Updated: April 8, 2023.
Learn how to find the sitemap of any website in these 8 easy ways + one bonus way.
Finding the sitemap of a website is a simple task that any SEO can do. This article will show you 8 easy ways to find the sitemap of any website.
I’ll start with the most popular sitemap format, which is XML, and then move on to other formats. Let’s get started!

What is a sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on a website that you want search engines to index. It’s like a roadmap that helps search engine bots crawl and understand the structure of your website.
Sitemaps come in different formats, such as XML, HTML, or TXT, and can include additional information about each page, such as the **** it was last modified or how important it is relative to other pages on the site.
- Having a sitemap can help search engines discover new content on your site more quickly and ensure that all your pages are crawled and indexed.
- It can also help you identify any crawl errors or pages that might be missing from your site.
- Creating a sitemap is an important part of on-site SEO optimization and can improve the overall visibility and ranking of your website.
Here is an example sitemap (that happens to be the sitemap of my site):
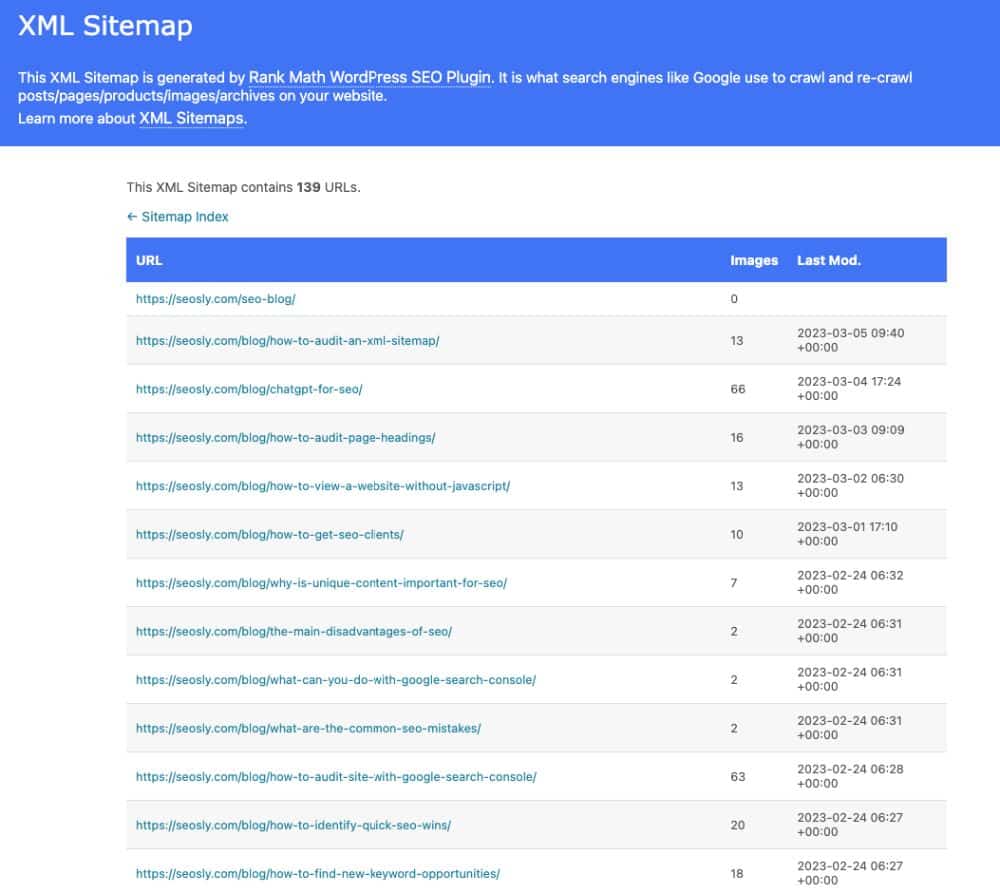
Here is the screenshot from the sample XML sitemap shown on sitemaps.org:

And here is the screenshot of the sitemap index on my website:
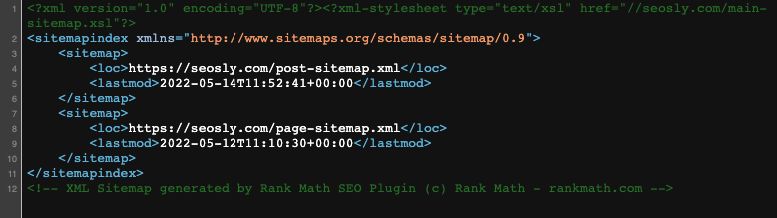
Why do need to find the sitemap of a website?
There may be a few reasons why you need to find a sitemap of the website. The most common ones include:
- You simply want to learn what pages, posts and blog categories a specific website has.
- You are an SEO auditor and you simply want to audit the sitemap.
- You want to assess if a site actually needs a sitemap. Huge websites usually need to have a website while smaller ones can do without a sitemap.
Make sure to check my article about how to audit an XML sitemap for a deeper dive into auditing XML sitemaps.
Simple ways to find the sitemaps of a website
And before we start, please note that:
- The most common and standard location of the sitemap is, of course, the root directory of the domain.
- However, this location is neither a requirement nor an official standard. This means that the sitemap may as well be placed in a subdirectory or even on an entirely different domain. Some folks do that to hide their sitemaps from competitors.
- The same is true for the filename which does not need to be “sitemap” or have the word “sitemap” in it.
That’s why I’m showing you here all the more and less obvious locations of a sitemap of a website. These are all the variations I’ve seen over my 10-year experience as an SEO consultant.
Okay, it’s time to start the detective work finally.
1. Manually check common XML sitemap locations
This is the most obvious and quickest way to find a sitemap of a website. In most cases, this is all you need to do to detect an XML sitemap of a website.
The most common locations for sitemaps are:
/sitemap.xml/sitemap_index.xml(which is the index of the sitemaps)/sitemap/(which often redirects to sitemap.xml)
Of course, anything that goes before “/” is the domain name of your website.
In the case of my website (which is based on WordPress), the default sitemap location https://seosly.com/sitemap.xml redirects to https://seosly.com/sitemap_index.xml.
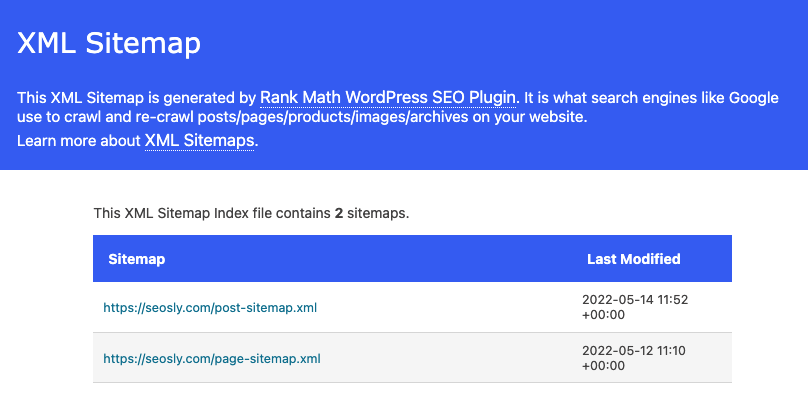
As you can see the sitemap index has the following two sitemaps:
And here are other possible filenames for the sitemap or the sitemap index:
/sitemap.php/sitemap.txt/sitemap.xml.gz(using gzip compression)/sitemap1.xml(if there are multiple sitemaps, this may be the first sitemap in a group)/post-sitemap.xml(sitemap of posts, like the one on my website)/page-sitemap.xml(sitemap of pages, also like the one on my website)/sitemap-index.xml(with “-” instead of “_”)/sitemapindex.xml(without separation)/sitemap_index.xml.gz(using Gzip compression)/sitemap/index.xml(in a subfolder)
And a website may also use its feed as a sitemap in which case the sitemap can be something like:
/rss/(an RSS feed as a sitemap)/rss.xml(an RSS feed as a sitemap)/atom.xml(an Atom feed as a sitemap)
Do you see? Lots of possibilities.
2. Check if the sitemap is indicated in robots.txt
Another obvious and quick way to detect an XML file is to check robots.txt.
Robots.txt is a special file that contains directives for search engine robots. This is also the place to include the link to the sitemap to make it easier for search engines to detect the sitemap and crawl the website.
To view the robots.txt file of any website, simply add /robots.txt to the domain. In the case of my website, it’s https://seosly.com/robots.txt.
Here is the content of the robots.txt file of my website:
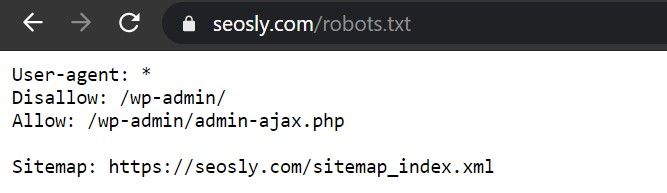
The last line indicates the location of the sitemap.
☝️ PRO TIP: If the website has a non-standard sitemap location, then the robots.txt file should indicate it.
If you want to learn more about robots.txt, what it is, what it does, and how it should be used, check the introduction to robots.txt on Google Search Central.
⚡ If you are using WordPress, check my guide on how to access robots.txt in WordPress.
3. Use Google Search Operators to find the XML sitemap
You can also look for an XML file with the use of Google search operators (click to view the full list of currently working search operators in Google).
There are at least a few operators you can use to try to find the XML sitemap of a website:
site:filetype:orext:inurl:
Let’s try to find the XML sitemap of moz.com using these search operators.
The command site:moz.com filetype:xml or site:moz.com ext:xml will look for XML files within the moz.com domain.
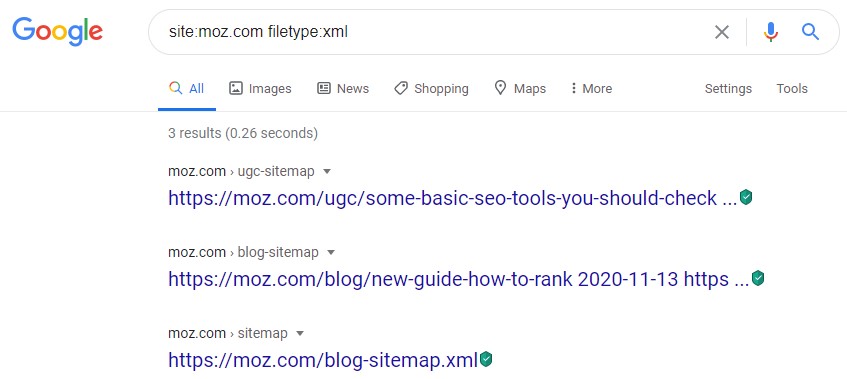
You can also narrow down the search a bit and try something like site:moz.com filetype:xml inurl:sitemap or site:moz.com ext:xml inurl:sitemap which will look for XML files that have the word “sitemap” within the moz.com domain.
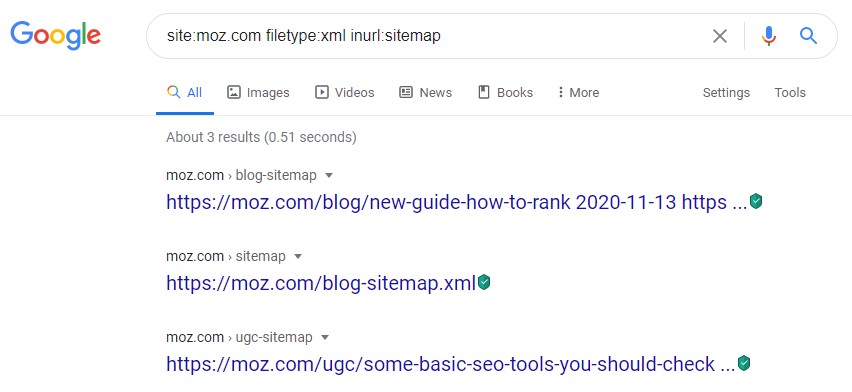
You can also look for sitemaps that are a different file type than XML, such as text files.
To do that, you can use the command site:moz.com filetype:txt inurl:sitemap or site:moz.com ext:txt inurl:sitemap which will look for the text files containing the word “sitemap” within the moz.com domain
PRO TIP: Note that this method will work only if the XML sitemap is indexable (and is actually indexed by Google).
PRO TIP 2: Many popular WordPress plugins that automatically generate XML sitemaps (like Rank Math) add a “noindex, follow” tag to sitemaps.
If this is the case, then you won’t be able to find a sitemap using Google search operators. This is how the XML sitemap is generated on my website. If I wanted to find it with the help of a search operator, I would not be able to find it.
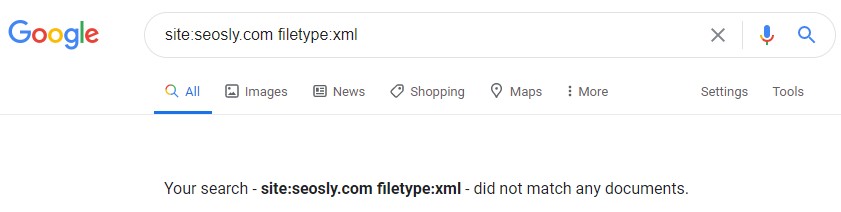
No results returned even though I do have a sitemap.
4. Check if the XML sitemap has been submitted to Google Search Console
Another place to look for the sitemap is in Google Search Console. This step will work only if you have access to the GSC account for the website. If you have one, here is what you need to do:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Under Index, go to Sitemaps.
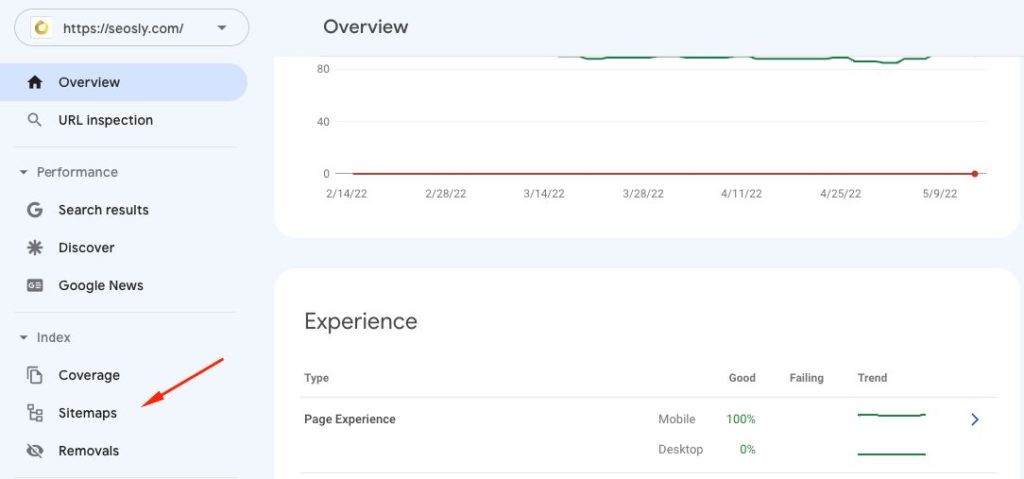
- If an XML sitemap has been submitted to Google, you will see it under Submitted sitemaps.
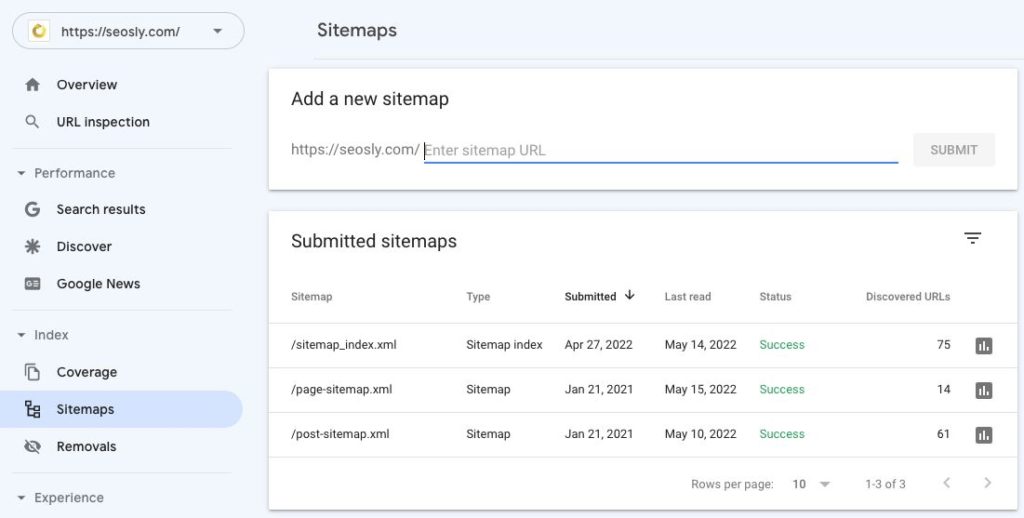
If you are new to Google Search Console or the website you are analyzing does not have a GSC account, make sure to check the basic guide to Google Search Console on Google Search Central.
PRO TIP: Google Search Console is a tool that any website that wants to be visible in Google should use.
👉 Speaking of GSC, you may want to learn about the new crawl stats report in Google Search Console. Also, check my guide on how to add a new user to GSC if you want someone else to access your GSC data.
5. Check if the XML sitemap has been submitted to Bing Webmaster Tools
You may also want to look for an XML sitemap in Bing Webmaster tools just like you did in Google Search Console.
This step only makes sense if the website has an account in Bing Webmaster Tools. Here is how to check if an XML sitemap has been submitted:
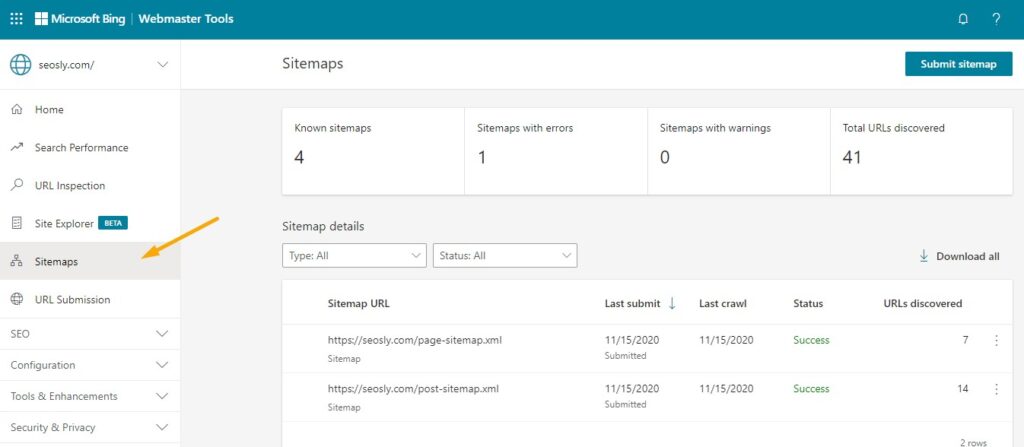
- If there are any sitemaps submitted, you will see them on the right under Sitemaps.
☝️ PRO TIP: This is also the place where you can submit an XML sitemap to Bing.
6. Use an Online tool
Since we are talking about tools, you may also want to use an online tool made especially for checking if a website has an XML sitemap.
The URL of the tool: https://seositecheckup.com/tools/sitemap-test
Here is how to check if a website has an XML sitemap with the use of the SEO Site Checkup tool:
- Enter the URL address of the website you want to check.
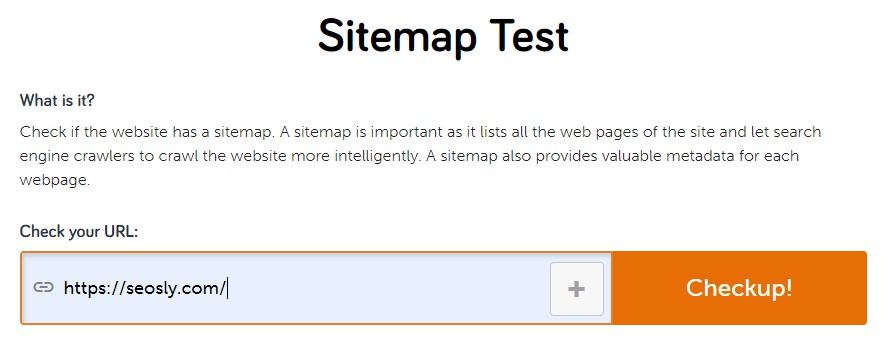
- Hit enter or click Checkup. The results will be available within a few seconds.
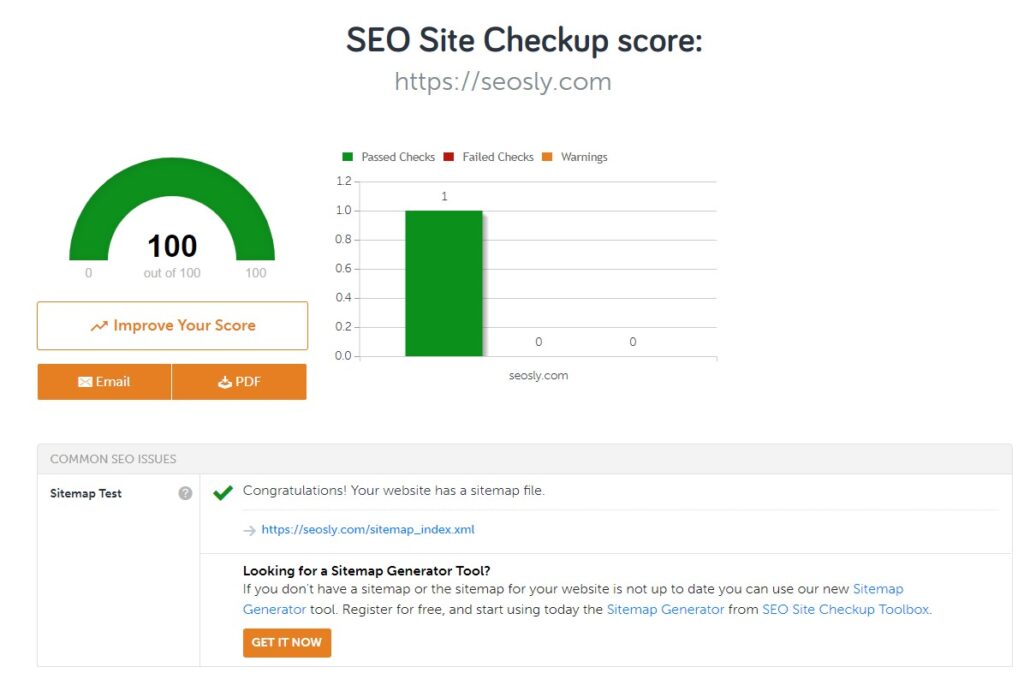
- You might also add other URLs (like URLs of competitors) and compare the results.
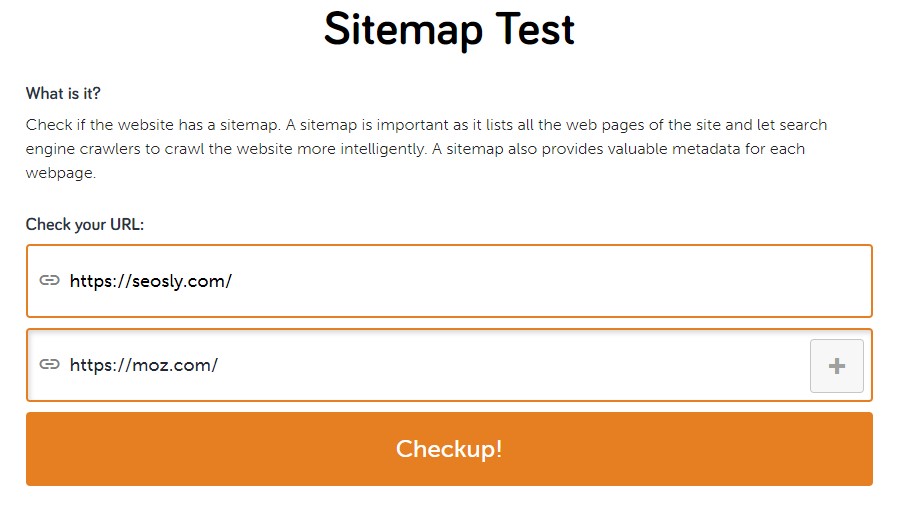
☝️ PRO TIP: Note that this tool checks possible standard locations of an XML sitemap and sometimes may not detect a sitemap even if a website has one.
7. Check the standard XML sitemap location of the CMS
Depending on the CMS of the website, XML sitemaps may be available at different URLs.
The most popular content management systems have their own default XML sitemap locations that are worth checking as well.
- If you know the CMS of the website you are examining, the chances are its XML sitemap is at a default location for this CMS.
- If you don’t know the CMS, you may want to check it with a tool like CMS Detect. All you need to do is type the URL and hit Detect CMS.

Below are the default XML sitemap locations for the most popular content management systems and links to documentation.
Default sitemap locations in WordPress
Since July 2020, there has been a new XML sitemap functionality in WordPress 5.5. This means you don’t need any plugin to generate a sitemap for your WordPress website.
If the WordPress website uses this functionality, then its sitemap is available at /wp-sitemap.xml.
If a WordPress website uses one of the plugins that automatically generate a sitemap, then it is available at one of the below addresses:
/sitemap.xml/sitemap_index.xml/post-sitemap.xml/page-sitemap.xml/category-sitemap.xml/tag-sitemap.xml
You can also simply check the settings of the plugin to see the exact location of the sitemap.
Most automatically generated sitemaps in WordPress also add the sitemap entry in robots.txt.
Default sitemap locations in Wix
Wix automatically takes care of the sitemap for you and your only task is to submit it to Google Search Console. The default location for the main sitemap in Wix is also /sitemap.xml.
Other URL paths in Wix for different sitemaps are as follows:
/pages-sitemap.xmlfor Pages/blog-pages-sitemap.xmlfor New Wix Blog/store-products-sitemap.xmlfor Wix Stores/booking-services-sitemap.xmlfor Wix Bookings/forum-pages-sitemap.xmlfor Wix Forum/event-pages-sitemap.xmlfor Wix Events/member-profile-sitemap.xmlfor Members/dynamic-pages-sitemap.xmlfor Wix Data &router pages/other-pages-sitemap.xmlfor other pages that don’t belong to any of the above categories
You can learn more about sitemaps in Wix here.
Default sitemap locations in Squarespace
Squarespace just like Wix takes care of the sitemap. The default sitemap location for Squarespace websites is also /sitemap.xml.
You can learn more about sitemaps in Squarespace here.
Default sitemap locations in Shopify
In Shopify, the sitemap also has a standard location that is /sitemap.xml.
You can learn more about sitemaps in Shopify here.
Default sitemap locations in Joomla
The extensions available for Joomla will also automatically generate the sitemap of a website. The standard location for a Joomla XML sitemap is simply /sitemap.xml.
You can learn more about sitemaps in Joomla here.
Default sitemap locations in Magento
And finally a word about sitemaps in Magento. This one also uses the standard sitemap location which is /sitemap.xml but you can modify it if you want.
You can learn more about sitemaps in Magento here.
8. Bookmarklet for finding XML sitemap
If you’re like me and always looking for ways to improve productivity and save time on your SEO tasks, I have a useful tip for you.
There’s a quick and easy bookmarklet you can use to instantly check the XML sitemap of any website.
All you need to do is add the following JavaScript code to your bookmarks:
javascript:void(location.href="http://" + location.host + '/sitemap.xml')
Once it’s saved, simply click on the bookmarklet and it will open the sitemap file for you, as long as it’s located in the default /sitemap.xml location.
This little trick can save you time and make it easier to check the sitemap of any website you’re working on.
How to find other types of sitemaps
XML is the most common sitemap format that is used to inform robots about the web pages of a website. However, there are also other possible sitemaps formats that search engine robots recognize and respect:
- HTML which is usually for users but it can also help robots discover web pages. The location of an HTML sitemap may be
/sitemap/. - RSS where a website can use an RSS feed as a sitemap. The location of an RSS feed sitemap is usually
/rss/or/rss.xml. - Atom where a website can use an Atom feed as a sitemap . The location of an Atom feed sitemap is usually
/atom.xml. - TXT which is simply a text file. The location of a text sitemap is often
/sitemap.txt.
If you detect any of the above types of sitemaps, don’t panic. They are also OK and Google understands them perfectly.
The sitemap for Google is simply a list of links to pages of the website that the website owner wants Google to crawl and index.
Found the sitemap of the website? Here’s what to do next.
There is a lot of awesome reading on sitemaps straight from Google. I really recommend you check the following:
Didn’t find the XML sitemap of the website? Do this.
The chances are that the website simply does not have a sitemap.
Once you’ve gone through the different ways of finding a sitemap, it’s important to consider what to do if there isn’t one already created. This is often the case with new websites that haven’t been online for very long or very small and simple sites.
It’s worth noting that not all websites require sitemaps. If your site only has a few pages, it should be able to function just fine without one.
However, if you do decide to create an XML sitemap, there are plugins available for your CMS system that can make it easier. For example, if you’re using WordPress, some good options include:
- Rank Math which has the feature to create an XML sitemap,
- Yoast SEO which can also create an XML sitemap automatically,
- Default WordPress sitemap feature,
- Google XML Sitemaps.
Alternatively, you could create a sitemap manually or use a crawler tool to scan your website and export a sitemap for uploading. It’s important to remember that there are always options available for creating a sitemap, even if one doesn’t already exist.
Recommended reading on sitemaps:
- Go to Sitemaps.org to learn what an XML sitemap looks like and how it is built if you don’t know this.
- If you are interested in learning more about the theory behind sitemaps, what they are, and what they do, go straight to Google Search Central to the section about sitemaps or see the recent updates for sitemap extension tags.
Frequently Asked Questions about sitemaps
Here are the most often asked questions about sitemaps.
What is a sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on a website that you want search engines to index. It acts as a roadmap that helps search engine bots crawl and understand the structure of your website.
Why do I need to find a website’s sitemap?
Finding a website’s sitemap is useful for learning about the pages, posts, and blog categories on a specific website. It also helps SEO auditors evaluate the sitemap and assess if a website requires a sitemap for better search engine indexing.
What are some common XML sitemap locations?
Common XML sitemap locations include /sitemap.xml, /sitemap_index.xml, and /sitemap/. These locations usually follow the domain name of the website.
How can I find a sitemap in the robots.txt file?
To find a sitemap in the robots.txt file, add /robots.txt to the domain name and view the file. If a sitemap is indicated, it will typically appear as a line in the file, showing the sitemap location.
Can I use Google search operators to find a sitemap?
Yes, you can use Google search operators like site:, filetype:, and inurl: to find sitemaps of a particular file type or containing specific keywords within a website’s domain.
How can I find a website’s sitemap in Google Search Console?
To find a website’s sitemap in Google Search Console, log in and go to the Sitemaps section under the Index menu. If an XML sitemap has been submitted to Google, it will appear under Submitted sitemaps.
How can I find a website’s sitemap in Bing Webmaster Tools?
To find a sitemap in Bing Webmaster Tools, log in, and choose Sitemaps from the left panel. If any sitemaps have been submitted, they will appear under the Sitemaps section.
Are there online tools to find a sitemap?
Yes, there are online tools like SEO Site Checkup that can help you find a website’s sitemap. Simply enter the website URL and let the tool search for the sitemap.
How do I find a sitemap based on a website’s CMS?
Most popular content management systems have their default sitemap locations. You can check these default locations or use a tool like CMS Detect to determine the CMS used by the website and then search for the sitemap in the appropriate location.
What should I do after finding a website’s sitemap?
After finding a website’s sitemap, you can review the structure and organization of the site, check for crawl errors, or submit the sitemap to search engines like Google and Bing for better indexing and improved search engine visibility.
Okay, I think I have beaten the topic of sitemaps to death, haven’t I?😂
