This article builds on my previous one, emphasizing the importance of aligning SEO with the customer journey, specifically for companies that provide software as a service (SaaS) that market to other businesses (B2B).
Crafting relevant content through a deep understanding of the customer experience is vital for enhancing SEO and fostering brand loyalty. Utilizing the customer journey map, which provides insights into user emotions and motivations, is a crucial tool in this process.
Harmonizing SEO with the customer journey map and optimizing it across six key stages empowers users to make well-informed purchase decisions.
This article will focus more on marketing for each stage and the step-by-step process of aligning SEO with the customer journey.
Understanding SEO and content for a smooth customer journey
1. Awareness of need
Customers become aware of a pressing issue that requires resolution in the initial stage. They assess the severity of the problem, allowing brands to capture their interest.
Marketing strategies should incorporate problem-related keywords, informative blog articles, engaging social media narratives, and instructional videos.
Additionally, events can be a powerful tool to deepen the audience’s understanding of the issue, showcasing the brand’s viable solutions.
- Use social media posts and public relations for brand and product awareness, linking to the website for SEO link building.
- Employ traditional offline marketing methods, including event booths, networking events, television, radio, and print ads.
- Implement content marketing through blog posts focusing on SEO for broad terms and questions.
- Use guest articles/posts that include links to the site for SEO link building.
- Create whitepapers and customer stories to connect with customers facing the problem.
- The goal is to attract users unaware of their needs, utilizing the content they consume for retargeting in the next stage. Keep marketing messaging light and non-invasive, allowing customers to come to you without pushing for sales.
2. Investigate options
During this phase, users conduct broad searches to gather information, read reviews, and define criteria for potential solutions. They outline outcomes, stakeholders, metrics, budgets, and more.
To assist users in their research, marketers should optimize blog posts, create informative website pages, share empathetic social media posts addressing pain points, and produce videos guiding users in selecting the best product or service.
- Employ SEO, SEM, and paid social media marketing to attract potential customers and solidify your brand or product in their minds.
- Leverage tags from the previous stage’s content for retargeting with resonant messaging.
- Collaborate with partners and influencers to feature your brand or product on “Best solutions for…” lists.
- Create videos addressing pain points and explaining why your brand/product is the best solution.
- Messaging should be customer-centric, focusing on solving their problems without pushing for sales.
3. Committing to change
In this stage, users commit to their goals, narrow their choices, and dive deeper into research. Sales engagements become more prominent, and stakeholders participate in the decision-making process.
Marketing strategies should focus on content that addresses doubts or objections, such as comparison pages that validate the company’s credibility. Influencers, email campaigns, and retargeting efforts can reinforce the commitment made by users.
- Focus on website pages, especially product pages, as a digital brochure with SEO and SEM targeting brand and product keywords.
- Launch email and social media retargeting campaigns that link to customer testimonials or downloadable PDFs.
- Use messaging that appeals to various stakeholders and challenges objections.
- Offer opportunities for potential customers to engage with sales, such as scheduling meetings or initiating chat conversations.
4. Solution selection
As users seek buy-in from decision-makers, they require content that justifies their expenditure, often emphasizing pricing, ROI, and overall value.
B2B marketing should speak the language of the C-suite, highlighting ROI and efficiency improvements. For ecommerce, testimonials and reviews play a crucial role in influencing selection.
- Create content targeting the C-suite, including the COO, CFO, and CEO.
- Optimize solution pages and pricing pages with SEO for brand and cost-related keywords.
- Develop an ROI calculator with SEO targeting finance-related terms.
- Produce PDF downloads with customer stories focused on messaging for these executive roles.
- Utilize email invites from the sales team to schedule meetings.
- Messaging should focus on ROI, efficiency improvements, and cost savings.
5. Validate choice
Users validate their choice in this stage by seeking management support and evaluating implementation logistics, costs, and ongoing support.
Brands should optimize for brand-related searches, leverage testimonials and reviews to showcase successful experiences and highlight exceptional customer service.
- Create content in the form of feature pages with SEO targeting brand-related terms.
- Use emails and social media to include testimonials from happy customers.
- Address implementation logistics and highlight ongoing support.
6. Purchase
After a thorough assessment, customers are on the verge of making their final purchasing decision. Discussions regarding pricing, terms, and implementation details may occur.
To facilitate this phase, brands can employ SEO and email marketing strategies, offering resources like user guides, setup manuals, and answers to frequently asked questions.
Leveraging influencers to create engaging unboxing videos can vividly illustrate the product or service.
- Provide content in the form of customer support, “Help,” and “FAQ” topics with SEO targeting keywords related to onboarding and getting started.
- Use influencer marketing to create unboxing videos and articles that reassure customers during the purchase stage.
- Offer resources like user guides and FAQs to support customers during buying.
7. Post-purchase
In this stage, it’s essential to keep customers engaged and satisfied. Content marketing and informative emails will make their everyday work easier. Additionally, utilize SEO to capture competitors’ customers searching for post-purchase help topics.
Content should include blog posts and help topics on your website with SEO for relevant post-purchase keywords. Emails and social media retargeting can focus on helping customers find customer service or answers to frequently asked questions to maintain their satisfaction and potentially attract competitors’ customers seeking assistance.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Connecting SEO to the customer journey
The keyword analysis
You can use Google’s Keyword Planner to gather as many words and phrases as possible that searchers use to find what they need on search engines.
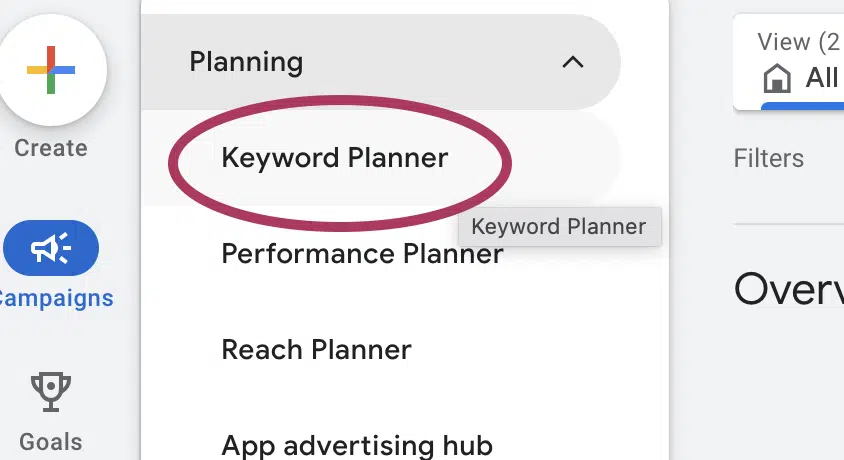
- Choose Discover new words in the Keyword Planner tool in Google Ads if you want keyword suggestions.
- Enter up to 10 phrases related to what your users might be searching for.
- Click Get results to view data for the specified keywords and a list of suggested keywords.
- You can download your keyword ideas as a spreadsheet. In this example, we use Google Sheets.
From here, you’ll want to clean up the data into a spreadsheet that is easy to work with. I usually remove the currency, bid, competition, and forecasting columns (as described in the document), leaving just the keywords and search volume.
You can also pull in data from Google Search Console, Keylime, or Moz to get current impressions, clicks, and average position so you can calculate where your gaps are.
Next, we’ll do keyword tagging, which is where aligning SEO with your customer journey will come into play.
Tagging keywords with the customer journey
You’ll want to fully grasp your customer’s journey and get inside their head as you tag your keywords.
For this step-by-step guide on tagging your keywords, I will use Excel as my tool, though you can use Google Sheets or any other spreadsheet program.
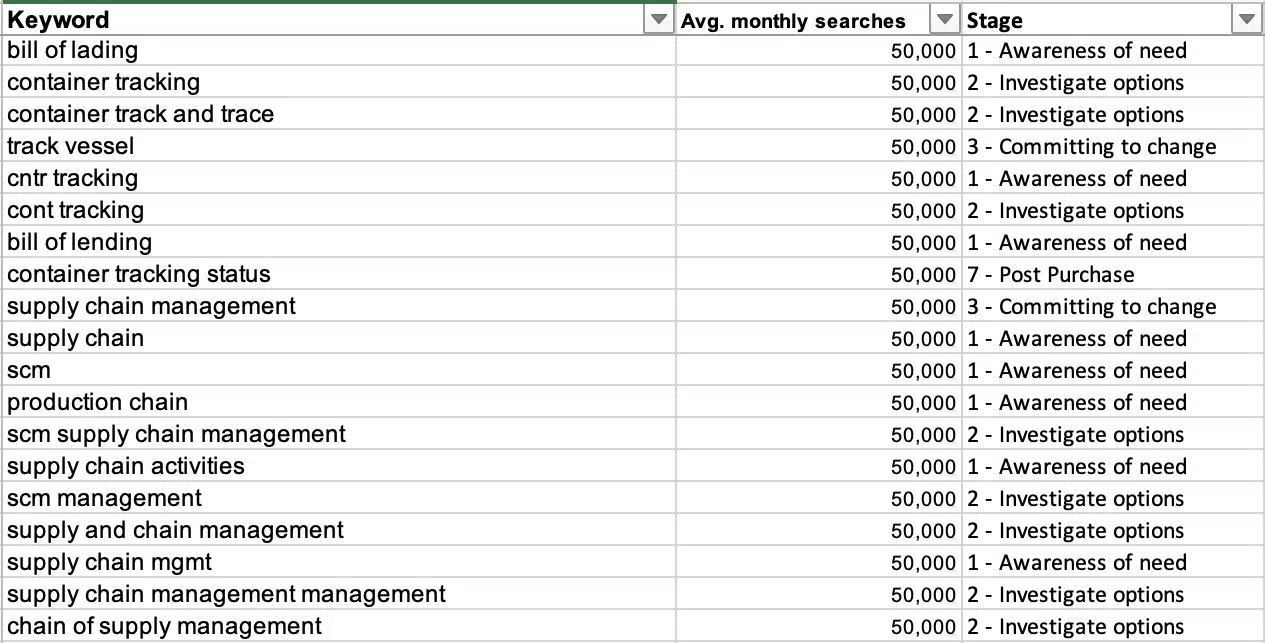
Your spreadsheet should look something like this:
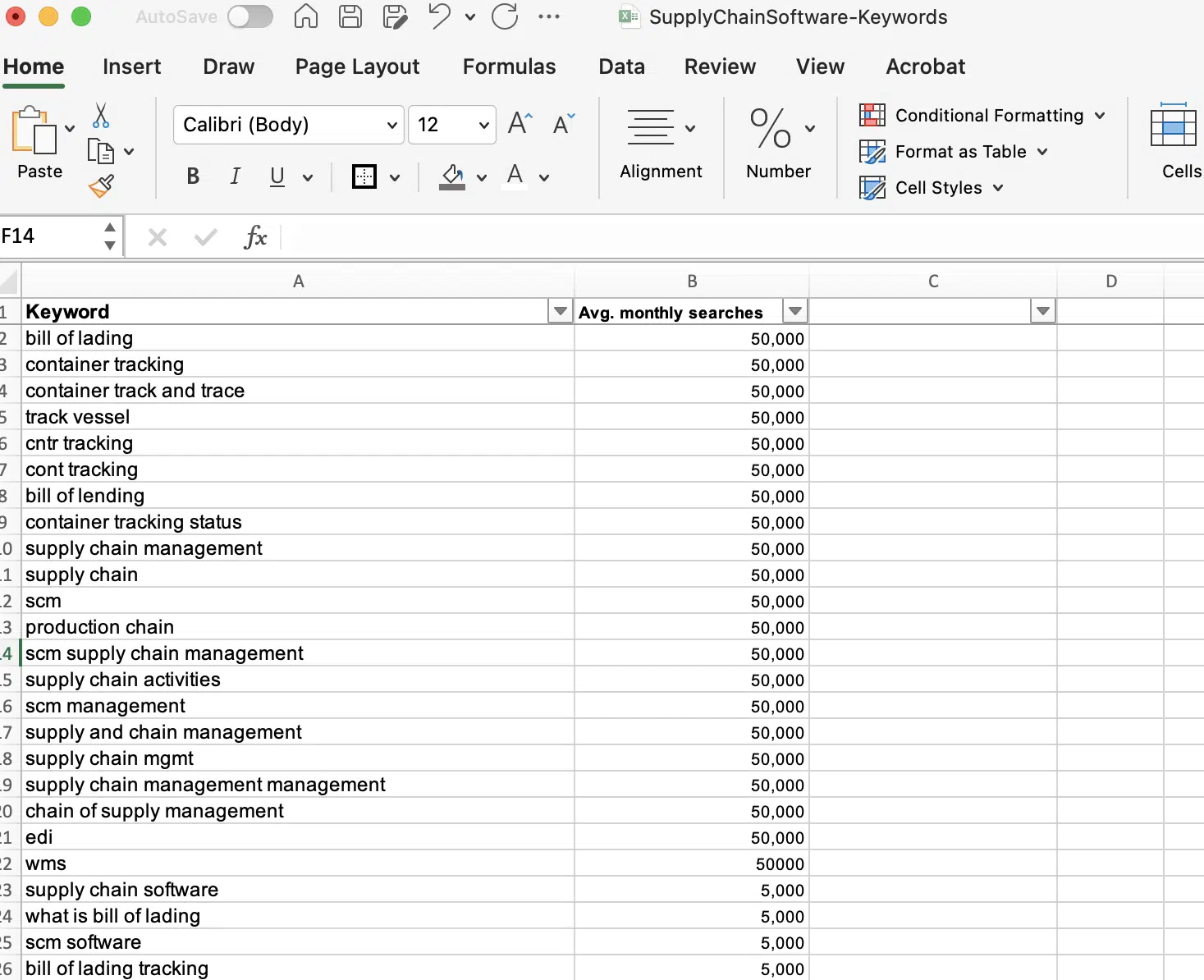
The ‘Stage’ tab and data validation
From here, I add a tab that holds my guide for the stages of the customer journey and use that guide as a data validation drop-down to select from.
This is especially useful if you’re working with other teams within the organization so that they can see the process and guidance for each stage.
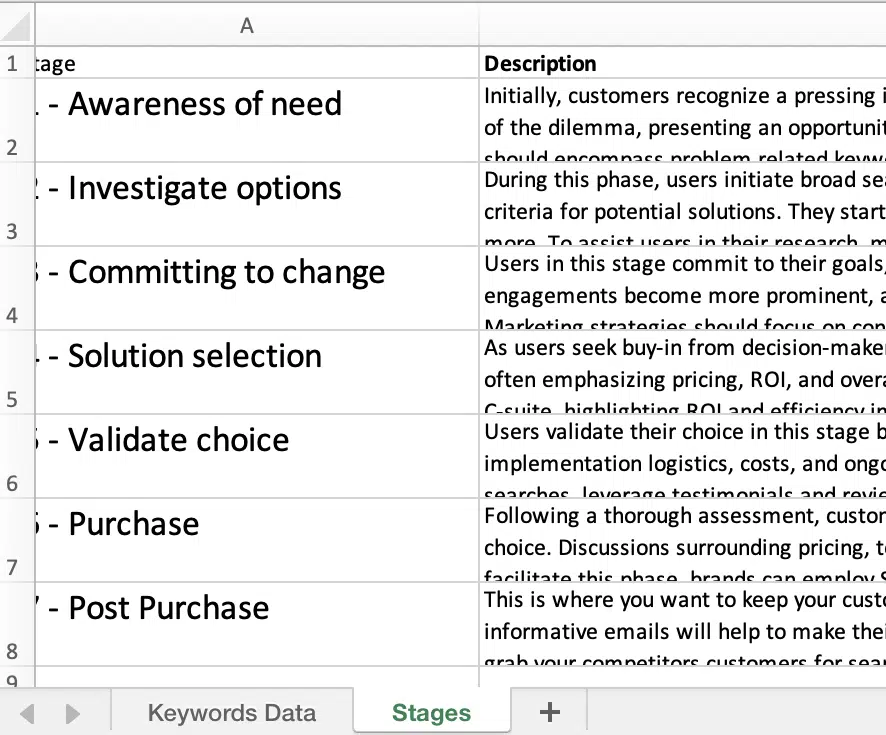
Using the “Stages” tab as a data validation dropdown in your spreadsheet makes for each tagging.
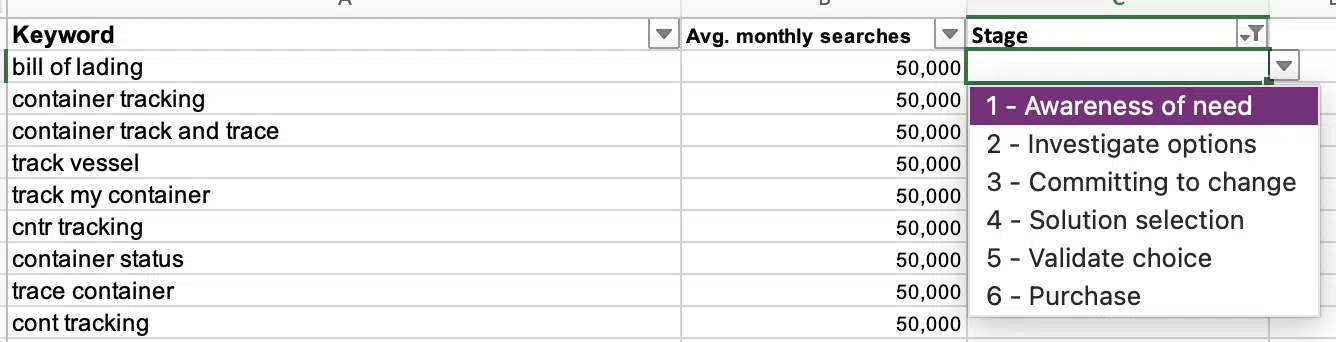
Tagging your keywords
Now that you’re all set up, it’s time to start tagging your keywords. This may seem like it’s a daunting task, especially when you have thousands of keywords to work with, but it can go quickly as you start to recognize words in phrases that fall under specific stages.
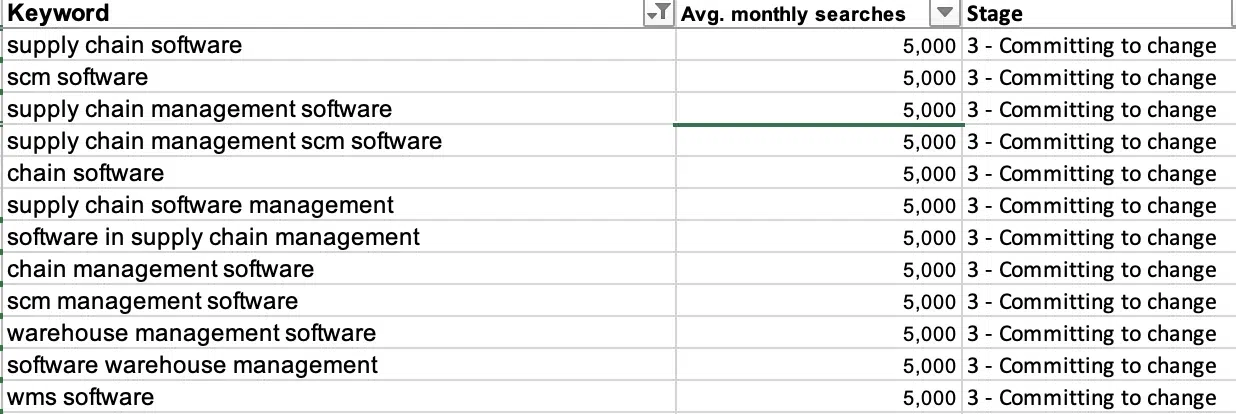
For instance, when selecting keywords for a company offering supply chain software, warehouse management software, and a digital logistics platform, terms like “software,” “tool,” or “system” in the keyword phrase belong to the “Committing to change” stage since they have already identified the problem, considering options for the solution and are now committing to change.
Set up a “Filter” in your spreadsheet program, and start sorting.
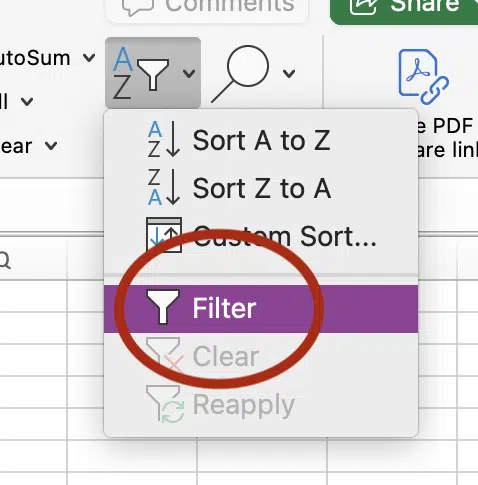
Filter by “Contains” and type the common word (in this case “software”).
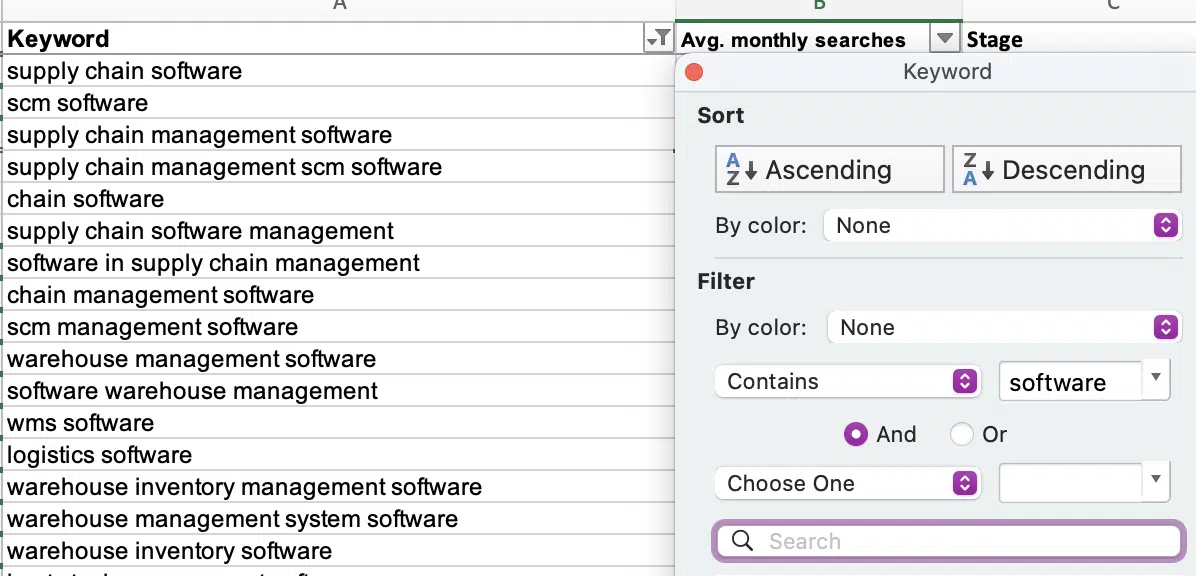
Tag all of the keywords with the stage (in this case, “Committing to change”).
Identifying the unknown
If you are still determining a stage, you can always search for the keyword in Google and see what type of results are displayed.
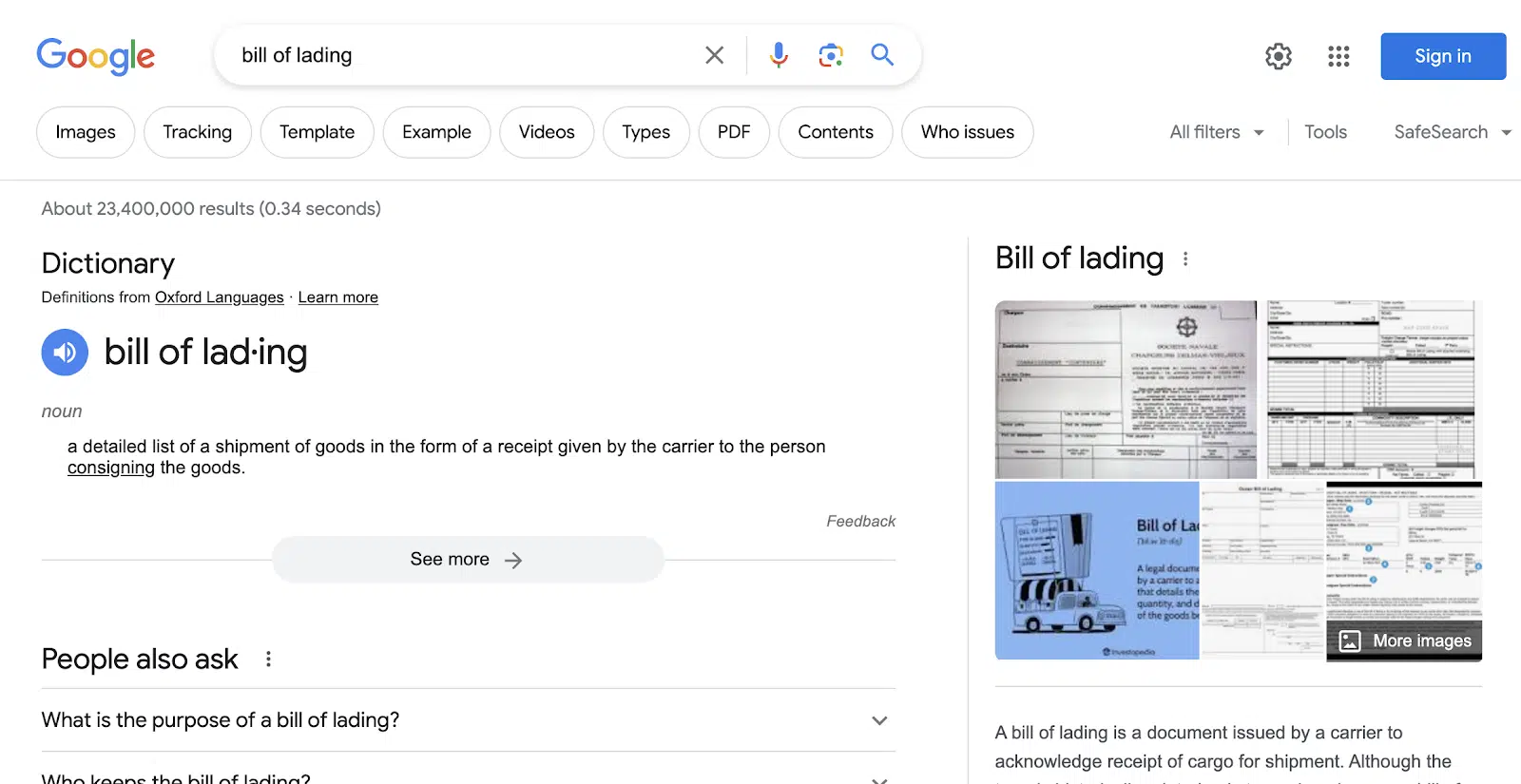
For these “supply chain” keywords, envision we’re picking terms for a company providing SaaS solutions like supply chain software and warehouse management software; a broad keyword like “bill of lading” could be confusing.
Broad terms will often show results as if the user is asking what it is since Google doesn’t know the user’s intent to search such a broad term. So, Google displays the definition, a snippet of the Wikipedia explanation, and People Also Ask results in their knowledge graph.
This content is clearly at the “Awareness of Need” stage as a user doesn’t know the problem or may not quite identify a problem, and there could be a solution.
Eliminating the irrelevant keywords
There will be times that the keywords you have exported from Google’s Keyword Planner. You can use this opportunity to cull out any irrelevant keywords.
For “supply chain” keywords, imagine selecting terms for a company providing SaaS solutions. A phrase like “track my container” may not be relevant since the person using this phrase is more likely to be a shipper’s customer, and we would want to focus on the shipper providing the service to that customer.
Simply highlight the entire row and delete the keyword from your list.
Narrow down your audience with more tagging
You can tag your keywords with more options as you go through this exercise. I usually like to include “Content Type” and tag it with:
- “Blog Post”
- “Product Page”
- “Solutions Page”
- “Home Page”
- “Customer Story”
- “FAQ – Help”
- And more.
In addition, tagging with the lead type such as “Influencer,” “Decision Maker,” or “Neigh Sayer” and even industry, company size, or other focuses will help you keep your SEO and your content focused.
Using the data from your stage tagging
When you finish tagging all of your keywords, your “Stage” column should be void of any blank cells and a mix of all of the stages you have identified.
You can use a simple pivot table to identify where the most estimated monthly searches fall.
In this context, picking keywords for a company that offers Software as a Service (SaaS) and not including any brand product, solution, or feature keywords that might be relevant to a specific company, we can see that most searches fall in the “Investigate Options.”
At the same time, “Awareness of Need” is second, and “Committing to Change” is third. We don’t see a lot of searches in the higher intent searches like “Solution Selection” or “Validate Choice” and no searches in the “Purchase” stage.

A complete analysis of a specific company, including its brand or product, solution, and/or feature terms, would need to be completed to see if those numbers change.
Defining your strategy
Using your data, you can now define a high-level strategy and list priorities based on the level of effort to impact. The impact is the estimated monthly searches or the gaps you found when pulling in your current search impressions, clicks, and positions for these keywords.
In the context of these “supply chain” keywords, let’s consider this is for a company offering Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions, including supply chain software, warehouse management software, and a digital logistics platform. I would recommend that the company include the following pages:
- Home Page
- Supply Chain Software (Product Page)
- Warehouse Management Software (Product Page)
- Digital logistics platform (Product Page)
- Blog
- Customer Stories
- Helpful Resources (FAQs)
- Pages for common questions
As the company works on blog post topics, product pages, and supporting content (customer stories and helpful resources), the keyword analysis with tagging should guide the keywords to optimize for and where that content lies within the customer journey.
Marketing strategies around those topics align with where those customers can be reached and the messaging in that content.
I hope this helps companies understand the vital synergy between SEO and the customer journey for B2B SaaS companies. You can create a roadmap to optimize the user experience by mapping and tagging keywords to their respective stages.
This meticulous process will empower companies to influence their audience strategically, ensuring their digital presence resonates across each journey stage. This approach enhances brand loyalty and makes informed, impactful purchase decisions.
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
Source link : Searchengineland.com
