So, you’ve done your keyword research and added a list of relevant keywords to your website content. Now what? How do you know if your SEO efforts are paying off? The answer is: by tracking search engine rankings.
With millions of websites competing in search results, it’s not easy to reach the top of SERPs. Still, by understanding how you rank for a specific set of search terms, you can create a tailored SEO strategy to help your business stand out and grow in a crowded market.
After reading this article, you’ll understand what search engine rankings are and what their role is in building a successful SEO strategy. What’s more, you’ll learn how to check your rankings in different search engines so that you can get the lion’s share of traffic, shares, and conversions.
What are search engine rankings?
When conducting an online search, you expect the most relevant results to appear at the top of the SERPs, right? But to discover and organize all webpages based on user needs, search engines go through three distinct processes: crawling, indexing, and ranking. While crawling seeks to discover the most important web pages, indexing assists search robots in storing content found during the crawling process.
When it comes to ranking, search engines prioritize the content that best answers a searcher’s query. In other words, search rankings refer to the position that URLs hold in SERPs for a particular keyword. Search engines use a variety of factors to rank content from most relevant to least relevant, ranging from topical authority and content quality to user experience and mobile-friendliness.
Most SERPs include 10 URLs, along with ads and other features like the People Also Ask section, rich snippets, knowledge graphs, and so on. The primary goal of SEO is to rank high on as many relevant SERPs as possible.
What search engines to track your rankings in & why
Did you know that the world has over 100 different search engines? Tracking your rankings in each of them would take months of your time and give you very poor results. There are also many local search engines, like Baidu, that are only used in specific regions, so it doesn’t make any sense to track SERP positions in all search engines available in the world. To get the most out of your SEO actions, let’s focus on the most popular ones.
With over 90% of global search market share, Google dominates the search engine market. Since it processes over 105,000 searches every single second, it’s estimated that more than 8.5 billion searches a day are conducted with this search engine. It makes this search engine highly appealing in terms of capturing both organic and paid traffic.
To put these statistics into perspective, let’s compare Google with its closest competitors, such as Bing and Yahoo. The latest data shows that Bing and Yahoo have a little over 3% and 1% of the total market share, respectively.
So the most important reason why you should start tracking search engine rankings on Google is that it has the most traffic potential. Also, Google’s algorithms are more ****** because they rely on a huge amount of previous user data points, such as your location (based on IP), previous search history, SERP behavior (e.g., click-throughs), and device. It, in turn, can help you reach your target audience and promote your business more effectively.
The impact of algorithm updates on search engine rankings
Businesses that rely on organic search traffic for generating revenue must pay close attention to the impact of algorithm updates on search engine rankings. The thing is, search engines like Google regularly update their algorithms to ensure that users get the most useful and high-quality results. Still, these updates can bring about noticeable changes in search engine rankings that lead to fluctuations in site traffic.
Let’s look at how algorithm updates affect search engine rankings.
Google vs Bing: Ranking algorithms
Google updates its algorithm hundreds of times per year, with most of its updates being minor changes that have little to no impact on search engine rankings. According to Google, the search company made 5,150 “improvements” in 2021 alone.
But it’s also true that several significant algorithm updates occur each year, with names like BERT (2019), Passage Ranking (2020), PSI Update (2021), and the Helpful Content Update (2022). These updates can have a profound impact on search engine rankings, and businesses need to be aware of them to avoid possible negative impacts.
As of April 2023, Google has already launched two major updates that could potentially affect search engine rankings: the Product Reviews Update and its Core Update.
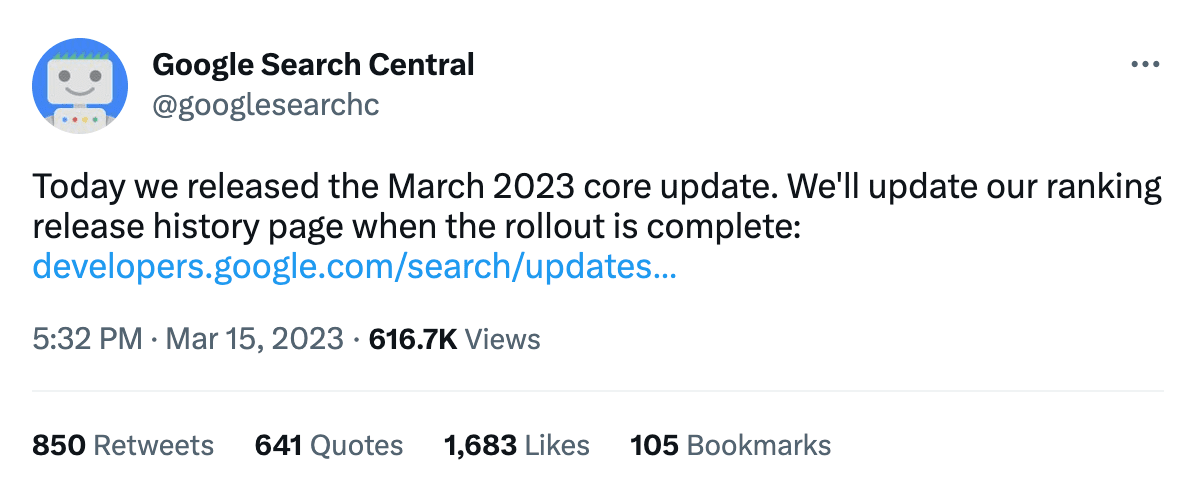
Google has announced its March 2023 Core Update via Twitter. The company mentioned that the ranking release history page will be updated when the rollout is complete.
The most recent broad core update before the one in March 2023 was its September 2022 update, which had a smaller impact than previous updates. But given the significance of the current update, it is recommended to prepare for potential changes in search rankings.
In terms of Bing, it also regularly releases algorithm updates aimed at improving the quality and relevance of search results. One of Bing’s most recent updates was applying AI to its core search algorithm, which led to Bing’s largest jump in relevance in two decades. Today, Bing’s ranking algorithm utilizes machine learning/AI in over 90% of search results.
It’s worth mentioning that Bing’s ranking algorithm is based on fewer ranking factors than Google’s algorithm, but it still takes into account many of the same factors, including content quality, backlinks, and user experience.
Both Google and Bing use complex algorithms to rank websites in their respective search engines, so while there are some differences between the two algorithms, they both consider many of the same factors when determining how websites should be ranked.
What to focus on when tracking search engine rankings
Identifying the queries leading users to your website is not enough for effective position tracking. When carrying out this process, you must consider a number of factors, including position, keyword, URL, target location, and snippets (if there are any). Let’s review them in detail.
1. Position
SERP positioning is typically the first thing SEOs analyze when tracking search engine rankings. In fact, most Internet users never look past the first two pages of search results. This could be because they’ve already accomplished their goal online, don’t want to scroll any further, have a limited amount of time, or some combination of all these factors. Simply put, the higher you rank, the higher your click-through rate (CTR).
Even if you don’t appear on the first page of organic search results, paid results can help you get to the top of the SERPs. They are typically identified with the word “Ad,” but otherwise, there isn’t much of a visual distinction between organic and paid listings.
At the same time, your position in SERPs can vary even for search keywords entered on the same search engine using the same type of device. Many factors come into play, including:
- The history of your Internet browsing.
- The amount of times that the person who is tracking rankings of a particular website clicks on it in search results (if you type the keyword in the search box and constantly click on a website in SERPs, the search engine will show you this site above others).
- Your current location.
2. Keyword (search query)
Keywords that drive traffic to your website can provide a wealth of valuable insights that you can then use to build successful marketing campaigns. For example, by analyzing them along with their associated metrics, you can determine how effective your keyword strategy is and which keywords have the greatest potential to attract the target audience to specific pages.
Keyword metrics playing the most important role in SEO include:
- Search Volume: This is the number of monthly searches for a given keyword.
- CPC: This is the cost an advertiser pays each time an online user clicks on their ad.
- Keyword Difficulty: This is a metric demonstrating how difficult it would be to rank high for a specific keyword.
All keywords can be divided into three categories based on search volume: high-volume, moderate-volume, and low-volume. Each of these groups has its pros and cons for SEO and is thus used in different situations. To determine whether or not a specific keyword should be bid on in your keyword campaign, consider your niche, business size, location, and other factors.
You can also identify user intent using search queries. When you have a solid understanding of why people perform a certain search, you can provide the exact solution they are looking for. For example, a person typing “garlic sauce” into a search engine is most likely looking for a recipe, not the history behind it. To reach the top of the SERPs, understand the reasoning behind a user’s search query and produce content according to their needs. Read our comprehensive guide on user intent and its role in the buying cycle to learn more.
3. URL
Analyzing URLs can help you check if multiple pages on your site are targeting the same keyword and have the same intent. If this is the case, none of these pages will perform well in the SERPs.
Let’s say you have an ecommerce website selling books, and books is the only keyword you target on all your pages. At first sight, it might seem like you’re doing a great job by telling search engines what your website is about. It’s actually not that simple.
In reality, when using this technique, you are essentially competing against yourself for one keyword, which is, by the way, far too broad to attract an engaged audience in the appropriate buying cycle. Instead, by optimizing each page for more specific keywords (like psychological books, detective books, books for children, etc.), you significantly increase your chances of ranking higher in SERPs and, as a result, improving conversion rates.
On top of that, by analyzing whether your URLs are ranking for relevant keywords, you can ensure that the most dedicated audience finds your website. If the audience you attract isn’t relevant to your target keywords, you may receive a lot of traffic that doesn’t convert. So, when tracking search engine rankings, don’t forget to analyze keywords, URLs, and content at the same time to make sure all these elements align with user intent.
4. Target location
When tracking search rankings, you can also target localized areas (countries or regions). This can help you identify where you have higher chances of getting to the top of SERP and where you’re falling short. As a result of optimizing your web presence for local search, you can target a ready-to-buy audience at the end of the sales funnel.
For instance, to change your country or region for Google search:
1. Go to the bottom-right corner and click Settings.
2. Then, go to Search Settings.
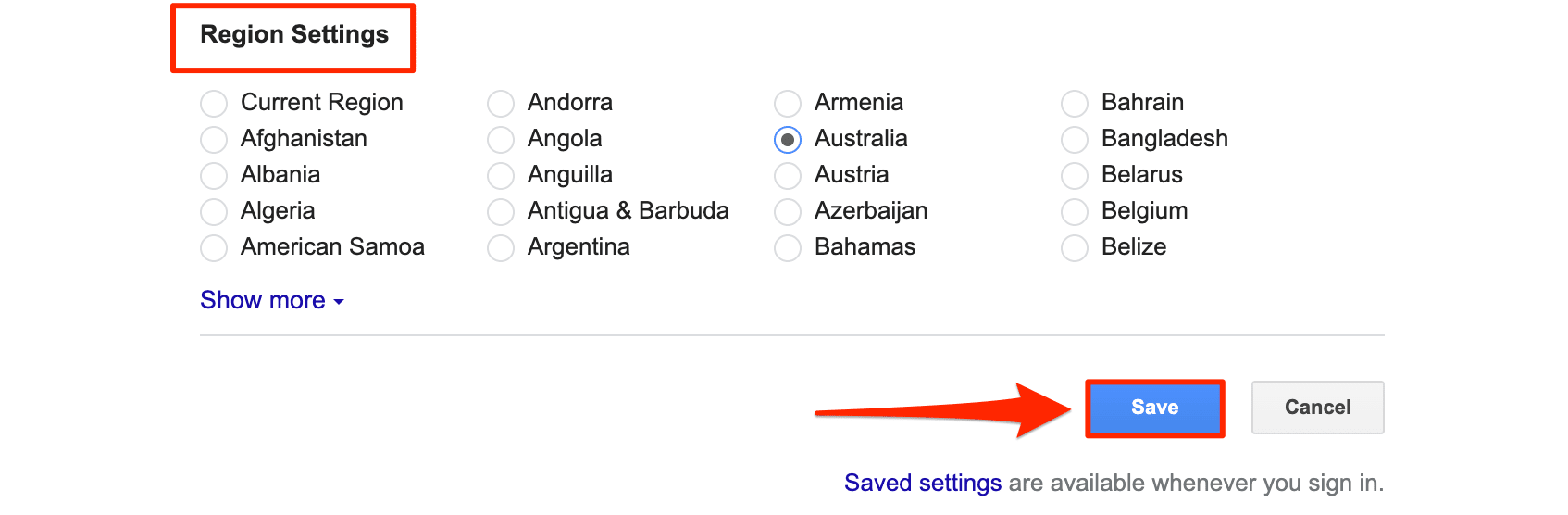
3. Scroll down to the bottom until you see Regions Settings. Here, you can select any country/region where you want to track your rankings. After that, click Save to save the changes you just made.
5. Snippets
Before going into detail, let’s clarify the difference between featured and rich snippets. Featured snippets, also known as zero-click searches, are information excerpts that appear at the top of SERPs in what is known as “Position 0.” Definition boxes, tables, lists, or videos, for example.
Rich snippets are enhanced search results containing additional data or functionality. Most often, you can find rich snippets in the form of reviews, recipes, movies, and events.
In the past several years, zero-click Google searches rose to nearly 65%. By tracking which keywords own featured snippets and optimizing for them, you can appear above the #1 spot on Google, thereby increasing your website’s traffic and authority. What’s more, featured snippets are especially important for mobile search. Mobile devices inherently offer less screen space, so your featured snippet will attract more of their attention. If you have featured snippets, oftentimes your target audience won’t even need to scroll down the page to get the info they need. This means they won’t be looking at your SERP competitors.
Rich snippets can also bring many other benefits to the table, including:
- Stealing attention away from simple blue links.
- Providing better traffic potential.
- Enhancing user experience.
Best ways to track search rankings
There are lots of ways today to check page rankings on Google and other search engines, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s go over each of them to see which one is best for your business.
Manually check the SERP you need
Performing a manual check is one of the most obvious yet complicated ways to find your website’s ranking in Google and other search engines. To do this, enter a keyword into search engines and scroll through all results until you find your URL. Needless to say, manually checking the SERP can be time-consuming if you don’t already rank on the first 10 pages of search results.
To find specific exact-match phrases and exclude synonyms when checking SERP results, use search operators. To do this, put your keyword in double quotation marks (“ “). For example, by typing “sports equipment” into the search box, you’ll see all the web pages whose content includes this phrase. If you want to view a list of all Google search operators that might be useful for keyword tracking, check out our in-depth article on this topic.
One of the main limitations to this type of rank tracking is that the order of search results depends on many factors, like your location (based on IP), previous search history, SERP behavior (click-throughs, pogo-sticking), and the device that you use. This means that if you and your friend type the keyword lactose-free ice cream from different locations and/or devices, you will get different SERP results.
If you still decide to use this method, don’t forget to sign out of your Google account, use a private browser session, and analyze search engine rankings from your target location. This will improve the accuracy of your search results.
Tracking rankings with Webmaster Tools
To simplify the process of rank-tracking, you can use webmaster tools that gather the main position ranking data in one place. Let’s take a look at each of them individually.
Google: Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free web service offered by Google that provides information about your site’s overall search performance (but only in this search engine). GSC can also help you track search rankings.
To find the list of keywords that are leading people to your website, follow the steps below:
1. Set up GSC. If you haven’t done this yet, here’s our separate Google Search Console guide explaining how to properly set up and use this tool.
2. Go to the Performance report.
3. Click the Queries tab.
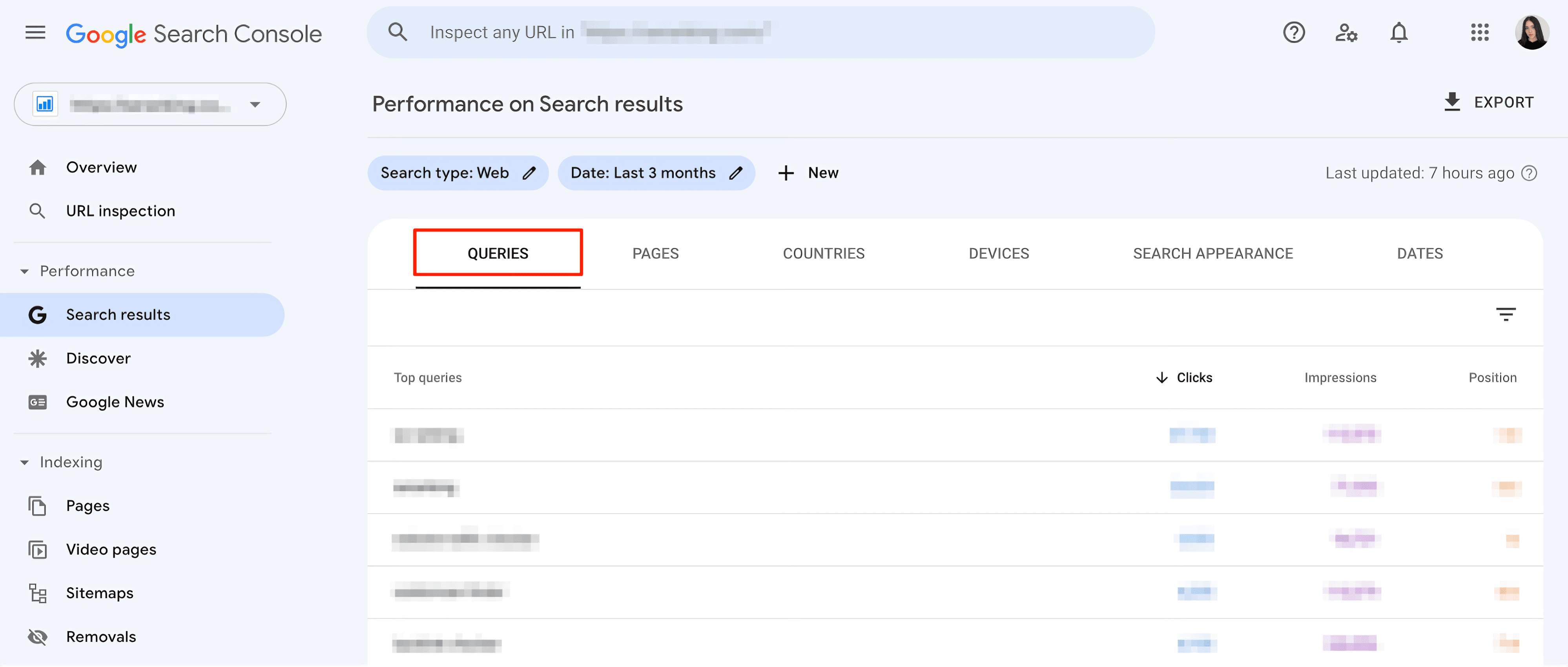
Remember that the list of keywords in this section represents how you appear in search results across your entire website. To find keywords driving traffic to a specific URL, go to the Pages tab and select the page you want to analyze. Then, click the Queries tab again. Here, you’ll see all of the queries for which the specific URL you selected in the last step ranks.
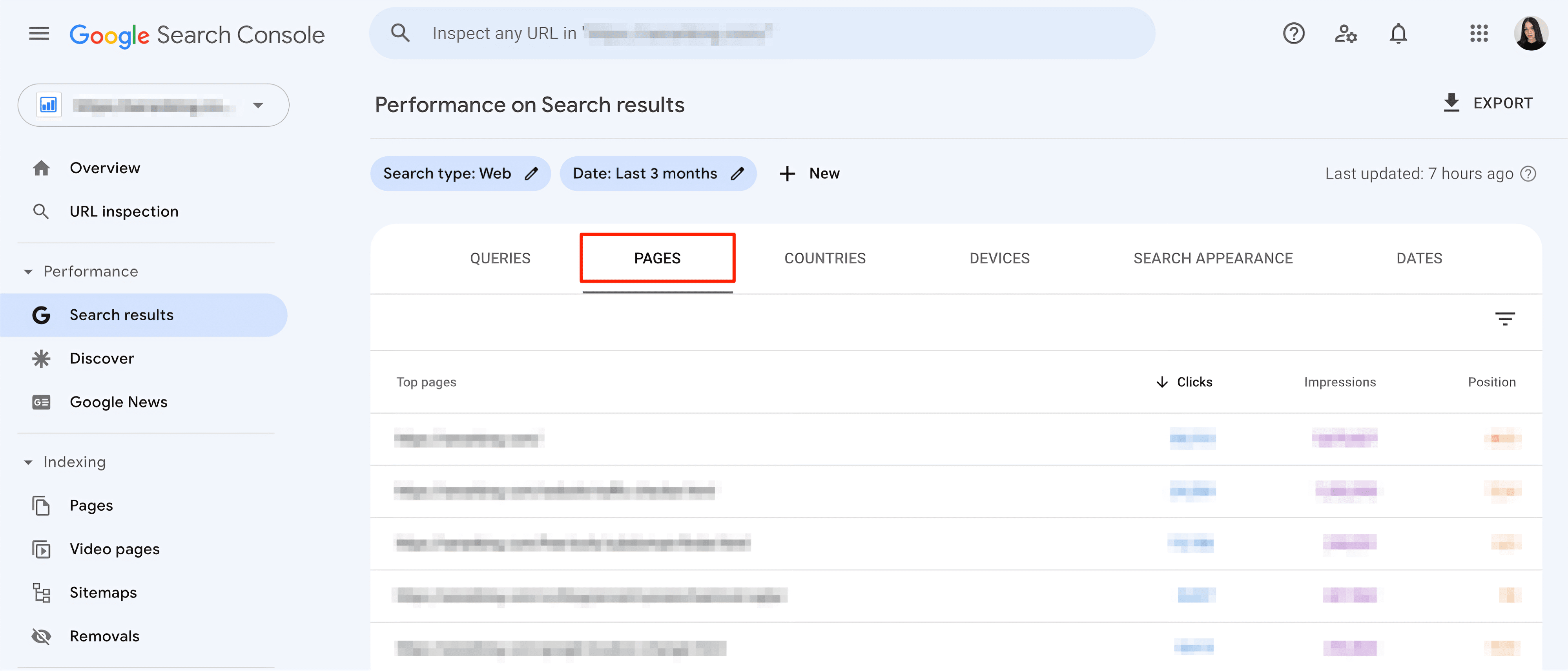
This method may be inconvenient because it requires you to go through each page separately. To see the URLs of all pages ranking for your keywords, create a table in Looker Studio (formerly Google Data Studio). Here’s how to do this:
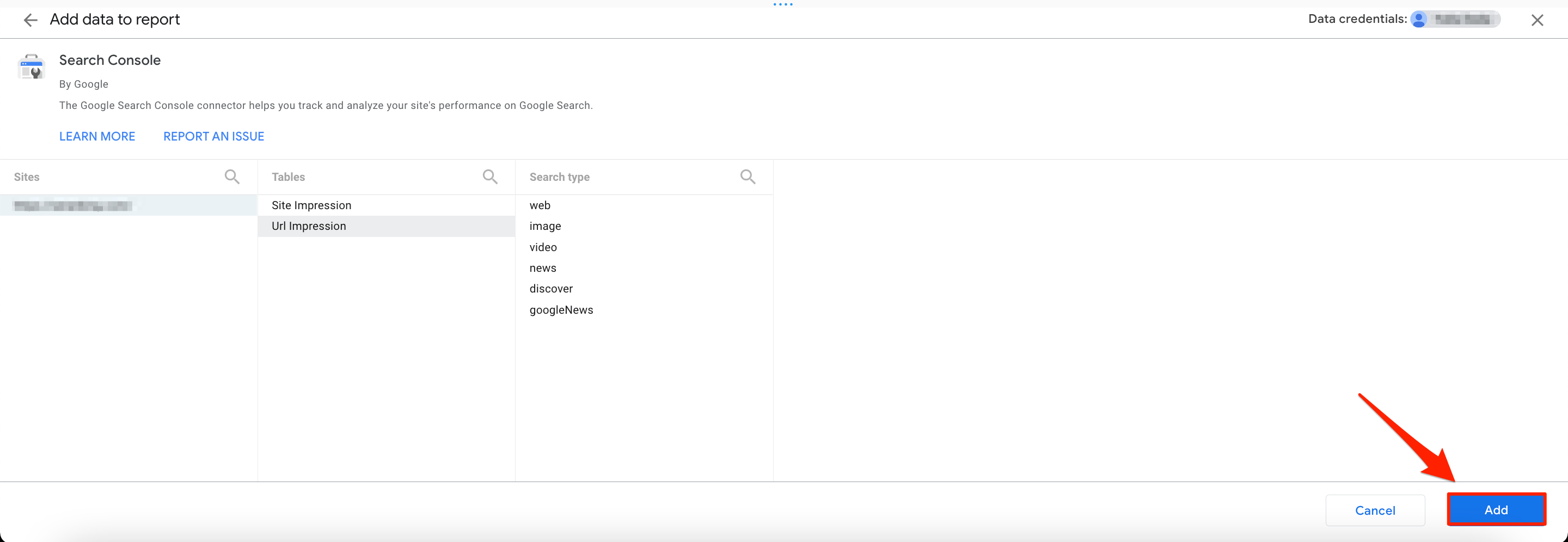
1. Create a new Looker Studio report. Add GSC as a data source and select URL Impression.
2. Create a table and set up its dimensions. To get a big-picture, add fields like Query, Landing Page, URL Clicks, Impressions, URL CTR, and Average Position to the dashboard.
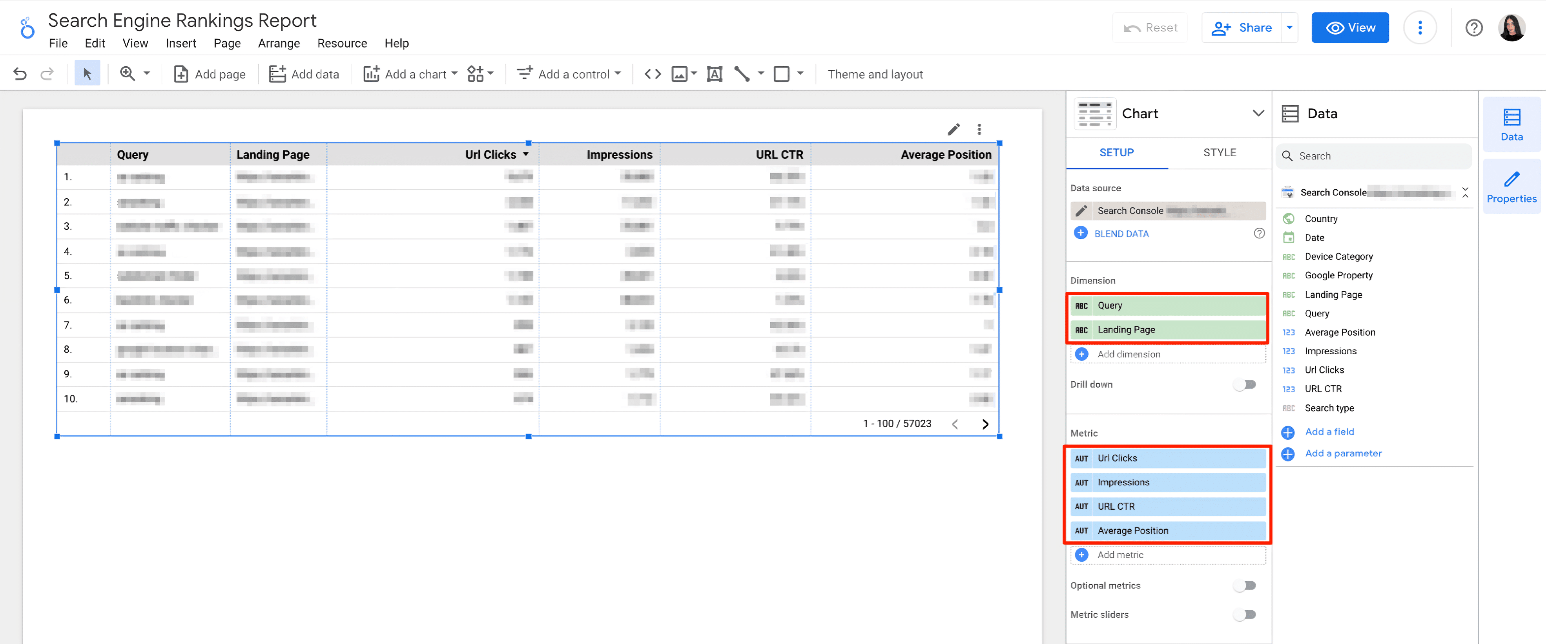
3. Now you’ve got a table with the main elements for checking Google rankings, including the keyword, landing page URL, average position, clicks, impressions, and URL CTR.
However, if you use GSC to check your Google search ranking, keep in mind that SERP positions present in this tool are not always accurate. Because of anonymized queries, page-and site-level reports may display fewer search queries than the Query report. On top of that, GSC updates your rankings every three days.
We highly recommend utilizing a specialized Google ranking monitor to continuously track and analyze your website’s performance on search engine results pages, allowing you to make informed decisions and adjustments to your SEO strategy as needed.
Bing: Bing Webmaster Tools
Just like with Google Search Console, you should set up Bing Webmaster Tools and verify ownership of your website using one of the following options:
- XML file authentication.
- Meta tag authentication.
- CNAME record via hosting provider.
Next, open this tool and navigate to Search Performance. Here, you can view detailed information like CTR, the total number of clicks, and impressions. Data related to rankings for a particular page or keyword is presented below the graph. It shows the average position, click-through rate, and the number of impressions for each keyword/page of yours that’s ranking on the SERPs.
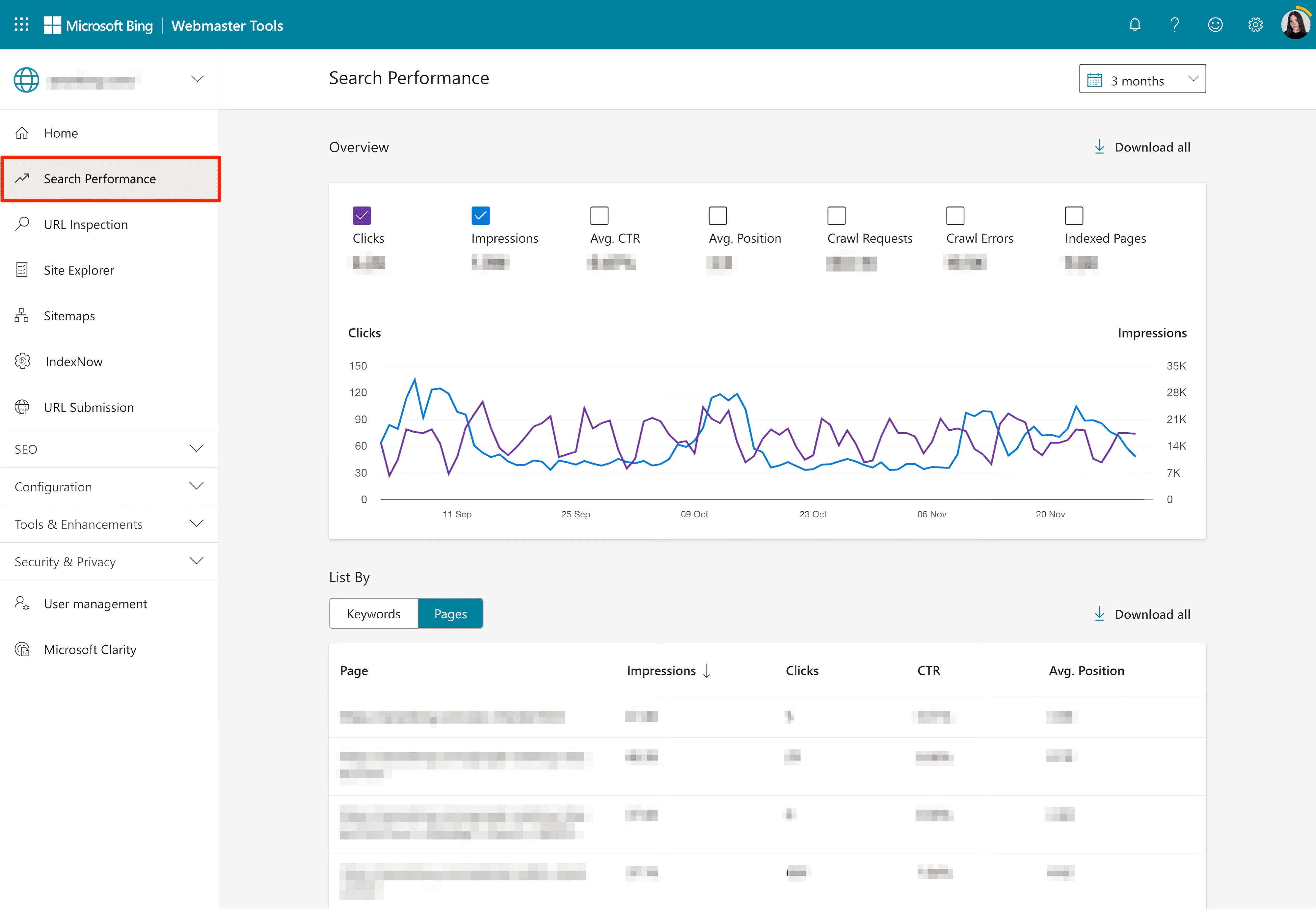
By clicking on the Download all button, you can export this data to a CSV file and use it as a data source for your Looker Studio report. To get a table with all the necessary dimensions like keyword, landing page URL, average position, CTR, clicks, and impressions, follow the same steps demonstrated above for Google Search Console.
At the same time, it’s worth noting that data presented in Bing Webmaster Tools is often delayed. On average, it takes a few days for accurate data to be available in this tool, which is why you shouldn’t rely solely on it for tracking information.
Yahoo: No separate webmaster tools
While both Google and Bing offer their own tracking tools, Yahoo no longer has dedicated webmaster tools. To monitor and maintain your website’s performance in Yahoo’s search results, use Bing Webmaster Tools. The subsection above contains recommendations for tracking search engine rankings with this service.
Tracking all search engines: SE Ranking Rank Tracker
As you’ve probably guessed, monitoring SERP rankings manually or with the help of free services offered by search engines is not that easy. At the very least, you’ll need to spend hours on end gathering all tracking data in one place. To save precious time on more important tasks and to get the most accurate information, most SEOs use a position tracking tool. SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker is one of them.
With Rank Tracker, you can simultaneously check your website’s Google search engine ranking and other search engines like Yahoo, Bing, and YouTube.
How to create a project in Rank Tracker
Track real-time rankings with SE Ranking by setting up your project in these five steps:
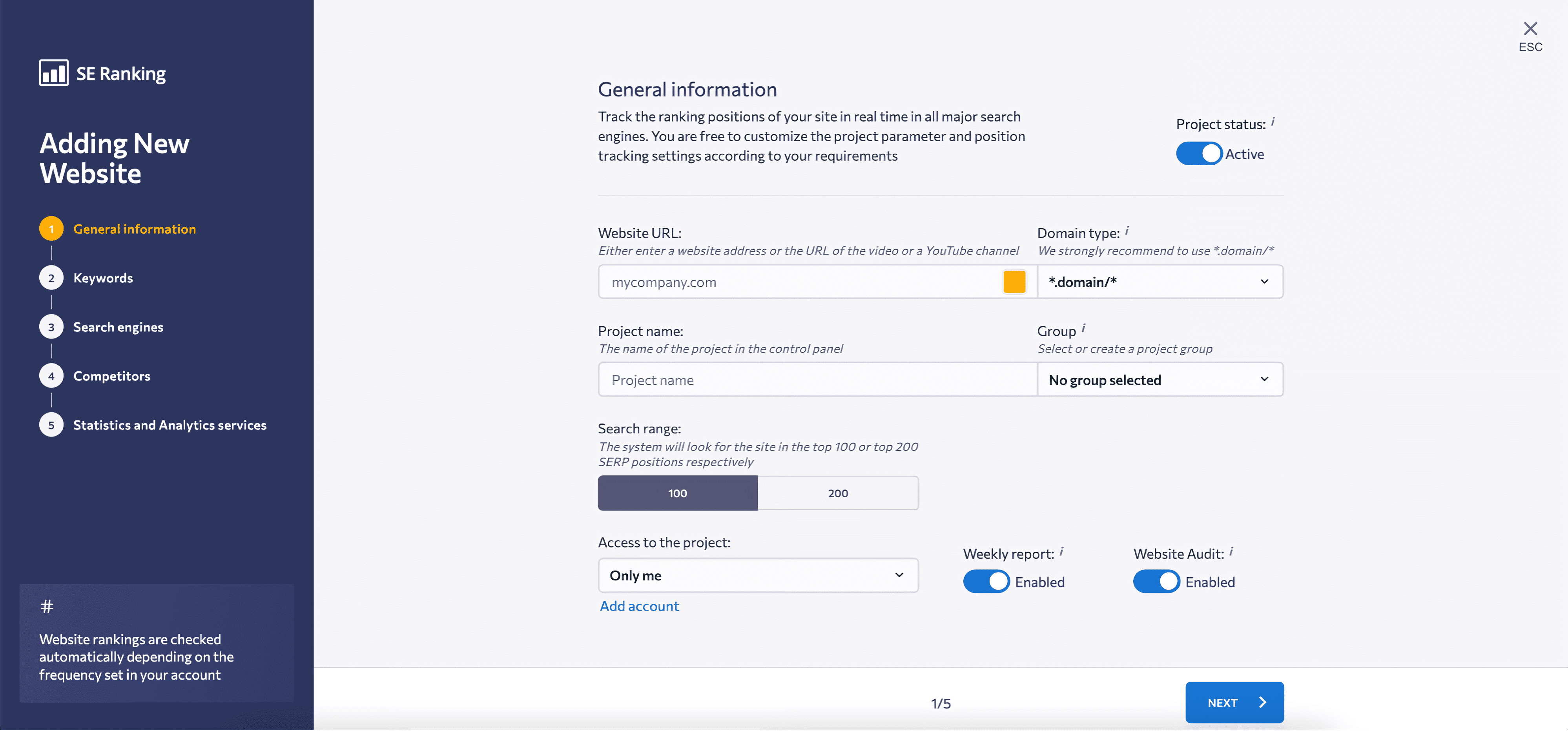
1. Click Create Project and add general information like the website URL, project name, search range, and access settings. During this initial step, you can also choose to receive a weekly report and conduct a website audit.
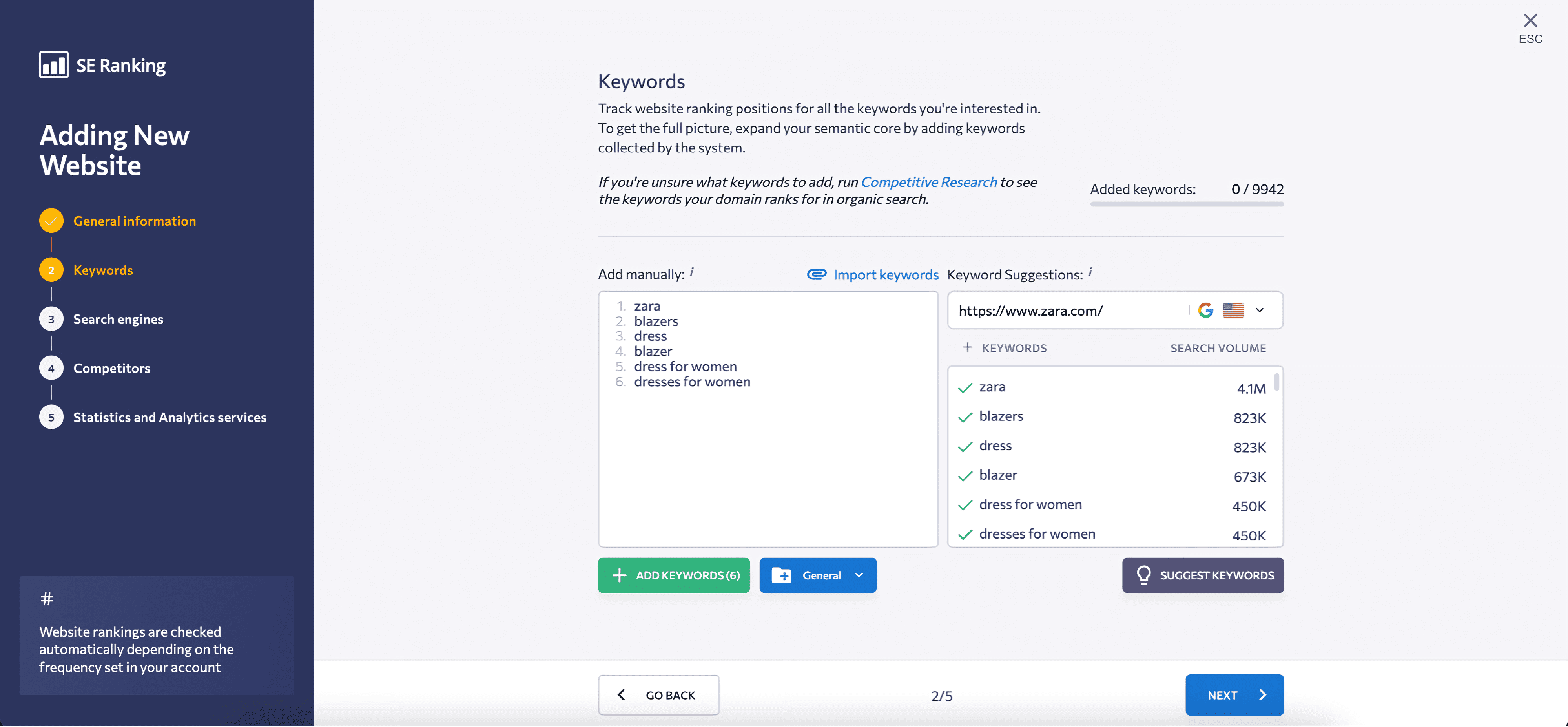
2. Manually enter and group the keywords you want to track or use keyword suggestions. You can also import keywords from Google Analytics or a CSV file.
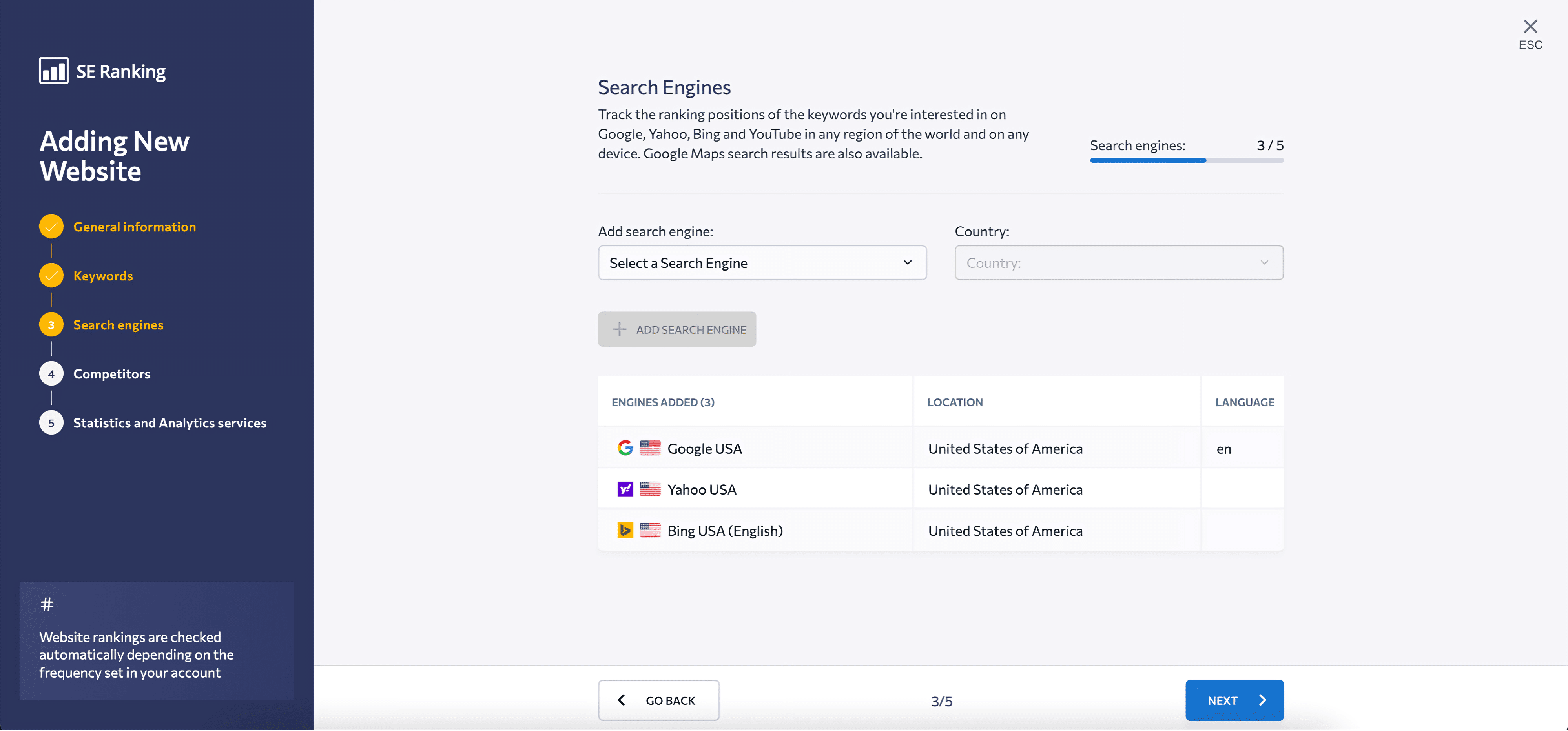
3. Select a search engine and a target location for monitoring keyword performance. You can compare rankings across counties or narrow your search to a specific city or postal code. On top of that, you can add up to five search engines per project at no extra cost.
4. Add competitors to your project. If you’re not sure which competitors to choose, SE Ranking will propose top competitors for your domain.
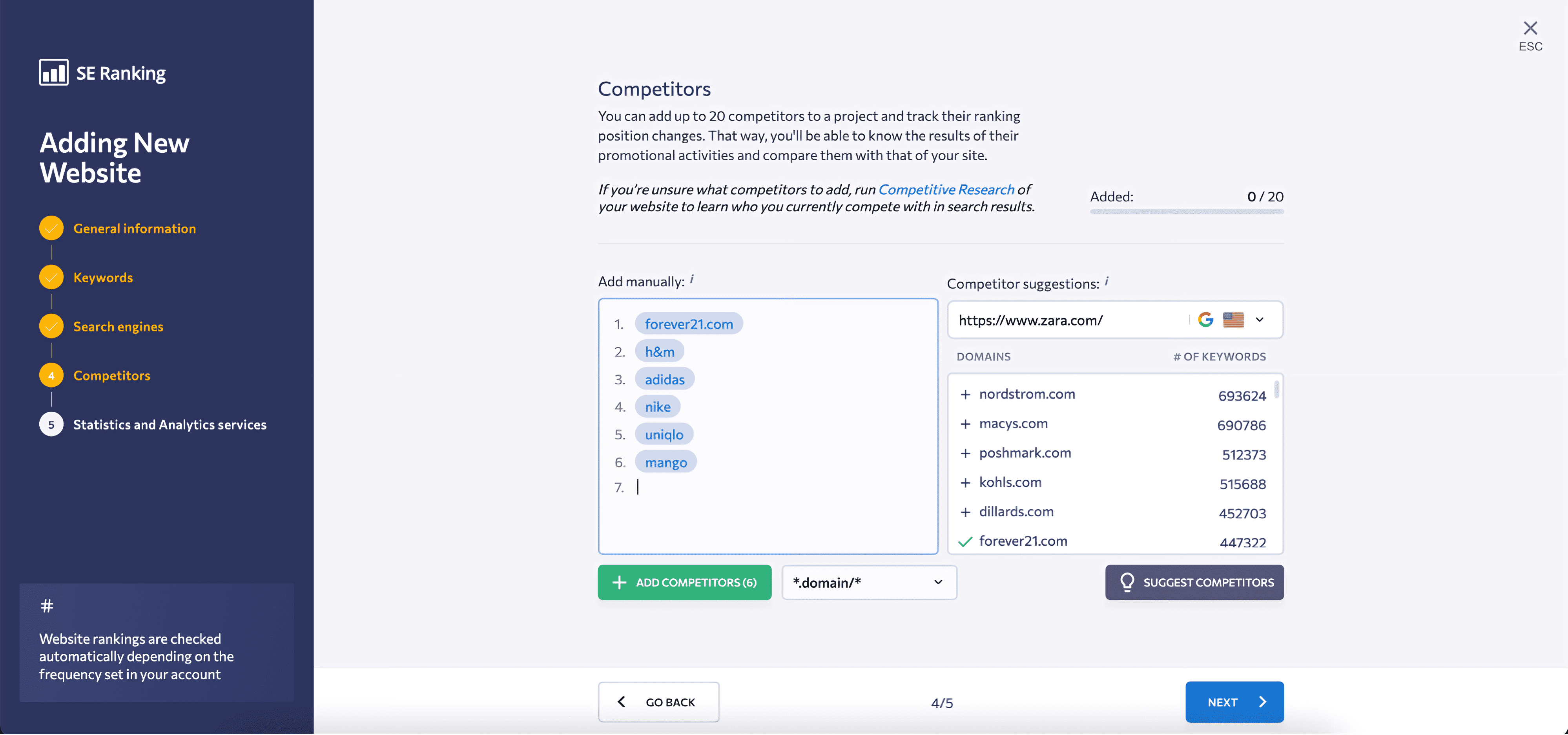
5. Integrate analytics services. For instance, to collect and compile more data on a single dashboard, you can connect SE Ranking with Google Analytics or Google Search Console.
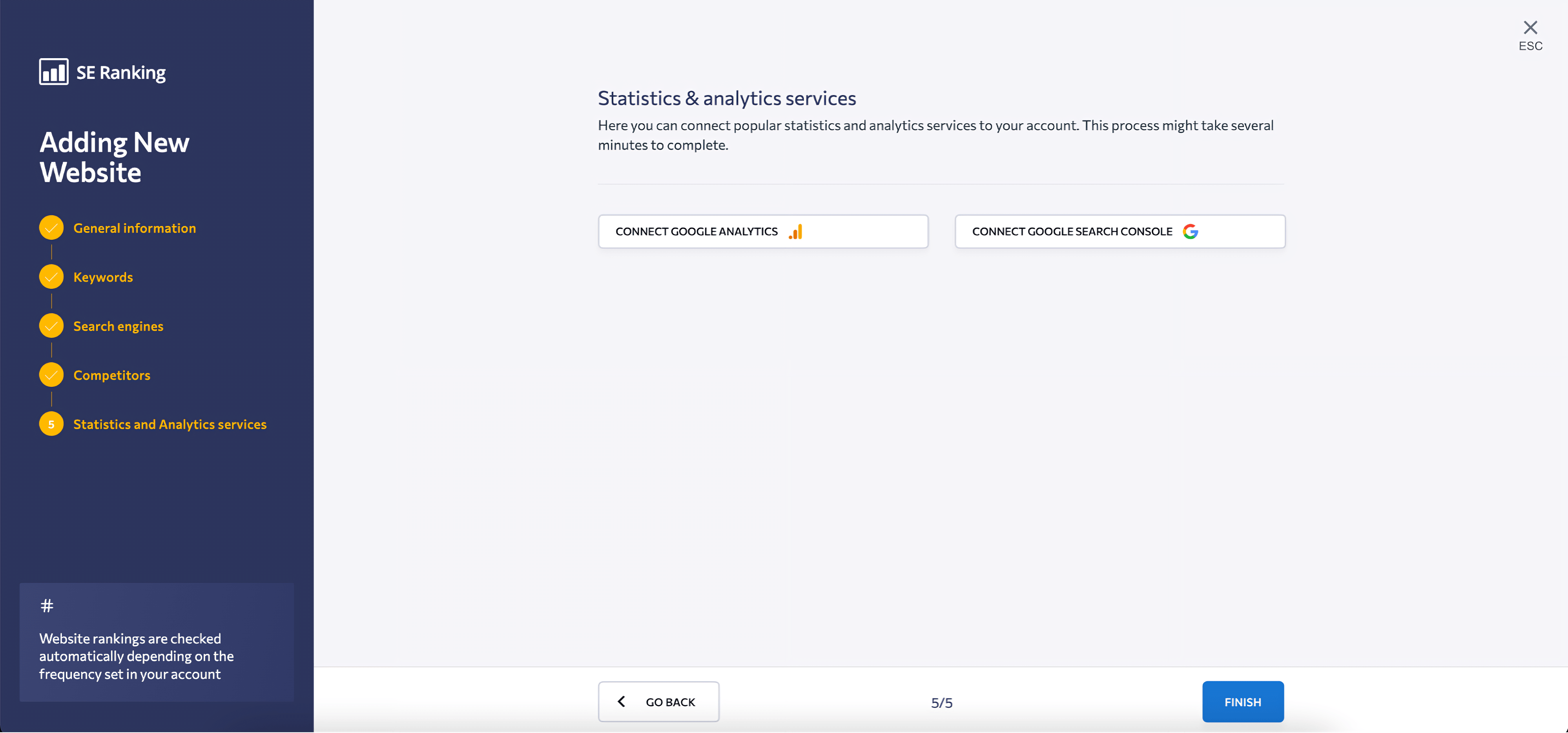
FYI, if you already have a project, you can access it from the left navigation menu or at the bottom of the main page.
How to use Rank Tracker
After completing these five steps, you can begin utilizing Rank Tracker with all its features. The Rankings module contains four main sections like Summary, Detailed, Overall, and Historical Data. The Detailed tab is the default option, so let’s start there.
You can adjust the location and search engine where you want to monitor your keywords, as well as select specific dates or a time period to view ranking data for, using the drop-down list at the top of the screen. Additionally, this section outlines the main keyword metrics needed for effective rank tracking. These metrics are as follows:
- The website’s average position
- Website traffic forecasting
- Search visibility
- SERP features
- The percentage of keywords ranking among the top 10 search results
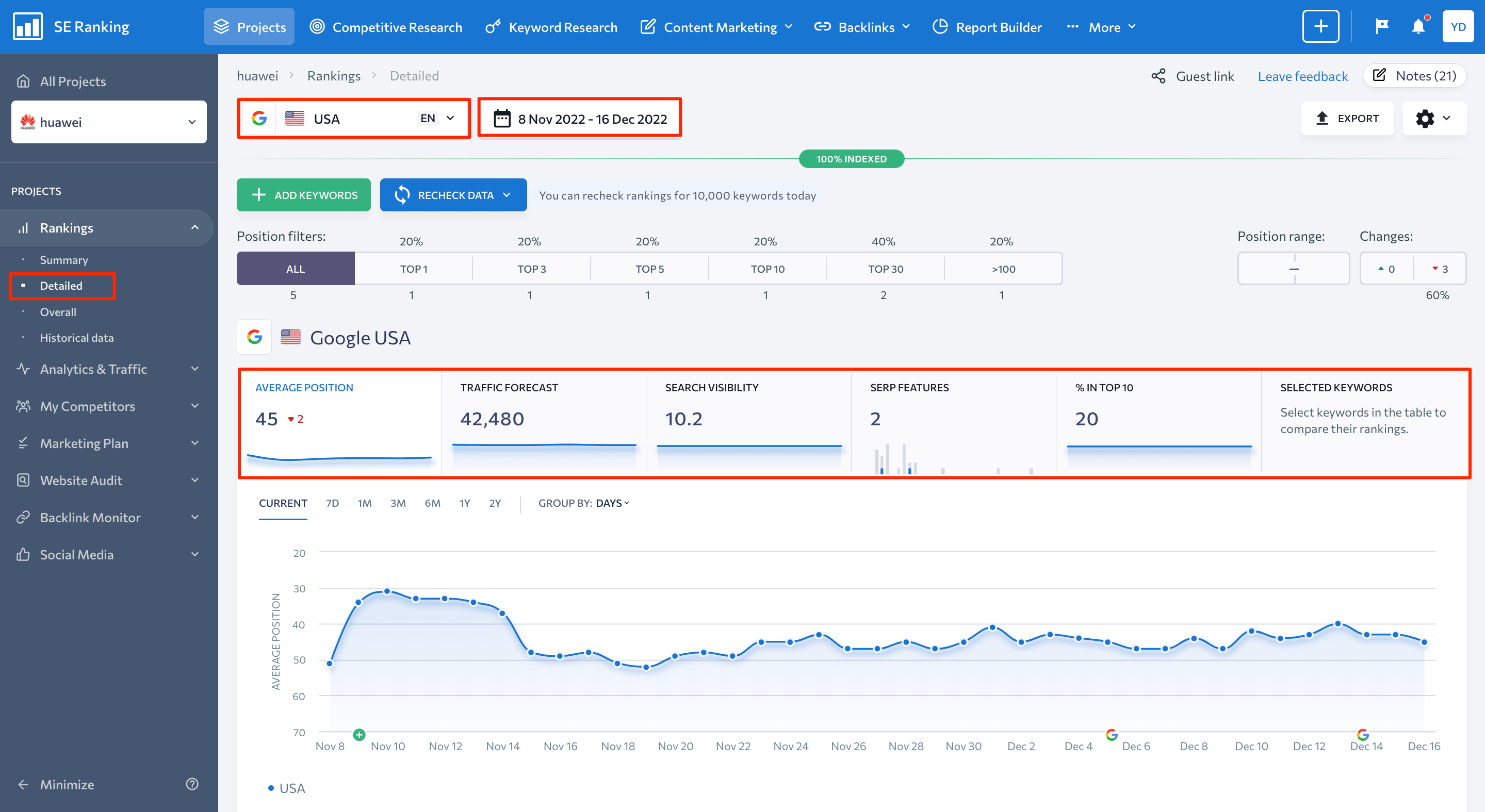
Each metric is represented by both numbers and charts, allowing you to gain a better understanding of how your keywords perform in both the short and long term.
You will find a keyword table with a variety of indicators alongside it as you scroll down the page. These include target URL, search volume, ranking dynamics, SERP features, competition, visibility, and so on. To fill the table with metrics that matter to you, go to the Columns section and only mark the parameters you want to see on the dashboard.
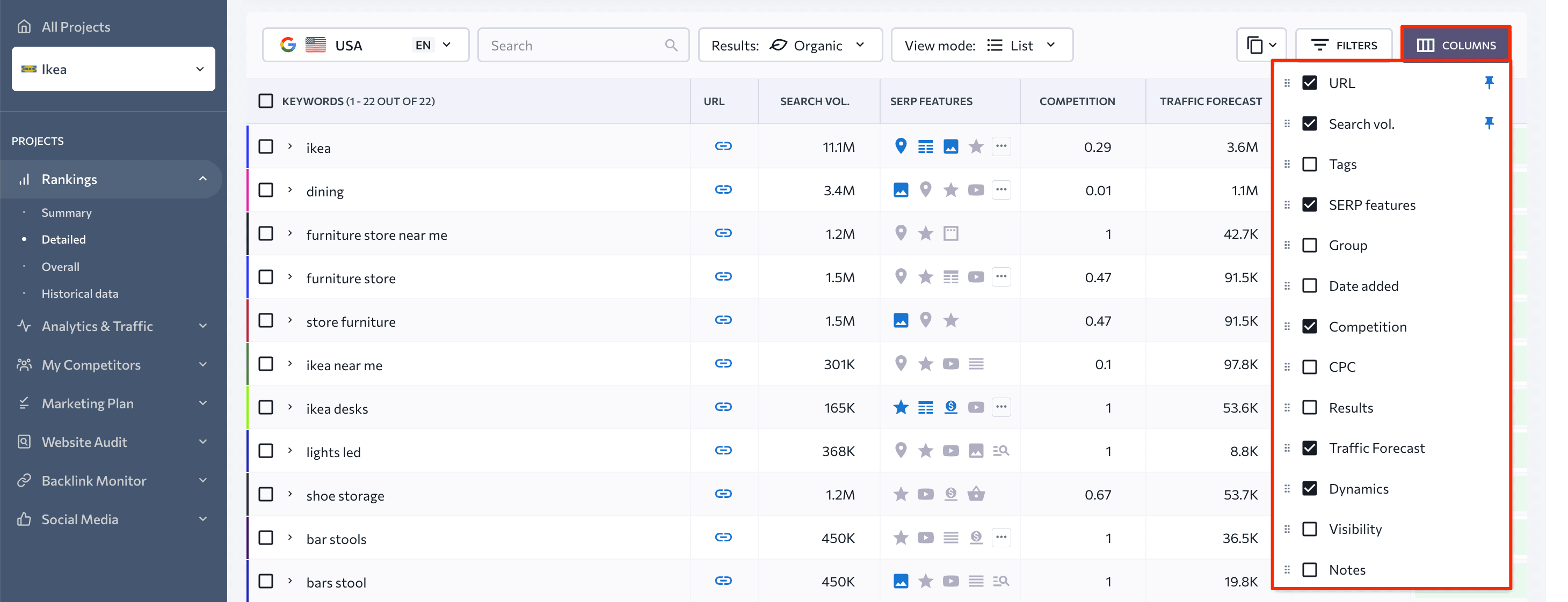
With the Filters feature, you can identify, select, and delete groups of keywords from the keyword list. For example, you can find a wide range of high-potential queries for your business by filtering keywords by a low competition score and high search volume.
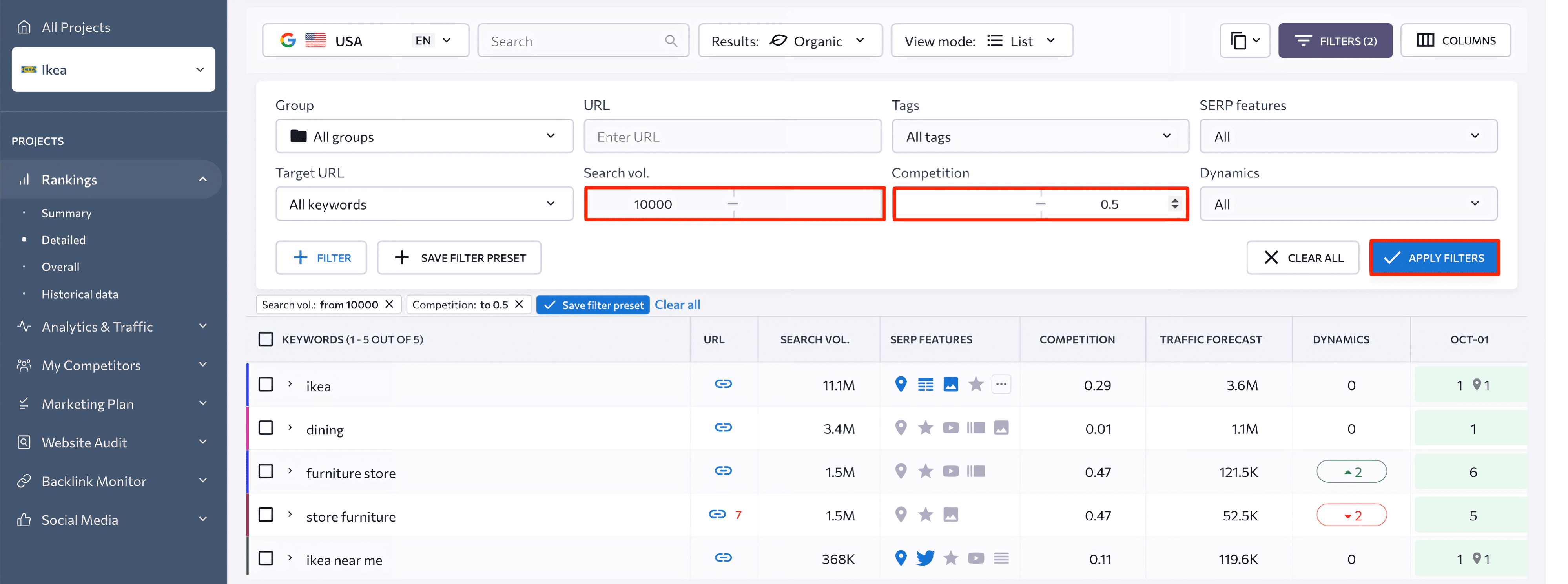
If you want to add a target URL to one or several keywords at once, you can do it in this section, too. Hover over the query in the table and choose the Target URL option from the dropdown list. Then, in the popup window, enter the target URL and click Save. To check the target URL’s rankings only, tick the corresponding field in this window.
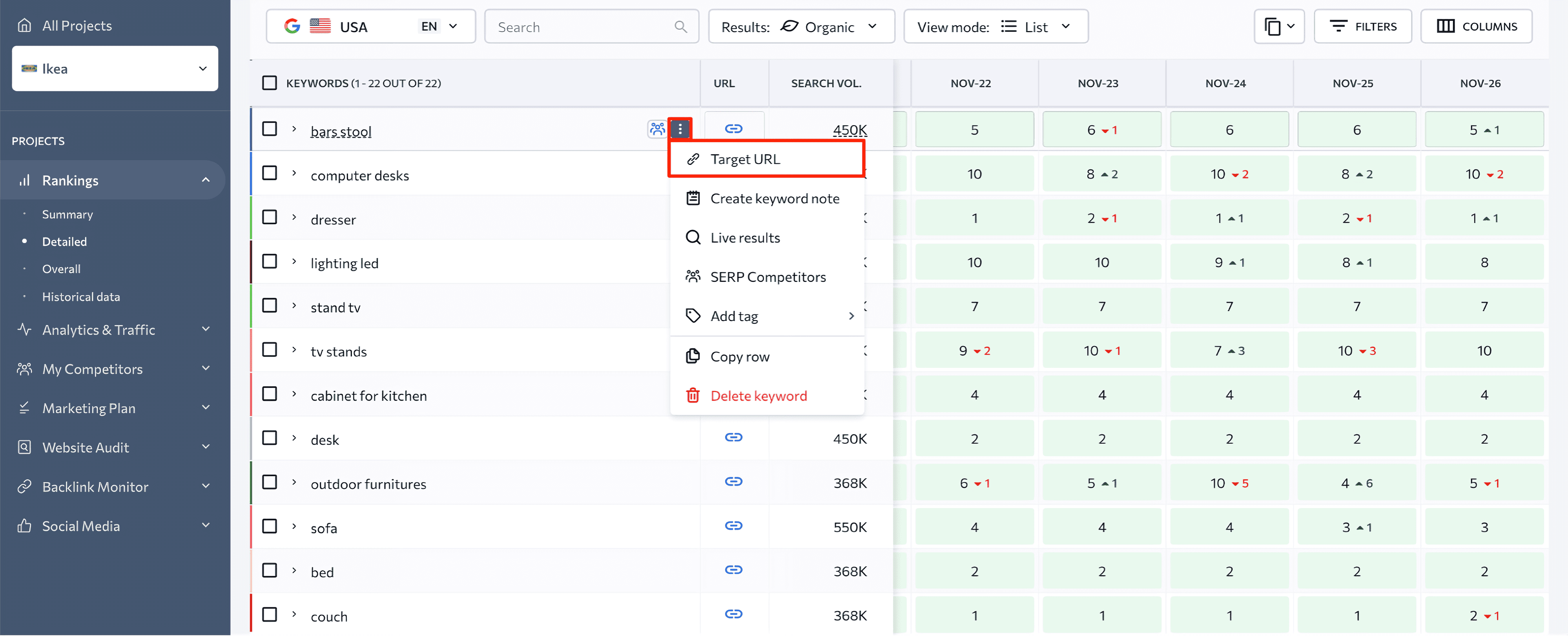
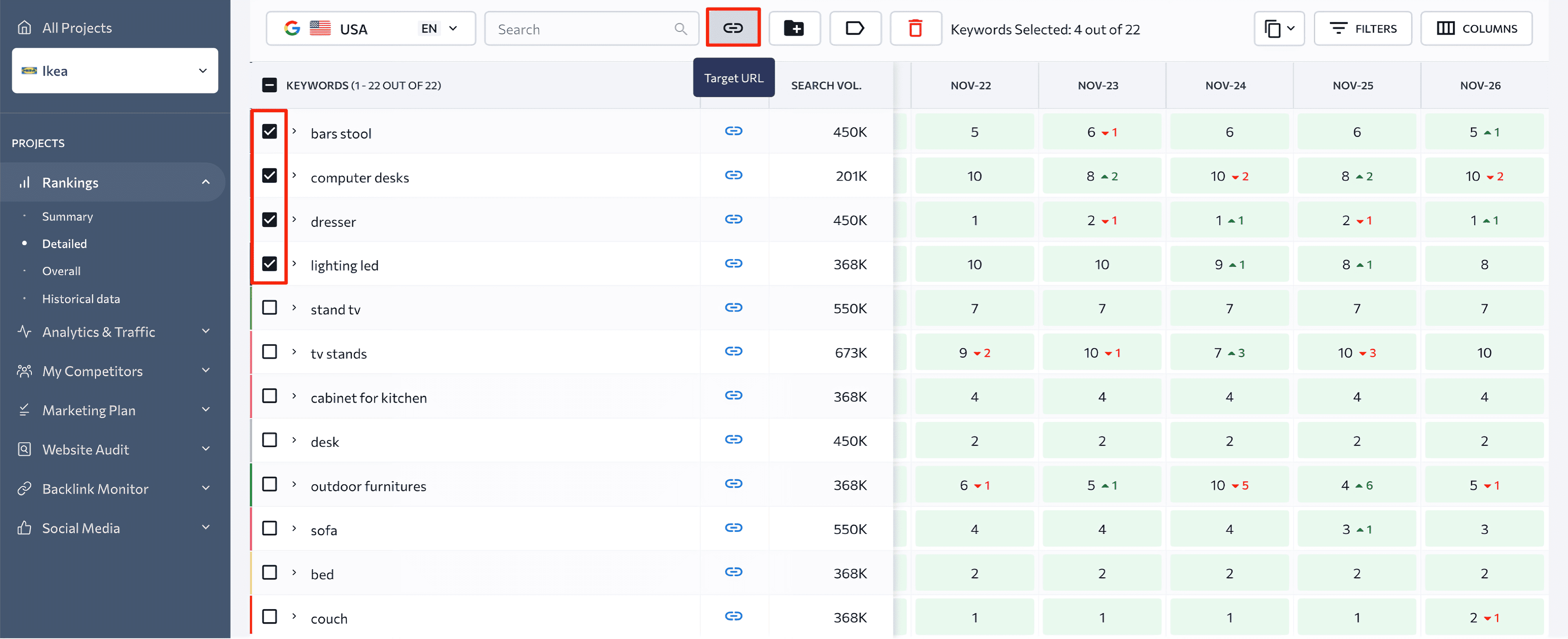
To set up a target URL for multiple keywords at once, select them in the table and click the Target URL button in the upper menu. Then, just as you would for a single keyword, enter the target URL into the popup window and mark the Check rankings for target URL only field as needed.
The Summary tab offers an easy and convenient way to analyze all keyword-related metrics in one place. All parameters are grouped into data blocks here:
- Search Visibility – this block represents the percentage of clicks received by your website based on your organic ranking positions in a specific search engine for all added keywords.
- Average Position – this graph shows the average SERP position of your website.
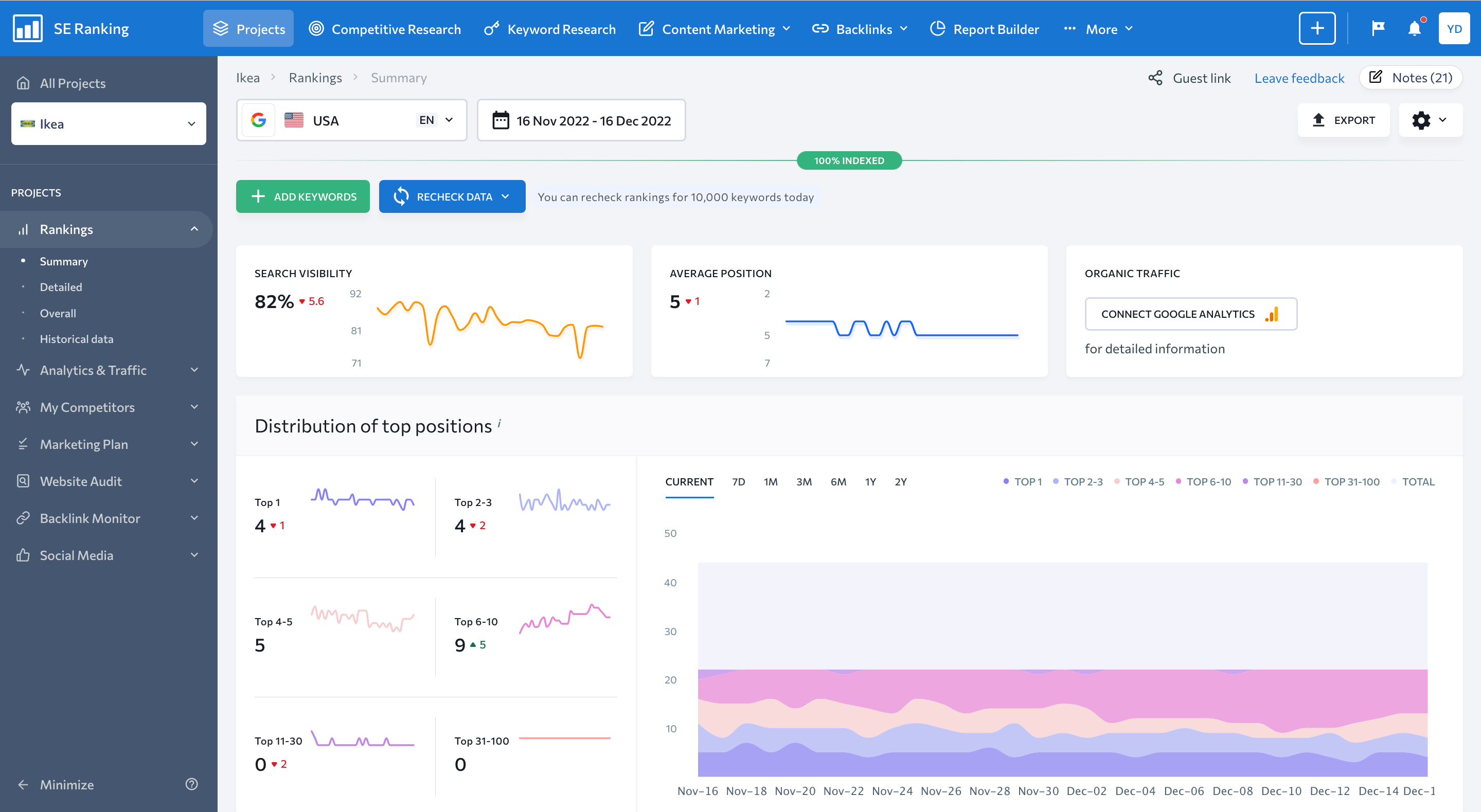
- Organic Traffic – this section represents the number of clicks on your organic search engine results.
- Distribution of Top Positions – this block shows the number of organic queries for which a specific website ranks among the top 1, top 3, top 5, top 10, top 30, and top 100 search results in the selected search engine.
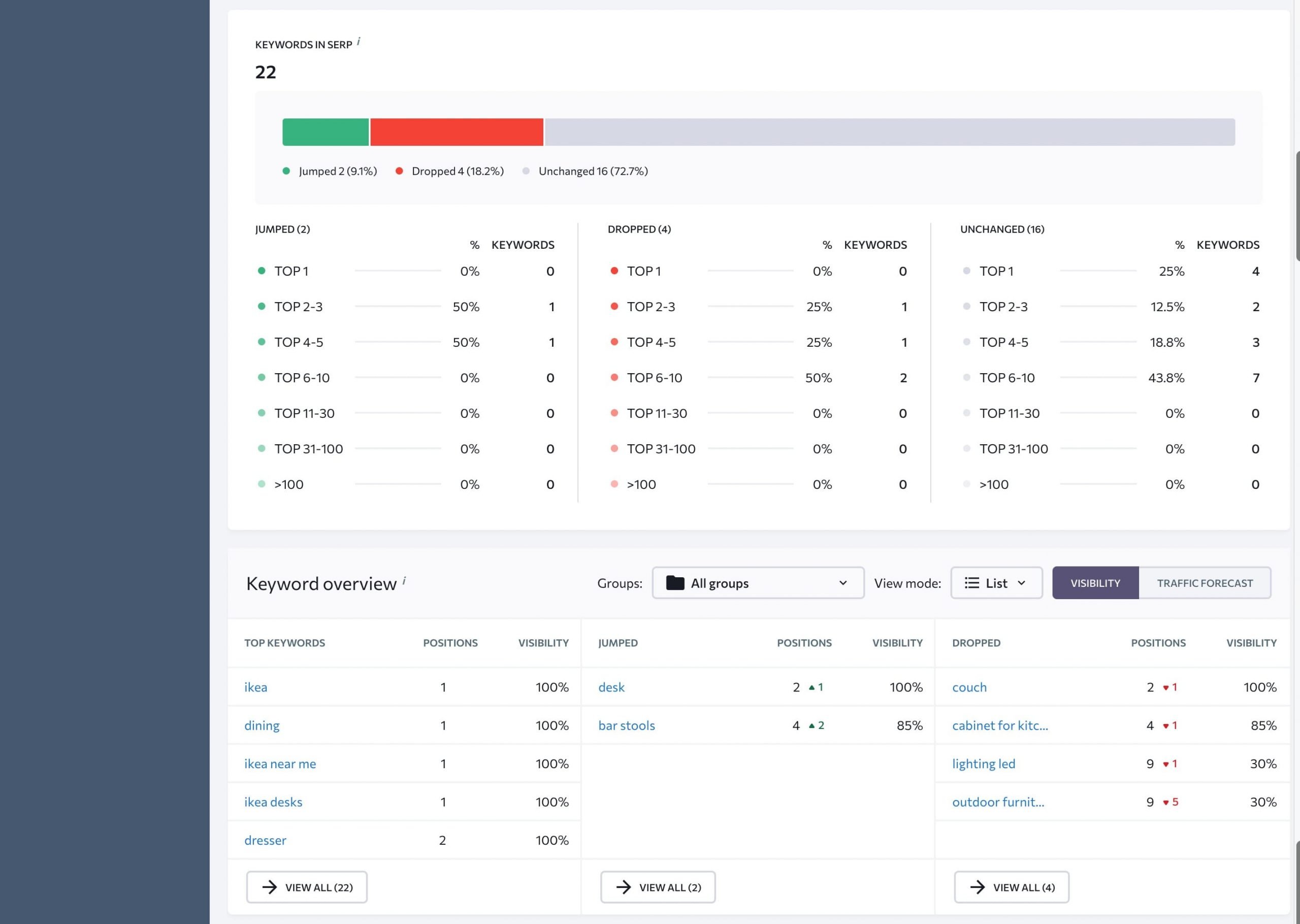
- Keywords in SERP – this tab outlines the number of keywords that appear at the top of SERPs. All keywords are divided into three categories, such as Jumped, Dropped, and Unchanged, allowing you to track trends, like keyword changes, in one place.
- Keyword Overview provides a list of top, improved, and declined keywords in the SERPs.
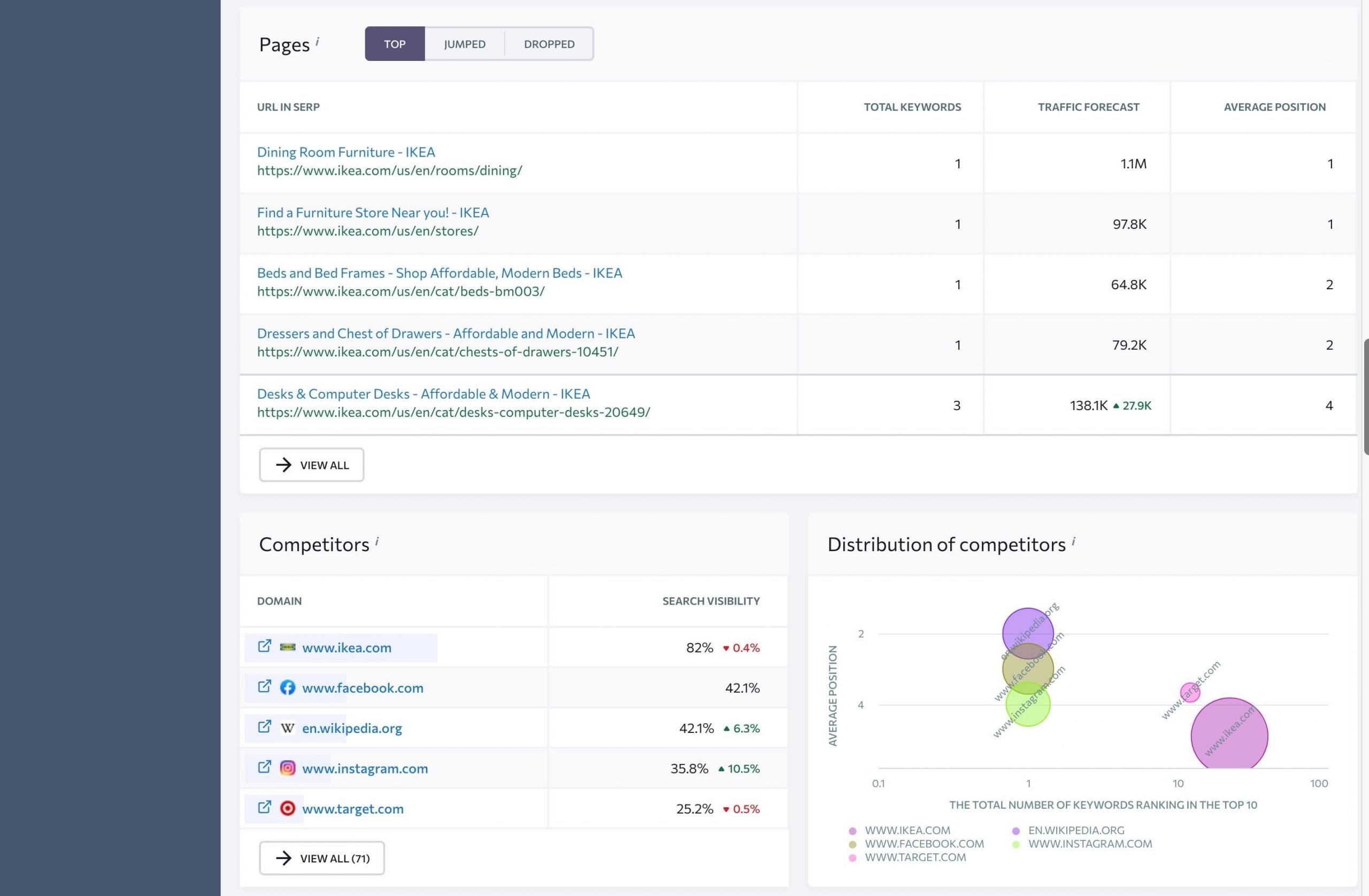
- Pages – this block shows all of your webpages that are at the top of the SERPs, as well as those that have jumped or dropped over time.
- Competitors – this section shows a list of websites ranking among the top five search results for each tracked query.
- Distribution of Competitors – this chart shows the distribution of competitors in organic results based on the number of keywords they rank for, the average position of these keywords, and the overall search visibility.
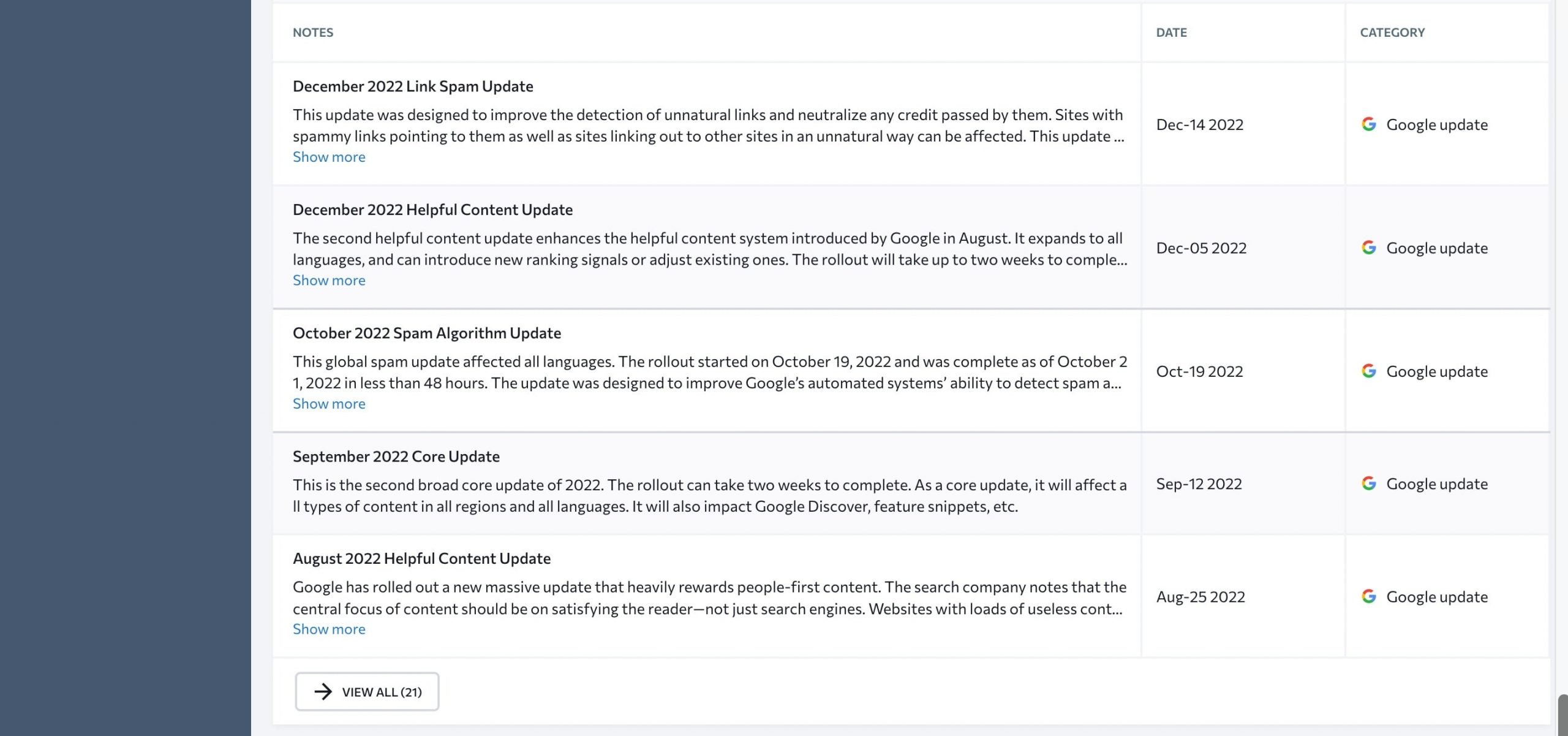
- Notes – this block outlines the latest project notes and search engine updates.
To get detailed information on the website’s performance in this tab, select the search engine from the drop-down list at the top of the screen.
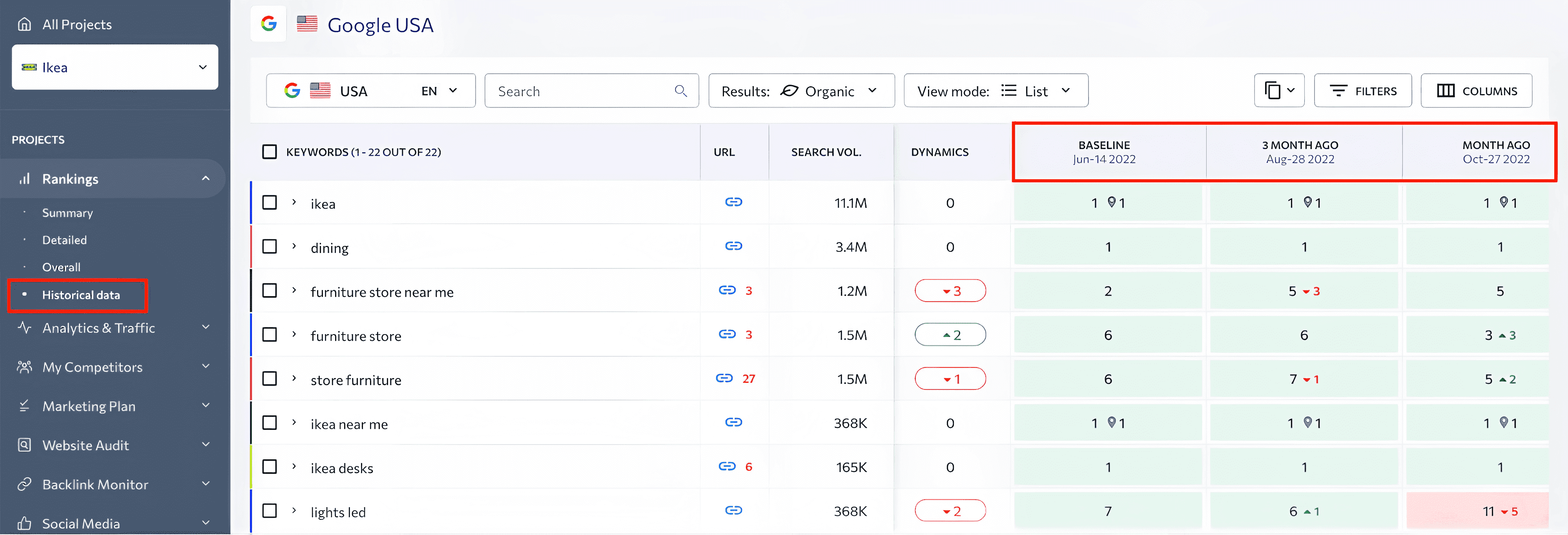
Under the Historical Data section, you can see how search engine rankings have changed starting from the baseline ****.
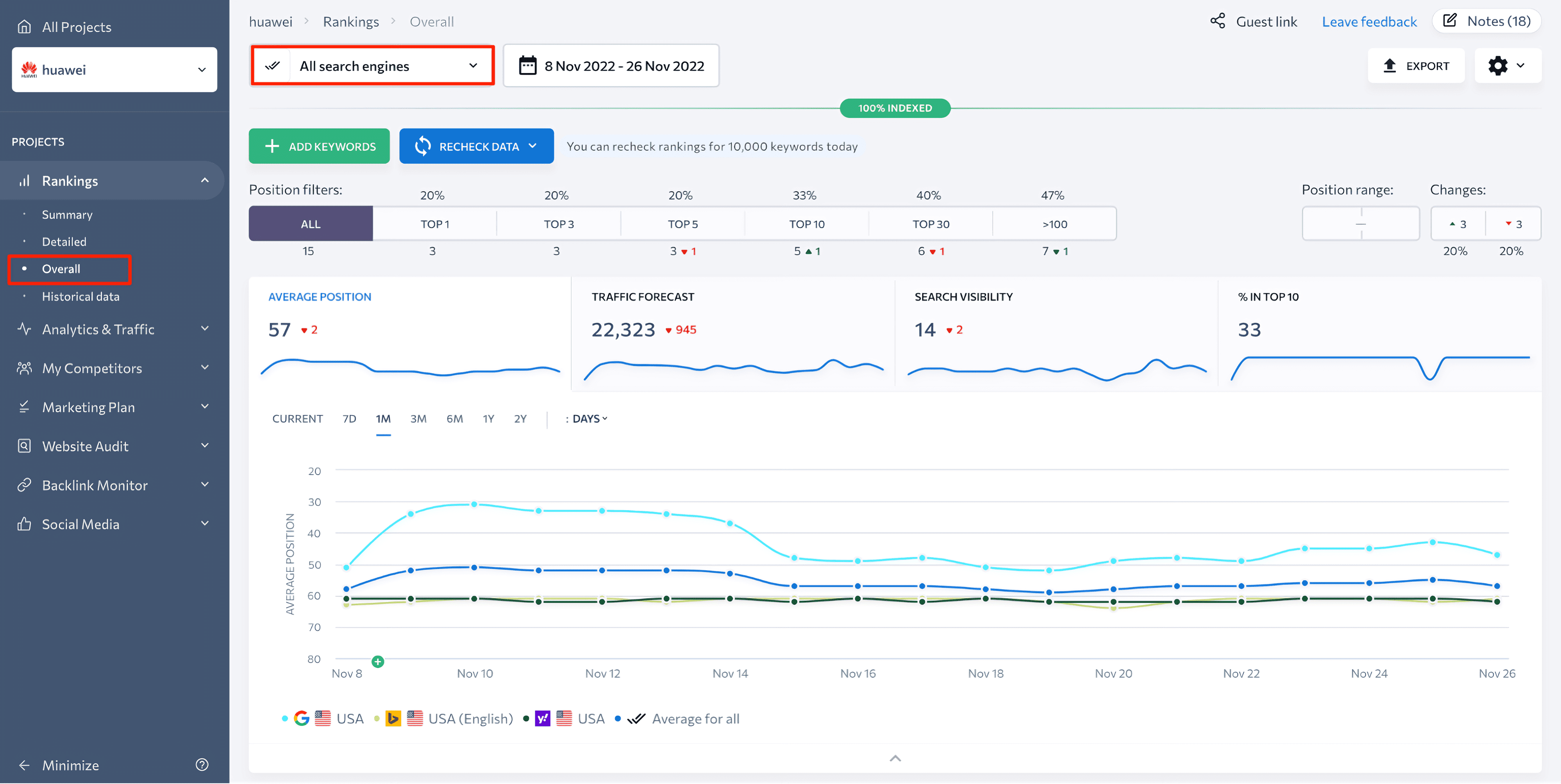
Finally, the Overall mode allows you to see rank-tracking data for all search engines on the same page. The latter page can be of great help if you need to compare performance data from different search engines without switching between dozens of tabs.
Tracking SERP and competitors
When tracking rankings, keep an eye out for other pages that search engines show in response to a user’s search query. This allows you to track where you and your competitors rank and learn how to rank at the top of search results in different search engines.
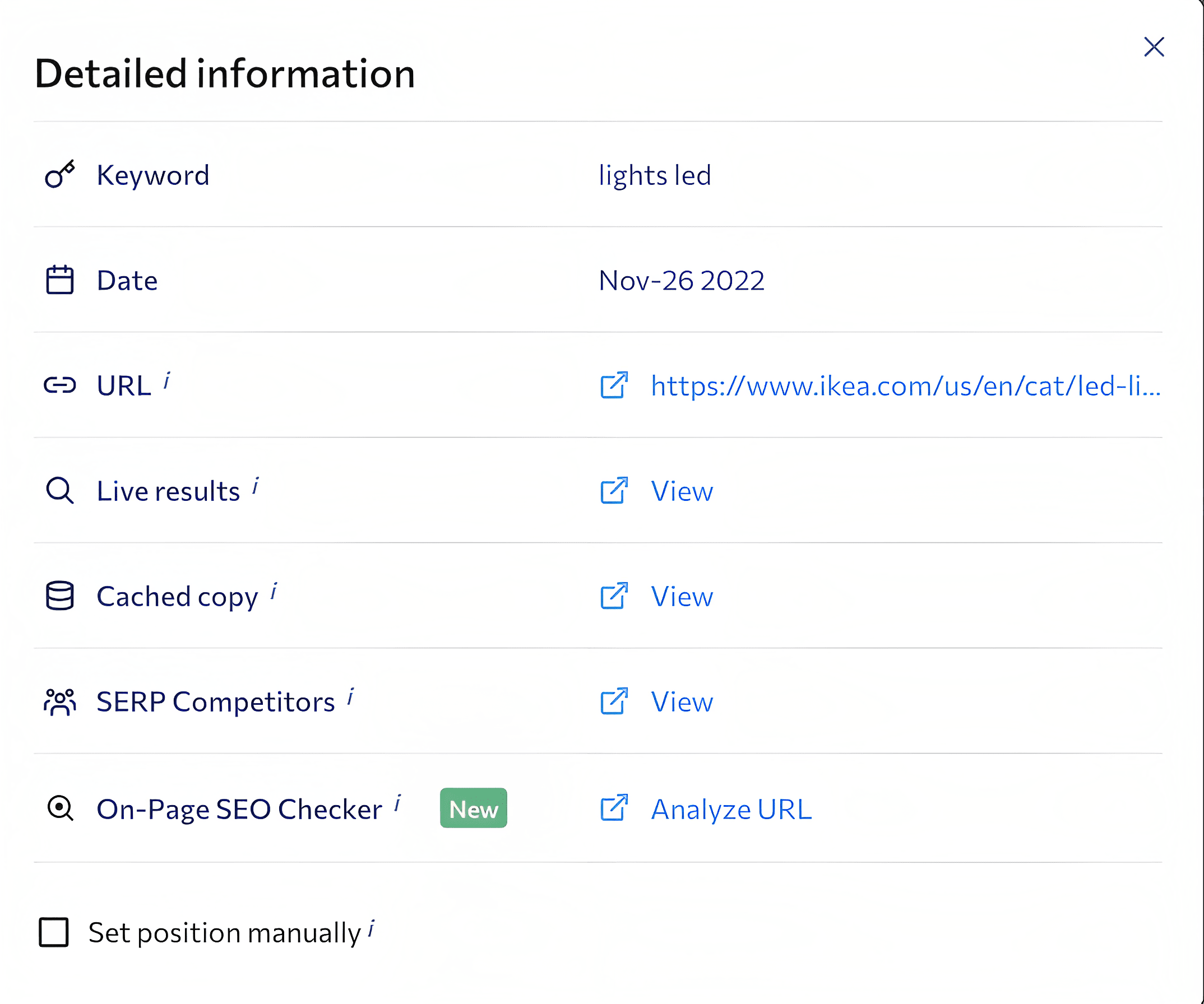
To do this, select a **** and then click on the position of any keyword. In the popup window, you’ll find:
- Live results for the keyword in the specified search engine based on the selected region.
- A cached copy of the SERP for the day when rankings were checked.
- SERP competitors for each of the queries that you’ve added to the project.
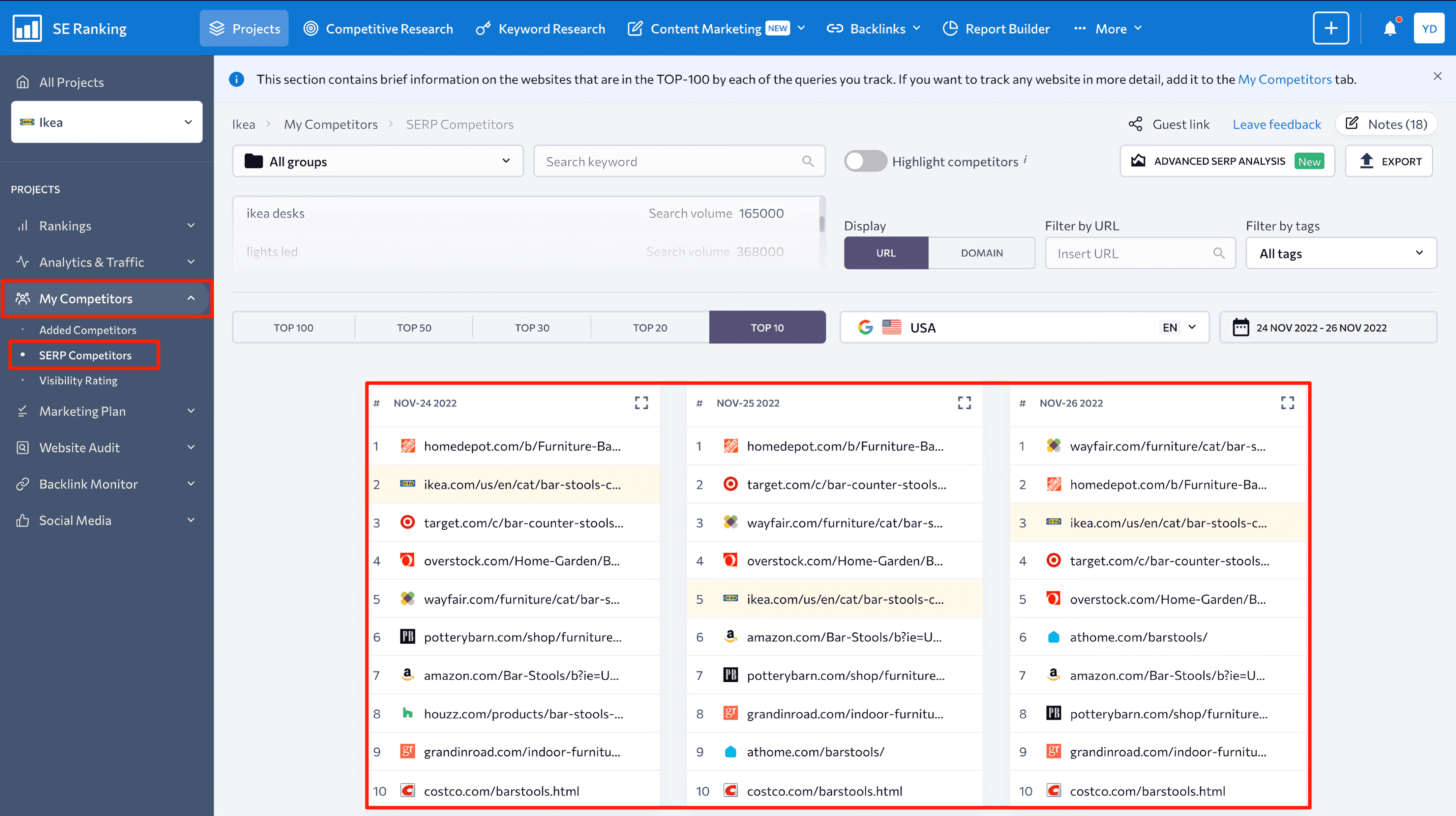
If you click on the View button next to the SERP Competitors feature, you’ll be taken to the My Competitors module. You can examine the top 100 domains ranking in SERPS for the same keyword. This analysis will eventually give you a deep understanding of:
- New competitors that are quickly moving to the top of SERPs.
- Dynamics of a competitor’s specific webpage.
- Websites that have long been ranking among the top spots on SERPs.
Consider this module a way to keep track of your entire keyword competition. In addition to the top domains with which you compete, you can monitor websites that only have only recently begun to climb the rankings. With this data, it will be much easier to predict potential competitors who are not yet ranking high in SERPs and plan a counter-strategy to outperform them.
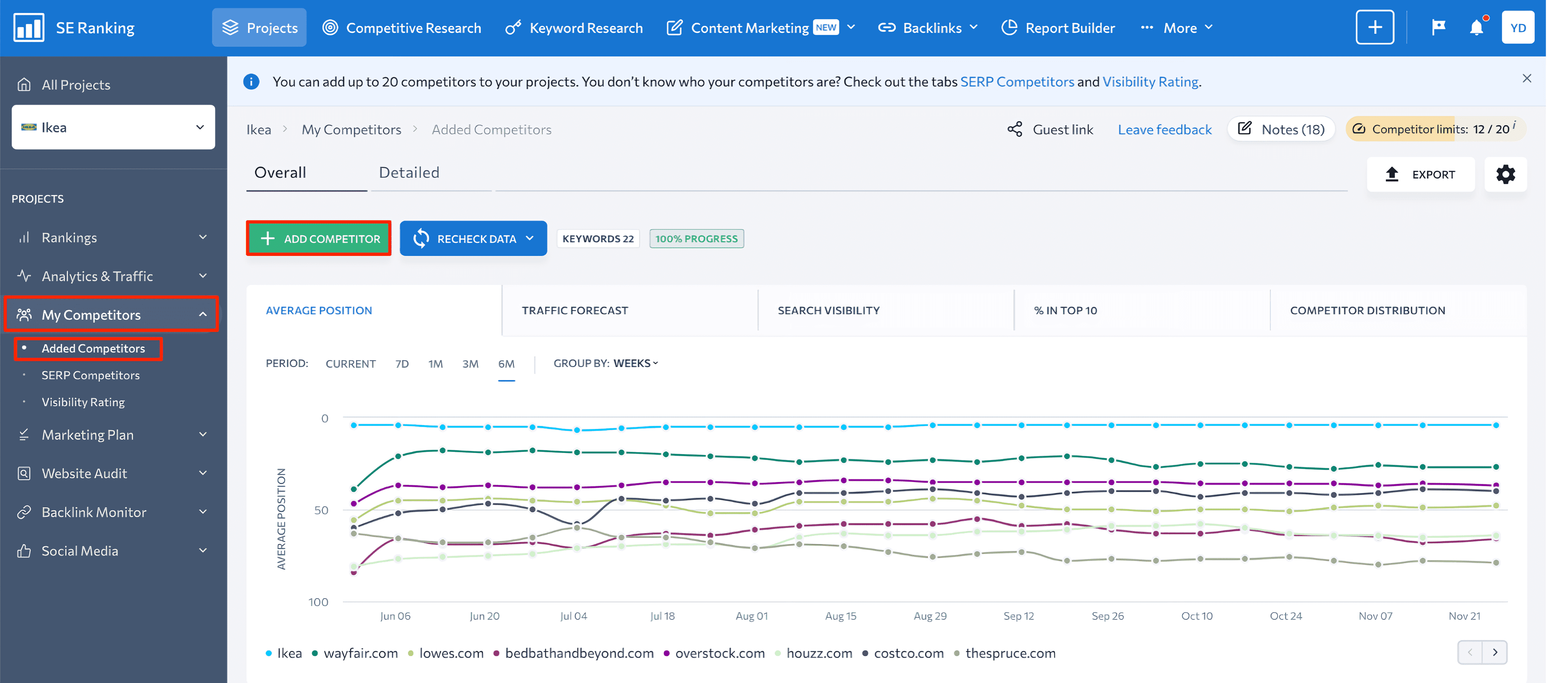
Go to the Added Competitors block if you only want to compare your keyword positions with those of competitors you initially added to the project. You can manually add up to 20 websites to compare your rankings with.
To do this, click on the Add Competitor button at the top of the screen. You can then track the performance of selected competitors and analyze their rankings through metrics like search volume, CPC, competition level, and the number of search results (website URLs) found by a search engine for this keyword in the specified region.
Tracking snippets
SERP feature tracking provides precise ranking data in terms of keywords traffic potential. Assume you have an ecommerce website that ranks first in organic search for the keyword, buy LED lights. Because this keyword has a high search volume, it’s reasonable to expect that it can bring in lots of traffic. But if you track this keyword in GSC, you may see that it’s driving fewer visitors to your site than you expected. This is due to additional SERP features resulting in a loss of traffic to your website. They can take the form of paid results, shopping snippets, people also ask elements, and more.
To find SERP features for your tracked keywords, go to Rankings > Detailed. Then, in the table, look at the SERP features column. If there’s no column like this, you can add it by expanding the Column section right above the table and check-boxing SERP Features.
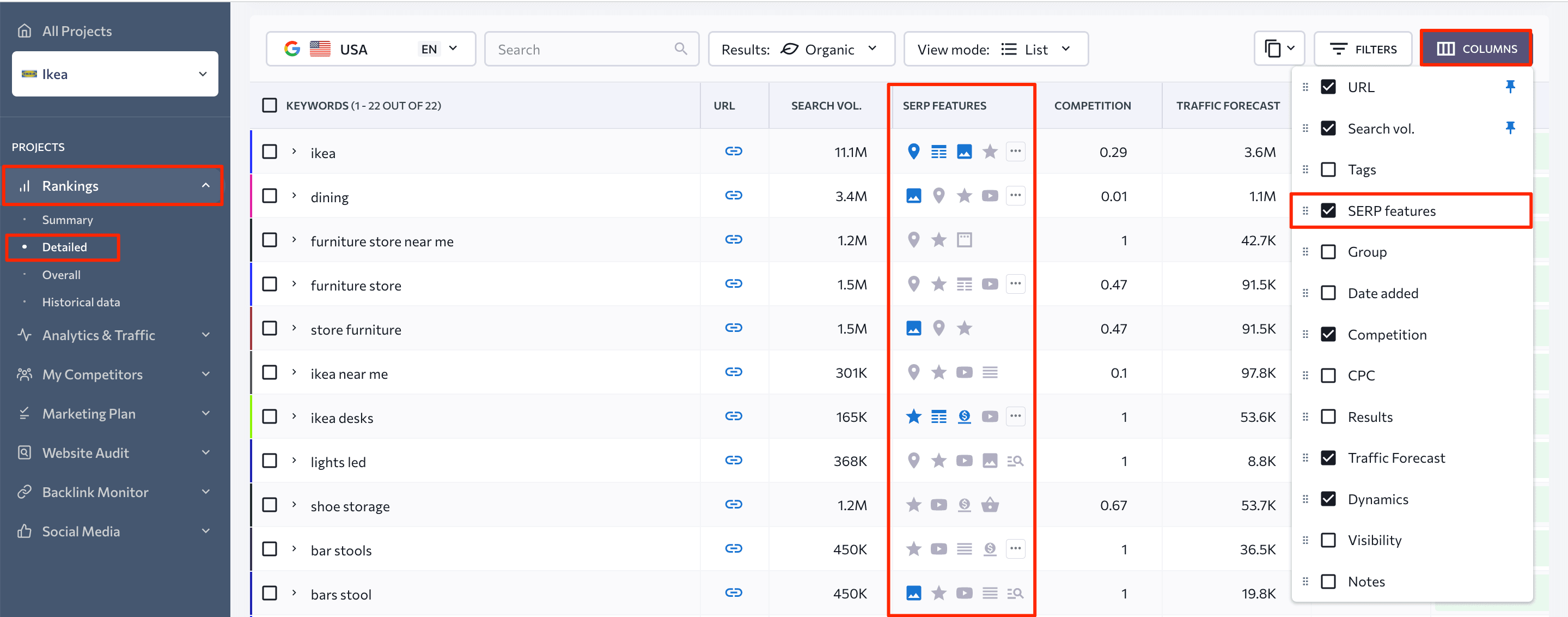
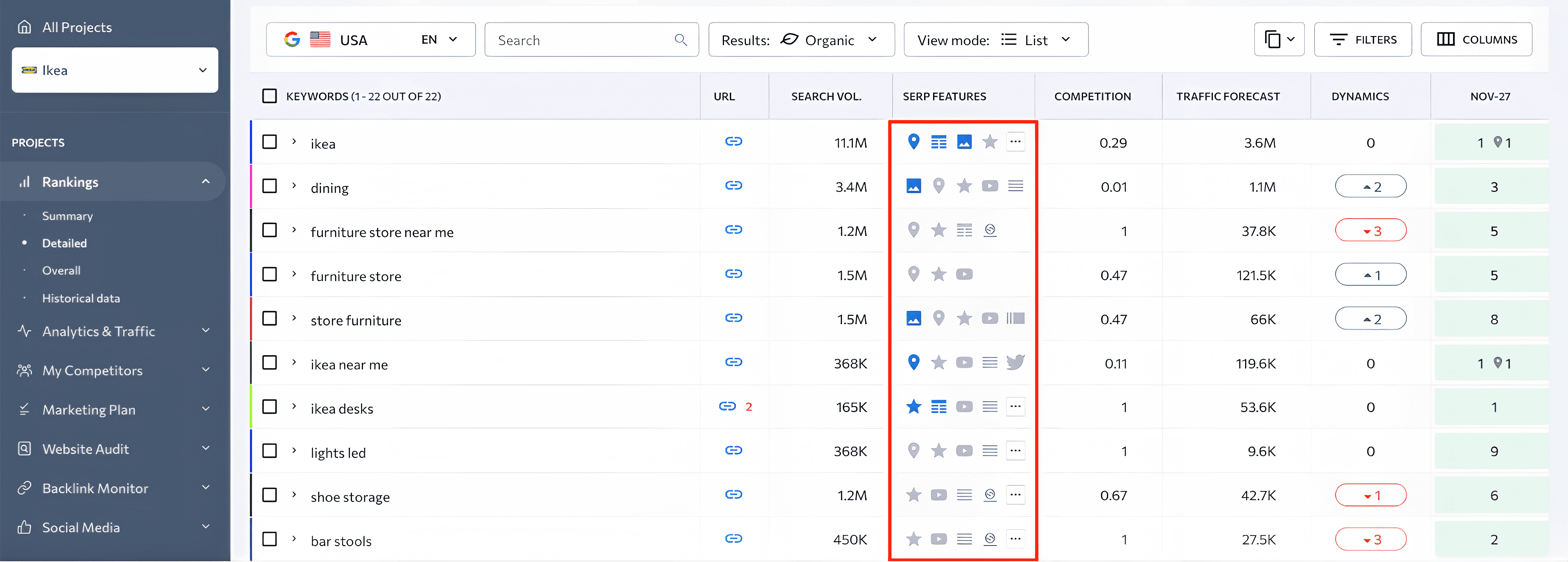
The presence of blue icons indicates that this page has been optimized for a specific SERP feature. The grey icons indicate that this SERP feature is owned by another webpage. If there is no icon at all, then there is no SERP feature for this keyword.
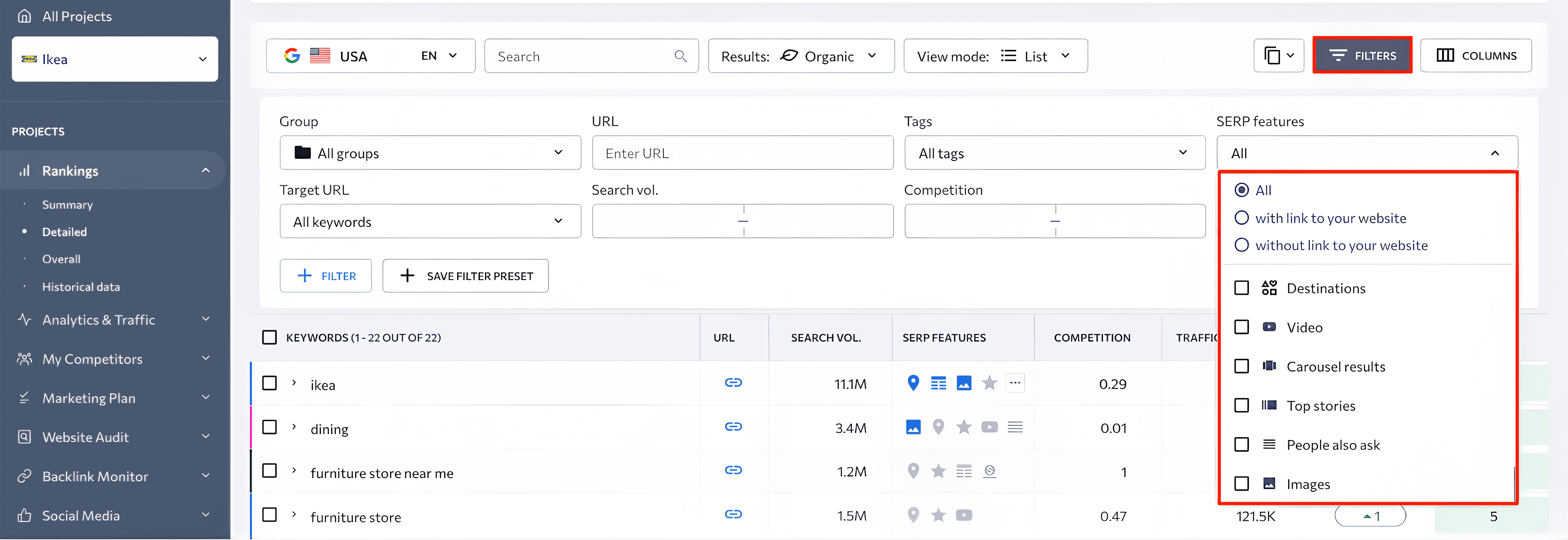
To track all keywords having a specific SERP feature, go to the Filters section and checkbox the type of SERP feature you’re interested in.
To track rich snippet accuracy and attractiveness, go to the Analytics & Traffic section > Snippets. This tab lets you customize settings for a keyword whose snippet you want to view, the **** range, and the search engine. Then, if necessary, you can review the snippet and export data in the XLSX file format.
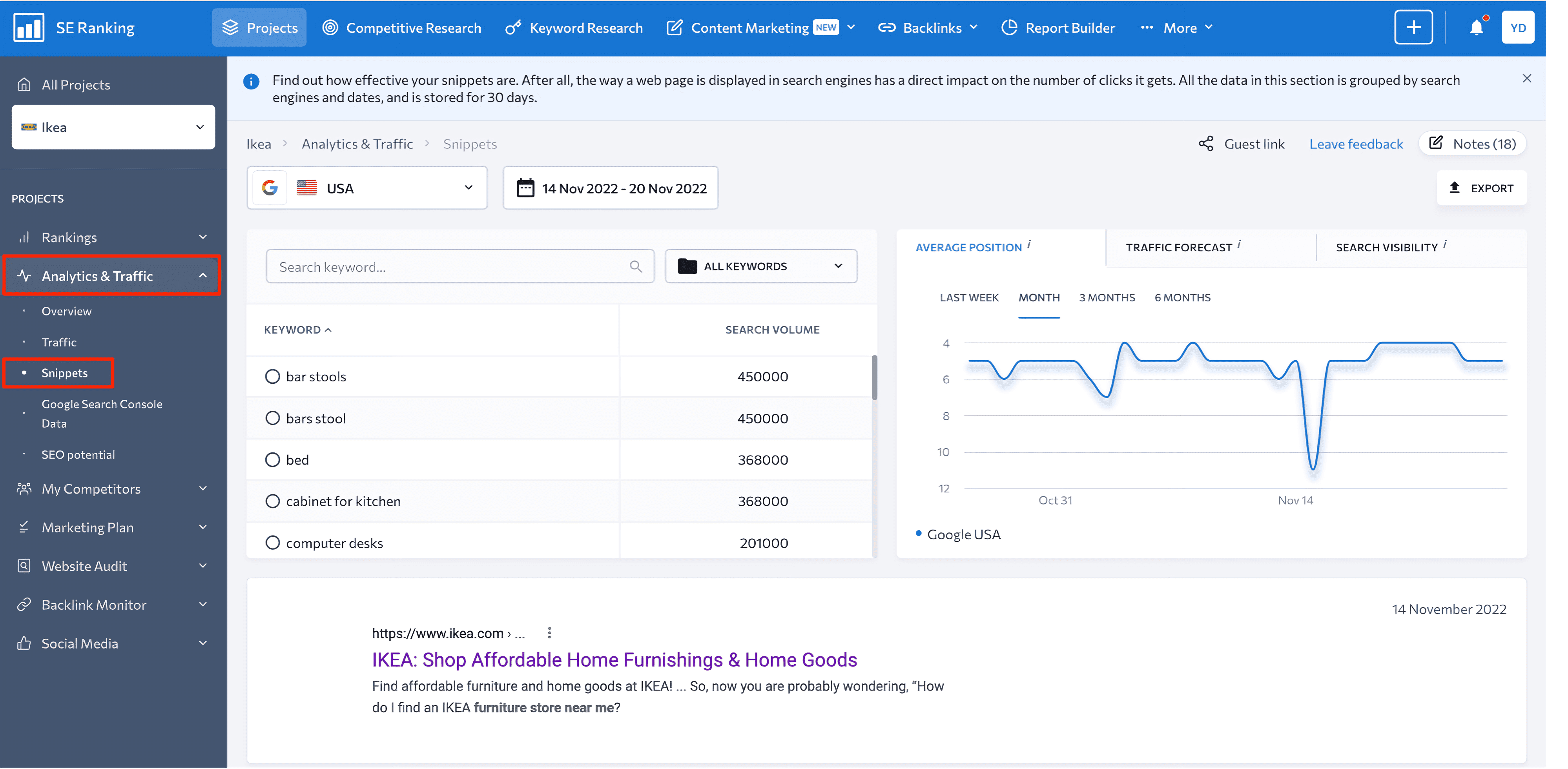
Since the appearance of a page in the SERP has a significant impact on a user’s decision to visit it or pass it by, it is essential to monitor how your website is displayed in search results. The better your URL, title, description, and makeup microdata, the more likely you are to see a significant improvement in CTR.
Tips on how to check your search engine rankings
To make the process of rank tracking as effective as possible, consider the following list of tips:
- Only track in the appropriate location.
Tracking search engine rankings of a website that offers offline educational courses in Germany should be limited to this country only. Otherwise, you risk wasting time and effort on work that won’t bring any results.
- Add and track competitors to gauge the landscape.
Because your website doesn’t exist in a vacuum, you should constantly monitor both direct and SERP competitors in order to understand the landscape. It can specifically assist you in uncovering the keywords they’re targeting, tracking their rankings, learning what type of content they generate, identifying trends in your niche, and much more.
- Monitor rankings after website changes.
For example, following the implementation of on-page SEO practices, it is best to monitor your website’s search engine rankings every few days. Since most of the signals used by search engines to rank web pages come from on-page elements, you’re likely to see a considerable increase or even a drop in rankings.
- Group keywords by clusters.
You can gain a thorough understanding of the type of content to create and how to organize it across all web pages by grouping similar, relevant queries and targeting them as a whole. As a result, using keyword clusters will allow you to improve your search rankings and organic traffic.
- Set a target URL to identify issues such as cannibalization or having other URLs in the SERP.
First and foremost, you must determine what your target URL is (preferably, you should have it documented). After you’ve identified it, compare it to other URLs that appear in SERPs for specific keywords. You can easily accomplish this by using SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker. The “How to Use Rank Tracker” subsection of this article contains detailed instructions on how to track ranking in different search engines and set a target URL to one or more keywords at the same time.
- Connect GSC to easily add keywords.
By connecting GSC to your project in SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker, you can compare GSC data with the keywords in your project and identify new keyword opportunities to rank higher.
- Schedule ranking reports automatically.
To save time and other resources when creating ranking reports manually, you can schedule them automatically. For instance, if you want to receive weekly updates on search engine rankings, you can easily do so with the help of SE Ranking’s Report Builder.
- Connect SE Ranking to Looker Studio to build a professional report.
Finally, link your SE Ranking project to Looker Studio to visualize the organic and paid ranking data. This allows you to display all of the necessary data on a single dashboard, which is very convenient. Here is an example of the report you can create by integrating SE Ranking and Looker Studio.
How to spot if your website has been influenced by an update
Search engine algorithm updates can have a significant impact on website rankings, causing fluctuations that can be difficult to track and understand. However, there are several ways to spot if your website has been influenced by an update. Here are some things to look out for:
Check for sudden ranking drops/increases: One of the most obvious signs that your website has been affected by an algorithm update is a sudden change in rankings, like a sudden spike or drop for several keywords. Monitor your rankings regularly to identify any sudden changes and take appropriate action if needed.
Look for ranking fluctuations: Even if your website’s rankings have not dropped suddenly, it’s possible that an update has affected your site if you notice significant fluctuations. Not all fluctuations are caused by algorithm updates, but you should check your rankings for specific keywords over a period of time to identify any fluctuations that are.
Monitor changes in the top search results: If you notice that the websites ranking at the top have changed for one or more of your target keywords, it could be a sign that an update has occurred. Look for any new or unexpected competitors that may have emerged as a result of the update.
What to do after an algorithm update
The steps you should follow after an algorithm update ultimately depend on the type of update made, but here are some general steps to follow:
- Understand the update: To begin, it’s important to understand the update and any changes that have occurred. To do this, read official statements from the search engine and discuss these statements with other specialists in your niche. The main task to follow here, however, is to analyze your niche to understand what has caused the decrease or growth of top SERP players.
- Evaluate your website: After learning as much as you can about the update, it is important to assess its impact on your website. Your task here is to understand what has boosted your performance or dragged you down during the update, whether that be your content, backlinks, or user metrics.
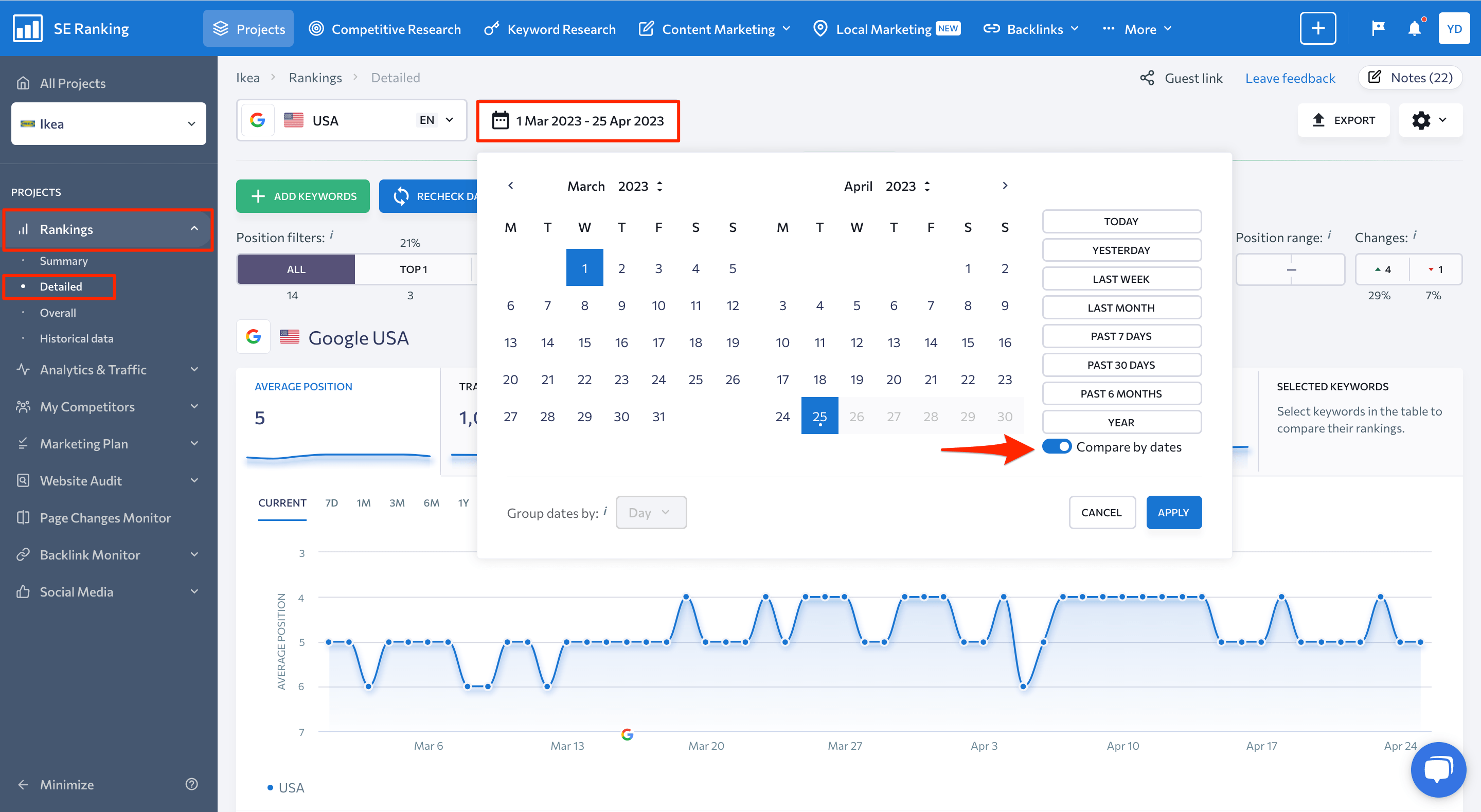
One way to find out if search engine updates have affected your website’s rankings is by using SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker. It’s easy; simply compare your rankings from before and after the release of the update. If you notice a notable shift in your rankings, whether it’s an increase or decline, during the same time frame as the update, chances are your site has been affected by it.
In particular, SE Ranking allows you to compare rankings by ****. For this, simply go to Rankings > Detailed, then click on the timeframe at the top of the screen and switch on the Compare by dates option. This will enable you to choose any specific dates for comparison and evaluate how updates during that period affected your website’s rankings.
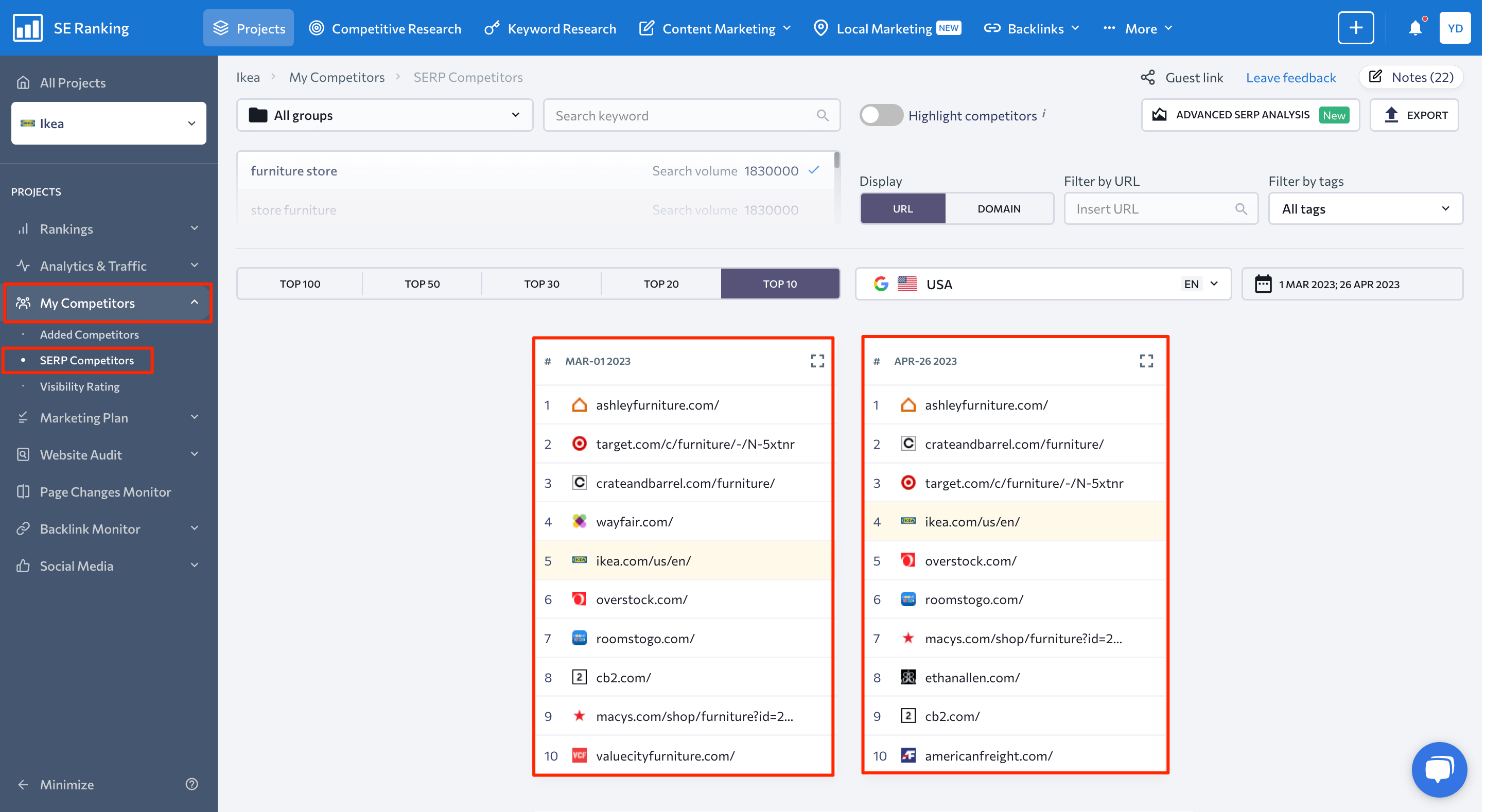
At the same time, the My Competitors > SERP Competitors report helps you understand your organic landscape by showing you how the SERP for your target keywords has changed. You can use this report to quickly spot any competitors that were penalized or rewarded during the update.
- Identify potential issues and take corrective action: To improve your website’s performance after the update, it’s important to look for potential issues. These could include things like lack of content relevancy, poor content structure, or low-quality backlinks. After identifying any issues, address them by quickly taking corrective action.
- Monitor your website: Once you’ve taken corrective action, keep an eye on your website for any improvements in search engine rankings and traffic. If you don’t notice any positive changes within a few weeks, you may have to continue optimizing your website. But more often than not, you’ll just need to wait for the next update to start noticing signs of recovery.
Future trends in search engine rankings
Keeping up with the latest trends in search engine ranking algorithms can be difficult because they are always changing. There are a few emerging trends, however, that are expected to influence the future of search engine rankings.
Personalized search results will become more prevalent
Search engines are already using users’ browsing history, search behavior, and location data to deliver tailored search results that match their interests and preferences better, and they’re continuously refining their algorithms, too. They’re even incorporating more personalized data points to make results pages even more relevant and beneficial for individual users.
Visual content will play a more significant role in SERPs
As visual search technology becomes more prevalent and people show a greater interest in visual content, search engines will introduce more visual elements to their search results pages. These elements will include additional images, videos, and even augmented reality experiences. This will give users more dynamic and informative search results and may also assist businesses in distinguishing themselves from their rivals.
SERPs will become more integrated with platforms and new technologies
As chatbots like Bing Chat and Google’s Bard continue to improve their ability to understand and answer users’ queries, the future of search engine rankings will likely focus on delivering highly relevant and accurate results. This will involve the integration of data from multiple sources, which could potentially lead to a decrease in traffic for some websites that primarily serve to answer informational user intent.
Search engines might also use results from social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or TikTok to create more personalized and interactive results. This will make it easier and quicker for users to find information and help businesses engage better with their customers.
Increased focus on local search
Local search has become more prominent as of late, and in the future, search engines will likely prioritize local search results even further, especially for businesses that operate within a specific area. For example, they might include the use of augmented reality or virtual reality technology to provide more immersive local search experiences.
Expansion of featured snippets
Search engines use featured snippets to quickly answer user queries. As their popularity increases, search engines may eventually expand the use of featured snippets to include more complex queries and different types of content, such as video or audio snippets.
Final takeaway
Monitoring SERP rankings is by far the most effective way to determine whether or not your site performance has improved over time and which SEO aspects require more attention. You can do this manually, with webmaster tools, or with position tracking tools such as SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker.
While the first two options have numerous limitations, tracking SERP positions with advanced SEO tools is very convenient and saves a great deal of time. Assume you want to find your website ranking in Google, Bing, Yahoo, or all search engines at once. Rather than clicking through dozens of different tabs to gather the necessary data, you can use SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker, which presents all the information in a single platform in simple, easy-to-understand tables and graphs.
What are your thoughts on tracking search engine rankings? Which option do you prefer, and why? Please tell us what you think in the comments section below.
