Updated: March 7, 2024.
Here I’m showing you step by step how to audit your site with Google Search Console only.
SEOs when doing SEO audits always use a site crawler like Sitebulb or/and Semrush Site Audit as the main tool and a bunch of other SEO tools.
But is it possible to perform a technical SEO audit using only Google Search Console? It turns out it is!
In my in-depth SEO audit guide, I showed you how to perform a technical SEO audit using standard SEO auditing tools.
Here, on the other hand, I will show you how to do that using Google Search Console only. This is going to be super interesting.
Check the twin article on how to use Google Search Console to do keyword research.

SEO Audit With Google Search Console (Step By Step)
Before you start, keep in mind that:
- You can do this SEO audit type only for existing sites that are indexed by Google and that have at least some traffic from Google.
There has to be enough data in GSC for you to be able to draw conclusions and make observations. If you are auditing a brand-new site, then you must use standard SEO auditing tools, such as Sitebulb,Semrush Site Audit , or Screaming Frog. - To be able to do this technical SEO audit, you need to have full access to the site in GSC.
- Ideally, the site should have both the Domain and URL prefix properties.
- You need to have full permission to the property or be its owner.
⚡ Check my article on how to add and remove users in Google Search Console if you have problems getting access to GSC.
☝️ If you are a beginner/intermediate SEO, you definitely want to take a look at the list of SEO best practices (from Google).
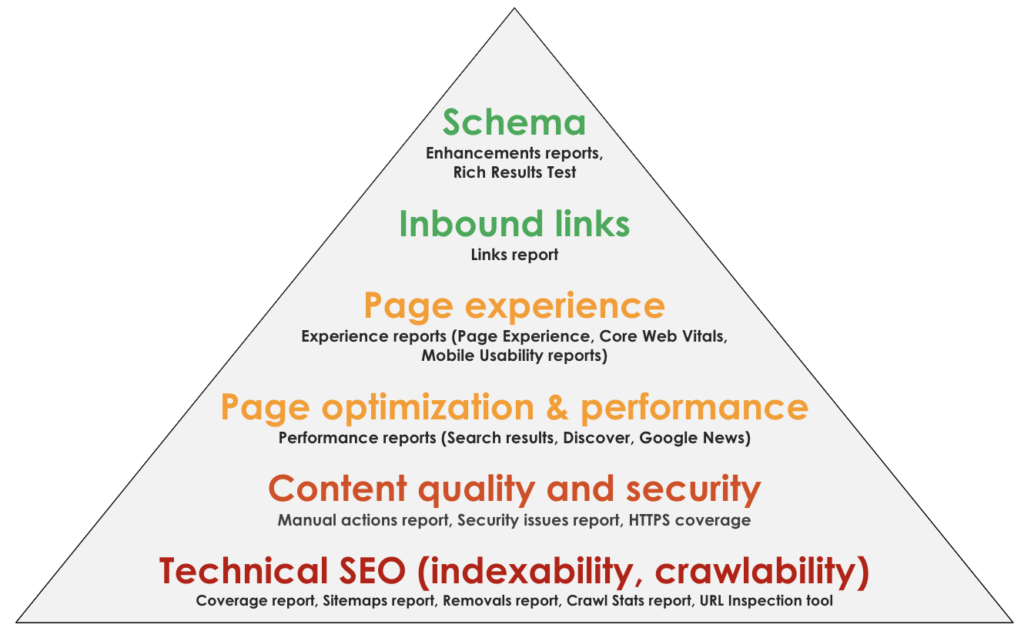
Basic overview of the site
1. Check the overview of the site
Go to Overview (you will automatically land in Overview after logging in) to get a quick overall picture of the site. If the site is having serious issues (a manual penalty or security issues), you will see them in Overview.
2. Check if the site has undergone some major change recently
This is a very important piece of information especially if you are hired to investigate a traffic drop. You can check if the site has been changed recently in two ways:
- Go to the Overview section and pay special attention to what you see under the overview of Performance and Coverage.
❗ If there is a significant drop or spike in Performance and/or Coverage, you will need to investigate it deeply. I will talk about the Performance and Coverage reports later in the audit.
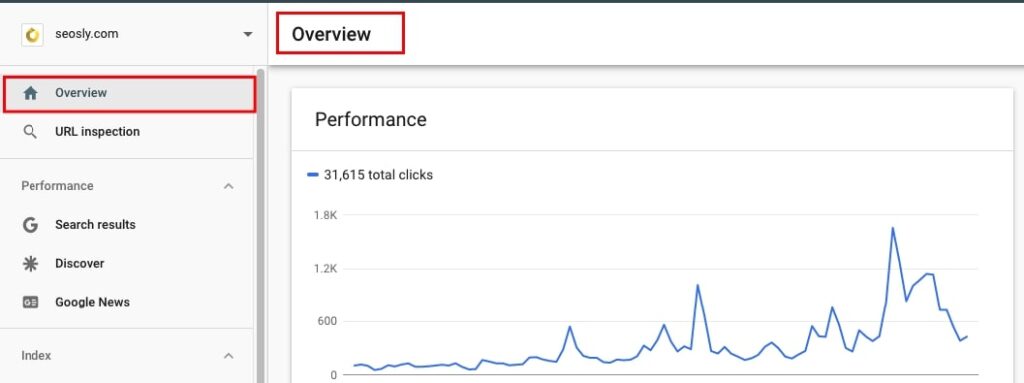
- Go to Settings > Change of address.
This Google Search Console tool is used to inform Google about the change of address to speed up the migration process.
You may want to check it to make sure that your client did not forget to mention that the site had been migrated. Note that this tool is not mandatory to perform a site migration but some people use it.
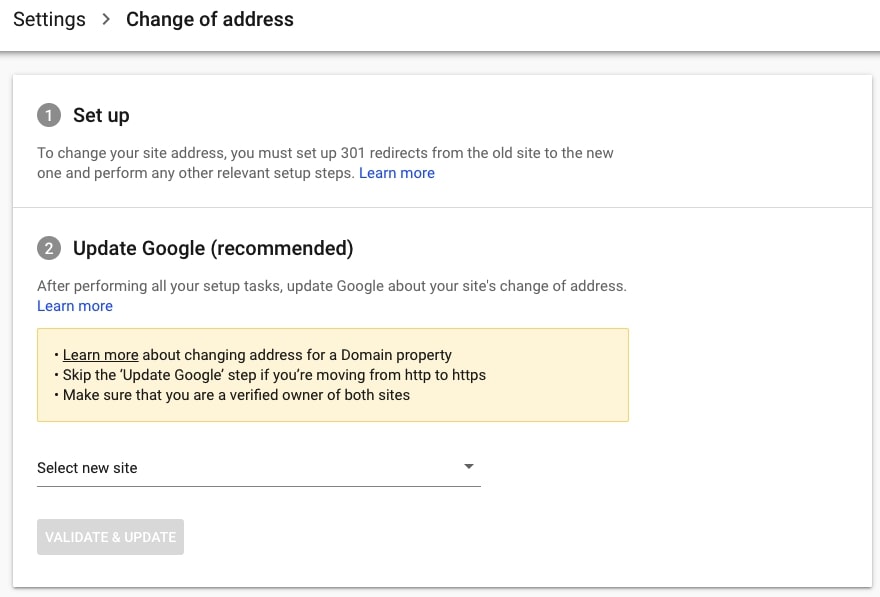
3. Check if the site has a manual action
To be sure you are not missing any important information, go to Security & Manual Actions > Manual actions. If you see “No issues detected”, then you can continue with the audit.
❗If there is a manual action, then dealing with it should be the top priority because the site is most likely demoted in Search.
4. Check if the site has security issues
Just as above. Go to Security & Manual Actions > Security issues and make sure it says “No issues detected”.
❗If there are issues, then removing them should be the top priority because the site may not be displayed in Search or displayed with some ugly warning!
Crawling, crawlability, robots.txt, and sitemap
5. Check how Google is crawling your site
That’s what the Google crawl stats report is for. No need to do a file log analysis. Go to Settings > Crawl stats and pay special attention to:
- The number of crawl requests and their trend. Is it upward or downward?
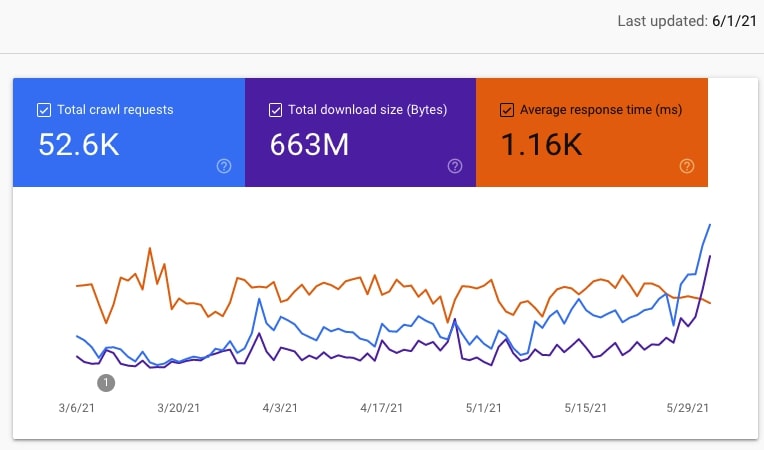
- The crawl request breakdown and especially the By response section to make sure the crawl budget isn’t wasted on, for example, crawling pages returning status Not found (404).
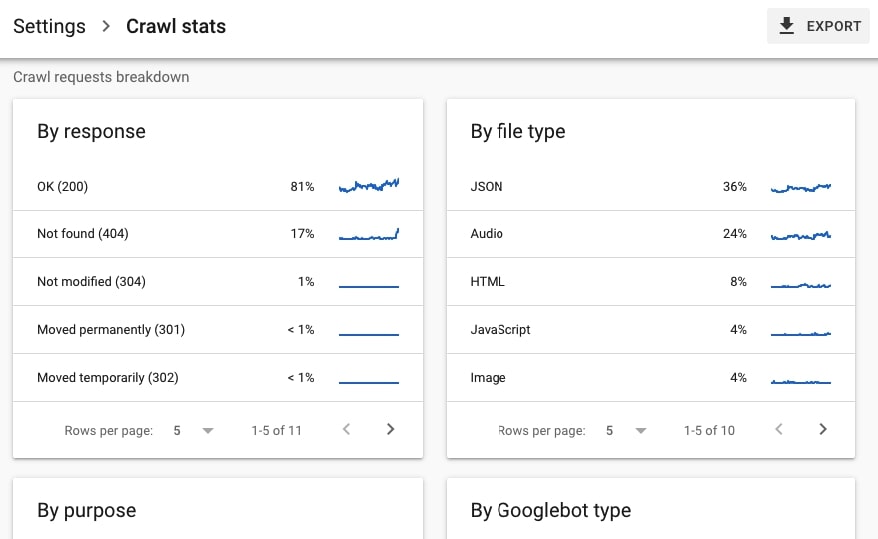
⚡ Check my in-depth guide to Google Search Console crawl stats report to learn more about this tool.
6. Check if your host has had issues that make it impossible for Google to crawl your site
The Crawl stats report will also show you if your hosts are having any availability issues. This is very important because these issues may make it impossible for Google to crawl your site.
When in Crawl stats report, navigate to Hosts and check if any issues are reported under Status.
- If you have a Domain property, then you will see all child domains under Hosts.
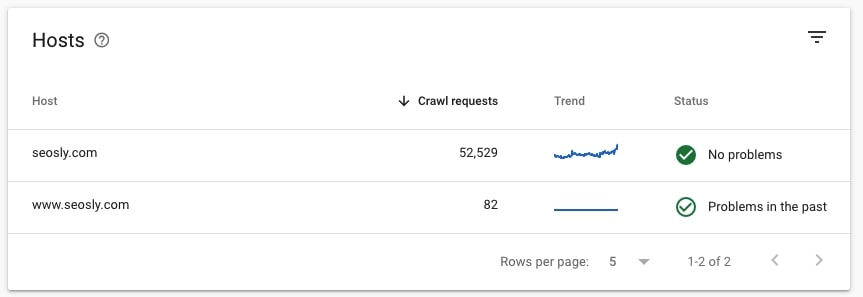
- If you have a URL prefix, then you will see the data for this one specific UR.
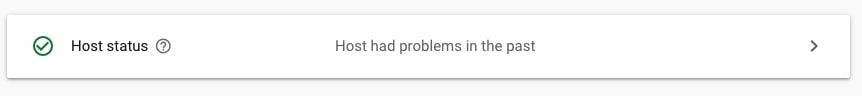
If you don’t see No problems under Hosts/Host status, make sure to check the details of the issues. Google reports on three types of host issues, such as robots.txt fetch, DNS resolution, and server connectivity.
7. Check if Google has problems requesting robots.txt
Yes, you can also use the Crawl stats report to check if there have been any problems with fetching robots.txt. If there were issues, you will the notification under Hosts/Host status. Make sure to click through to investigate it further.
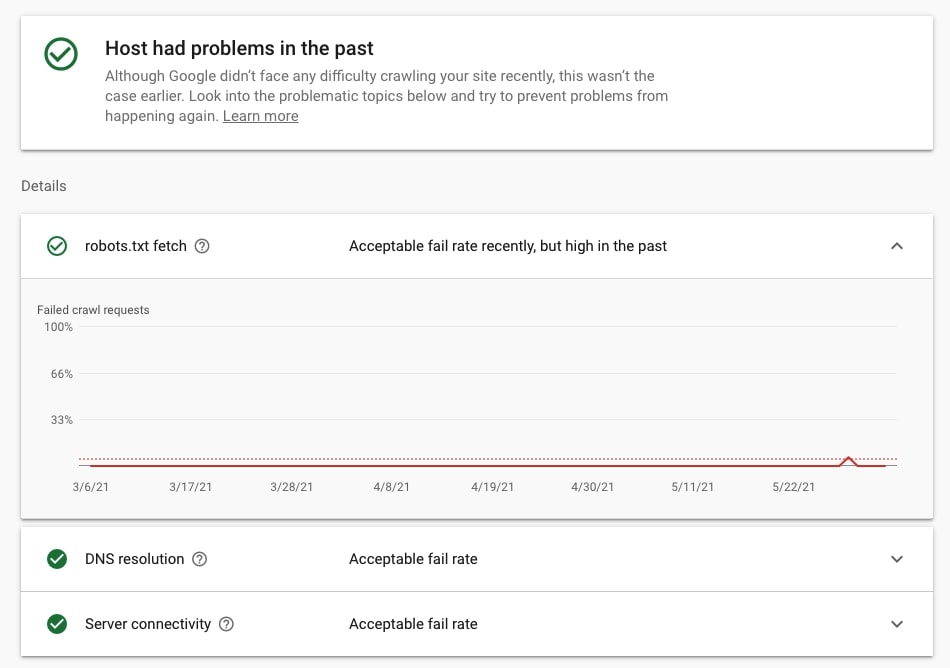
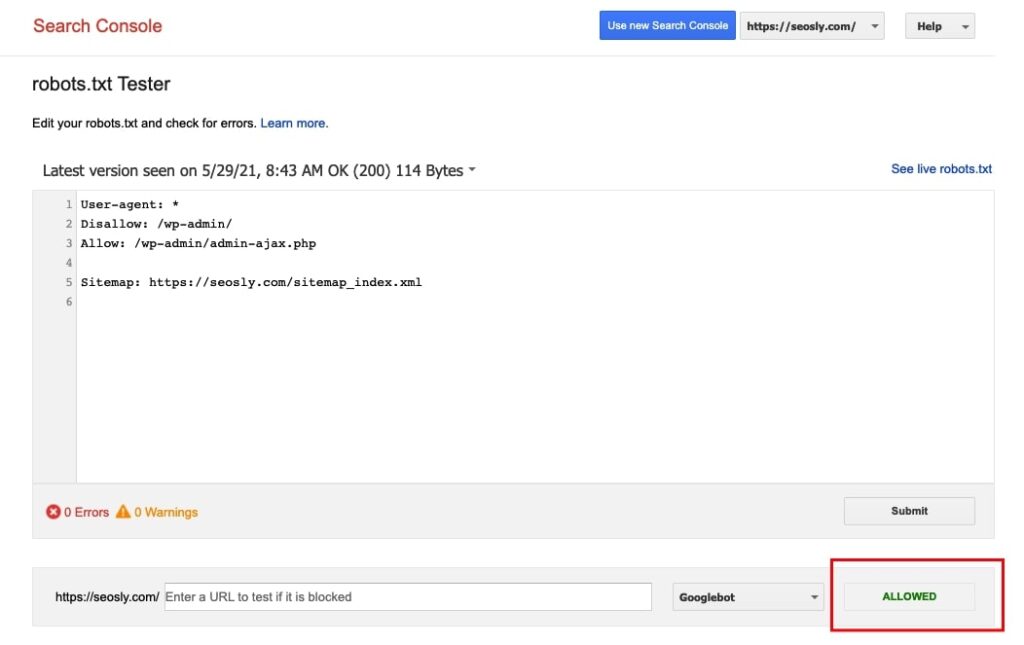
8. Check if robots.txt allows Googlebot
To test robots.txt, you can use the (old) Google Search Console robots.txt testing tool. To be able to use the tool, you need to have a URL prefix property.
The tool will show you warnings and errors and will let you check if Googlebot can access the site.
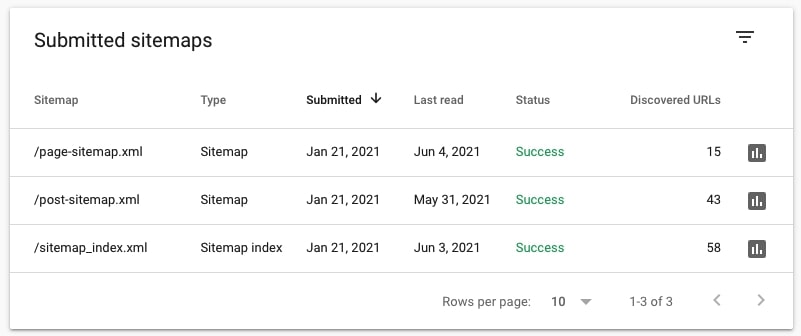
9. Check if sitemaps have been submitted to Google and if Google can fetch them
Go to Index > Sitemaps to check if sitemaps have been submitted to Google.
If the sitemaps are valid and Google has no problems fetching them, you will see Success under Status. If there are issues, you will see Couldn’t fetch.
10. Check if the XML sitemap contains incorrect URLs
Yes, you can use GSC to check if sitemaps have incorrect URLs, such as URLs with a “no-index” tag.
To do that go to Index > Coverage, click on the arrow down, and under Filter to Sitemaps, choose the sitemap to check.
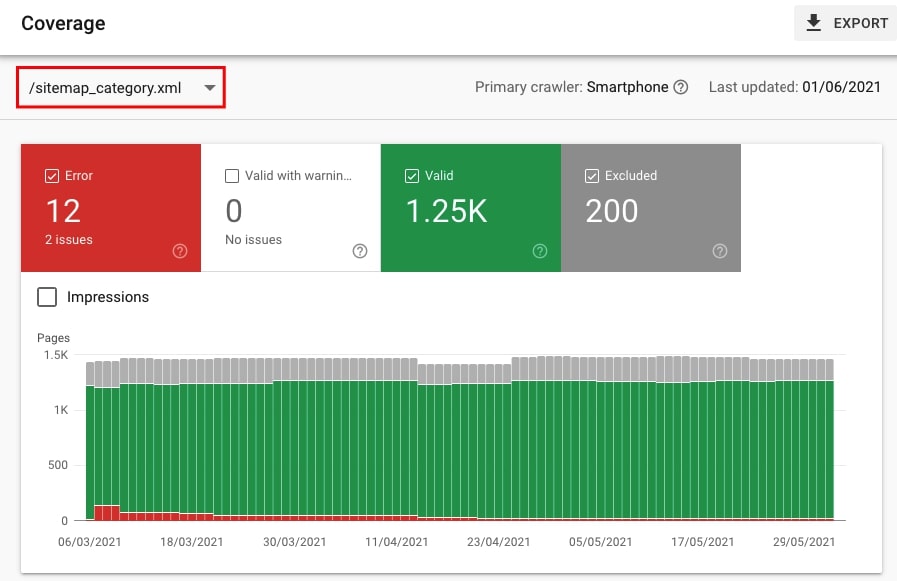
If the sitemap contains incorrect URLs, you will them under Error or Excluded. Make sure to read the details of the issues with those URLs and analyze these URLs.
Indexing & indexability in Google Search Console
11. Check how many web pages are indexed
Go to Index > Coverage and check Valid and Valid with warnings. These are the URLs that have been indexed by Google and can appear on Google.
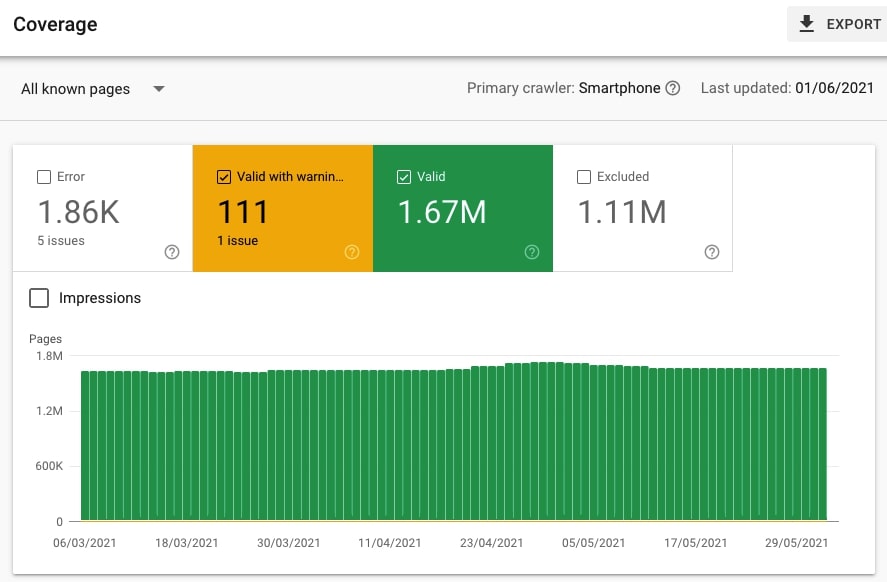
Make sure to analyze the pages that are Valid with warnings. These URLs have been indexed but there are some issues with them. Your task is to investigate further.
12. Check if any weird or irrelevant web pages are indexed
To make sure that Google has not indexed the URLs that should not be indexed, simply go through the list of the Valid and Valid with warnings URLs. Of course, depending on the size of the site it will be more or less doable.
When in Coverage, check Valid and Valid with warnings and scroll down to Details. Pay special attention to Valid URLs with Type Indexed, not submitted in sitemap. You need to manually review these URLs and decide if they all should really be indexed.
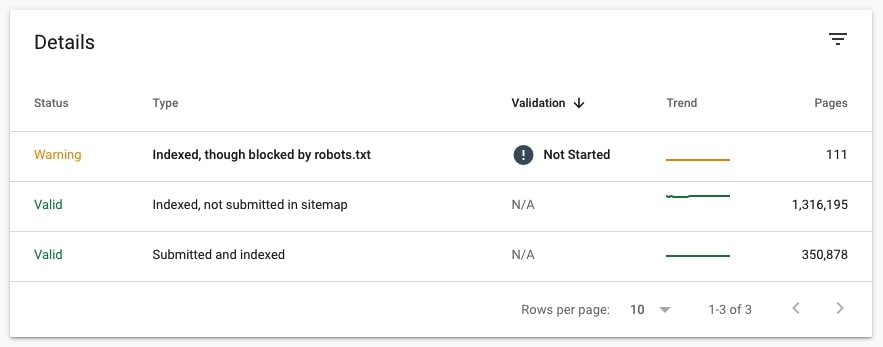
13. Check if there are pages that couldn’t be indexed
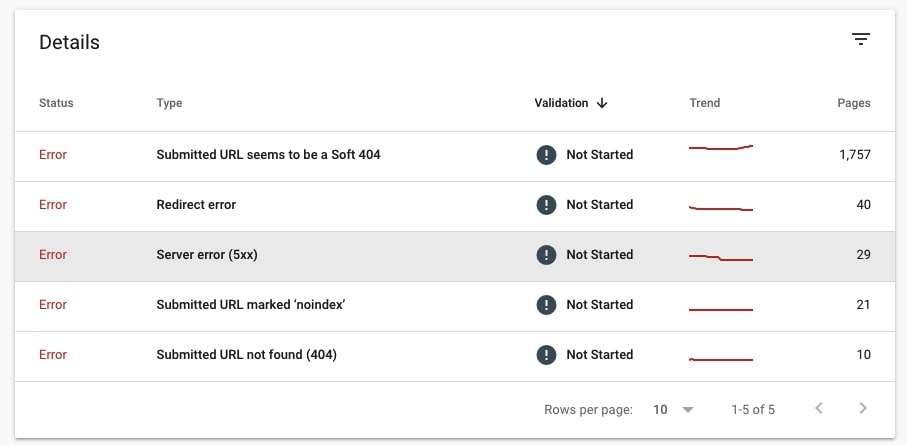
Go to Index > Coverage and check Errors. These are the pages that cannot be indexed.
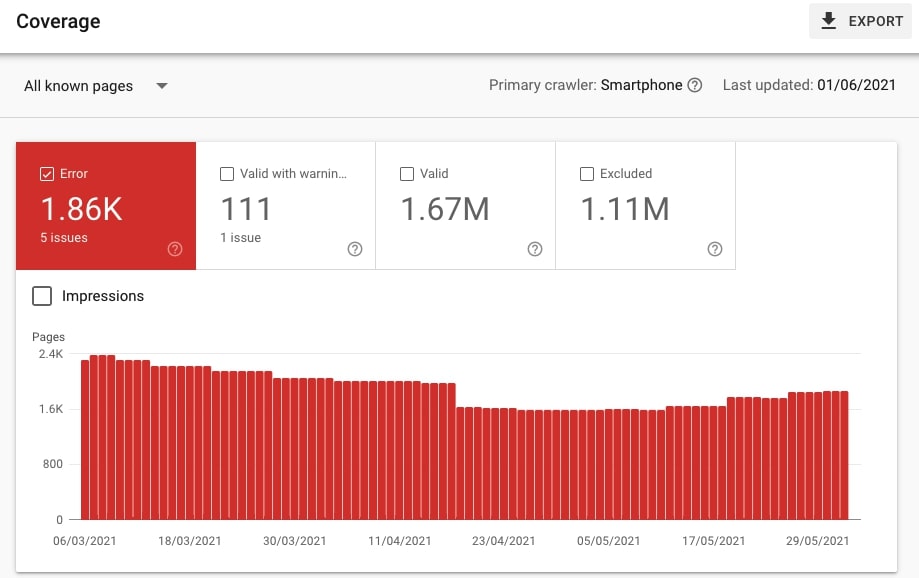
Navigate to Details to learn why these pages haven’t been indexed and to view the examples of those pages (click on the type of error and you will see the example pages).
14. Check if there are pages that were excluded from indexation
Go to Index > Excluded to see the pages that have intentionally been excluded from indexation.
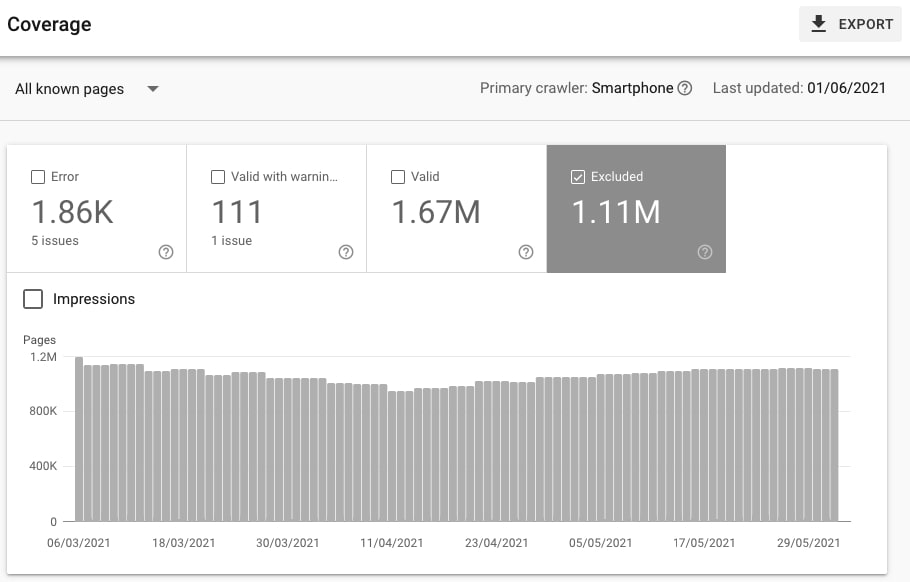
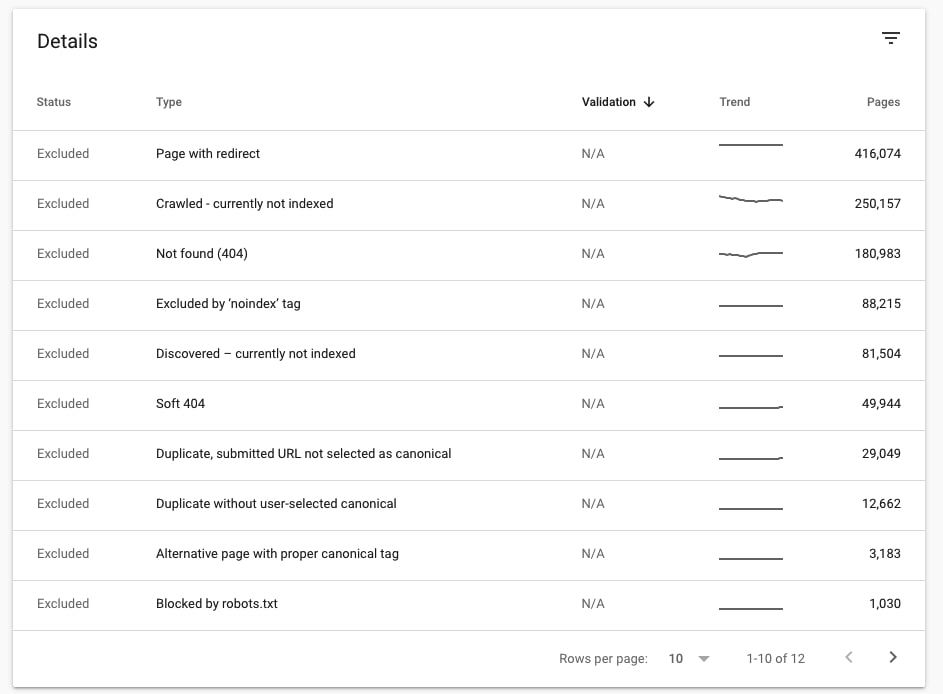
Navigate to Details to learn about the reasons why a specific page or a group of pages have been excluded. Click on the specific type of exclusion to see the list of URLs.
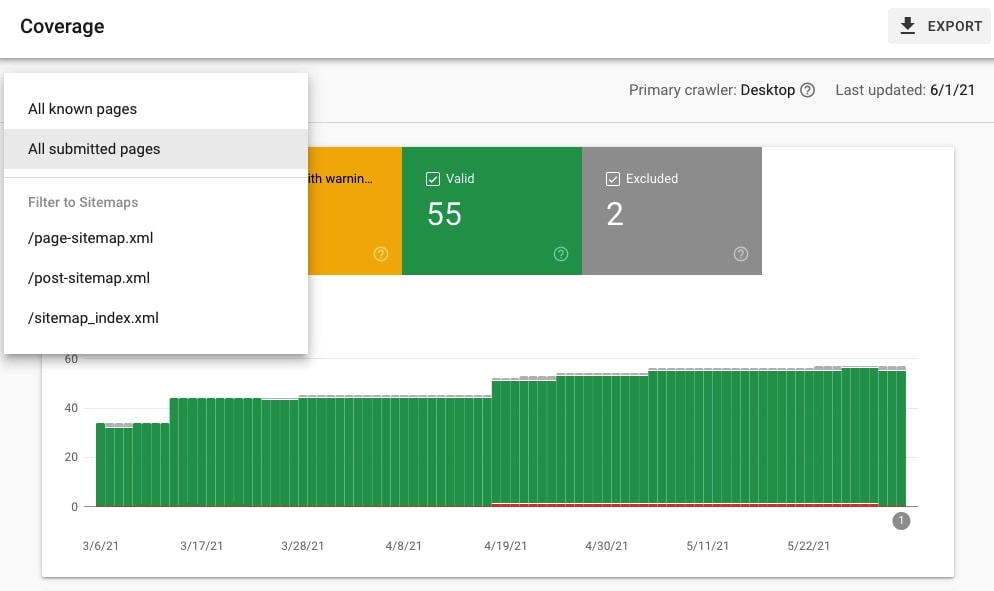
15. Analyze the coverage of the submitted URLs only
Quite similar but the results may be quite interesting. Choose All submitted pages instead of All known pages. Check if there are any pages with errors or warnings.
16. Check if there are any removal requests
Go to Removals and check what’s under TEMPORARY REMOVALS, OUTDATED CONTENT, and SAFESEARCH FILTERING. As an auditor, you want to know if someone has filed one of these requests and whether it has been done on purpose.
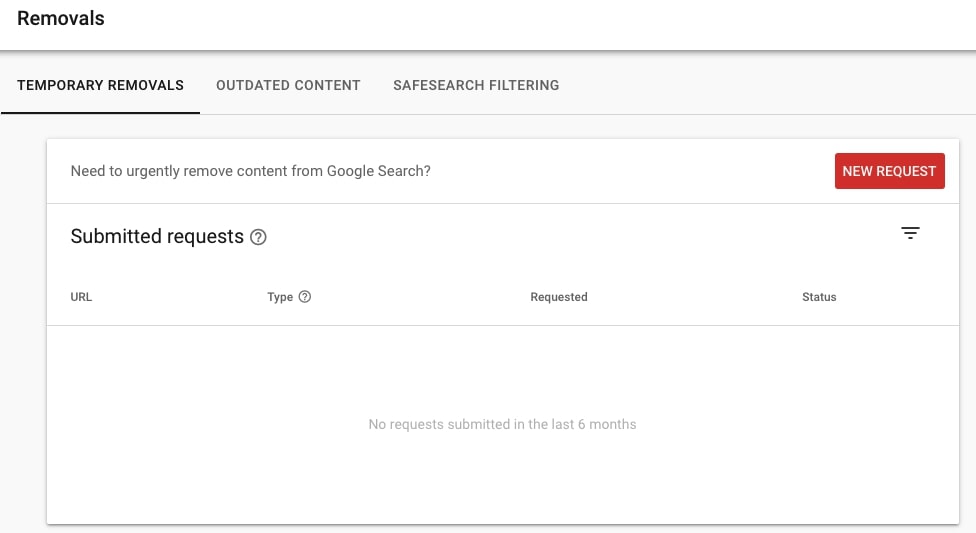
GSC also allows to you audit canonical links on your site. You can either check one specific URL or identify groups of URL with a specific canonical tag implementation or issues.
- To check the canonical tag of a specific URL, simply use the URL inspection tool, unfold Coverage and check what’s under Indexing.
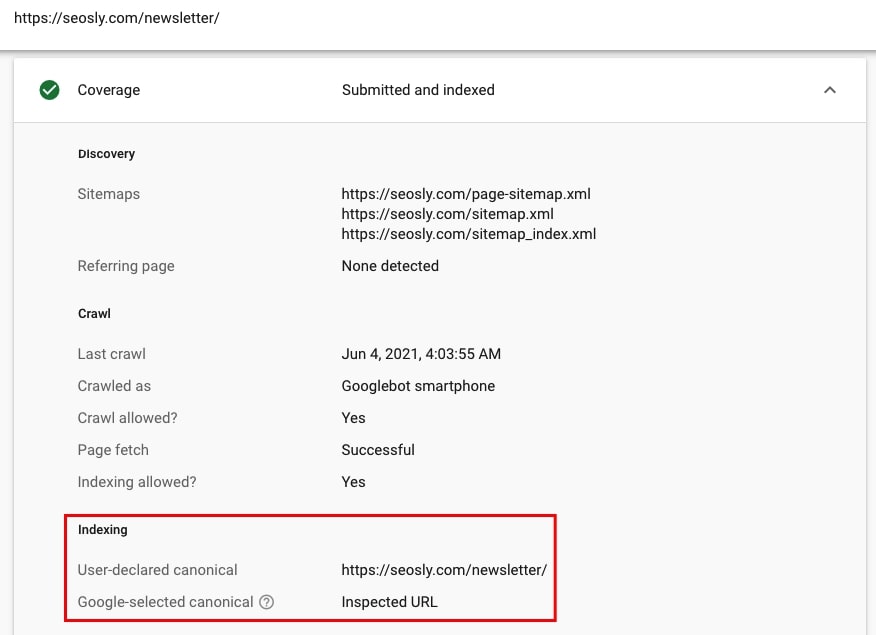
- You can also go to Coverage > Excluded and look for:
- Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user
- Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Alternative page with proper canonical tag
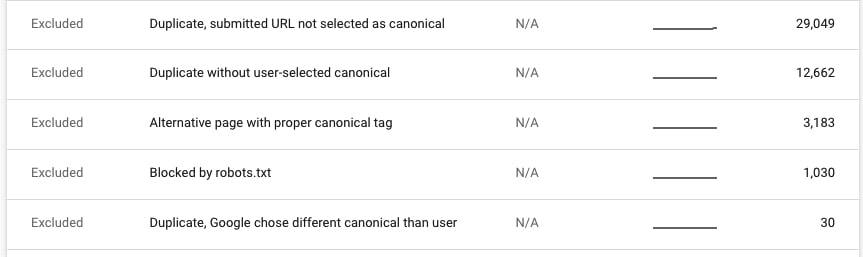
Make sure to analyze example pages folded under each of these four types of canonical tag issues/implementations.
Rendering & mobile-friendliness
18. Check how the pages of the site render
Another thing you can check using GSC is how the pages of the site are rendered.
- To do that, go to URL inspection, type the URL, and hit enter. Next, click on TEST LIVE URL.
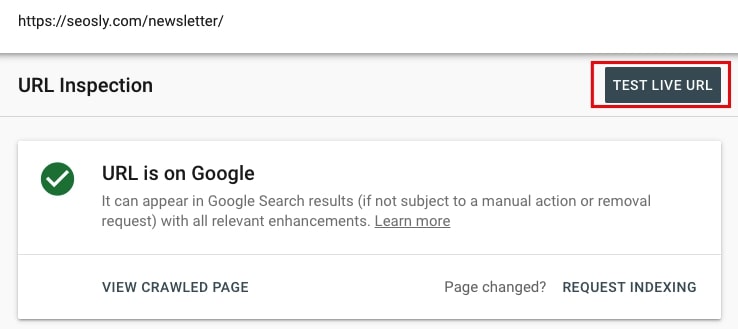
- Click VIEW TESTED PAGE and the panel on the right will appear. You can now view the rendered HTML, see the screenshot, or display more data (HTTP response, content type, page resources, JS console messages).
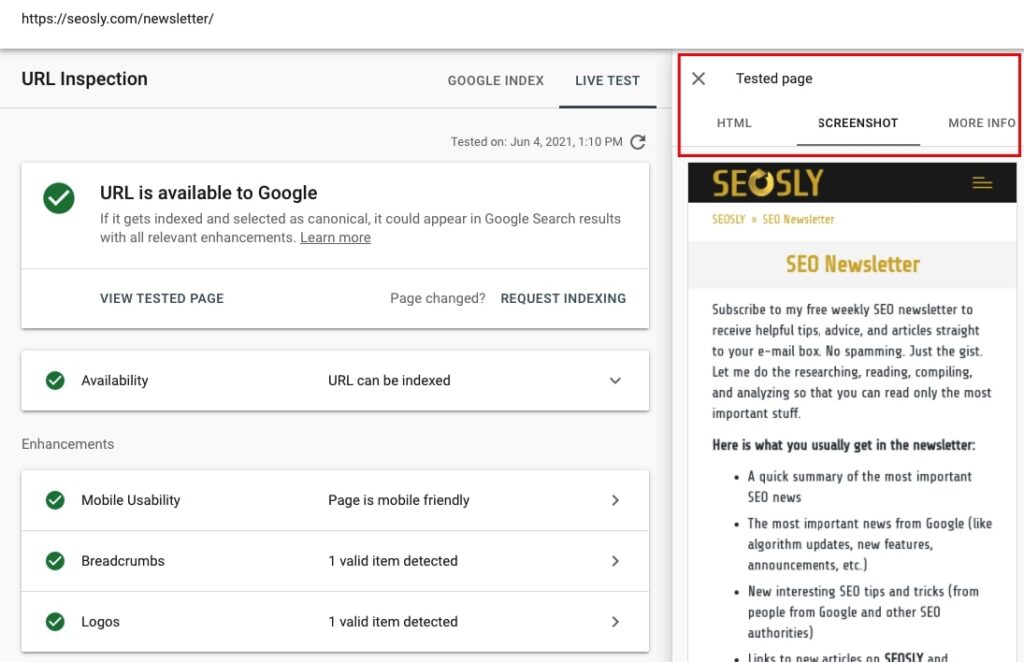
19. Check if the site is mobile-friendly
This is quite important, especially in the era of mobile-first indexing.
Go to Experience > Mobile Usability. If the site is mobile-friendly, then all of its pages will be marked as Valid.
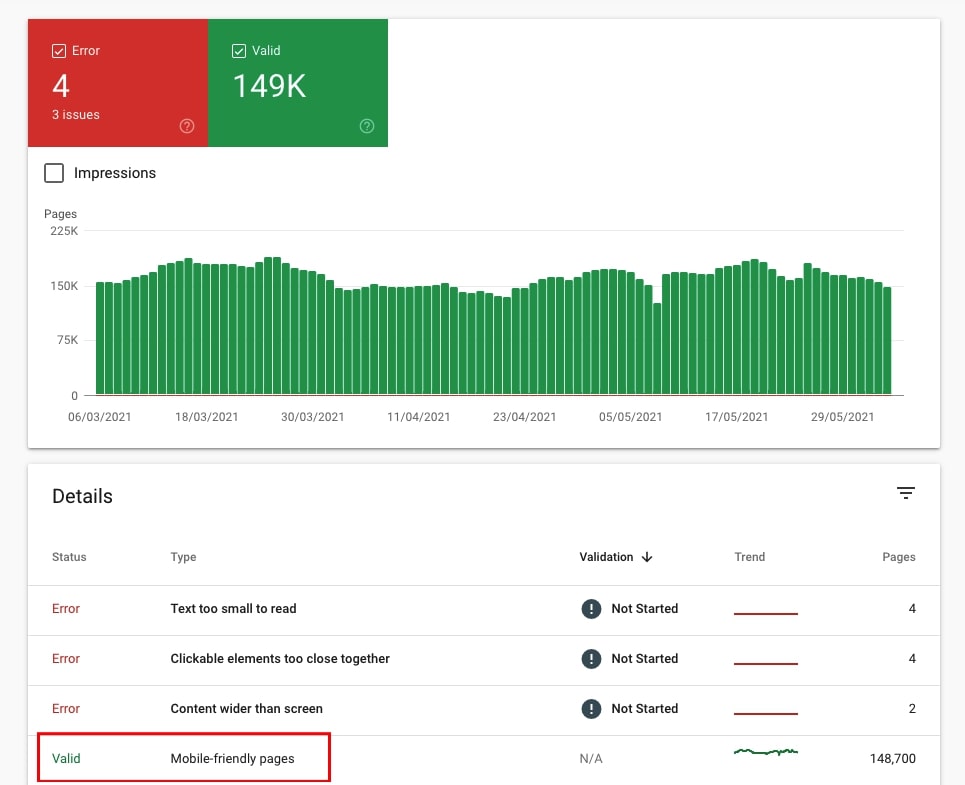
20. Check if there are any issues with mobile-friendliness
If the site has mobile-friendliness issues, then you will see them under Error. Pay special attention to these because these URLs may have serious problems in Search.
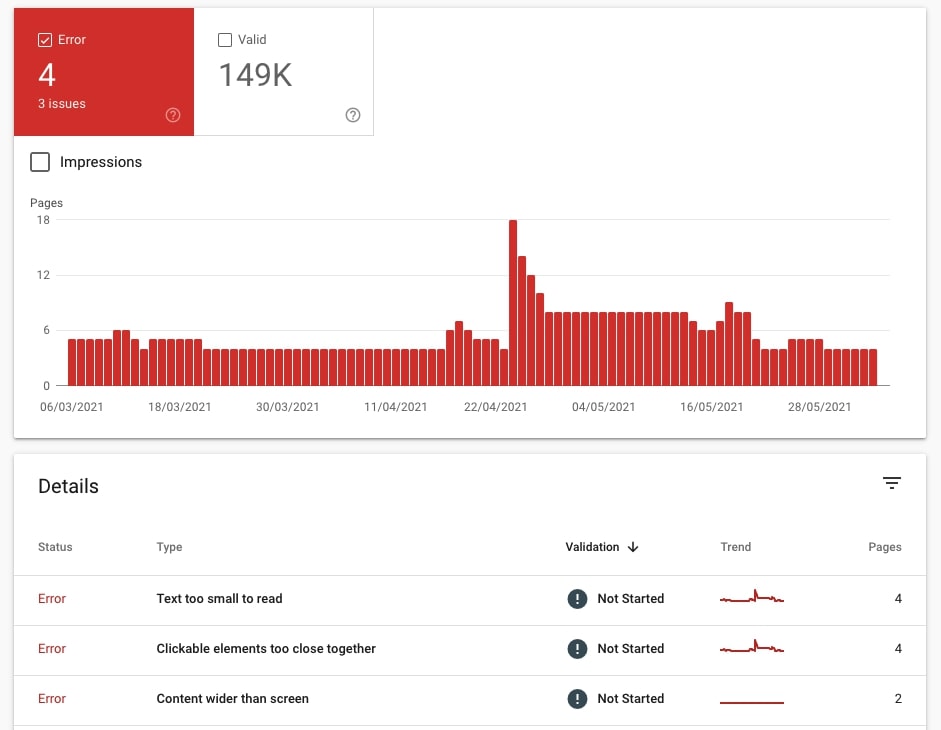
Google checks for the following six types of mobile-friendliness issues (I learned it from the GSC documentation):
- Uses incompatible plugins (e.g. Flash)
- Viewport not set
- Viewport not set to “device-width”
- Text too small to read
- Clickable elements too close together
- Content wider than screen
Not that the site can be mobile-friendly (e.g. has the viewport set properly) but it may have issues like Content wider than screen. You cannot ignore any of these issues.
Page Experience & Core Web Vitals
With the new Page Experience report and the Core Web Vitals report, Google Search Console allows you to thoroughly analyze and assess your site in terms of Google page experience signals.
21. Check the percentage of Good URLs
Go to Experience > Page Experience. Ideally, you want to see 100% of Good URLs. Note that Good URLs are the URLs that are considered Good if they pass all of the three Core Web Vitals metrics (for mobile).

⚡ Make sure to check my Core Web Vitals guide and my Core Web Vitals audit.
22. Check the overview of Google Page Experience signals
The Page Experience report shows you the summary of all five Google Page Experience signals.
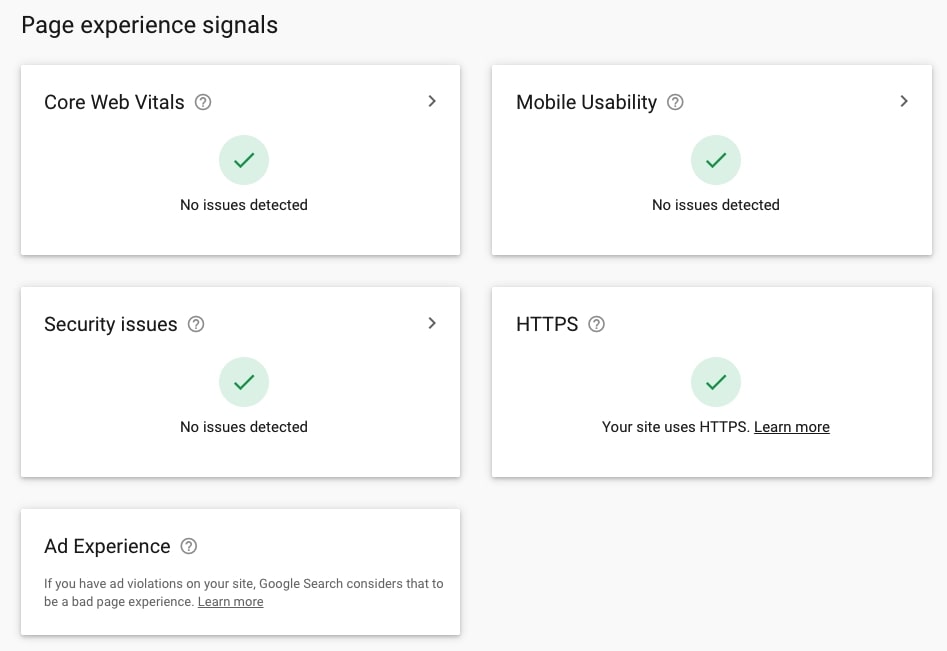
However, keep in mind that HTTPS is a site-wide check confirming that the majority of URLs on your site load over HTTPS, and Ad Experience – meaning no intrusive interstitials – is only a reminder that Ad Experience is one of Google Page Experience signals. This is not the actual Ad Experience status of the site.
⚡ Check my Google Page Experience audit to learn more about how to audit your site in terms of these five signals.
23. Analyze Core Web Vitals metrics for Mobile and identify groups of URLs with similar issues
Go to Experience > Core Web Vitals > Mobile and OPEN REPORT. Check Poor and Need improvement to display the details of URLs with issues. Navigate to Details and analyze each issue type and the URLs it affects.
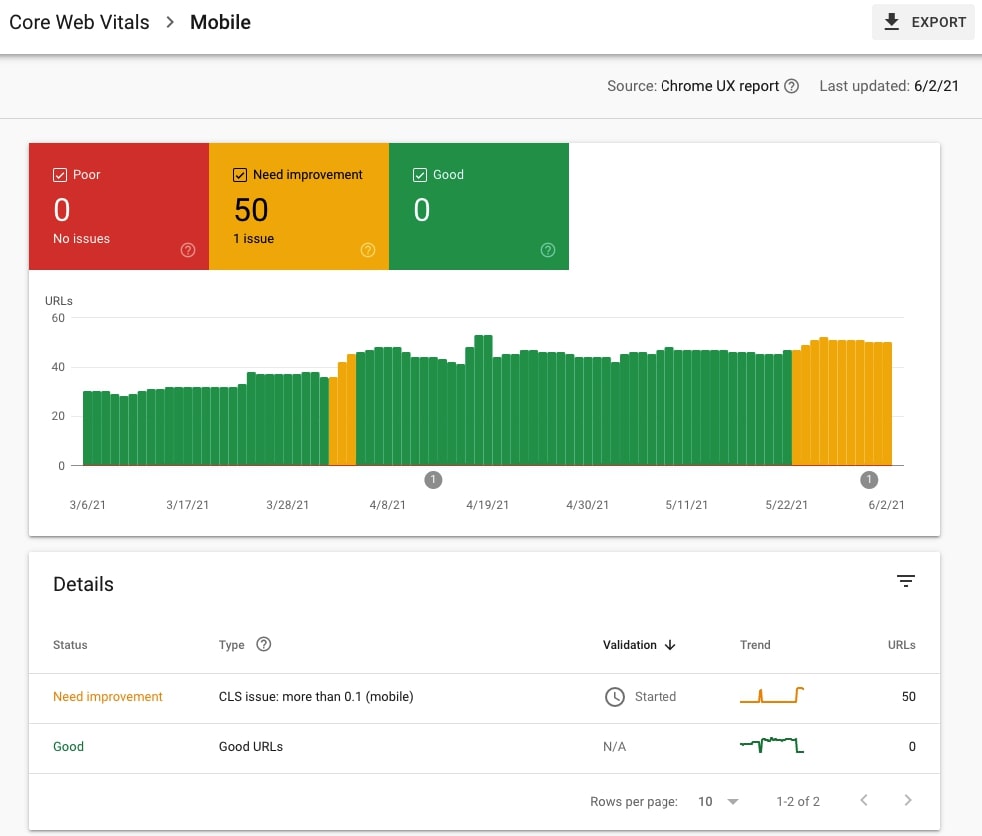
If all URLs are Good, then congratulations.
24. Analyze Core Web Vitals for Desktop and identify groups of URLs with similar issues
Core Web Vitals assessment is coming to desktop soon, so you definitely should look at how the site is doing in terms of Core Web Vitals for desktop.
Go to Experience > Core Web Vitals > Desktop and OPEN REPORT. Check Poor and Need improvement to display the details. Navigate to Details and analyze each issue type and the URLs it affects.
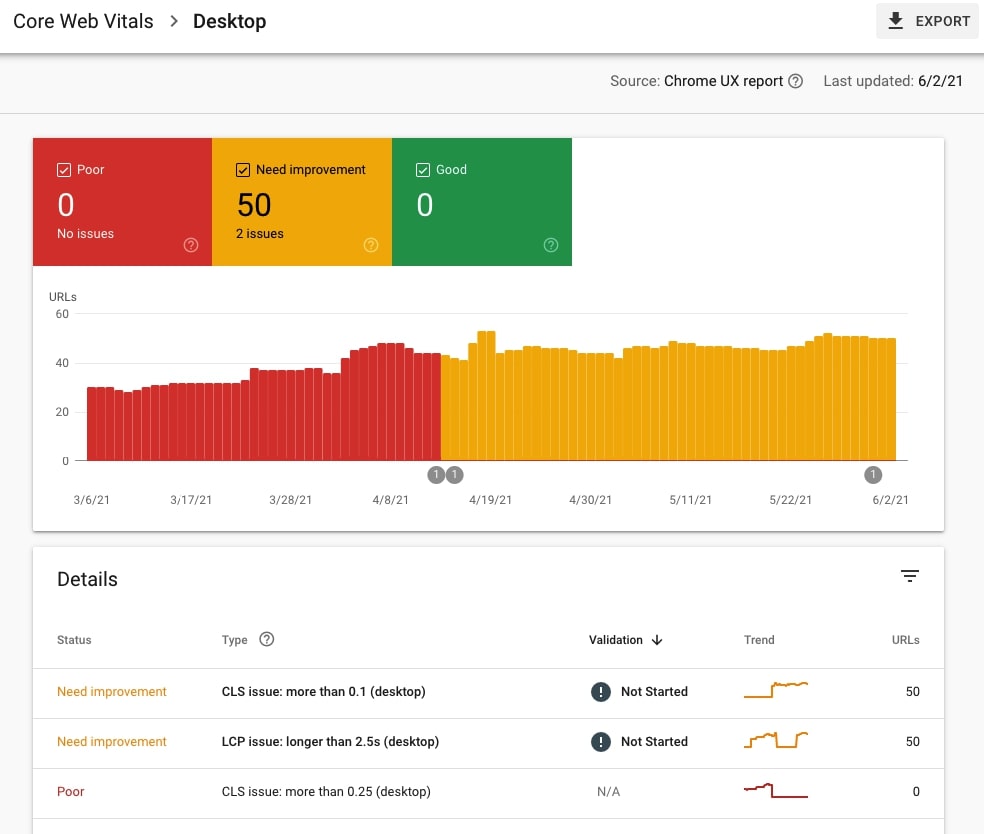
All green? Congrats!
Structured data (Schema.org)
25. Check the types of Rich Results implemented on the site
You can see the types of Rich results implemented on the site under Enhancements in the left sidebar in Google Search Console.
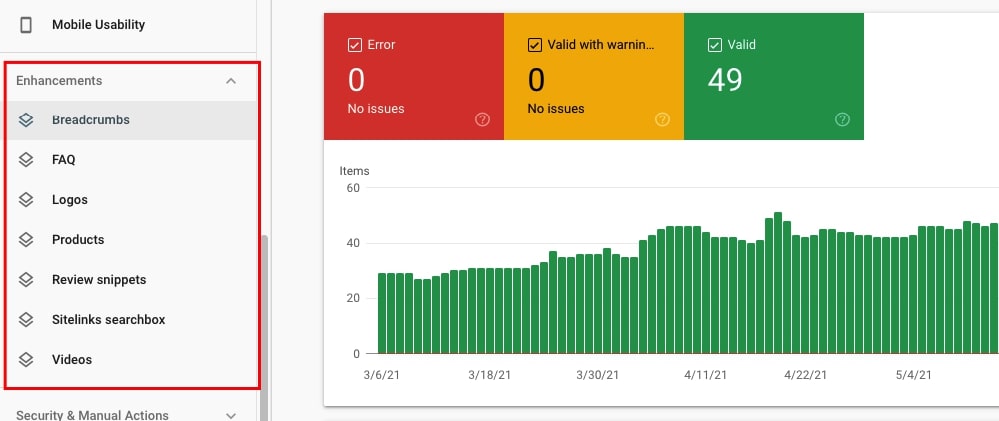
26. Check if specific structured data types implemented are correct
Simply click on each specific Rich results type displayed under Enhancements. If there are no issues with a specific type, you will see 0 under Error and Valid with warnings.
If there are any errors or warnings, then check what’s under Details and analyze the specific URLs or groups of URLs with these issues. Note that URLs listed under Errors cannot be displayed with the use of Rich results.
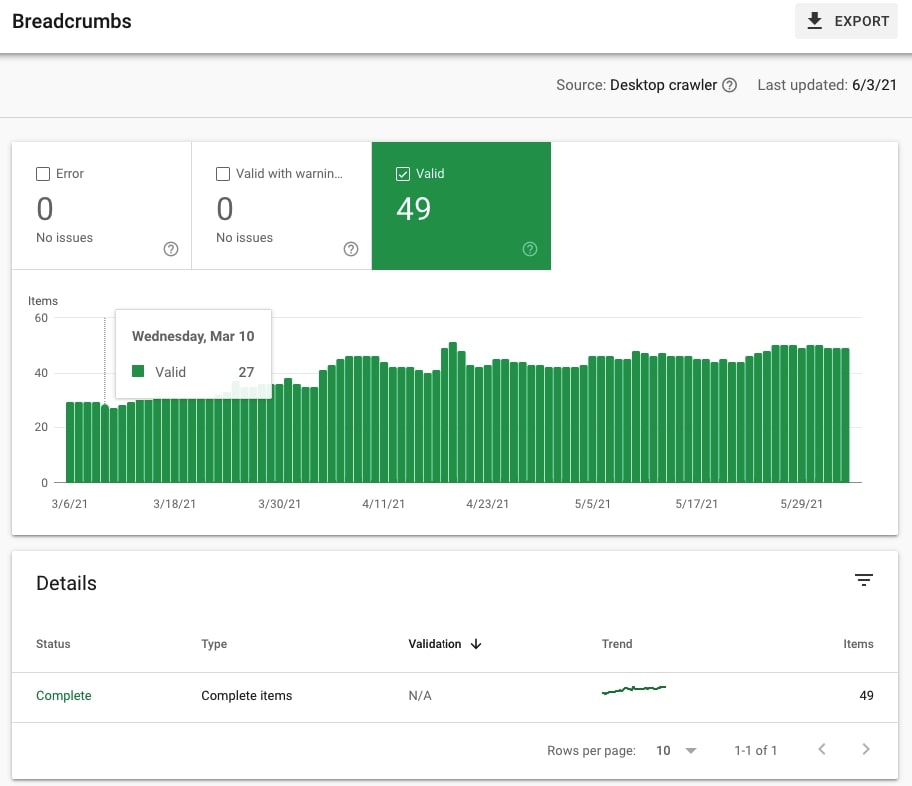
Having breadcrumbs on the site is almost always a good practice (especially in the case of larger sites).
Check if there are Breadcrumbs under Enhancements and if breadcrumbs are Valid (i.e. can be displayed in search results).
28. Check if the site uses the FAQ Schema and if it is valid
Having the FAQ Schema also makes a lot of sense in the case of many sites. Check if there is FAQ under Enhancements and if it is valid (i.e. can be displayed in search results).
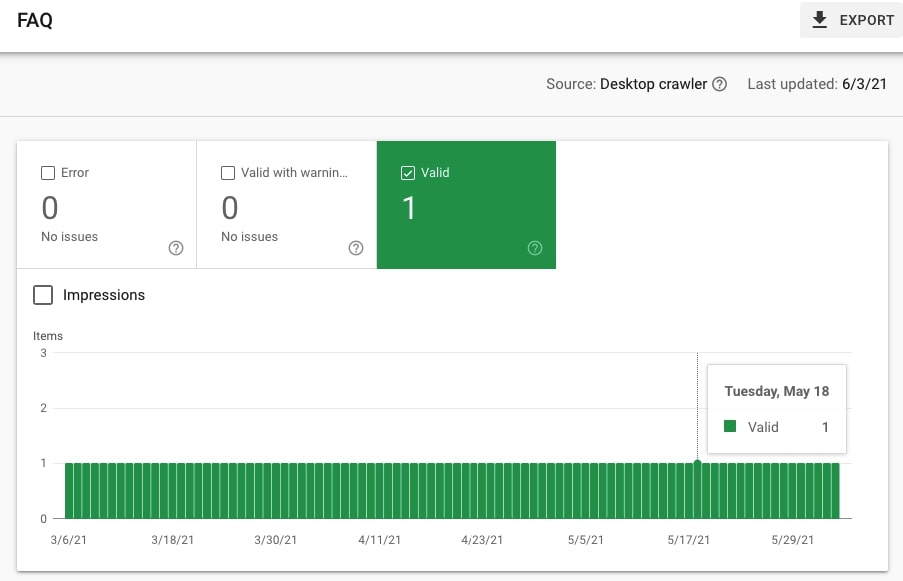
Language versions
Google Search Console (the old version) can also help you analyze and troubleshoot international targeting on the site.
Go to Legacy tools and reports > International targeting to check if the site has hreflang tags. Note that this report is not available to Domain properties.
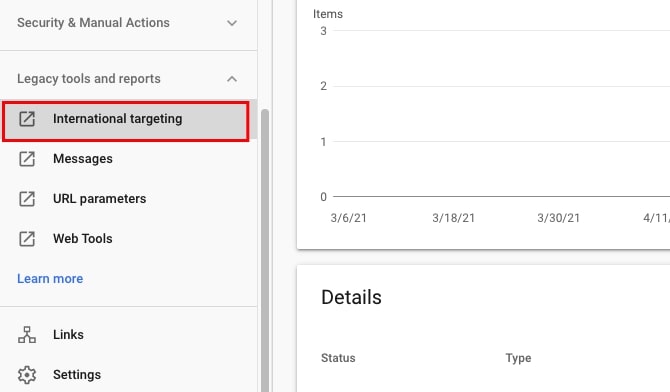
Once you click on International targeting, you will be moved to the old GSC. In tab Language, you can check whether the site has hreflang tags. Note that if there are serious issues with the implementation of hreflang tags, then GSC may show the info that there are no hreflang tags even if there are.
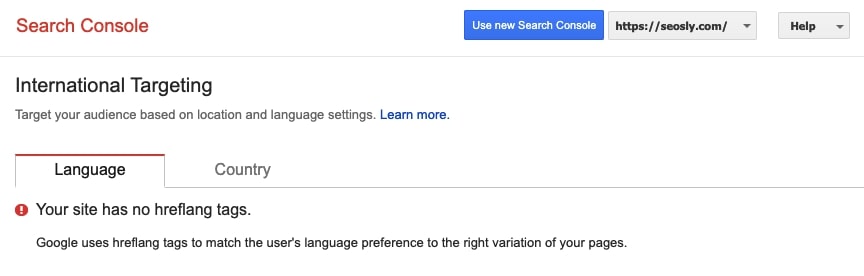
If Google can recognize hreflangs implemented on the site, then you will be able to see if there are issues and what types of issues they are. For example, GSC will show if there are no return tags.
Internal links
31. Check the top internally-linked pages
Google Search Console also allows you to analyze internal links and check what internal pages you link to the most.
Go to Links and on the right, you will see column Internal links with table Top linked pages. Click MORE to view the entire report.
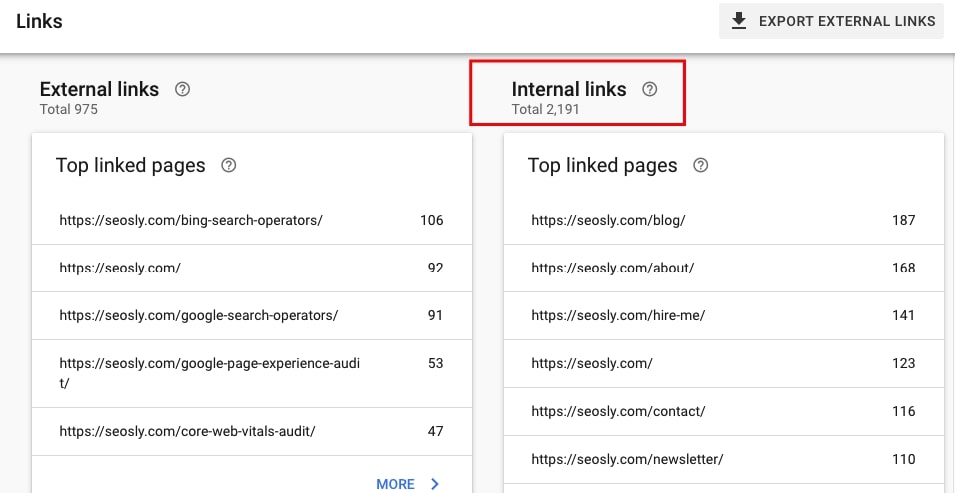
Are the top linked pages the most important pages of the site?
Status codes
Google Search Console is also a great tool for analyzing status codes on your site. You can do that using the Coverage report and the Crawl stats report. However, note that the Crawl stats report will show you all the resources of your site while the Coverage report will only show you the status codes of your pages.
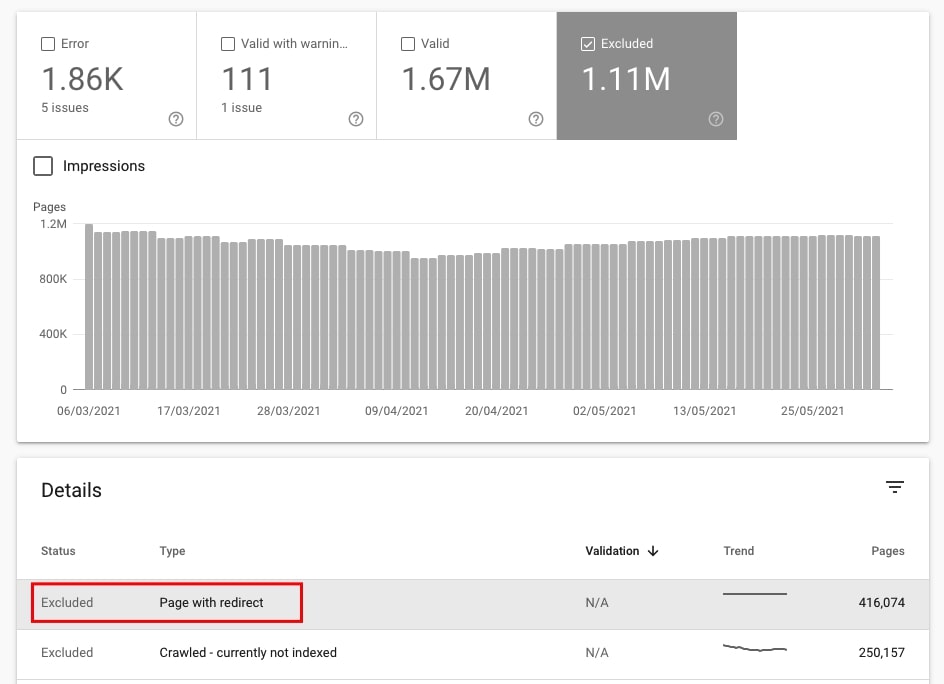
32. Check if there are 301 or 302 redirects on the site
There are two ways to analyze redirects in a site using Google Search Console.
- Go to Index > Coverage and check Excluded and scroll down to Details. Look for Page with redirect under type. Click to see the examples of redirected pages.
- Go to Settings > Crawl stats and scroll down to Crawl requests breakdown. Analyze what you see under By response. Are there 302 or 301 redirects?
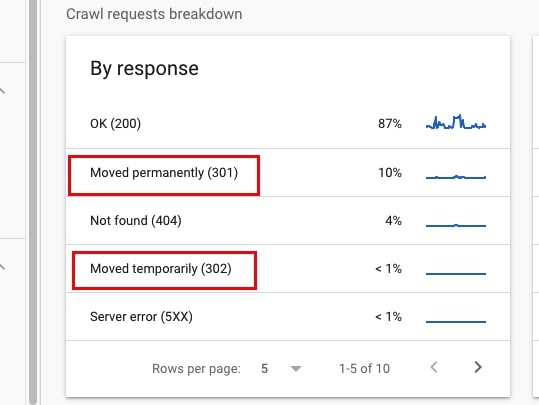
33. Check if these redirects have correct statuses
Now let’s check if the redirects have correct statuses, i.e. for permanent redirects 301 status is returned and for temporary redirects, it’s 302.
Go to Settings > Crawl stats and click on 301 and 302 redirects to check what URLs/resources are redirected and what status they return.
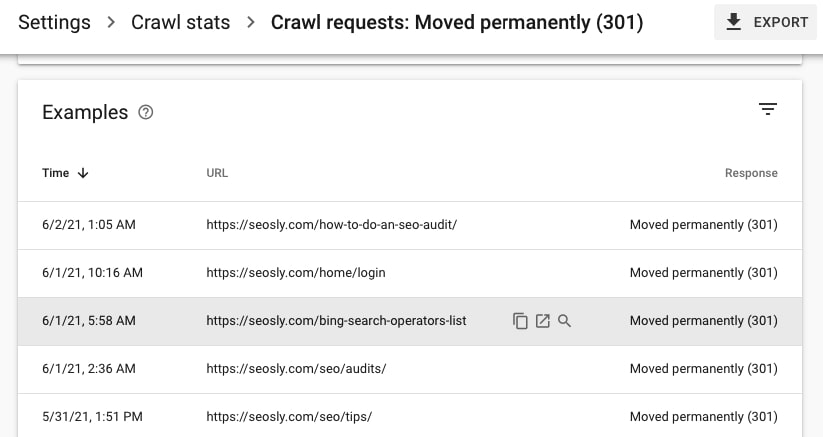
Many sites implement 302 redirects in the places where 301 redirects should be used. Google is getting better and better at recognizing such situations and treating these 302s as 301s.
34. Check if there are URLs returning 5xx errors
There are two ways to check if there are server issues.
- Go to Coverage > Errors and check if there are Errors with type Server error (5xx). Click on the issue to check details and see the URLs affected.
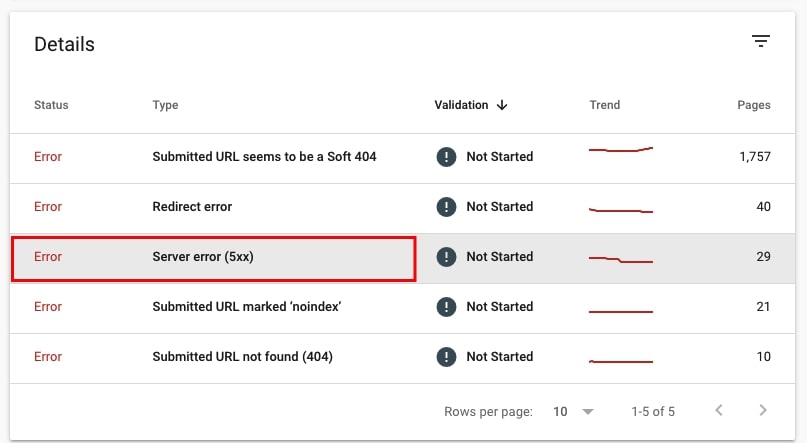
- Go to Settings > Crawl stats and look for Server error (5xx) under By response section of Crawl requests breakdown. Click on this issue to see example pages that returned 5xx.
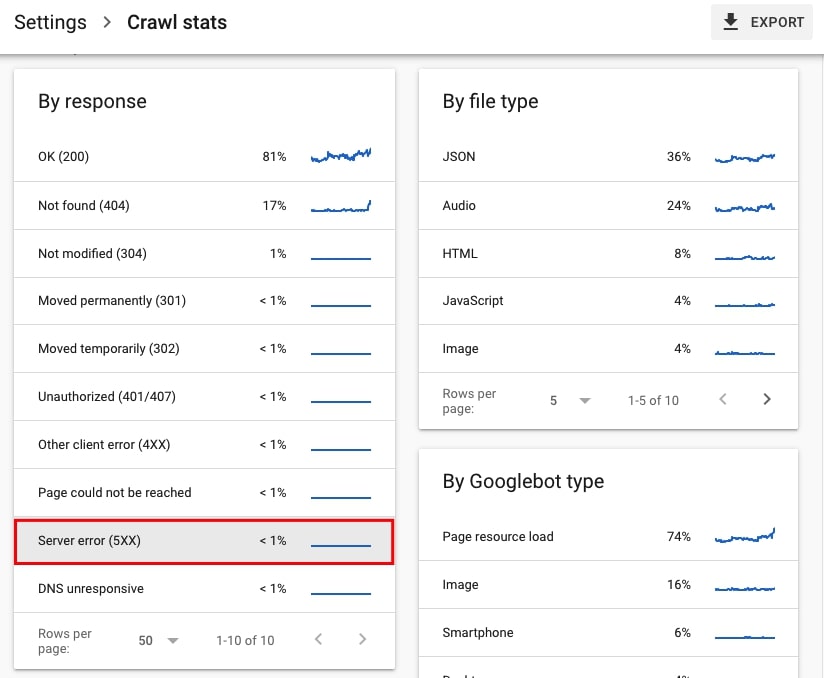
If the number of those URLs with issue Server error (5xx) or/and the requests with the response Server error (5xx) is huge you may want to further investigate the server of the site.
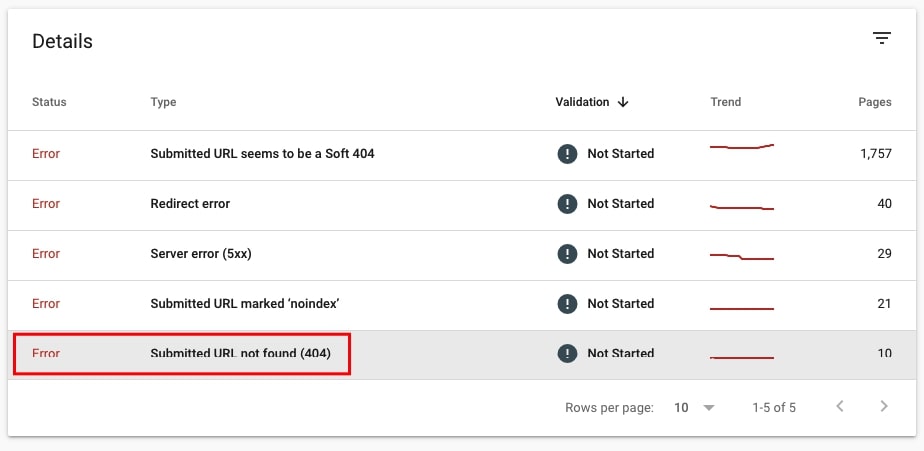
35. Check if there are URLs returning 4xx errors
Again, you can check that in two ways.
- Go to Index > Coverage and select Errors. Look for the Error type Submitted URL not found (404). Click on the error to see the ULRs affected. Check if they still return 404 and if this is the status code they should be returning.
- Go to Settings > Crawl stats and navigate section By response. Check what’s under Not found (404). Click to see the examples of resources returning status 404.
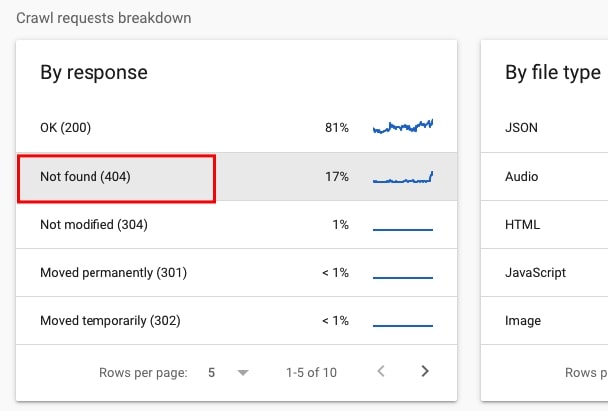
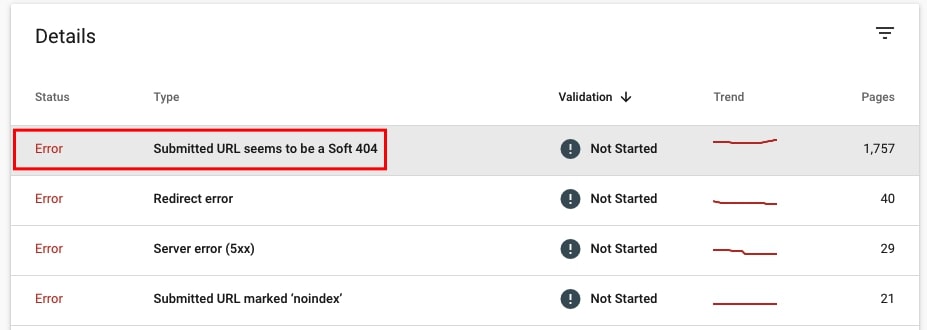
36. Check if there are soft 404 pages
Here the process is very similar.
- Go to Index > Coverage and select Error. Navigate to Details and look for error type Submitted URL seems to be a soft 404. Click on the error to see sample URLs.
Security
I have already touched upon security but it won’t harm if I devote a separate section to it as this is a highly important aspect of SEO.
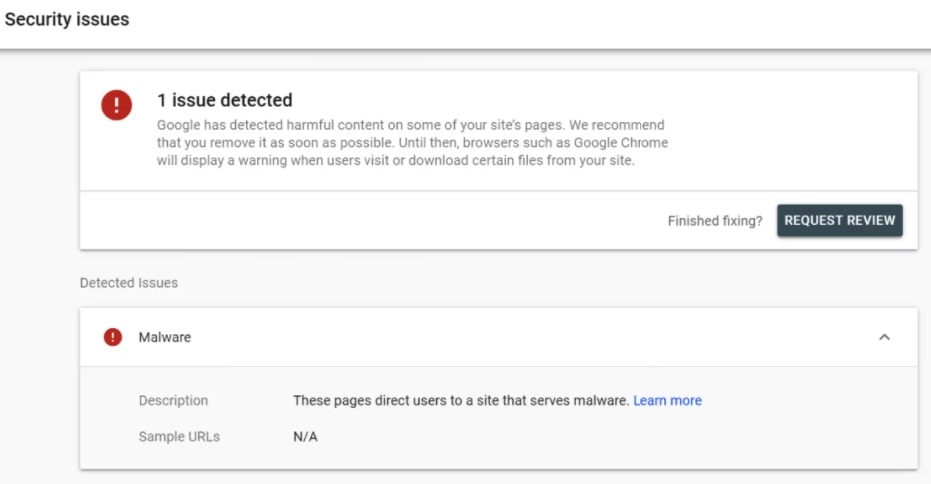
37. Check if there are any security issues on the site
If the site has any security issues and is filtered by Google Safe Browsing, then you will most likely see the notification in Overview visible after you log in to GSC.
You can check if the site has security issues by going to Security & Manual Actions > Security issues or Experience > Page Experience > Page experience signals.
38. Check if the site uses HTTPS
Google Search Console does only a site-wide check of the HTTPS coverage, which means it will tell you if the site has an SSL certificate and if the majority of its URLs are loaded over HTTPS. To check your site’s status, go to Experience > Page experience.
However, note that Google Search Console will not do a thorough check for mixed content. To do that, you need to crawl the site using Sitebulb or Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
Website speed
Did you think that it is not possible to analyze the speed and performance of the site using GSC? Think again! Of course, this is not a standard Google PageSpeed Insights test but you will get an idea.
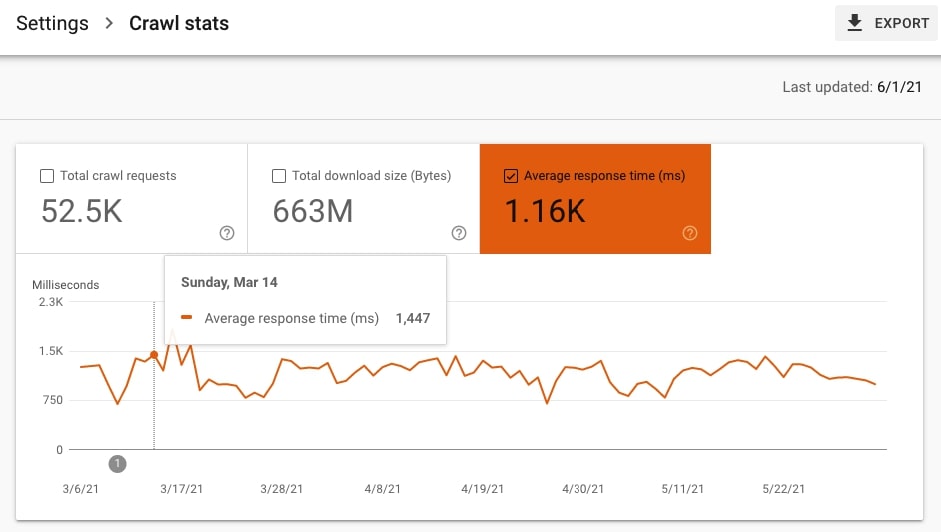
39. Check if the site has had some speed issues
Google Search Console does not display your Lighthouse or Google PSI score but it can show you whether your site has become slower than usual recently.
- Go to Settings > Crawl stats and check Average response time. Are there any unusual spikes?
Performance & visibility in Google
This is not strictly technical SEO but I believe that every high-quality SEO audit should also analyze the site’s visibility and performance in search. Once you identify these areas, you will know what to focus on in your audit recommendations.
So we are now switching to the Performance report.
40. Identify the queries and pages that bring the most clicks
Navigate to Performance > Search results or just Performance (if the site does not have traffic from Discover or/and Google News).
Scroll down the table and analyze what appears under tab Queries (Top queries) and Pages (Top pages). In most cases, these are going to be the queries and pages to focus on in the first place.
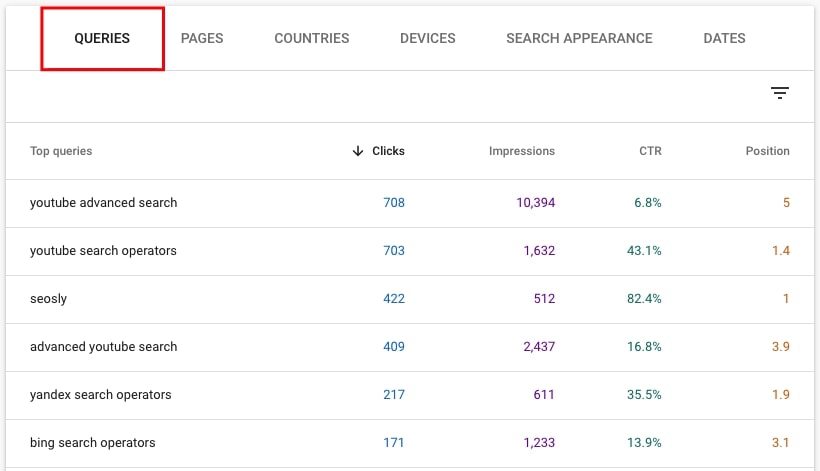
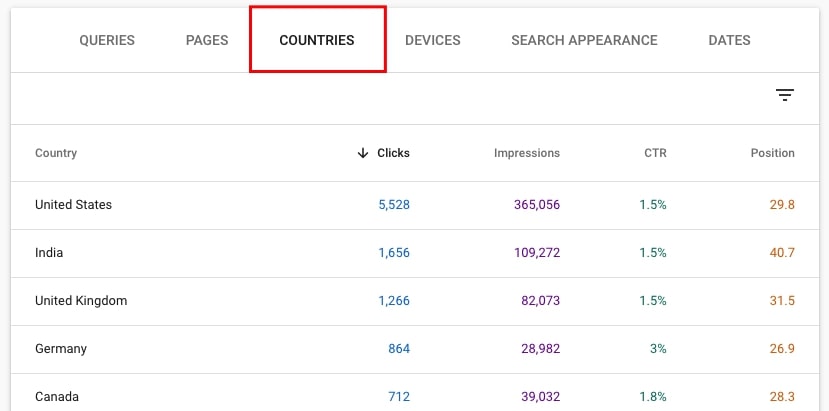
41. Identify the country that brings the majority of traffic
Now go to tab COUNTIRES to see the countries that bring the most clicks. You may also want to analyze the CTR and Average position in those countries.
Just click on a specific country to see the filtered view with data only for that country.
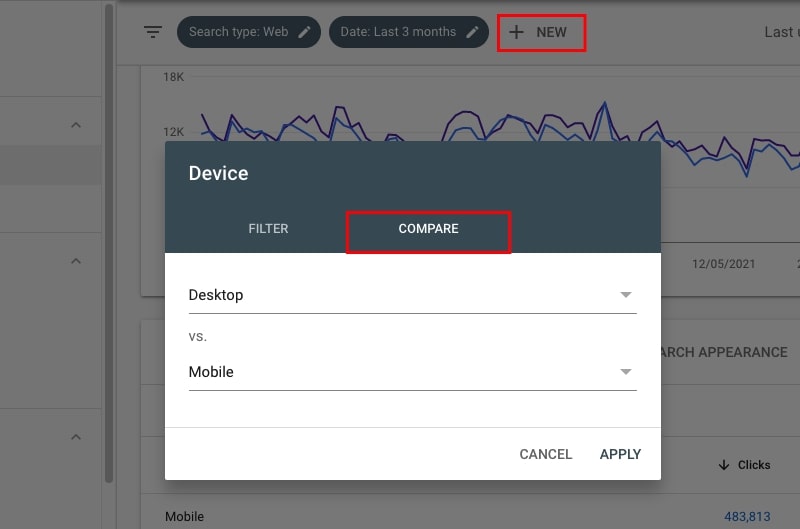
42. Compare the traffic coming from mobile and desktop
Yes, you can also use Google Search Console to compare organic traffic coming to your site through mobile and desktop.
Now move to tab Devices to see the number of clicks coming from Desktop and Mobile. Analyze the CTRs and average positions as well.
To compare the mobile and desktop traffic, click on NEW at the top, select Device, tab COMPARE, and click APPLY.
43. Check if Google Image Search brings a significant amount of traffic
For some sites, Google Image Search traffic is very important and these sites should adjust their SEO strategy accordingly and not forget to optimize for Image Search.
When in the Performance report, click on Search type: Web, click COMPARE, and hit APPLY. You can now compare web and image traffic coming to the site.
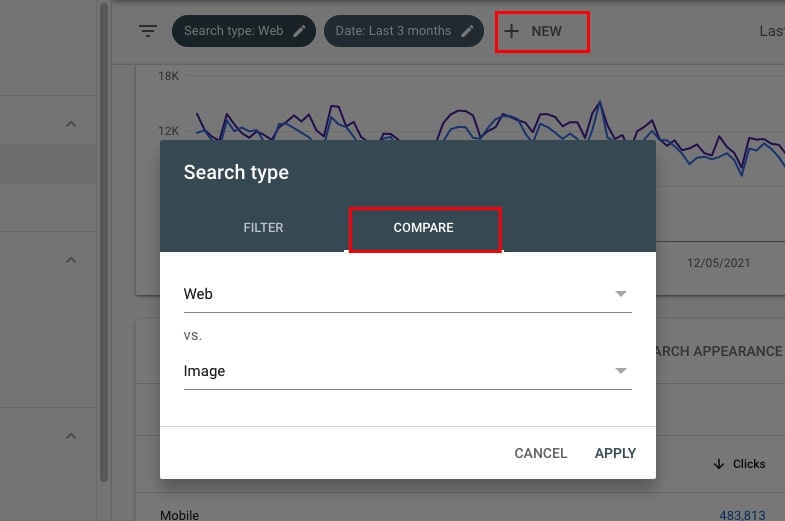
You can now see the view comparing these two types of traffic sources.
44. Analyze traffic coming through specific types of Rich Results
When in the Performance report, click on +NEW, select Search appearance and select a specific type of rich results (FAQ rich results, for example).
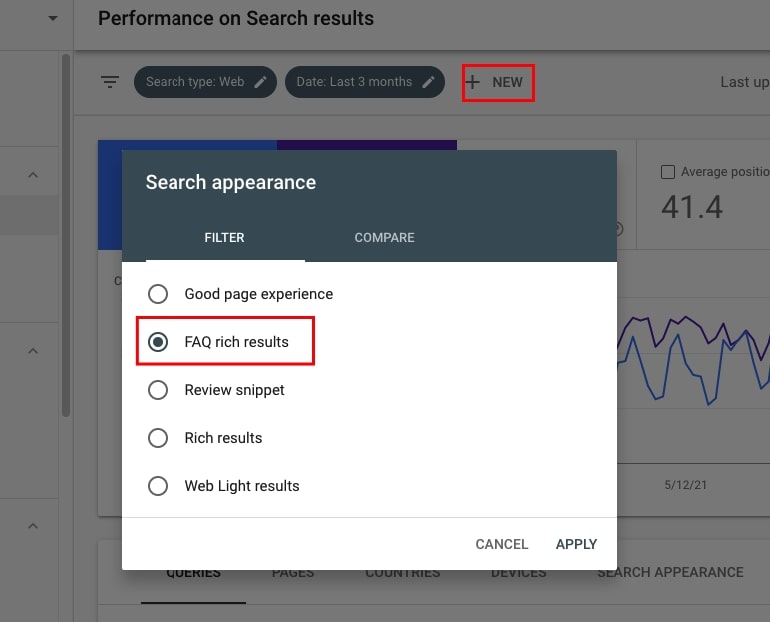
You will see the filtered view with data about the traffic coming through this one type of rich results. It’s very powerful information!
45. Analyze how pages with good experience perform
When in the Performance report, click (again) on +NEW, select Search appearance, choose Good page experience and hit APPLY.
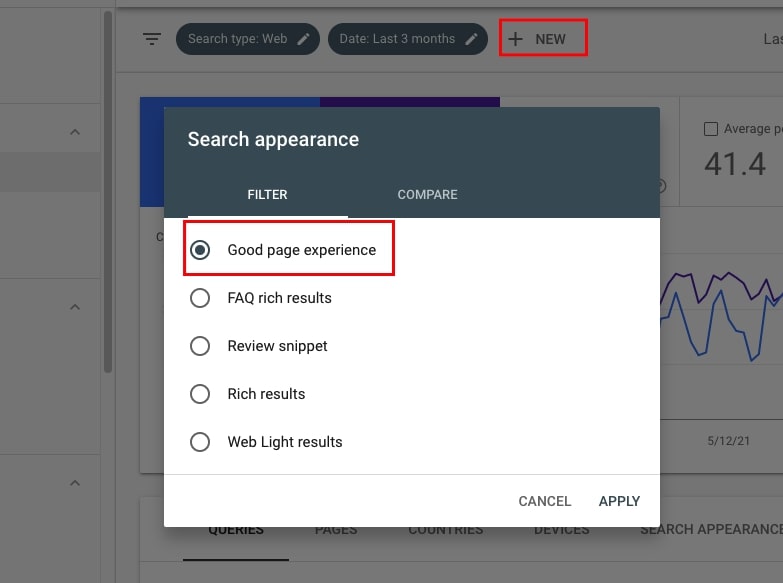
Now you can see the filtered view showing you only the pages that pass Core Web Vitals. How are these pages doing in Search?
Website Quality & Relevance
Whenever a Google Core Update happens, we talk about quality. Even if I do a technical SEO audit of the site, I always look at the site from a quality and relevance perspective. In addition to making use of the quality guidelines Google provides, you can also find some clues in GSC.
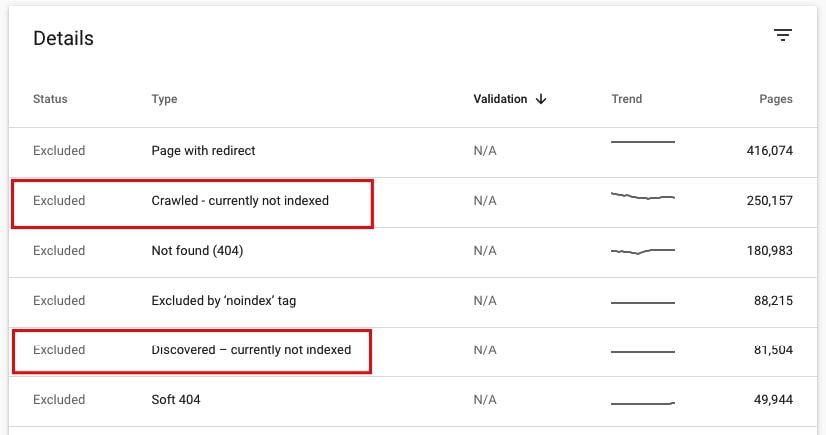
46. Check if there are pages that Google may consider low quality
This is of course not a final verdict but I noticed that it happens more and more often. Google is not obliged to index every page of your site.
If a site adds a lot of low-quality web pages, they may sometimes be visible in Coverage > Excluded under Crawled – currently not indexed or/and Discovered – currently not indexed. If the pages displayed there are “normal” pages of the site, then something is not OK for sure.
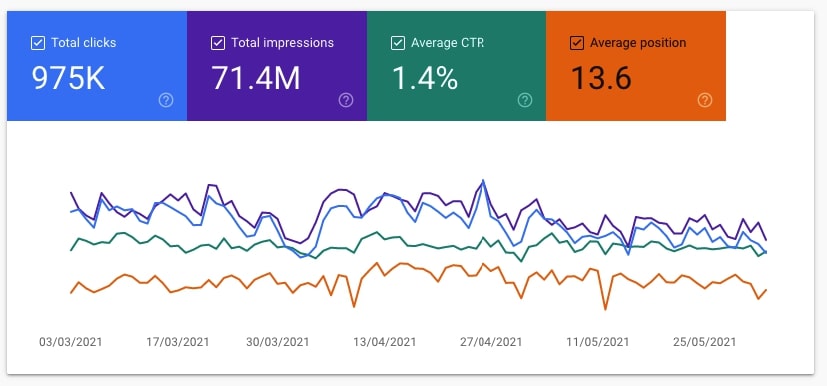
47. Check the pages that rank on the second or third pages of search results
These pages sometimes may lack quality and/or relevance. This is, of course, not always the case and there are tons of awesome pages on the second or third page of results. Anyway, it won’t harm anyone if you take a deeper look at these pages.
- Go to the Performance report, check all four metrics (Total clicks, Total impressions, Average CTR, Average position) and scroll down until you see the table with dimensions.
- Go to tab PAGES. Unfold the additional filter menu and check Position.
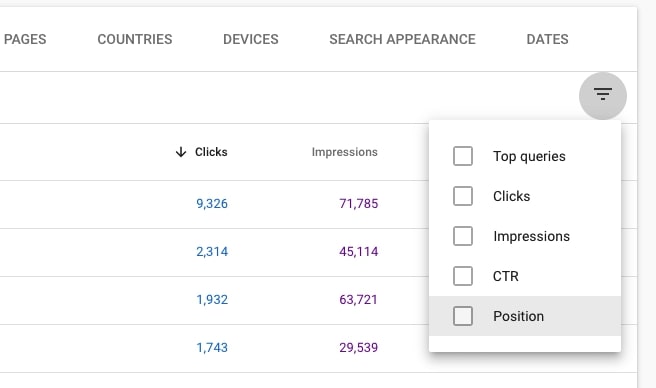
- Choose Greater than and type 11. You will now only see the pages whose average position is above 11. Analyze these pages using your common SEO sense and experience.
⚡ If you want to dig deeper into the quality and relevancy of the site/pages, I recommend you check my Google Product Reviews Update audit where I analyze every word and piece of advice Google gave regarding quality and E-A-T.
Backlinks
Yes, you can use other SEO tools to check the backlinks of the site. But you may as well use Google Search Console and see the backlinks that Google sees.
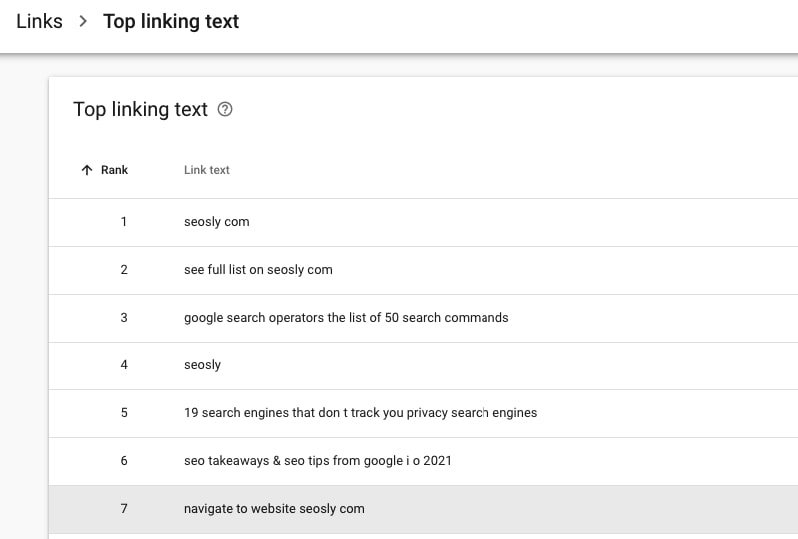
48. Analyze the backlink profile of the site
Go to Links (in the left sidebar) and analyze in details section Top linked pages, Top linking pages, and Top linking text. This is not a link audit but I believe you should still take a look at that section.
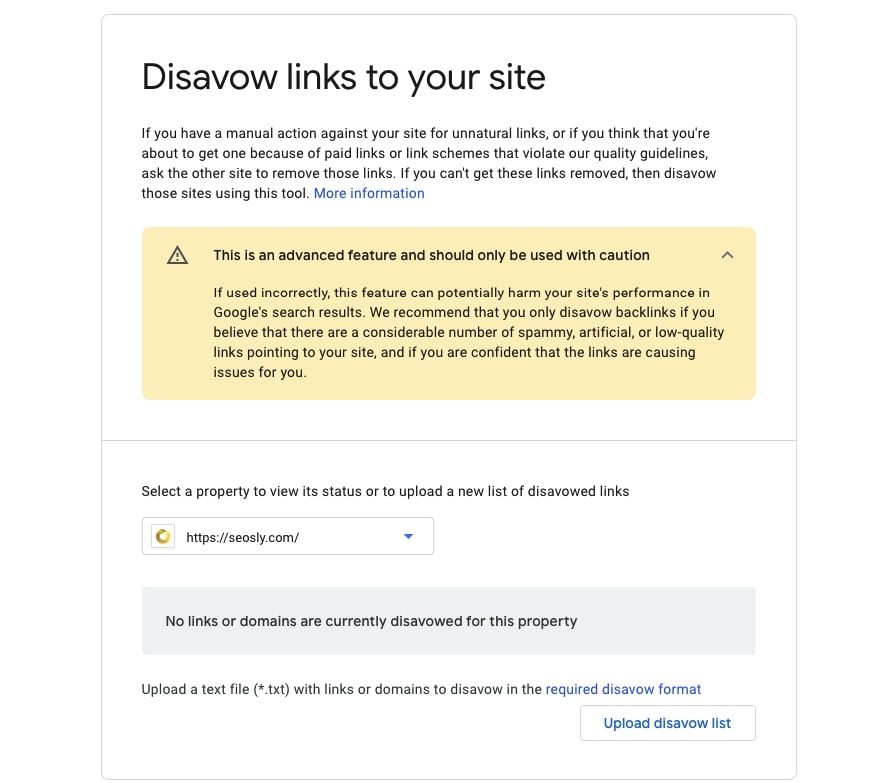
49. Check if the disavow file has been submitted
You definitely need to know if the disavow file has been submitted for the site. You can access the Disavow tool here.
Note that you can check if any links have been disavowed only if you have a URL Prefix property. If no links have been disavowed, you will see something like this.
As you can see, it is indeed possible to perform an SEO audit using only Google Search Console, the free SEO tool that everyone should be using on a daily basis.
In this guide, I touched upon the majority of technical (and non-technical) SEO elements that every SEO audit should check. A big advantage of this GSC approach to auditing is that the data and information come straight from Google, the only search engine we really care about. How cool is that?
Make sure to check my other SEO audit and technical SEO guides:
