SEO metrics such as rankings are great, but what matters most is SEO’s impact on business growth.
This means you can only understand SEO’s value if you track the right metrics and how it can increase revenue.
Your metrics should focus on:
- Audience quality: Are you attracting visitors who are likely to become customers?
- Engagement and behavior: Are users finding the information they need, spending time on your site, and taking desired actions?
- Conversions: Is your organic traffic translating into desired outcomes?
- Brand impact: Is SEO influencing your brand’s reputation and visibility?
In this article, we’ve categorized important metrics to focus on at a high level.
User Engagement Metrics
Here are some user engagement metrics to track:
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is the percentage of users who return to the SERP, or exit the webpage (and your site) without interacting with another page on your website. A high bounce rate can indicate that visitors are not finding what they want on your site, which causes them to exit quickly.
Why Is Bounce Rate Important In SEO?
Bounce rate helps you fix issues such as:
- User Experience: A high bounce rate may indicate issues with your website’s content, design, or alignment with user intent. When you notice a high bounce rate, address these issues to improve user experience.
- SEO Rankings: Search engines aim to provide users with the most relevant results. However, a high bounce rate may signal to Google that your site is not meeting user expectations and will lose visibility. This will also affect conversions as users didn’t even engage with your page.
How To Analyze Bounce Rate
Check your Google Analytics 4 for the percentage of single-page visits and divide that by the total number of visits. The result is a percentage of your bounce rate.
For example, if your website received 500 visitors and 100 interacted with more than one page, then 400 visitors bounced. Therefore, your bounce rate would be 80% (400 single-page visits / 500 total visits times 100).
Read more: 20 Proven Ways To Reduce Your Bounce Rate.
Dwell Time (Engaged Session Duration)
Engaged session duration measures the amount of time a user actively spends on your website during an engaged session. This metric indicates how long users interact with your content before leaving the site or becoming inactive.
For example, if a user searches for “best running shoes,” clicks on your link, spends three minutes reading your content, and continues to interact with other parts of your site, the engaged session duration is three minutes.
Why Is Engaged Session Duration Important In SEO?
- It indicates content engagement and relevance: Longer engaged session durations show that users find your content valuable and are willing to spend time interacting with it.
- It impacts rankings: High-engaged session durations signal to search engines that your page provides content that satisfies user intent, which can improve your rankings.
- It helps gauge content effectiveness: If users spend more time on your site, it suggests your content is meeting their expectations and providing the information they need.
To Analyze Dwell Time
- Open GA4 and click on Reports in the left-hand menu.
- Choose the Traffic acquisition: Session default channel group.
- Click on the pencil icon at the top right corner and select Metrics.
- In the bottom search box that says Add metric, type “average engagement time” and hit Apply.
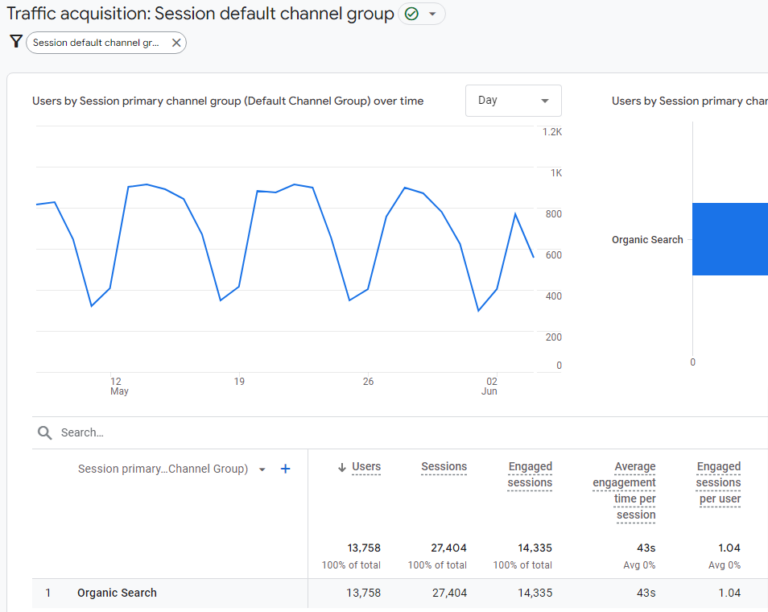 Screenshot from GA4, June 2024
Screenshot from GA4, June 2024Engaged Sessions Per User
Engaged sessions per user is a metric that measures how frequently users interact meaningfully with your website.
In Google Analytics, an engaged session is defined by user activity that includes spending a certain amount of time on the site, viewing multiple pages, or completing specific actions like form submissions or purchases.
For example, if a user lands on your homepage, spends more than a minute exploring your content, clicks on a product page, and completes a form, this counts as an engaged session.
Why Is Engaged Sessions Per User Important To SEO?
- It reflects user engagement and satisfaction: High engaged sessions per user indicate that visitors find your content valuable and are willing to interact with it in a meaningful way.
- It impacts SEO positively: Search engines use engagement metrics as signals of content quality and relevance. High engagement suggests that your site meets user needs, which can boost your rankings.
How To Calculate Engaged Sessions Per User
Google Analytics provides this metric directly, but to calculate it manually, divide the total number of engaged sessions by the number of unique users.
For example, if your website had 50,000 engaged sessions and 20,000 unique users in a month, engaged sessions per user equals 50,000 divided by 20,000 (2.5).
This means, on average, each user had 2.5 engaged sessions during that month.
Read more: Essential GA4 Reports You Need To Measure Your SEO Campaigns.
Conversion Metrics
Here are helpful conversion metrics to track:
Organic Conversion Rate
The organic conversion rate is the percentage of visitors who find your website through organic search results and complete a desired action. This could be
- Making a purchase (usually on ecommerce sites).
- Submitting a lead form (for businesses focused on lead gen).
- Newsletter subscription (to build an email list)
Or any other goal that moves them further along the customer journey.
This metric shows how SEO drives valuable clicks that contribute to your business objectives.
How To Calculate the Organic Conversion Rate
- Determine what constitutes a conversion for your business (e.g., form completion, sales, subscription).
- Track the number of users who complete the desired action and the total number of organic visitors over a specific period.
- Divide the number of conversions by the total number of organic visitors, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
For context, the organic conversion rate equals the number of conversions divided by the number of organic visitors multiplied by 100.
This means if 500 out of 10,000 organic visitors complete the desired action, the conversion rate would be 5%.
Read more: What Is Conversion Rate & How Do You Calculate It?
Goal Completions
A goal completion is recorded whenever a user completes a specific action you’ve defined as valuable. The actions could be the same metrics bulleted out in the previous point.
Goal completions matter because they tell if your SEO is driving the right traffic and if visitors are taking the actions you want them to take.
How To Track Goal Completions
- Choose an analytics platform such as GA4, Adobe Analytics, Matomo, etc.
- Define your goals and be specific (e.g., “purchase confirmation page viewed”).
- Set up goal tracking.
For this article, we’ll use GA4, and tracking looks like this:
- Go to the Admin section.
- In the Property column, click on Events.
- Click the “Create Event” button to set up a new event.
- Name your event (e.g., “form_submission” or “purchase_completed”).
- Define the conditions for your event. For example, if tracking a form submission, set parameters like event name equals “form_submit” or similar.
- Click Create to save your new event.
- Mark that event as a Key Event (conversion).
- Then, monitor and analyze the reports to track goal completions.
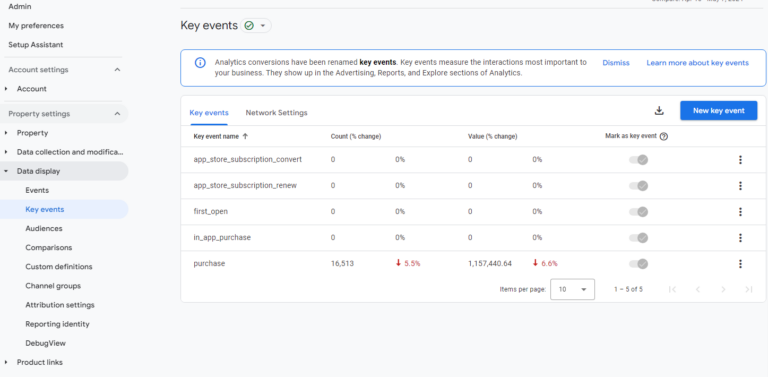 Screenshot from GA4, June 2024
Screenshot from GA4, June 2024Ecommerce Transactions
In ecommerce, a conversion is completing a desired action that generates revenue.
The most apparent conversion is a purchase, but other valuable actions include adding items to a cart, creating an account, or subscribing to emails.
What Does Tracking Ecommerce Transactions Look Like?
- A user searches for [best running shoes] on Google.
- They click on your blog post, “Top 10 Running Shoes for 2024,” which ranks high in organic search results.
- They read your review and click on the buy button link to a product page on your website.
- They add the shoes to their cart and complete the purchase.
If you enable enhanced ecommerce in GA4, it’ll track the entire customer journey (from product view to purchase).
UTM parameters will identify the blog post as the conversion source, your attribution model will assign credit to the post, and your CRM can link the purchase to the user’s profile for further analysis.
Follow this process to track ecommerce sales on Google Analytics 4.
Traffic Metrics
Here are some traffic metrics to prioritize:
Organic Traffic Volume
Organic traffic volume is the number of visitors arriving at your website through unpaid search results – organic clicks from search engine result pages (SERPs).
High organic traffic indicates that search engines consider your website relevant and authoritative for your target keywords.
This way, as long as you write quality content, your website will convert users without relying on paid advertising.
How To Measure Organic Traffic
Log into GA4 and go to Acquisition Reports. Navigate to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition.
This report provides a detailed breakdown of your traffic sources, including organic search.
Organic Traffic Value
Organic traffic value goes beyond numbers to assess the actual worth of visitors your SEO efforts attract. It quantifies the potential revenue or business impact of your organic traffic.
Organic traffic value is ROI-focused; it answers the question, “What is the monetary value of the organic traffic we’re getting?”
The answer then informs decisions on how to allocate marketing resources.
How To Calculate Organic Traffic Value
You can either use the cost-per-click (CPC), conversion-based value, or the customer lifetime value (LTV) metrics:
- The CPC method estimates the value of organic traffic by calculating how much you would have spent on paid advertising (PPC) to get the same number of clicks. It uses the average CPC for your target keywords.
If your website receives 1,000 organic clicks per month for a keyword with an average CPC of $2, the estimated organic traffic value would be $2,000.
- The conversion-based value metric calculates the revenue generated from organic traffic by tracking conversions and assigning a value to each conversion. For example, if your website receives 1,000 organic visitors and 50 convert into customers with an average order value of $100, the organic traffic value would be $5,000.
- Another method is the customer lifetime value (LTV). This method takes a long-term view by considering the total value a customer brings over their entire relationship with your business. It factors in repeat purchases, customer retention, and average order value.
For example, if your average customer from organic search makes three purchases per year with an average order value of $100 and remains a customer for two years, their LTV would be $600.
Technical SEO Metrics
Technical SEO metrics provide insights into your website’s infrastructure to ensure search engines can access, crawl, and index your content. Here are some metrics to focus on:
Crawl Errors
Crawl errors occur when search engine bots (like Googlebot) encounter issues while crawling pages on your website.
These errors can prevent search engines from understanding your content, potentially leading to lower rankings and visibility in SERPs.
Types of Crawl Errors
- 404 (Not Found): The requested page doesn’t exist. This could be due to a broken link, a deleted page, or a typo in the URL.
- 5xx (Server Errors): The server encountered an error while processing the request. This could be due to a temporary outage, a misconfiguration, or a server overload.
- Robots.txt Errors: The robots.txt file blocks search engine bots from accessing certain pages or sections of your website.
How To Identify Crawl Errors
Head to Google Search Console (GSC). Go to Index > Coverage to see a list of crawl errors and warnings. Click on each error for more details, including the affected URLs and the error type. Then, prioritize the most critical errors, such as 404 errors on essential pages.
You can also check your server logs for crawl errors that might not appear in GSC.
To fix 404 errors, try these processes:
- Restore the page if it was accidentally deleted.
- Create a 301 redirect to the new URL if the page has been moved permanently.
- Create a helpful custom 404 page that guides users back to relevant content.
- Afterward, validate your fixes using the URL Inspection tool in GSC to test if the fixed page can be crawled and indexed correctly.
Indexation Status
Indexation status refers to whether or not a specific webpage has been added to a search engine’s index.
When a page is indexed, it appears in search results when users search for relevant queries. In contrast, if a page is not indexed, it’s invisible to search engines and won’t be found by users.
How To Ensure Proper Indexing of Pages
- Create high-quality, unique content and use relevant keywords to signal to search engines what your page is about.
- Submit a sitemap to help search engines discover and crawl your pages.
- Optimize internal linking to help search engine bots navigate your site and discover all your pages.
- Check Robots.txt to ensure your txt file is not blocking search engines from crawling and indexing critical pages.
- Monitor indexation status by checking the Index > Coverage report in GSC to see which pages have been indexed and if there are any indexing errors.
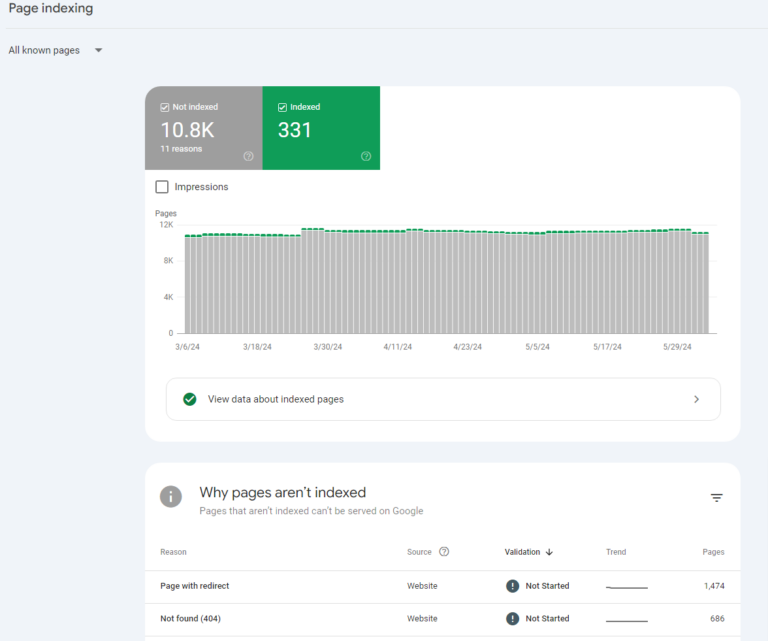 Screenshot from GA4, June 2024
Screenshot from GA4, June 2024Site Speed
Site speed is the time a website’s content takes to load and become fully interactive for users. Think of it as the digital stopwatch that measures the responsiveness and efficiency of your website.
Why Is Site Speed Important for SEO?
- User experience (UX): Studies have shown that users expect websites to load within a few seconds. Fast website speed keeps users engaged, encourages them to explore more pages, consume more content, and ultimately convert into customers or leads. It also enhances the mobile experience.
- Search engine rankings: Search engines prioritize faster websites because they provide a better user experience, which can help your faster website outrank slower competitors.
Read More:
Content Performance Metrics
This explores how effective your content is via:
Content Engagement
Content engagement measures users’ level of interaction and involvement with your web pages.
It goes beyond passive consumption and delves into how visitors actively engage with your content to indicate genuine interest and value.
How To Measure Content Engagement
- In GA4, track metrics like average engagement time, sessions, and engagement rate to gauge how long users actively interact with your content. You can also implement event tracking to measure specific interactions (video views, downloads, form submissions, or clicks on internal links).
- Use heatmaps and session recording tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg to visualize how users interact with your pages. This will reveal where they click, scroll, and spend the most time.
Content Shares And Backlinks
Content shares, or social signals, are the number of times your content is shared across social media platforms.
Social shares indicate that your content is valuable and worthy of being shared and can amplify reach, build brand awareness, and attract backlinks.
Backlinks, on the other hand, are links from external websites that point to your web pages. Quality backlinks from other authoritative sites act as “votes of confidence” and signal to search engines that your content is trustworthy and authoritative.
High-quality backlinks can boost rankings, drive referral traffic from other websites, and increase your domain authority.
To track social shares, use the built-in analytics tools provided by social media platforms to track the number of shares, likes, comments, and overall engagement for your content. You can also use third-party tools like Hootsuite or Buffer.
To track backlinks, use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Moz to see your total backlinks, referring domains, and link quality.
Read more:
Local SEO Metrics
Local SEO ensures your business appears when users search for products or services in your geographic area. Let’s start with getting insights from Google Business.
Google Business Profile Insights
Google Business Profile (GBP) is a free tool for businesses to manage their online presence across Google, including Search and Maps.
GBP Insights provides valuable data on how customers find and interact with your business listing.
How To Track GBP Performance
Log in to your GBP account and click the Insights tab. Look for the section titled How customers search for your business.
You’ll see a breakdown of:
- Direct searches (branded searches),
- Discovery searches (non-branded searches— when customers search for a general category, product, or service that you offer) and
- Maps searches: When customers find your business through Google Maps.
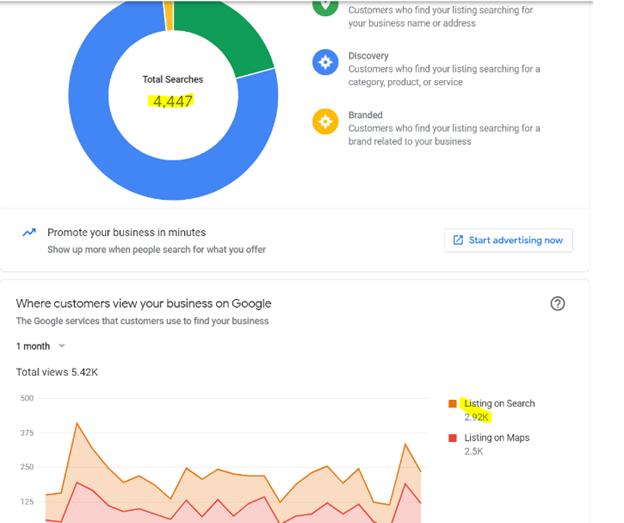 Image from Google Support, June 2024
Image from Google Support, June 2024In the same Insights tab, look for the section called Where customers view your business on Google. It will show whether customers find your listing more often in Search results or Maps.
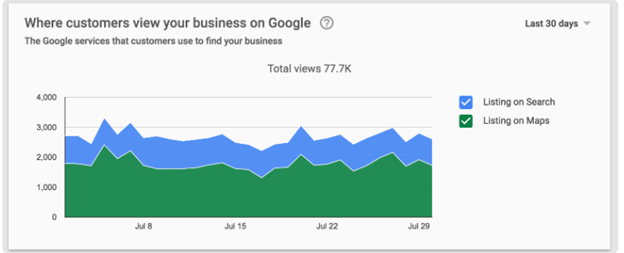 Image from Google Support, June 2024
Image from Google Support, June 2024Also, check for customer actions in the Insights tab. Here, you can track website visits, calls directly from your listing, and direct requests to your location. This data reveals how customers engage with your business after finding your listing.
Other data to track include photo views and search queries.
Local Search Rankings
Local search rankings refer to your business’s position in the SERPs for queries with local intent.
These searches include location-specific keywords like “coffee shops near me” or “best dentist in Albany.”
Local search results often include a map pack (a group of three to four businesses displayed on a map) and organic listings.
How to Track Local SEO Success
- Tracking local keyword rankings through tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or Moz Local. Monitor your rankings for critical local keywords, as well as your map pack rankings and organic rankings.
- Monitor GMB Insights to know how customers find your business, their actions, and which search queries they use.
- Analyze local traffic and conversions on GA4 to segment your traffic by location and track conversions (phone calls, direction requests, website visits, purchases) that originated from local searches.
- Track online reviews and ratings.
Read more on how to rank for Local Pack SEO.
Customer Reviews And Ratings
Customer reviews and ratings provide valuable customer feedback about their experiences with your business, products, or services.
These reviews are often publicly accessible on Google, Yelp, Facebook, and industry-specific review sites.
Why Are Reviews Important For Local SEO?
- It’s a ranking factor, as businesses with positive reviews are more likely to appear higher in local search results, including the map pack and organic listings. For instance, Google ranks your business higher if you have many reviews, a high frequency of new reviews, multiple review sources, and an overall star rating.
- Star ratings (or positive reviews) displayed alongside your business listing in search results can increase CTR.
- Positive reviews enhance customer trust and conversion, as customers now rely on online reviews when making purchasing decisions.
Competitor Analysis
Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking in SEO involves identifying, analyzing, and comparing your website’s performance to that of your top competitors in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
This helps you uncover your strengths and weaknesses, discover opportunities, and make data-driven decisions.
Some competitor performance metrics to analyze include:
- Their keywords, search volume, and keyword gaps.
- Their high-performing content format.
- Backlink analysis.
- Technical SEO audit (site speed, mobile friendliness, crawlability, and indexability.
Read more: SEO Competitive Analysis: The Definitive Guide.
Conclusion
Rankings are great, but conversions pay the bills.
Conversions are important they determine the efficacy of all your marketing efforts.
Tracking these metrics (and how they contribute to sales) will help you intensify marketing efforts on the strategies that work and allocate budgets effectively.
More resources:
Featured Image: Deemerwha studio/Shutterstock
In article screenshots taken by author
Source link : Searchenginejournal.com
