website.
There’s a concern that many websites will see a decline in search traffic from AI Overviews, and some SEOs even suggest trying to optimize your content for AI Overviews.
While we wait to see what impact AI Overviews has on traffic from Google Search, the best response is to focus on topics that can’t be neatly summarized in a single paragraph.
We call these “deep topics”: areas where AI can’t provide everything the reader needs, because there are lots of possible answers, or it requires firsthand experience.
Does Google reward first-person experience?
Theoretically, yes.
Google already has a plan for stopping SERPs from being swamped by copycat AI content, and it involves prioritizing content that includes EEAT: expertise, experience, authority, and trust:
“There are some situations where really what you value most is content produced by someone who has first-hand, life experience on the topic at hand.”
EEAT is used by Google’s Quality Raters, whose experiences may be used to train Google’s machine learning ****** to help them identify “quality” content.
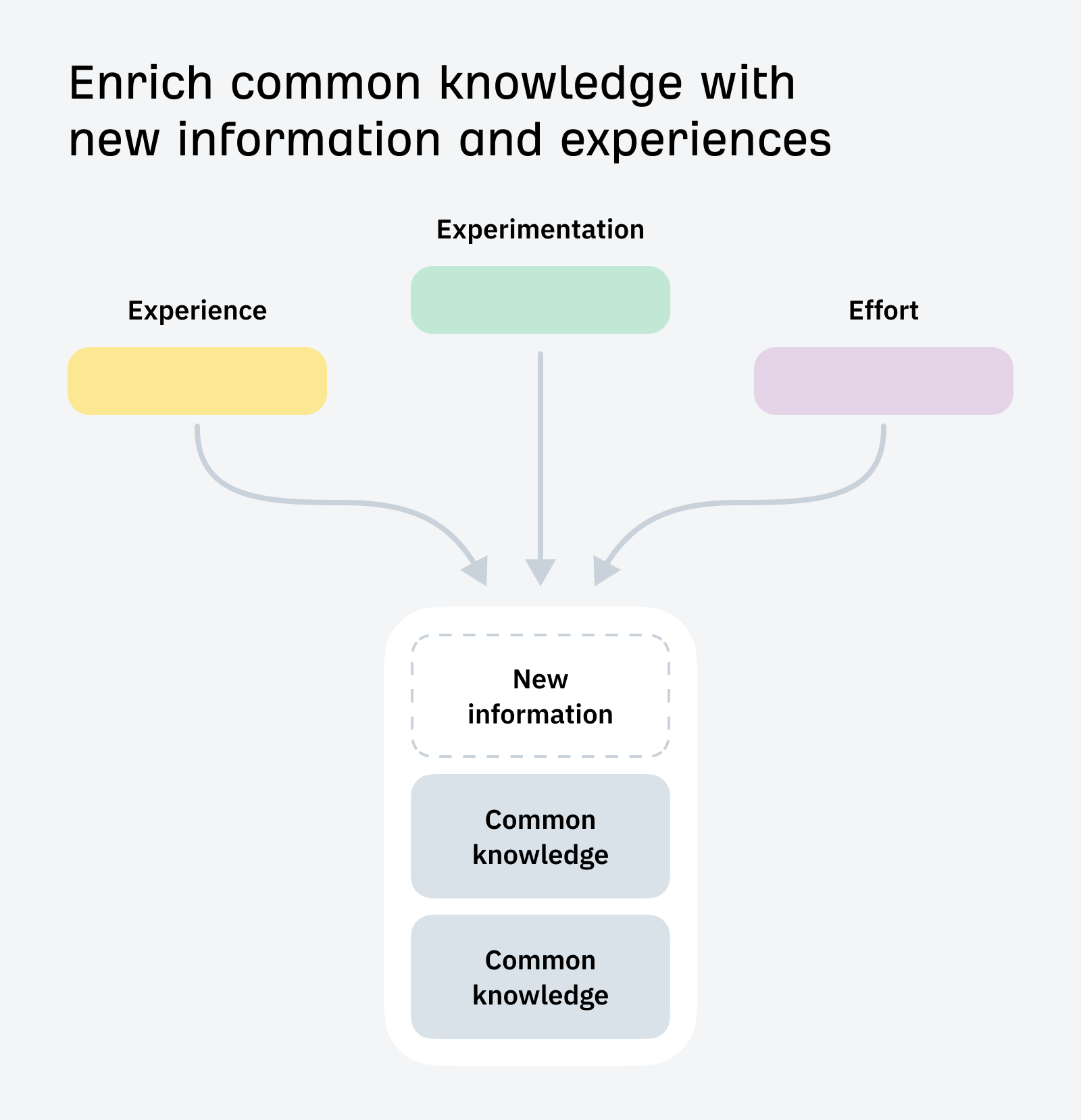
But Google aside, EEAT is great for readers, so it’s worth incorporating into your SEO strategy even if you won’t see an immediate ranking boost. There are three simple ways we recommend standing out from AI content:
- Experimentation: create proprietary data.
- Experience: share your real, lived experiences.
- Effort: go further than competing content.
Final thoughts
SEO isn’t something that can be automated to perfection at the click of a button (and any tool that promises otherwise is lying). But AI can help speed up and improve the more tedious parts of your job.
If you want to test out some AI tools in the easiest possible way, try experimenting with our 40 free AI writing tools. They can help with everything from writing clickable titles to generating tons of meta descriptions, and help you separate AI fact from AI fiction.
Source link : Ahrefs.com

