Understanding consumer behavior (why people do what they do) is the single most pressing issue for marketers of all industries. How do we get a read on our potential customer’s decision-making journey? This is why market and consumer research is so important to communicate with a target audience.
Psychological, sociological, and economic drivers can help marketers understand why users make decisions. Pulling from user data and buyer personas can also inform consumer behavior. But there’s still a lot of confusion about the things that impact consumer behavior, the nuances of it, and how we can impact it.
So, here’s a guide to get you up and running with the most important aspects of consumer behavior. This will benefit all aspects of your marketing strategy, foster customer loyalty, and maximize your marketing message impact.
We cover the types of consumer behavior, its drivers, and how marketers can influence consumer decisions. Let’s get to it.
4 Types of consumer behavior
Behavior analysis defines consumer behavior through the lens of:
- High involvement — Purchases that are higher cost are higher risk and require more buyer involvement to make a buying decision.
- Low involvement — Purchases that are low cost are lower risk and require less buyer involvement to make a buying decision.
- Few differences between brands — Product categories that contain undifferentiated, commodity-like goods regardless of the brand. This limits consumer choice.
- Significant differences between brands — Product categories that contain differentiated, unique goods from brand to brand.
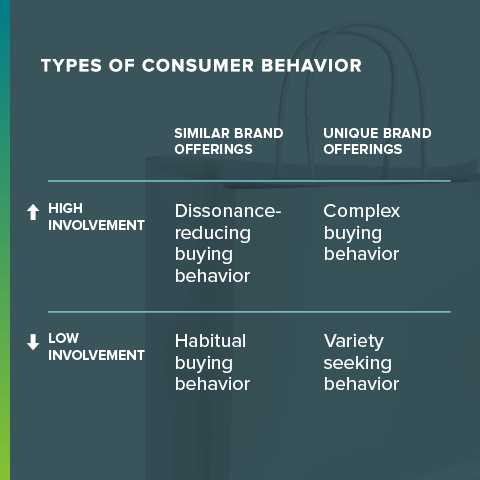
There are all kinds of consumer behavior across industries, but the marketing discipline has narrowed it down to four big categories:
- Habitual buying behavior
- Variety seeking behavior
- Complex buying behavior
- Dissonance-reducing behavior
Each differs in unique, nuanced ways that are worth examining.
Habitual buying behavior
Purchases of common day-to-day products like a favorite toothpaste or other in-store grocery items. Habitual purchases tend to be lower cost and therefore not perceived as risky. Less risk means a quicker decision, with limited thought or research. Habitual buying can be considered pattern buying because it’s an ongoing purchase of the same product.
This is not the same as brand loyalty because brand loyalty is less relevant in habitual buying. There’s little involvement in these decisions and that does not mean consumers are buying from a place of loyalty. They’re simply making the choice because other offerings are so similar, not because they **** your brand.
Variety seeking behavior
Variety seeking purchases break a pattern of buying, not because there’s a better product or due to dissatisfaction, but to shake things up. Humans often seek out a different product to see what else is out there and from a curiosity perspective. Like habitual buying, variety seeking behavior involves inexpensive, low-risk purchases and limited involvement.
Complex buying behavior
Complex buying behavior comes into play with large purchases like homes or vehicles, which are infrequently purchased. Because complex buying involves costly items and high risk, first-time buyers are highly involved in the decision-making process. High-cost investments require comparison and research before a decision.
Dissonance-reducing buying behavior
Dissonance-reducing buying behavior occurs when consumers feel a strong tension about making the wrong buying decision. Dissonance happens when consumers struggle to identify the difference between various brands or offerings. Dissonance-reducing purchasing behavior aims to relieve the tension by making the right decision and requires high involvement as a result.
What drives consumer buying behavior?
There’s an endless list of individual drivers of customer behavior but they fall into three major categories: psychological factors, personal factors, and social factors.
Psychological factors
Psychology is a foundational aspect of consumer behavior. Stimuli like needs and desires, thinking patterns, and other mental processes all impact purchasing decisions. All of these elements start with perception.
Exclusivity
A major aspect of brand perception is the idea of exclusivity. This may be characterized by rarity, luxury, high cost, and as status symbols. Exclusive products create demand through these perceptions of value.
Shoppers desire to stand out in social groups and one way to do so is by acquiring luxury items. Establishing an exclusive reputation is a powerful method of fostering customer loyalty and gaining a competitive advantage.
Getting the “best”
When searching for a new product or service, it’s safe to say that all of us desire and seek out a perceived “best” among a number of alternatives. “Best” markers include numerous 5-star reviews and customer satisfaction, customer experience, social media sentiment, and perceived quality. Being the “best” brings new people in the door and strengthens customer retention.
Thinking patterns on an individual level
Individuals in very specific situations solve their real-time unmet needs and desires with purchasing decisions. Most of these individual-level decisions are grounded in the consumer’s perception of pain points and their solutions. Things like value, utility, and convenience are some common examples. If you have an unmet need, convenience can lead to a quick, in-the-moment decision.
Personal factors
Demographic and segmentation factors play a substantial role in consumer behavior. These include:
- Age
- Gender
- Sexual orientation
- Nationality
- Religion
- Cultural values
- Interests and lifestyle
Depending on the demographic, or other identity marker, consumers seek solutions to unique pain points. For example, a young, new mother may seek products for post-pregnancy solutions, fitness, or baby products to solve a variety of needs
Social factors
Social psychology elements like socioeconomic status, education level, living conditions, familial dynamics, and social group interactions also drive buying habits. In fact, without the social element, which supports the other consumer behavior factors, perception doesn’t really matter.
Our social needs largely determine how we perceive our pain points and their solutions. Exclusivity, luxury, the “best” concept, and other perceptions all happen because of the social context. We all want to fit in and keep up with our peers, and the products one likes or dislikes is another aspect of gaining acceptance.
Five ways you can influence consumer behavior in marketing
Here are some ways you can start influencing consumer behavior with your marketing efforts.
1. Tell stories
Operating from a purely data-driven perspective is great but sometimes it all comes down to storytelling. Storytelling is the best way to connect what you know about your audience with a clear narrative that evokes emotion and speaks to their needs.
Given the ability of all brands to create sophisticated personas, creating stories to match up with the desires of your real audience has become much more actionable.
The creation of great, narrative-driven brand stories is not only doable, it’s one of the most effective ways to create authentic communication that fosters real customer loyalty.
2. Create a seamless buying experience and customer journey
Consider creating totally seamless buying experiences across all your assets (web pages, social, emails, blog, etc.) that require a few simple clicks from awareness to transaction.
By building a seamless full-funnel infrastructure, you gain consistency through the process and a stronger path to a transaction. Built well, this system grabs attention, nurtures each visitor towards a transaction, and makes it easy to close the loop with a customer review.
Focusing on making the customer experience seamless helps you identify the bigger opportunities to better orchestrate the overall buyer’s journey. Making the customer journey logical and convenient sways your audience in the right direction.
3. Personalize campaigns with marketing technology
Using quantitative and qualitative marketing data and technology, brands can influence consumers with hyper-targeted campaigns. Based on different audience actions, many services deliver unique content, emails, webpages, and more to encourage engagement.
Many platforms also provide reporting, so you can set metrics to measure the success of your personalized campaigns. Then, with this data, your team can optimize and improve future campaigns.
The ability to micro target and then assess your performance gives you actionable insights about building your influence.
One highly effective consumer behavior influence strategy is to create an online community. Examples include creating a social page, Facebook group, using a forum, or other community-centric strategy to develop an online home for your customer base.
A community based around your brand achieves several objectives. You create a new customer touch point to interface with your audience, develop informal brand evangelists, engage powerful social psychology effects, and establish an in-group.
All of these aspects can create shifts in consumer behavior that favor your brand and its offerings.
5. Offer incentives to boost sales and loyalty
E-commerce brands can utilize incentives like promo codes, sales promotions, and other short-term campaigns to drive sales and customer loyalty. Offering special codes exclusive to certain podcast audiences, running social media contests, hosting special events, and even offering classic sales all play a major role in influencing your target demographics.
Don’t underestimate the power of associating your brand with popular culture trends like podcasts. The impact can be substantial.
Final Thoughts
Consumer behavior is a fundamental aspect of marketing but parts of it are often misunderstood and not fully leveraged to achieve brand goals. This is a big mistake.
It’s wise to spend time developing your team’s consumer behavior knowledge to ensure, at every level, your marketing efforts actually align with your real customers. It’s also vital to establish this if you seek to influence the behavior of these real-world customers.
Get consumer behavior right and you stand to achieve a level of customer engagement that even the biggest brands dream about.
