What are keywords in SEO, and where should we put them?
The information in this article will help you understand:
- What page elements should have keywords.
- How to craft the Title and Description properly so that the page gets more traffic.
- Why page headings are so important and how to use them.
- What text should be on the site pages.
Let’s get started right now!
Why Keywords Matter?
Keywords are the foundation of search engine optimization. They bridge what people are searching for and the content you’re offering on your website.
Here’s why keywords matter:
- User intent. Keywords reflect the intentions and needs of your target audience.

- Content relevance. They help search engines understand what your content is about.
- Ranking opportunity. Proper keyword usage can improve your chances of ranking higher in search results.
- Traffic generation. The right keywords can drive targeted traffic to your website.
Keyword research is essential in making your website more visible and accessible.
Keywords Usage Rules
Several general rules apply to the distribution of search queries. Let’s review them shortly:
- The site structure should have separate pages with different intents (commercial, informational, etc.). The same applies to the site’s keyword list, which should cover the various search intents users may have.
- One page can be optimized for multiple related search queries. One group of similar queries would correspond to one page — a cluster. However, one page can be created for keywords with the same intent. If you mix different keywords on one page, search robots can fail to rank it for diluting content relevant to the query.
- Content should read naturally for users, not be stuffed with keywords. Search engines now prioritize high-quality, relevant content over keyword repetition. Modern algorithms consider the context, not just exact keyword matches.
- It is essential to optimize keyword density in the text—the frequency or percentage of times a keyword appears in a piece of content relative to the total number of words. Excessive keyword use (known as “keyword stuffing”) can result in search engine penalties.
- Using synonyms and related terms is often more effective than repeating the same keyword.
- Avoid keyword cannibalization, e.g., don’t target the same primary keyword across multiple pages.
- All products featured on the online store’s pages should align with a single primary purpose. The intent of a query such as “buy a refrigerator” should match all related products in the category, for example.
10 Places to Insert Keywords on Your Website Pages
You should include keywords in these primary elements of your site:
1.Page content. Search queries should be present in every text.
2.Metatags and title. These tags should contain medium and high-volume queries. They often form a snippet, but since it depends more on the user’s query, there may be other options for the text that Google considers more relevant.
Serpstat Audit helps you find and fill in empty alt attributes quickly.
5.Ads. Keywords must also appear in paid search results (Google Ads).
6.URL. Including a keyword in the domain name will help Google better understand the site’s content.
7.Anchor text. Remember to include keywords in an anchor list for both internal and external links.
8.Body text. Add primary keywords, synonyms, and variations in the first and last paragraphs of the content, as well as in the conclusions of articles.
9.Post category. You can improve searchability with categories that group related posts using primary keywords.
10.
How to Use Keywords in SEO
Each of the search terms use-cases listed above has caveats that are important to be aware of.
Meta Tags
The H1 and Description tags are among the first elements a search robot checks on a page.
Basic description requirements:
- The optimal tag length is from 120 to 160 characters. The description must be fully visible to users in search results without being cut off.
- The description should attract attention, be succinct, and clearly reflect the content of the page. This tag can be compared to a sales text or an ad.
- It must contain keywords at the beginning. These should be high-volume or middle-volume queries.
- It’s advisable to use a CTA at the end of the description. This may be a call to buy, go to the site, or order.
- The description tag must be unique for each page. At the same time, the structure of the tags and the wording in them may be similar.
- The Title and Description tags must be different.
You can check for errors in writing tags using the Serpstat Audit. It will show all problems along with recommendations for resolving them.
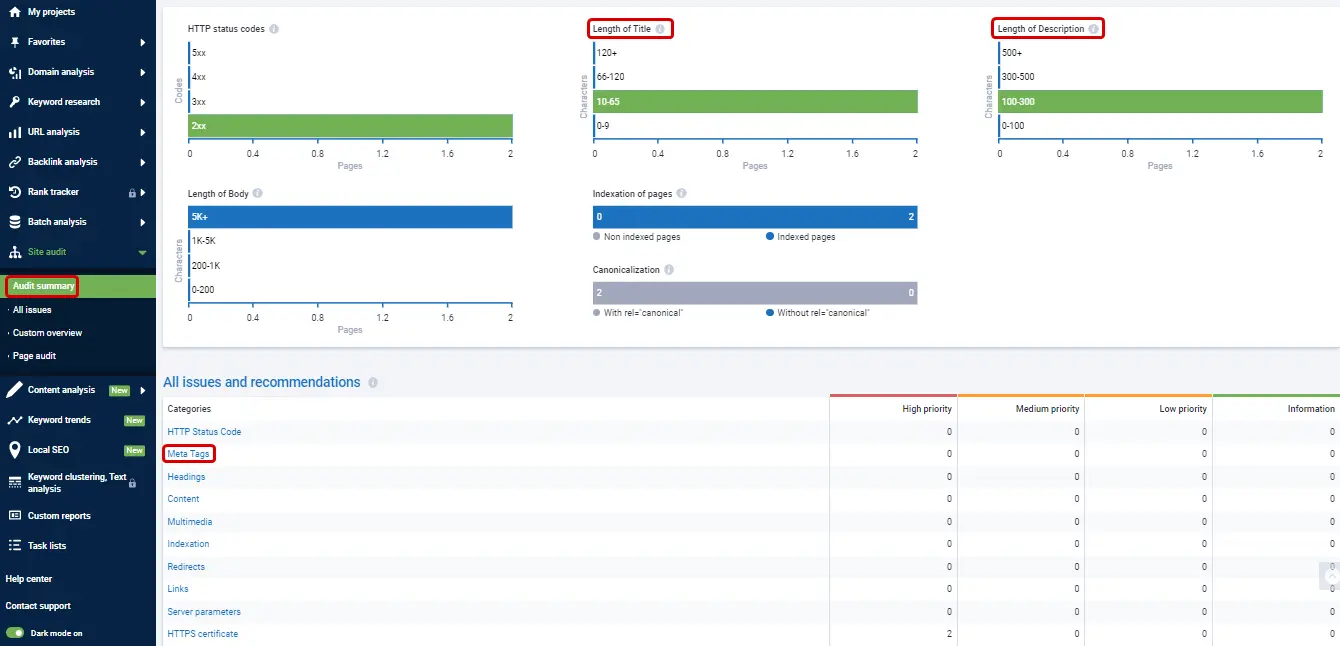
Pay attention to how H1, Description, and Title are built for sites from your industry’s top 5 search results for seed keywords. The Serpstat SEO Checker will help with this:
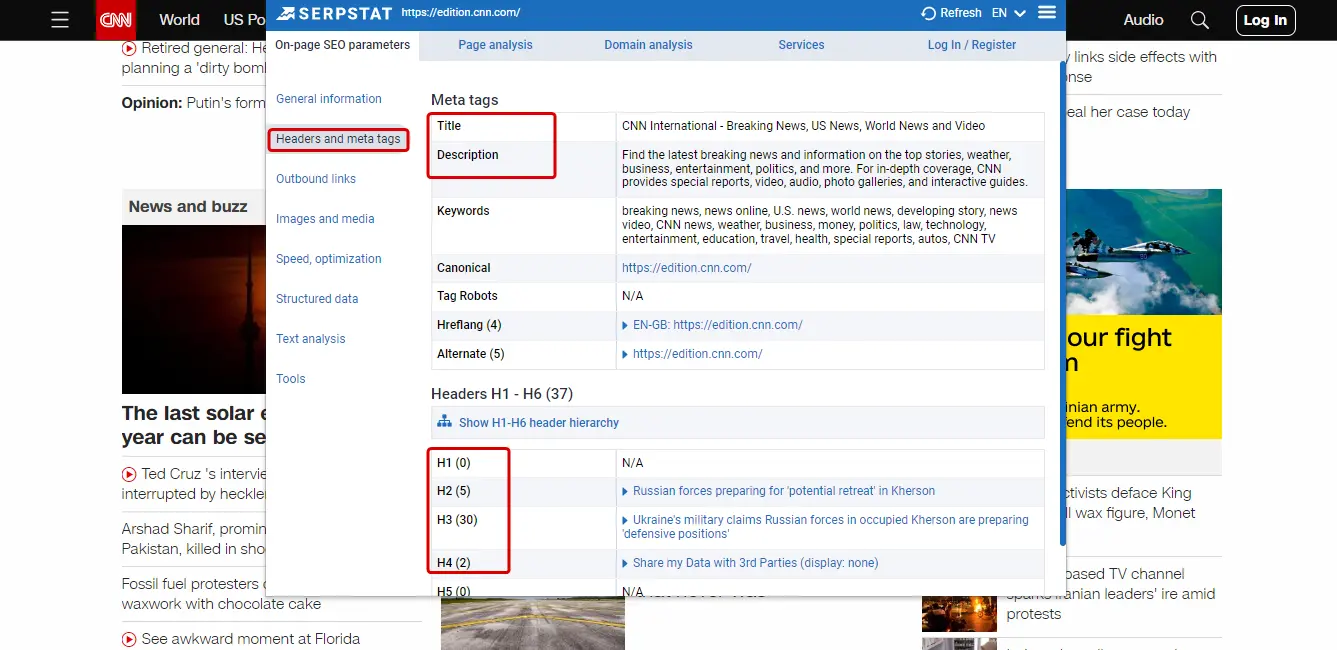
So you don’t have to look for tags in the page’s code.
Title
The Title is an HTML tag that describes the content of the page, determines the ranking of the page in the search, and affects the click-through rate in the search results. There are several basic requirements to follow:
- The primary keyword should appear at the beginning of the title. You can add low-volume and middle-volume keywords but modify them if needed so that the text in the title remains well-read.
- The tag must be unique for each page. It is important that the pages of a site do not compete with each other. Pay special attention to titles on product pages that usually differ slightly.
- The title should be meaningful and readable and clearly reflect the content of the page.
- The length of the title should be between 60 – 80 characters.
- The title tag must be placed inside the HTML element.
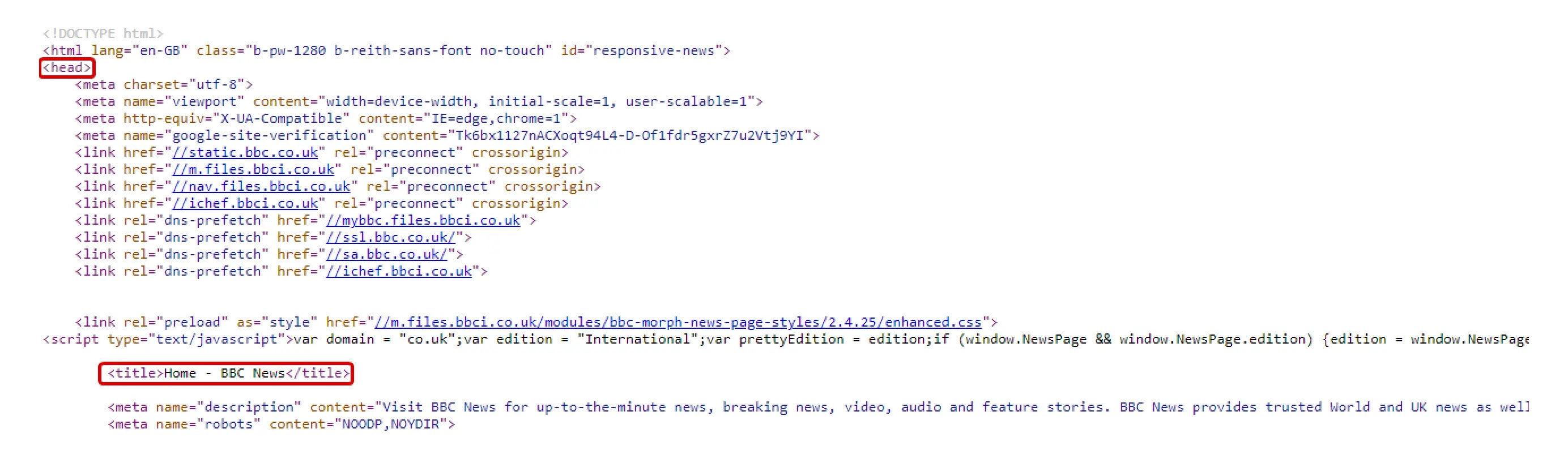
Serpstat tools will help you automate title generation to save time.
Meta Keywords
The Meta Keyword is a tag that highlights the main search terms for the page. According to official Google statements, the tag has not been ranked since 2009, but some site owners and SEOs are filling the tag even now. Some are counting on the fact that Google’s policy will change, while others believe that there is a minimal chance that the keyword tag will affect rankings. Keep in mind that by filling out this tag, you will tell your competitors what queries you are promoting each page for 🙂
Headings H1-H6
In HTML, headings are defined by <h> </h> tags, with six levels available. The main heading of the page is marked by the <h> </h> tag.
Headings are often the first thing users notice on a page. Most visitors scan headings to decide whether to stick around or bounce. Search engines also pay close attention to headings to figure out which search queries a page should rank for.
Key points about H1-H6:
1.Your H1 should differ from the page title but stay relevant to the content.
2.Keep headings under 60 characters for better readability.
3.Use only one H1 per page.
4.Include a high-volume keyword in your main heading.
Remember, a great page heading should be both concise and clear. While it’s important to know writing techniques, don’t try to cram them all into one heading.
To check if your headings are structured correctly, use Serpstat’s site audit tool. You can also view the heading hierarchy using the Serpstat SEO Checker plugin.
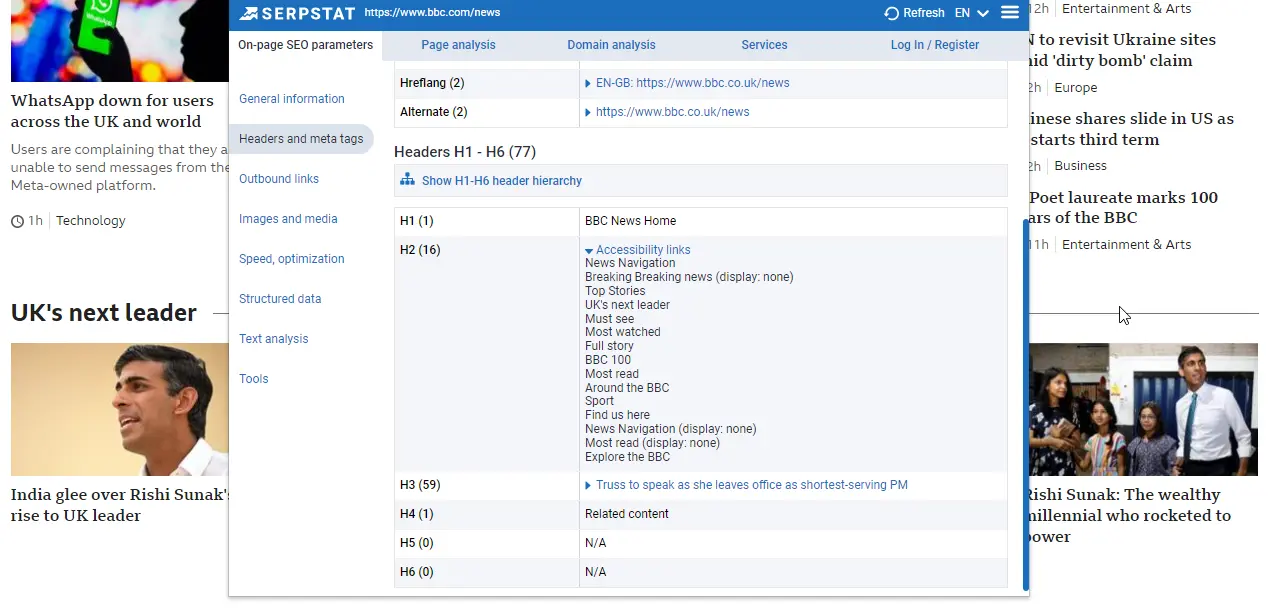
Rules for other headings:
1.Maintain a clear hierarchy. For example, in a listicle of useful services, all service names should be the same level (h2 or h3).
2.Avoid links in headings, as they can hurt your site’s ranking.
3.Ensure headings are informative and easily understood at a glance.
4.Skip the emojis and special characters in headings — they can complicate things for search engines.
5.Don’t go overboard with subheadings. There’s no hard rule about how many you should use per 1,000 words, but remember that a large number of h2-h6 tags is only justified in long-form content on complex topics.
Image Optimization
To boost your site’s performance in search results through images, you need to properly set up the Title and Alt attributes for all photos and images.
The Title attribute provides extra info about the image for the user, tooltip that pops up when they hover over the image.
The Alt attribute is the alternative text that shows up if the browser can’t display the image. Google uses alt text, along with computer vision algorithms and page content, to figure out what an image is about.
By optimizing images and their attributes, you can drive more traffic to your site from image search results.
General guidelines for image tags:
- Keep Alt text under 125 characters.
- Make sure the text in tags is meaningful and informative.
- Use several keywords in each tag.
FAQ Blocks
Keywords can also be placed into lists and FAQ blocks.
Pro tip: If you’re using keywords in list items, make each item detailed. This improves the text quality for both readers and search engines.
An FAQ can be a content block on a page or a separate page on your site with a list of common questions and concise answers.
Why are FAQ blocks great for Google optimization?
- They help you cover a topic more thoroughly and give extra info to site visitors.
- FAQ blocks can boost traffic and help you reach your target audience more effectively.
- They improve user experience. By providing complete, useful answers about a product or service, users can avoid confusion and complications.
You can create an FAQ using data from Serpstat’s Search Questions tool.
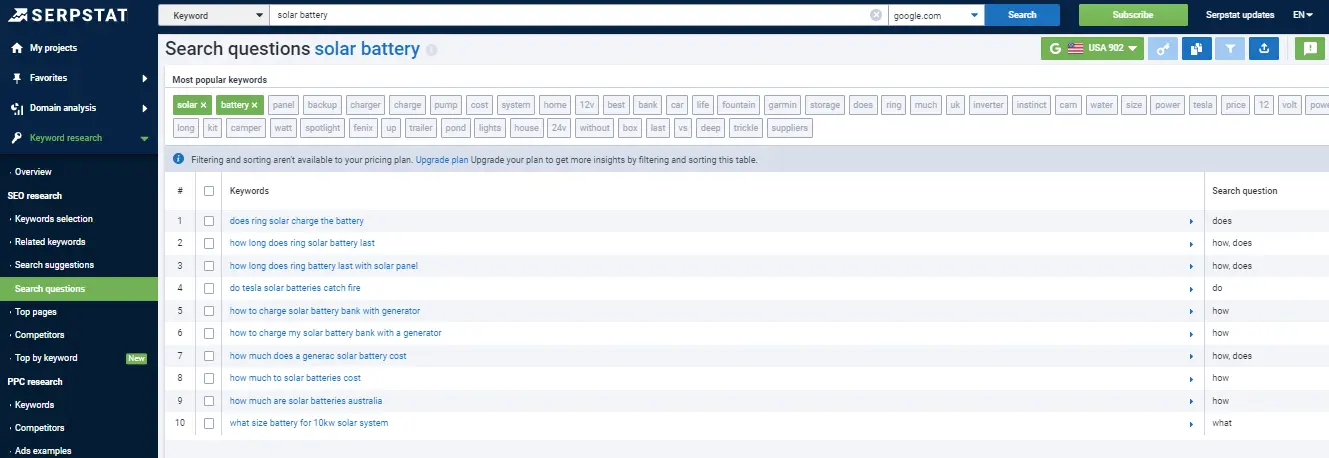
Depending on your topic and page type, pick two or more questions for your FAQ block. We don’t recommend making it too long.
Page Text Requirements
Your page’s traffic, conversion rate, and other metrics depend on the quality of your content. What makes page keywords good?
1.Usefulness for your target audience. Good content matches user intent. For example, if someone wants to know how to get a driver’s license, a solid article should cover all the steps, course duration, required documents, and exam process. If you skip important info, your page probably won’t make it to the top of Google’s search results.
2.Mobile-friendly text. Your content’s format and structure should look good on all devices, from smartphones to desktop monitors.
3.Use headings to structure your text. This helps users quickly find what they need.
4.Use lists. They’re great for highlighting key points or describing step-by-step processes.
5.Keep paragraphs short. Aim for no more than five lines per paragraph. It makes the text easier to read.
6.Avoid long sentences. Try to keep sentences under 15-18 words.
7.Also, make sure your text follows the guidelines in your content brief.
8.Include each keyword from your content brief at least once. This signals to search engines that your page should rank for those queries.
9.Use search queries directly, indirectly (with different word forms), or diluted (by adding other words to the query).
Creating high-quality, unique content isn’t easy, but there have been many changes in this area. We now have great AI tools, a game-changer in content marketing. AI tools help you spot popular topics, gather trends and news for your audience, and optimize titles, meta tags, and page content. Serpstat uses AI in its content analysis tools as well.
Negative Keywords and Clichés
Negative keywords are phrases you can cut from your text without losing meaning (note, this term also has other meanings for PPC). Some negative keywords examples:
- “It has long been known that”
- “All in all”
- “Worth saying”
- “For sure”
You can’t completely eliminate these but try to reduce negative keywords and clichés as much as possible. It’ll make your text easier for visitors to understand.
Clichés are overused words or phrases in a particular industry. They’re often two or three words that could be replaced with just one. Common clichés include:
- “Flexible approach”
- “Team of professionals”
- “Unique techniques”
These phrases are vague and raise more questions than they answer. It’s best to ditch clichés in your text.
Wrapping Up
We’ve explored the ins and outs of using keywords in your content. Remember, it’s crucial to include search queries in several page elements:
- • Title and description tags
- H1-H6 headings
- Title and alt attributes for images
- The main body text
Use search queries wisely, always prioritizing usefulness, information, and quality for your visitors. And don’t forget to keep an eye on your content’s SEO parameters throughout the process.
