Updated: July 1, 2023.
Discover three easy ways to check if Google crawled your site.
If you’re here, you’re probably trying to figure out whether Google’s mighty web crawlers have paid a visit to your site. Understanding if and when Google has crawled your site is a vital part of any solid SEO strategy, and I’m here to help you decode that process.
In this article, I will be diving into the world of Google crawling – what it is, why it matters, and most importantly, how you can find out if your site has been crawled by Google.
By the end of this read, you’ll have all the tools you need to not only confirm if Google has crawled your site, but also take action if it hasn’t. Let’s get started!

TL;DR: How to check if Google crawled your site
TL;DR: To quickly check if Google has crawled your site, use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console (GSC). Enter your URL into the tool, and it’ll provide information on the last crawl ****, any crawl errors, and indexing status. It’s a handy, reliable way to know if Google has indeed crawled your site.
What is Google crawling and how it works?
Google’s constantly seeking new and updated pages to add to its ‘known’ pages list, a step they call “URL discovery”. Sometimes, it finds new pages by following a link from an existing page or from your submitted sitemap.
Once a URL is discovered, Google may decide to visit, or “crawl”, that page using a program called Googlebot. Googlebot’s mission is to fetch information from billions of web pages, while balancing the frequency and number of pages it fetches from each site to prevent overloading them.
But Googlebot doesn’t crawl everything. Sometimes, the site owner may have disallowed crawling, or the page might require login access.
As Googlebot crawls, it renders the page, running any JavaScript it encounters through a version of Chrome that’s similar to your browser. This is crucial as many websites use JavaScript to bring content to the page, and Google needs to see this content.
However, there can be hiccups. Googlebot may face obstacles like server problems, network issues, or access rules set by robots.txt files. So, while Google is eager to crawl, it’s not always possible.
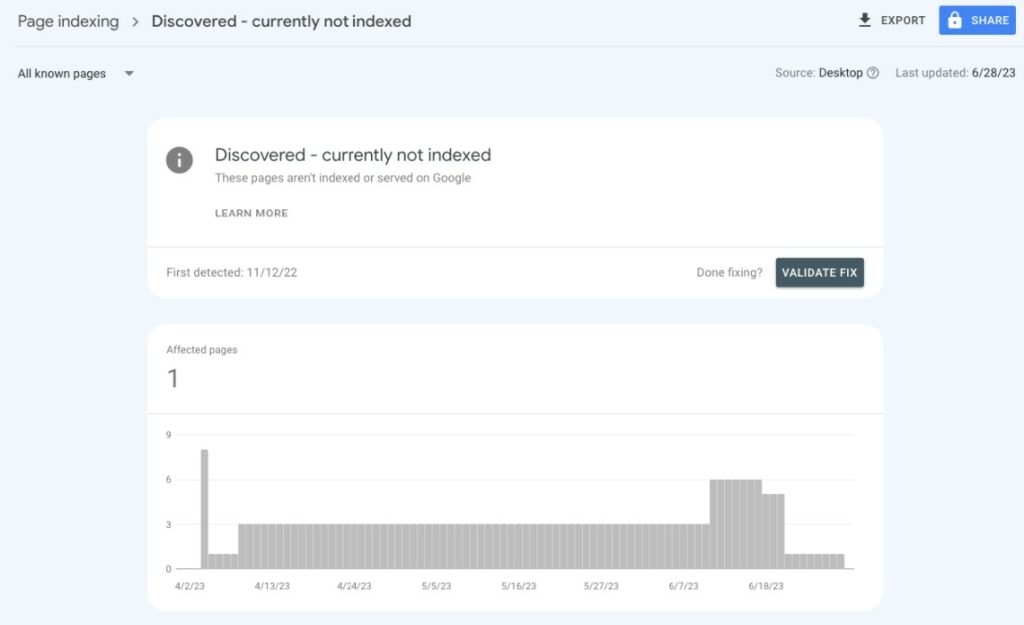
TIP: The pages under ‘Discovered – currently not indexed’ in Google Search Console are the pages Google knows about but hasn’t crawled yet.
You can find a very detailed guide on how Google Search works at Google Search Central. I strongly recommend you read this guide.
How to check if Google has crawled my site (in 4 ways)
Here are the four ways I know of to check if and when Google last crawled your site.
Google Search Console (URL Inspection Tool)
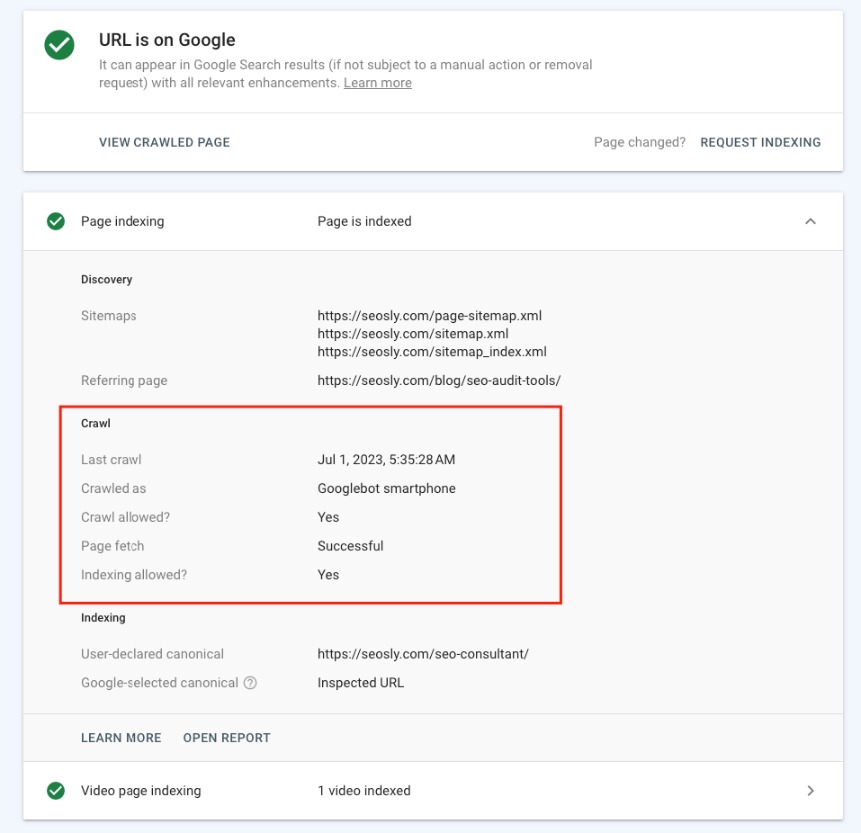
Nothing beats Google’s own Search Console when it comes to accurate and reliable information about your website. The URL Inspection tool, in particular, is your go-to resource for determining if and when Google last crawled a specific page on your website. Here’s what you do:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- On the left-hand side menu, find the “URL Inspection” tool.
- Enter the URL of the page you want to check into the search bar.
- The ‘Page indexing’ section will display detailed information about the page, including when it was last crawled and if it’s indexed.

Do keep in mind that to access this information, you’ll need to have your website verified in Google Search Console.
Log File Analysis
Log files are like a diary of your website, capturing all requests made to your site, including those made by Googlebot. You can manually analyze these files to see exactly when Google last crawled your website.
- You’ll need access to your website’s log files. Check with your hosting provider or your tech team.
- Once you have the log files, you can use software like Excel to open and analyze them.
Be aware that this method can be quite technical and complex, so it may not be suitable for everyone.
Example log file showing Googlebot’s visit
Log files will typically look like a plain text file with lines of data. Each line represents a server request, and the data points in each line are often separated by spaces or commas. A line in a log file that shows Googlebot has accessed your site might look something like this:
66.249.66.1 - - [01/Jul/2023:12:01:27 -0700] "GET /your-page.html HTTP/1.1" 200 4523 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)"This is an example of a log file entry in the Common Log Format. Let me break down what each part means:
- 66.249.66.1: This is the IP address making the request. Google has a range of IP addresses it uses to crawl the web, and this one is a known Googlebot address.
- -: These are placeholders for the client’s identifier and the user ID. In this case, neither is recorded.
- [01/Jul/2023:12:01:27 -0700]: This is the **** and time of the request. In this case, the request was made on July 1, 2023, at 12:01:27 PM, Pacific Daylight Time.
- “GET /your-page.html HTTP/1.1”: This is the request line. “GET” is the method used to request the page, “/your-page.html” is the URL of the page that was requested, and “HTTP/1.1” is the protocol used.
- 200: This is the status code of the response. A 200 status code means the request was successful and the page was delivered.
- 4523: This is the size of the response in bytes.
- “-“: This is the referrer, which is the page that linked to the page being requested. In this case, there’s no referrer.
- “Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)”: This is the user agent, which identifies the software making the request. This user agent identifies the crawler as Googlebot.
Note that different servers may configure their log files differently, so not all log files will look exactly like this. Some may include additional data, and some may omit certain parts.
Third-Party Tools
If delving into log files isn’t your cup of tea, there are third-party tools available that simplify the process. For instance, the JetOctopus Log Analyzer or Semrush Log File Analyzer:
- With these tools, you simply upload your log files and the tool will do the analysis for you.
- You can then easily see when and how often Googlebot visited your site.
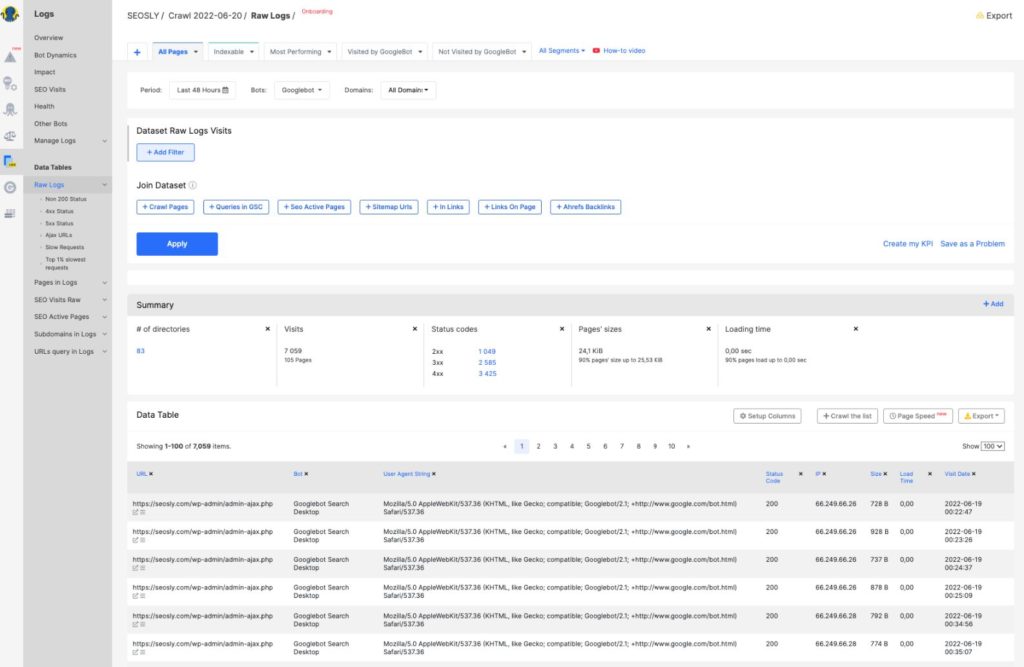
Check my full guide on how to do a log file analysis with JetOctopus.
‘Site:’ Command in Google
Finally, a simple, quick, albeit less precise method is using the ‘site:’ command directly in Google search. Here’s how it works:
- Go to Google and type ‘site:’ followed by your website’s URL into the search bar.
- If Google returns pages from your website in the search results, it means it has crawled and indexed those pages.
Remember, this won’t tell you when Google crawled your website, but it’s a quick way to check if your site has been crawled and indexed.
What to do if your website is not being crawled
If you find out that your website isn’t being crawled by Google, don’t panic. Here are some steps to prompt Google to do its job:
Steps to prompt Google to crawl your website
- Submit your URL to Google: You can do this directly through the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. Once there, you can request indexing for any URL associated with the property you have verified.
- Use a sitemap: This is like a map for your website that you submit to Google. It can help Google discover and understand your site’s structure. Make sure your sitemap is updated and correctly formatted, then submit it through Google Search Console.
- Earn (not build) external links: If no other sites link to yours, Google may have trouble discovering it. While you can’t directly control who links to your site, you can improve your chances by creating high-quality, shareable content.
- Quality: Make sure your site offers unique and high-quality content. E-E-A-T and content helpfulness have never been more important than now.
I’ve also written the entire guide on how to get Google to crawl your site. Make sure to check it for more details.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on how to check if Google crawled your site
Here are the most often asked questions about Google crawling (or not crawling) your site.
What does it mean for Google to crawl my website?
Crawling is the process where Googlebot visits new and updated websites to report back to Google. It’s how Google discovers your content and considers it for its index.
How can I check if Google has crawled my site?
You can use tools like Google Search Console, log file analysis, third-party log file analyzers, or the ‘site:’ command in Google search. Each method provides slightly different information, but all can confirm whether Google is aware of your content.
What is Google Search Console and how does it show if my site has been crawled?
Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site’s presence in Google Search results. The ‘URL Inspection’ feature can show when your site was last crawled by Google.
Can I use log files to check if Google has crawled my site?
Yes, server log files contain a record of all requests made to your site, including those by Googlebot. By analyzing these logs, you can see when and what Googlebot has accessed.
What third-party tools can I use to check if Google has crawled my site?
Tools like JetOctopus Log Analyzer or Semrush Log File Analyzer can provide insights into Googlebot’s activity on your site. They can help identify which pages are being crawled and how often.
Why is it important to know if Google has crawled my website?
Knowing if Google has crawled your website can help you understand how your site is being perceived by Google. If your site is not being crawled regularly, it might mean there are technical SEO issues that need to be addressed.
What should I do if Google hasn’t crawled my website?
You can take steps like submitting your URL directly to Google, submitting a sitemap through Google Search Console, optimizing your site’s load speed, and checking for common issues like robots.txt disallow directives, site errors, poor site structure, or lack of external links.
Does Google crawling my site mean my content will appear in search results?
Not necessarily. Crawling is just the first step. Google needs to index your content for it to appear in search results. However, crawling is a good sign that Google is aware of your site or changes to your site.
How often does Google crawl my site?
The frequency of Google crawling varies and depends on factors like the site’s health, changes made to the site, and the site’s authority. Some sites may see daily crawling activity, while others might see it less frequently.
