-
Interface and features:
In this aspect, SearchGPT isn’t quite a rival to Google yet, as its functionality is fairly simple. However, it does have some useful features, like summarizing information and conversational AI, which are the main benefits of their primary product: ChatGPT. You can get answers directly without having to visit other websites, and if you need more details, you can easily ask SearchGPT for additional information.
-
Quality of search results:
The information is much more limited (including the variation of sources listed in its answer)—on average 15 results vs. more than 100 results in Google, and they are less diverse in terms of sources (SearchGPT has only 57.04% unique domains in its search results). It lacks additional elements like maps, videos, or different useful SERP features that Google has.
-
SERP by search intent:
SearchGPT is best for informational queries because it delivers detailed, high-quality summaries from various sources. In commercial queries, SearchGPT provides useful lists and comparisons. However, for navigational, local, and transactional queries, SearchGPT does not perform as well but seems to be in the process of improving.
-
Similarity to Bing and Google:
SearchGPT is 73% similar to Bing and 46% to Google in search results, with top domains like openai.com, amazon.com, and forbes.com appearing across all three search engines. Domains listed in SearchGPT often get significant traffic from Google. Meanwhile, 26% of domains in SearchGPT receive no traffic from Google, suggesting new visibility opportunities.
-
Media presence:
About 32% of the results for all the queries were media sources. For media-related queries, the presence of media in the SERPs exceeded 75%. SearchGPT still needs improvement with providing the latest news. We found some news was quite old, including content from a month ago and even from 2023.
Since its boom in 2022, AI has become a part of almost every aspect of our digital lives. These days, generating quality texts and images doesn’t surprise anyone. But what if we told you that OpenAI might be giving Google a run for its money?
In July 2024, OpenAI launched a prototype of its search engine, SearchGPT. It’s currently in its testing phase and available only to 10,000 users. Luckily, one member from the SE Ranking team was fortunate enough to get access to SearchGPT, so we decided to conduct a study that compared the interface, functionality, and quality of results between SearchGPT and Google.
Data we used for research:
- Keywords: 36 keywords with different intent (informational, navigational, commercial, transactional and local) and length. The number of keywords is small because each of SearchGPT’s SERP results for these keywords were researched manually.
- Locations for SERP and URL analysis: New York and London
- Location for domain analysis: United States
- Analysis period: August 19-23, 2024
- Tools for domain & SERP analysis: Competitive Research API for bulk domain analysis, plus a SERP Competitors feature for bulk SERP analysis with the SE Ranking platform
So, does SearchGPT have the potential to come close to Google’s power and popularity? Spoiler: it just might! Especially with the recent biggest lawsuit affecting Google’s reputation and confirming its monopoly status. Google may need to accelerate its shift from a search engine to an answer engine or combine both approaches to stay competitive in the GenAI industry, where it is not currently the leader.
Check out the full details of our study below. Let’s dive in!
What is SearchGPT?
SearchGPT is a temporary prototype of new AI search features from OpenAI. It combines a generative AI with the latest web data to deliver contextually relevant and up-to-**** answers.
As mentioned earlier, SearchGPT was launched with limited access for a select group of users. This gradual rollout helps OpenAI gather real-world feedback and refine the system. Once it’s satisfied with the results, OpenAI plans to integrate SearchGPT directly into the ChatGPT interface.
While many things will likely change before the full release, let’s look at what OpenAI has accomplished so far.
SearchGPT’s main features and interface
SearchGPT introduces some helpful features, but is it enough to challenge the King of Search (aka Google)? Let’s find out.
To use SearchGPT, you need to use a browser extension. Once installed, type your query into the address bar and search Enter. SearchGPT will then display its results. A new search within SearchGPT looks like this:
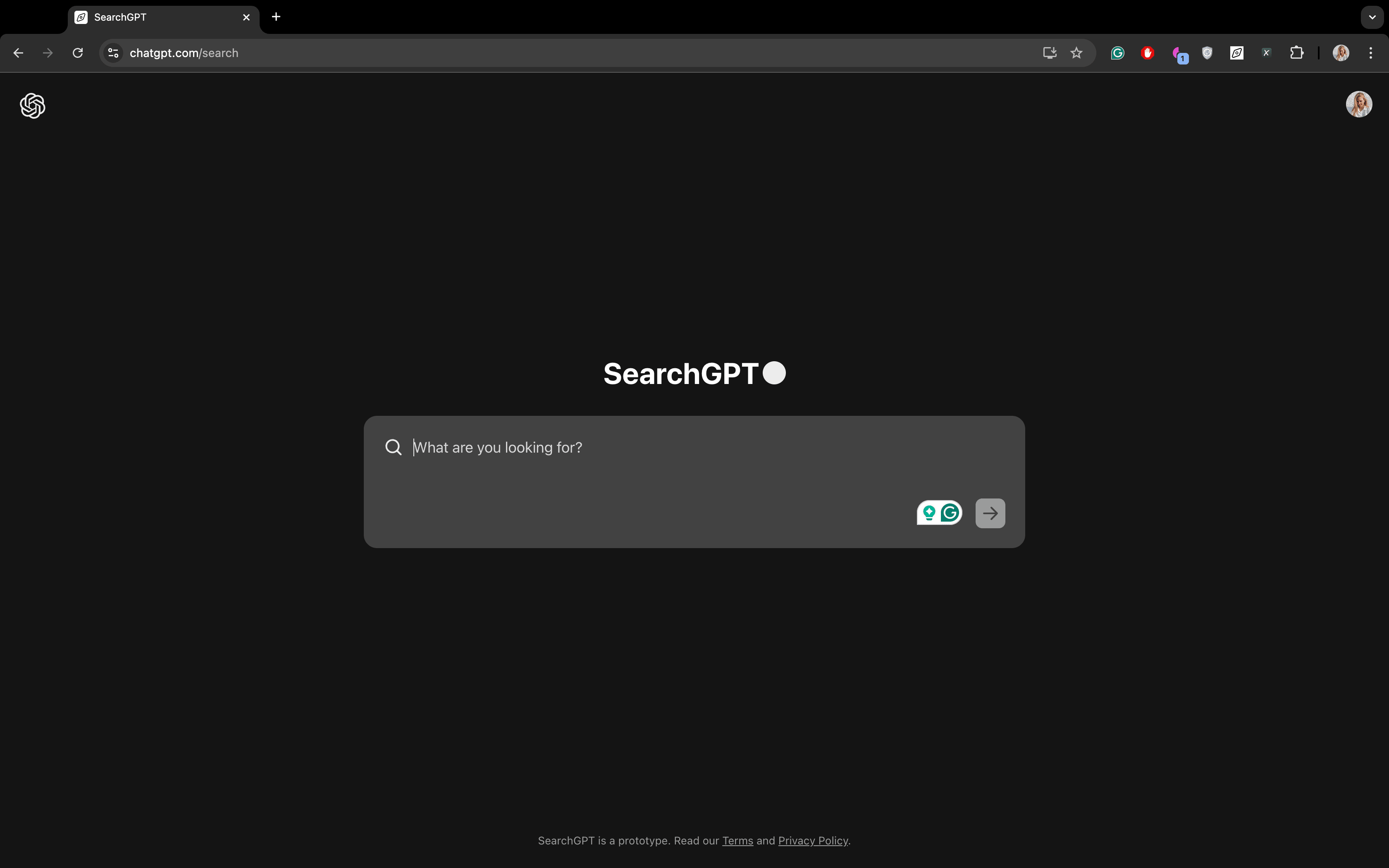
The SearchGPT homepage is super minimalist. It comprises a search box and a search button and a mostly white or black background. This keeps the focus on the search query and helps with avoiding distractions. You’ll also get suggestions, much like Google, but with one key difference: SearchGPT provides one suggestion per query instead of a list.
Here’s what the search results look like:
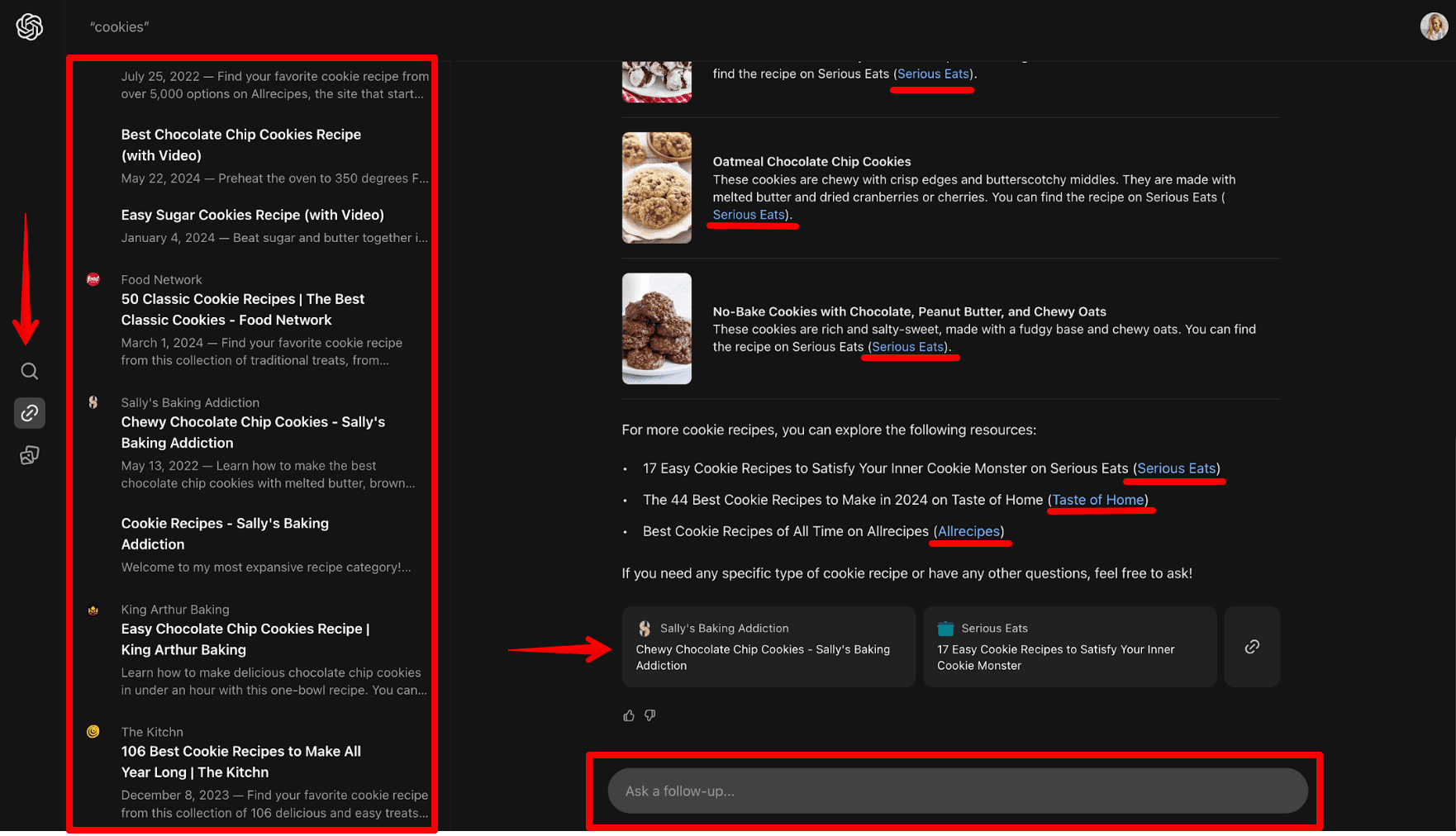
- On the right-hand side, you’ll see an AI-generated response with a list of products with descriptions, step-by-step instructions, tips, or short guides. This depends on the query. Beneath the answer, there’s usually a carousel with links to resources. Some generated answers contain links directly in the text. Here, you can also ask follow-up questions.
- On the left-hand side, you’ll see the SERP with links (by pressing the Links button) or images (by pressing the Images button). There’s also a button to start a new search.
The SERP itself looks like this:
The snippets look similar to what you’d find on Google. They show the domain name with a logo, followed by an H1 or title (though rarely) that often includes the brand name separated by a dash. Below that, you’ll see the publication **** and a short description, usually pulled from the page content rather than a website meta description.
What are the main features of SearchGPT?
- Summarization. SearchGPT shifts the focus from presenting a list of pages (where users need to click to find the answer) to delivering a generated answer immediately, drawing from various authoritative sources. This approach is similar to what we see when Google shows AI Overviews, which also offer answers to topics based on various sources. However, the difference is that SearchGPT integrates generated answers as a central feature in its search engine and displays them for every query. Google treats these summaries as an additional SERP feature, often compared to a featured snippet, and is still testing its implementation. Moreover, AI Overviews (AIOs) don’t appear that often. According to new research by SE Ranking (to be published soon), only 12.47% of searches triggered AI Overviews.
- Conversational AI. Like ChatGPT, SearchGPT lets you refine queries with follow-up questions for better results. In Google, each query stands alone with no connection to the next. SearchGPT, on the other hand, aims to keep context across multiple queries, making your search experience more connected and seamless. This feature was once available in the previous version of AIOs, but it has since disappeared.
SearchGPT’s quality of search results and SERP links
Undoubtedly, the summarization feature is a big plus for SearchGPT. But let’s look closer at the SERP and links provided by this new search engine.
- The first thing you’ll notice is that the list of URLs in the SERP panel is short. SearchGPT typically displays an average of around 13 URLs, with a minimum of 10 and a maximum of 18. This is significantly fewer than Google’s index, which can provide hundreds of results. However, the number of links in the generated response is roughly the same as in the AIOs. We discuss this in more detail in this section.
- Second, SearchGPT provides a uniform SERP with no additional elements. Unlike in Google, you won’t see SERP features, videos and maps. In addition, while SearchGPT provides images for each query, they are fewer in number and of lower quality than Google.
- Third, SearchGPT tends to repeat the same domains in its SERPs for a single query. For example, during our research, we frequently saw domains like 50isnotold.com, investopedia.com, and hubspot.com appearing multiple times. For the query “How to build a successful business,” the domain investopedia.com appears three times in the SERP. Google, on the other hand, usually avoids showing the same domain more than once in its top 10 results (except for some top domains and forums, probably since HCU 2023). According to our calculations, SearchGPT has only 57.04% unique domains in its search results (meaning over 40% are repeated two or more times for a single query). In comparison, Google has a domain uniqueness rate of 71.85%, while Bing’s is 61.11%.
- The search results did not include any links to Reddit or Quora. This is similar to Google AIOs, where, according to our recent research, there are also no links to these forums.
- SearchGPT gives less weight to Wikipedia compared to Google: Wikipedia appears in 2.7% of SearchGPT results, whereas it is the most popular site on Google. According to SE Ranking, its monthly traffic reaches 2.7 billion in the US and 751 million in the UK. Additionally, Wikipedia ranks 6th on SE Ranking’s list of the top 20 domains that appear most frequently in both the top 10 organic search results and AIOs simultaneously.
- We also noticed that some links in the generated answers aren’t present in the SERP. This means the top search results and the sources SearchGPT uses to generate its main response might not always align. In contrast, on Google, most keywords (about 72%) trigger AIOs with 1-4 links that match the top 10 organic search results.
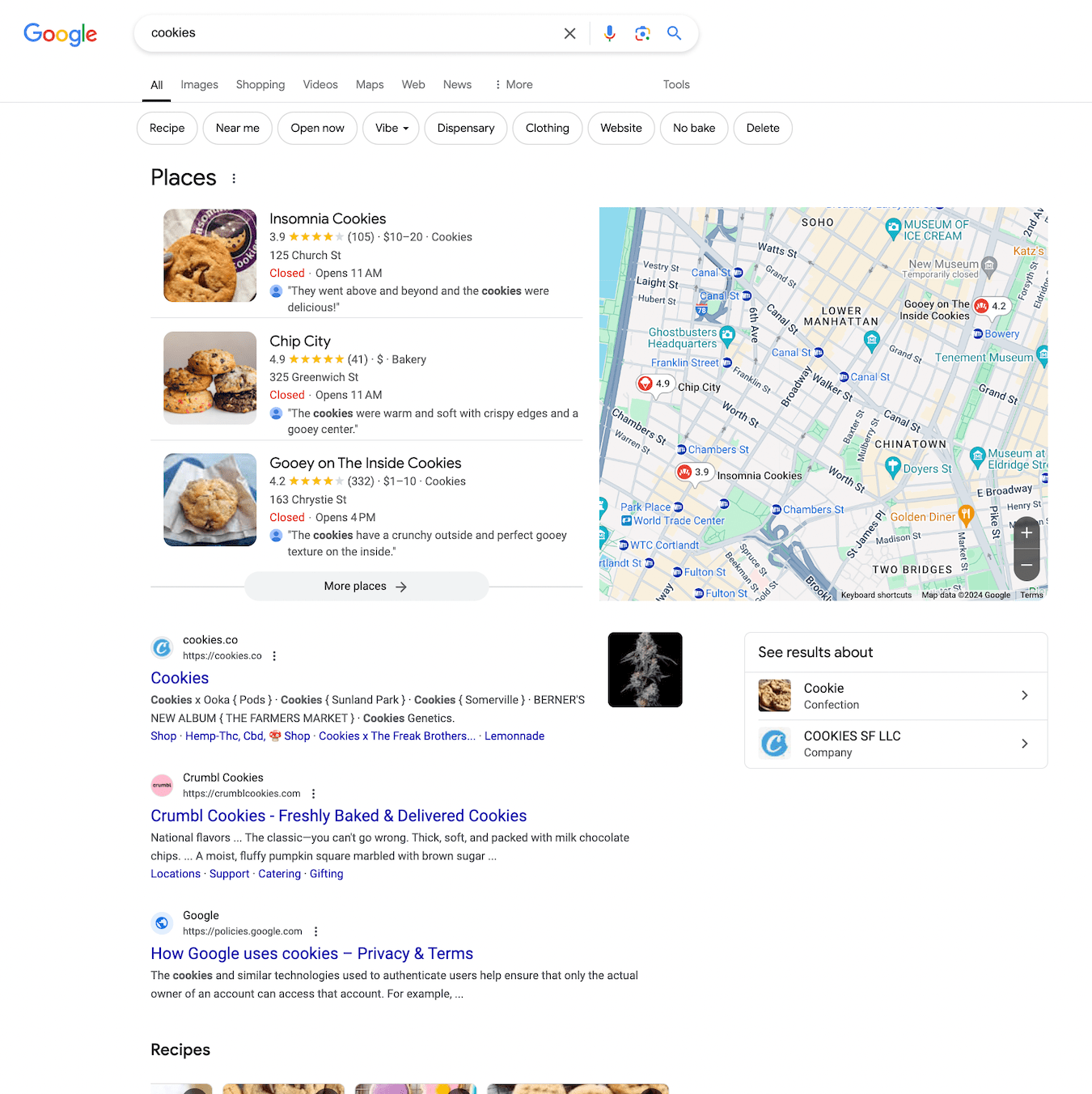
- SearchGPT seems to grasp different meanings of ambiguous words but doesn’t offer results for these interpretations. It also doesn’t always show brands as effectively as Google. For instance, Google shows brands like https://cookies.co/ for “cookies,” while SearchGPT only shows the planet when searching for “Mars,” missing the brand altogether. We’ll dive into these cases in more detail in the next section.
- Some search results are quite old. For example, for the queries “cookies”, “how to build a successful business” and “sunglasses under $50,” we noticed articles from 2018-2019. However, we also see older domains linked in AIOs.
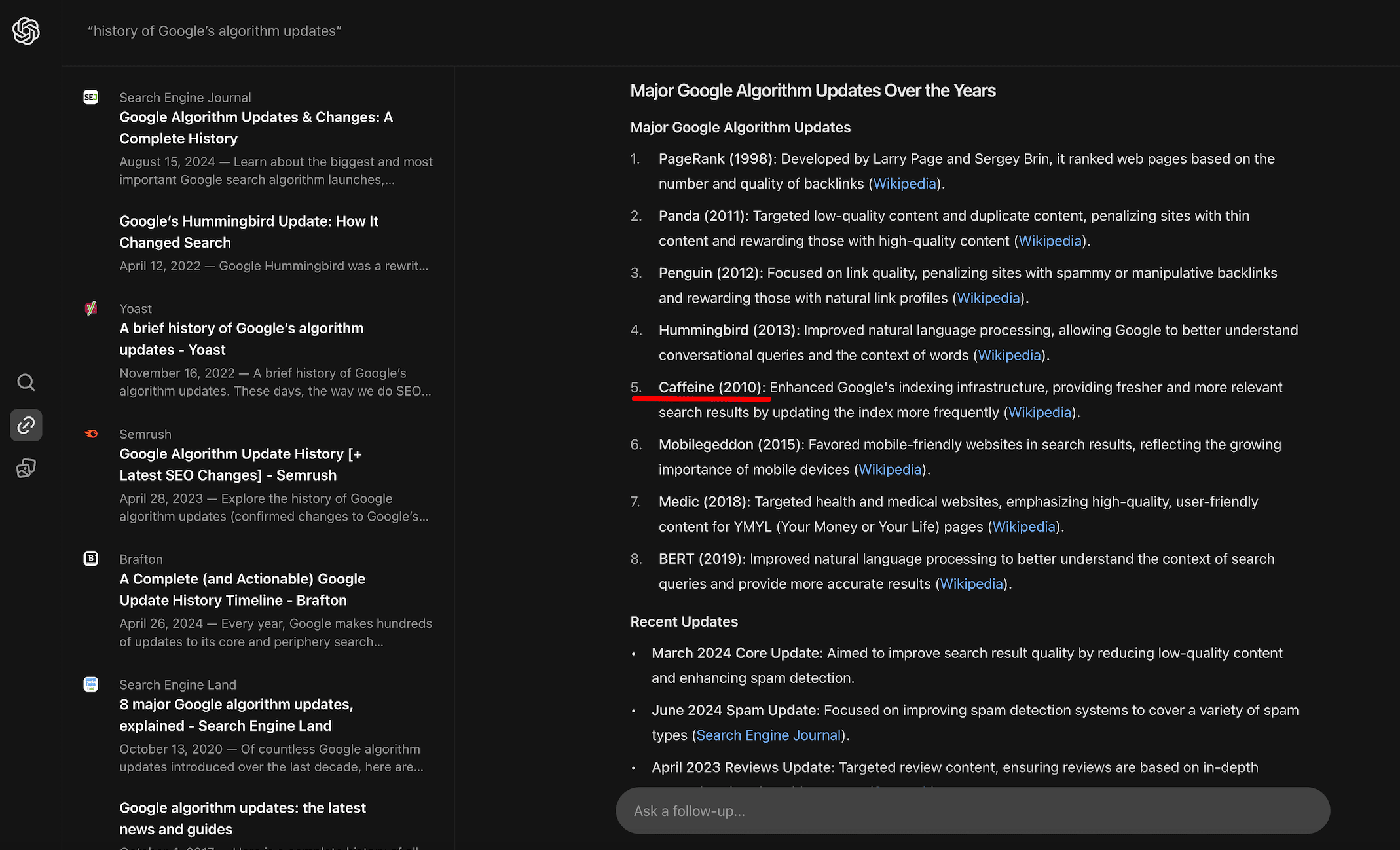
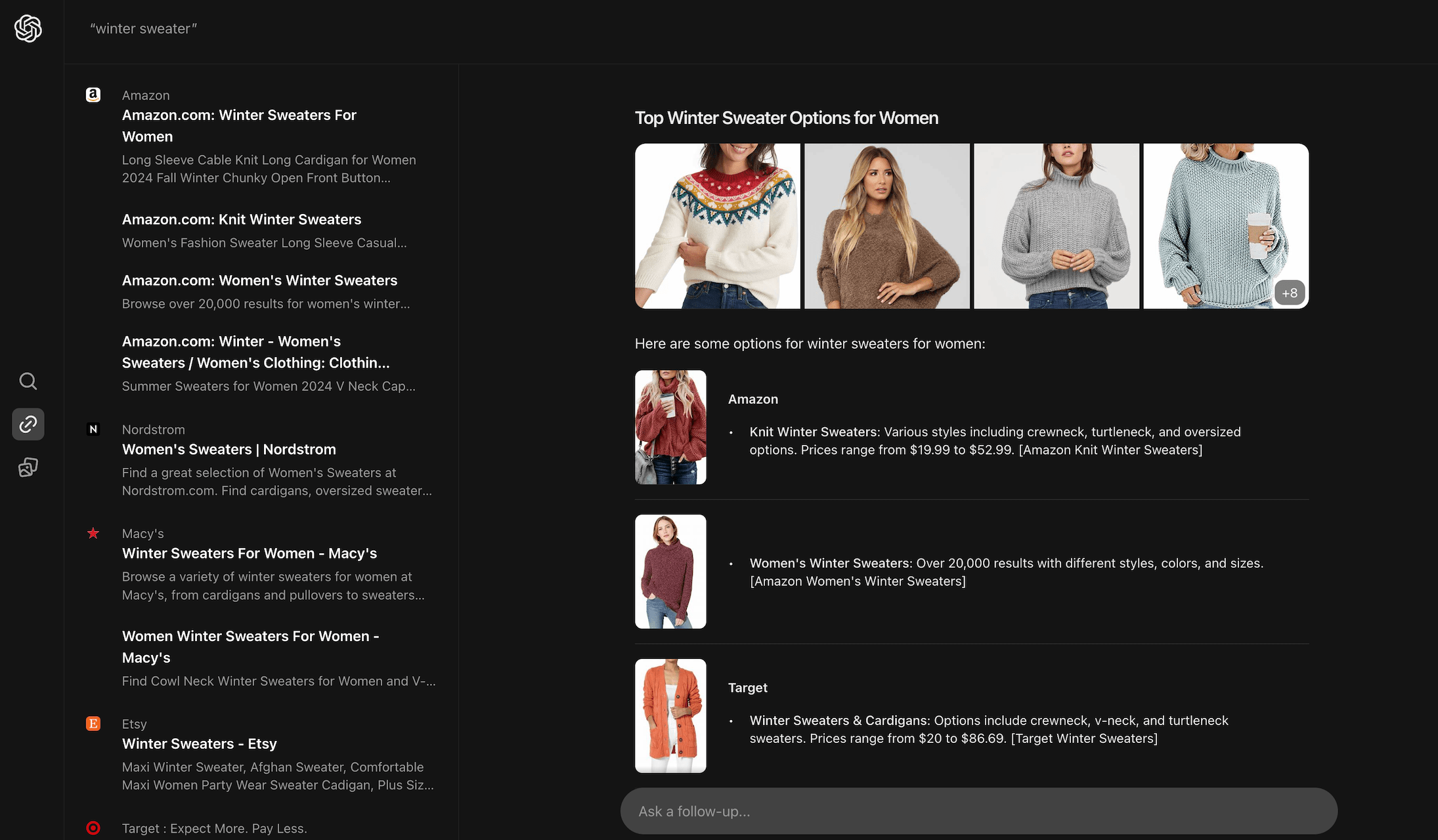
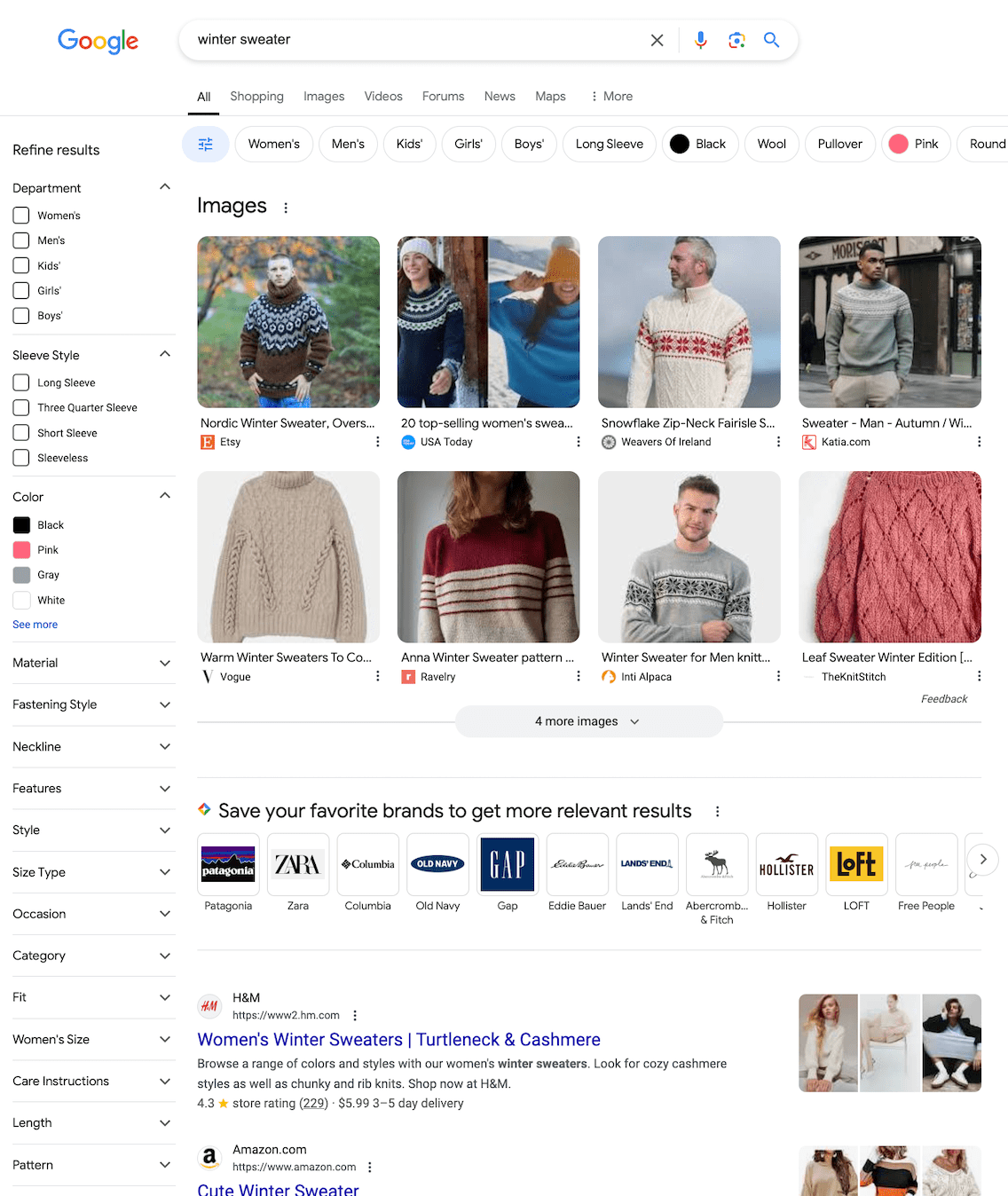
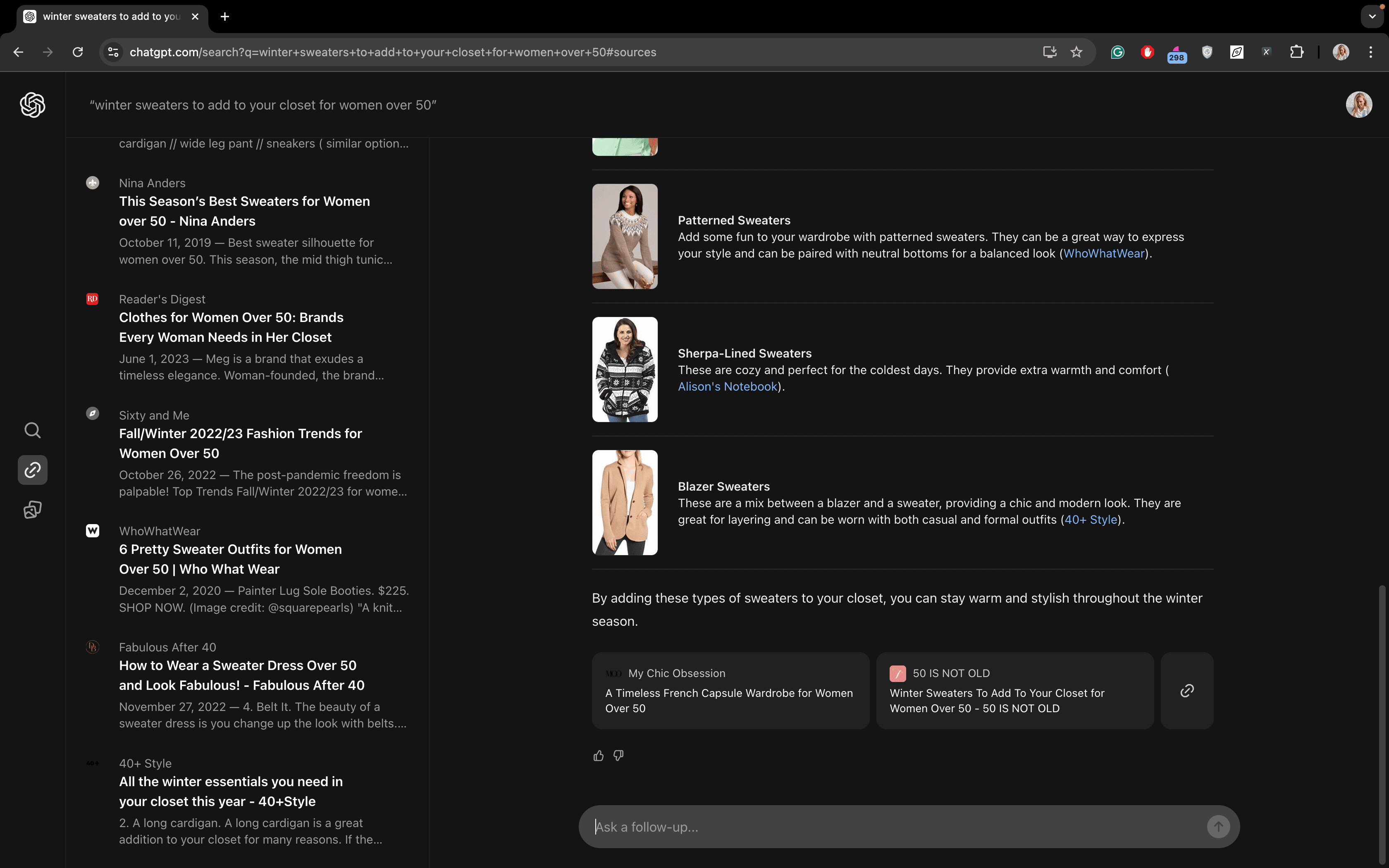
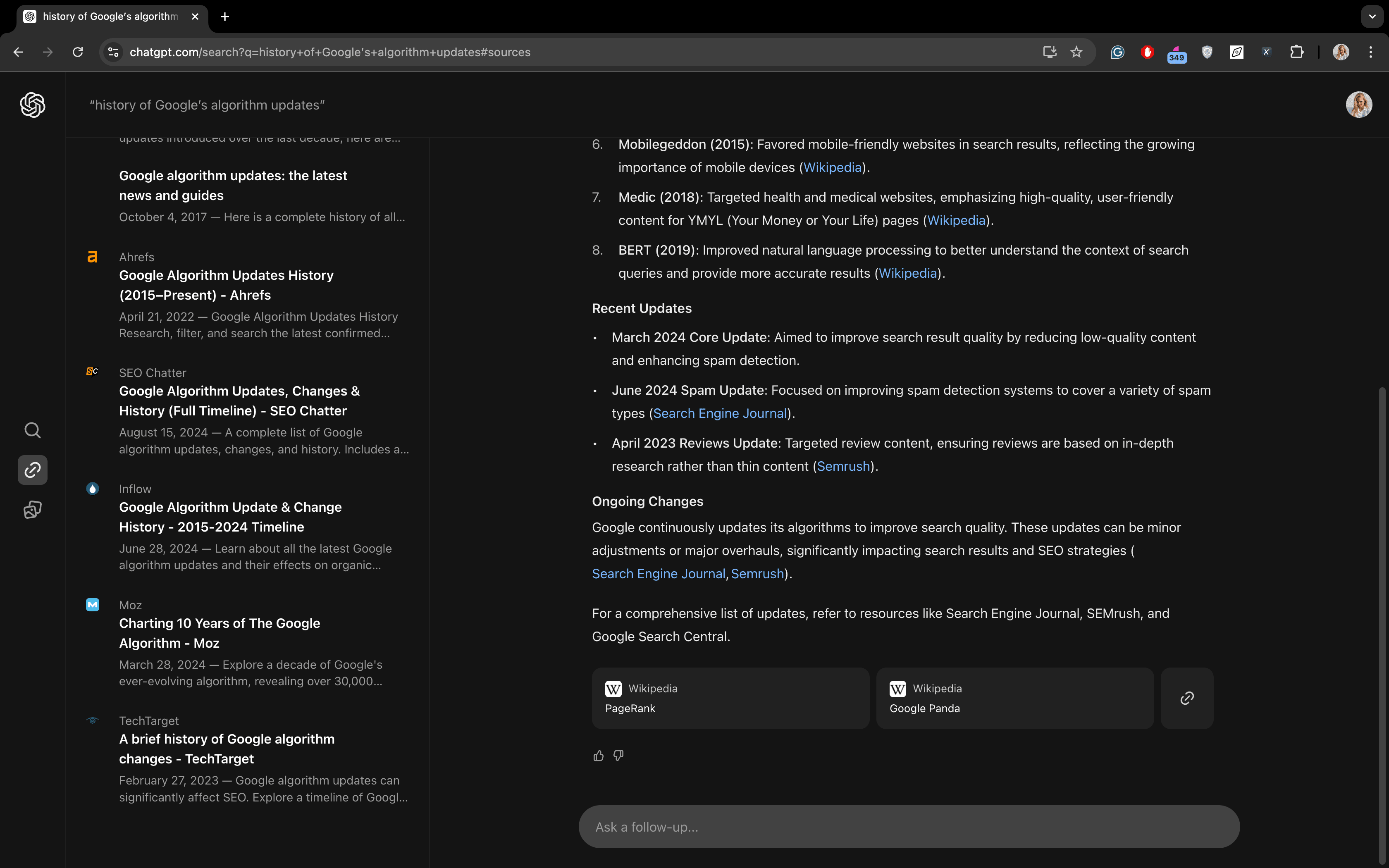
- Some generated answers could use improvement. For instance, the “history of Google’s algorithm updates” isn’t presented in chronological order, which can be confusing. Additionally, you might get AI-generated text for navigational queries, like information about Facebook when you just want to log in or details about Amazon Prime when you simply want to purchase on the site. This isn’t always helpful. Also, when you click on an image, it doesn’t immediately take you to the website where the image is located. For example, if you search for “winter sweater,” SearchGPT displays images of sweaters, but you need to click on an image first, and then, when the image opens fully, click on the link below to go directly to the page to buy one.
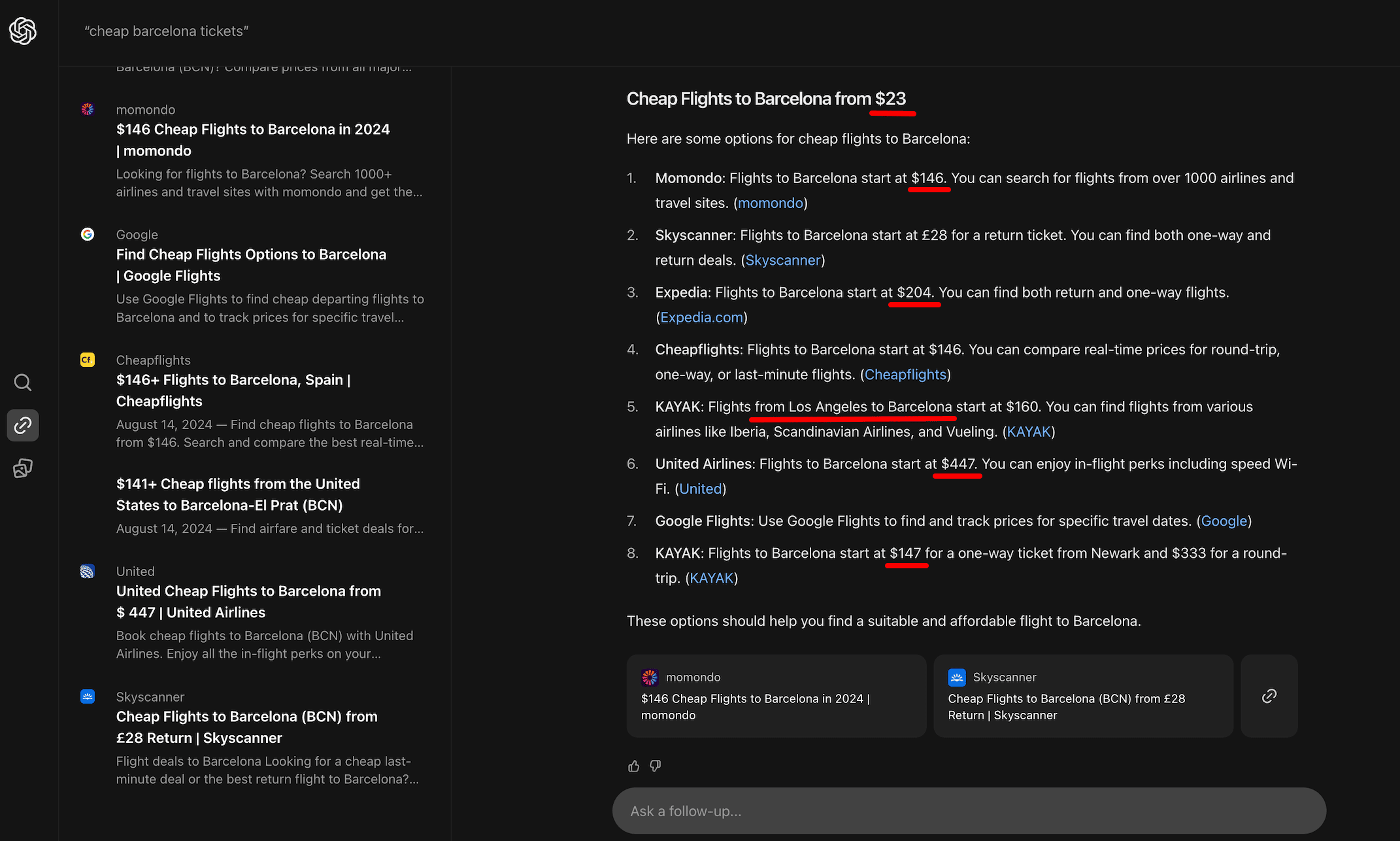
- We found many similarities when comparing location-based results (we analyzed London vs. New York). SearchGPT appears to perform better for US markets. The SERP similarity between London and New York is about 75%, with both featuring many Amazon and news sites. But for many commercial queries in London, prices were displayed in dollars rather than pounds. Plus, some searches return fewer results than in the USA, and SearchGPT provided inaccurate results for some queries. For instance, for the query “cheap barcelona tickets,” it provided links to flights from the USA, even though the search was made from London.
Overall, we monitored the SERPs over a several-day period. While there were slight changes, the results largely remained consistent, showing one new domain or one additional link from the same domain on average.
Keyword-based search analysis of SearchGPT: Exploring search intents
To better understand how SearchGPT performs, we evaluated its results for specific keywords, examining how it handles both short and long-tail keywords. We also observed the different keyword types by intent: informational, commercial, transactional, navigational, and local. Let’s take a look.
Short-tail vs. long-tail keywords
Our goal here is to look out for any difference in search results between short-tail (one to two words) and long-tail keywords (prompt-like long queries). We will also explore what SearchGPT shows for keywords with multiple meanings and intents. Let’s look at the keyword results.
Short-tail keywords
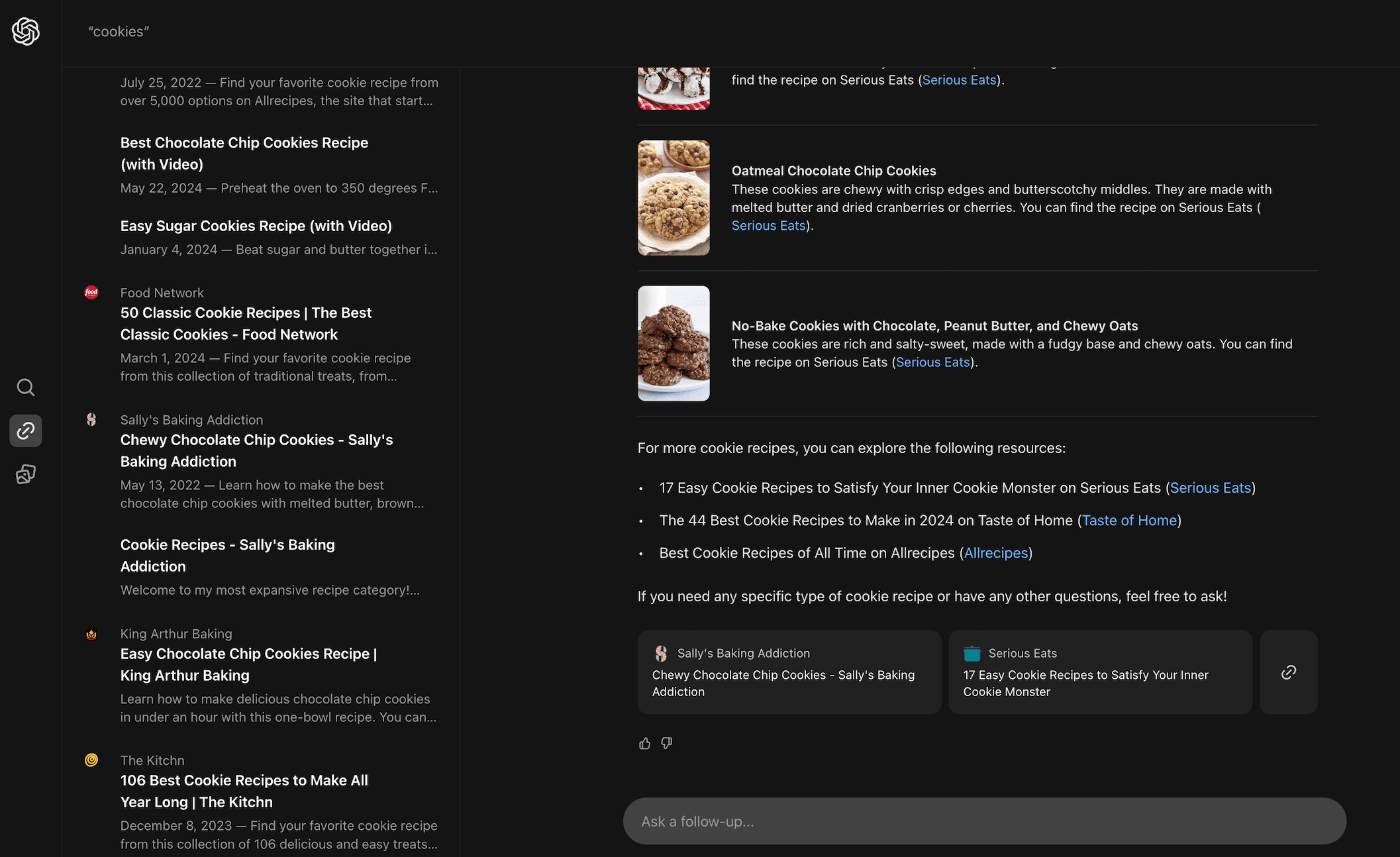
For the keyword “cookies,” we see various cookie recipes. Only one link in the results points to a cookie policy on a website.
Meanwhile, Google enhances its search results for this brief query by offering a refinement option—you can specify whether you meant a clothing brand, recipes, website cookies, and so on. Overall, Google’s search results for this keyword are much more diverse than those from SearchGPT. Google presents the clothing brand’s website, locations to try cookies in New York, and website cookies.
For the query “AI tool,” both SearchGPT and Google tend to provide links to various AI tools or top lists.
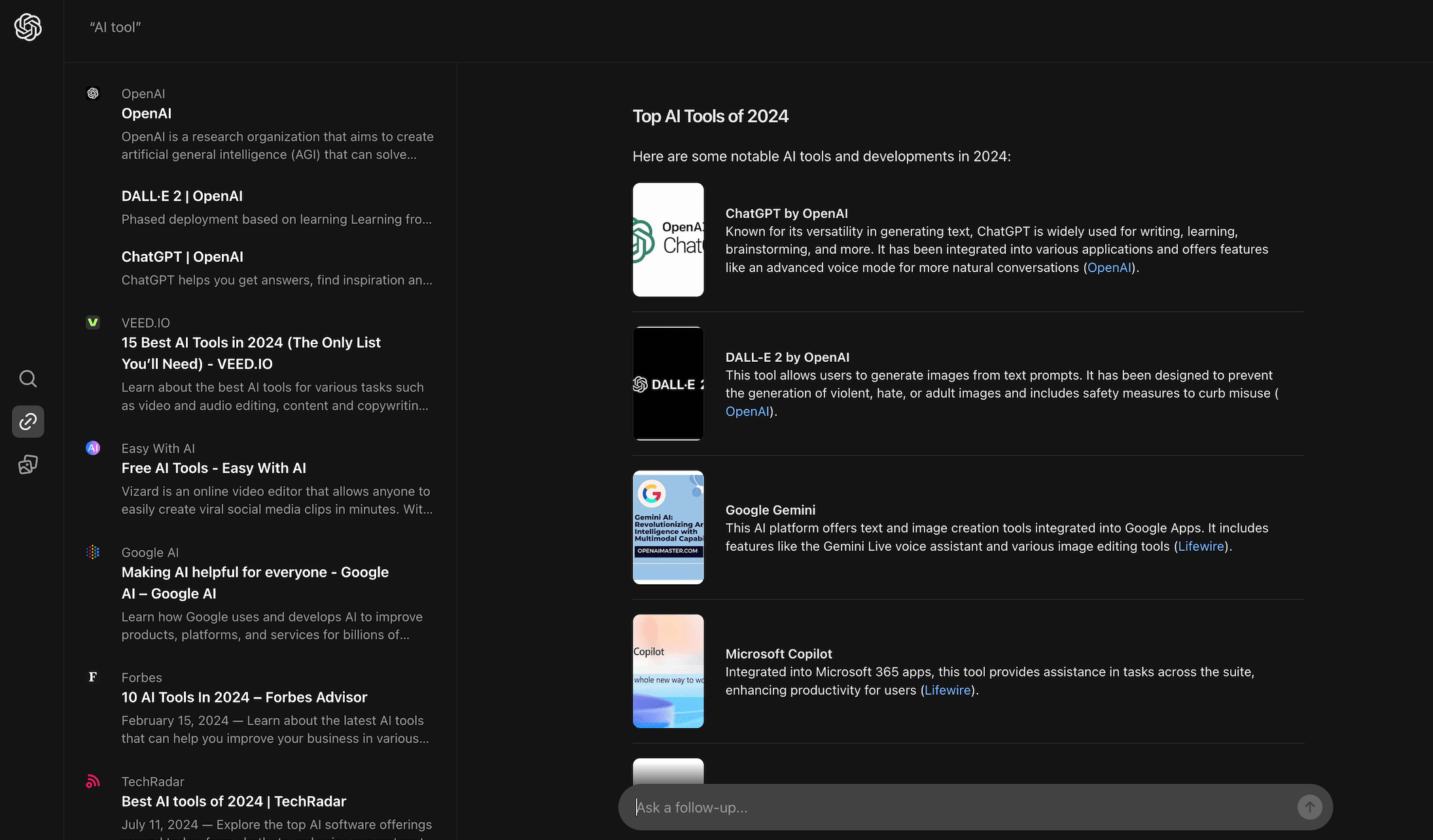
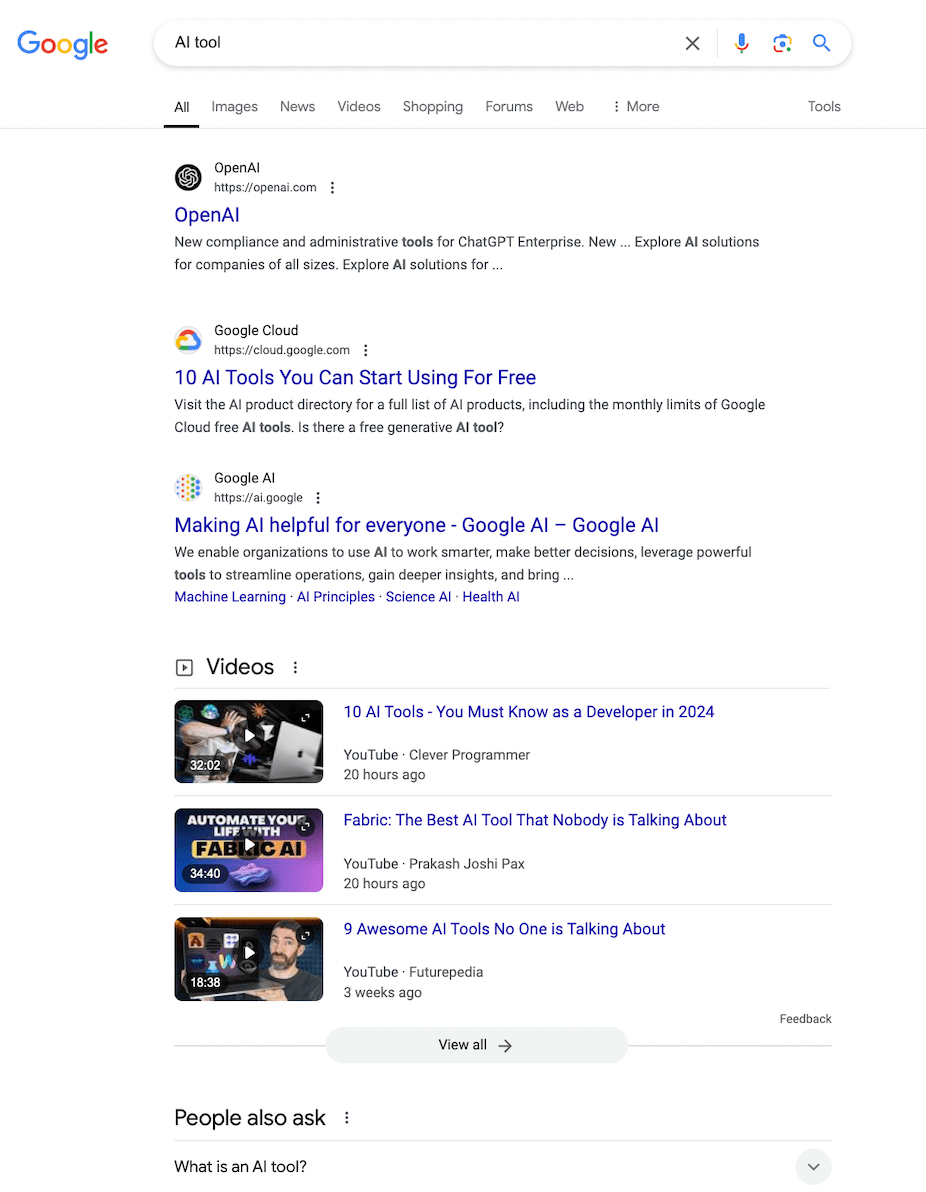
For the query “winter sweater,” SearchGPT displays a list of websites where you can buy a sweater (but without links). The list looks similar to Google’s results, featuring sites like Etsy and Amazon, but is less helpful for making quick purchases.
For the query “Mars,” SearchGPT provides detailed information about the planet and sources discussing it, while Google also includes links to the website: Mars Inc.
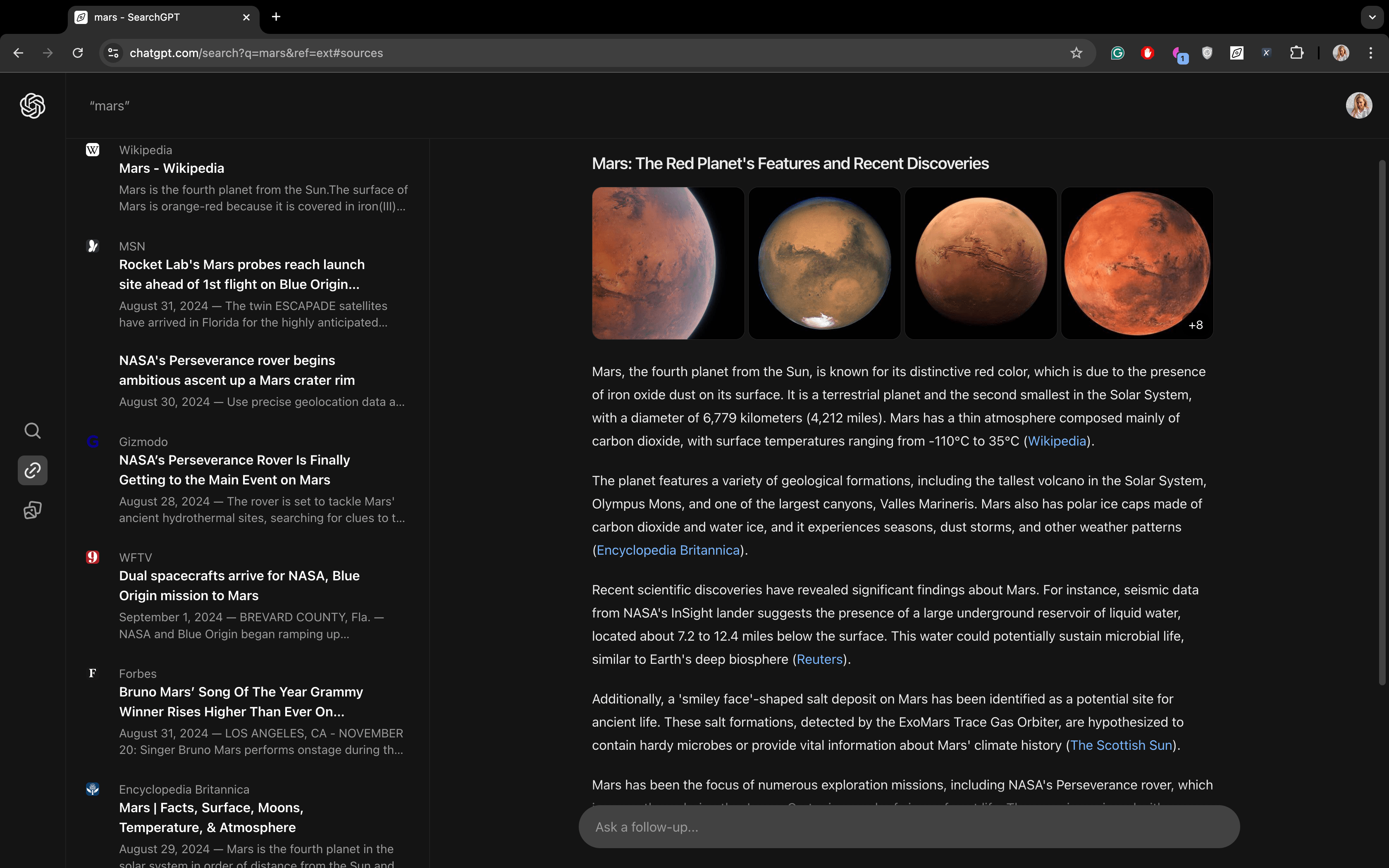
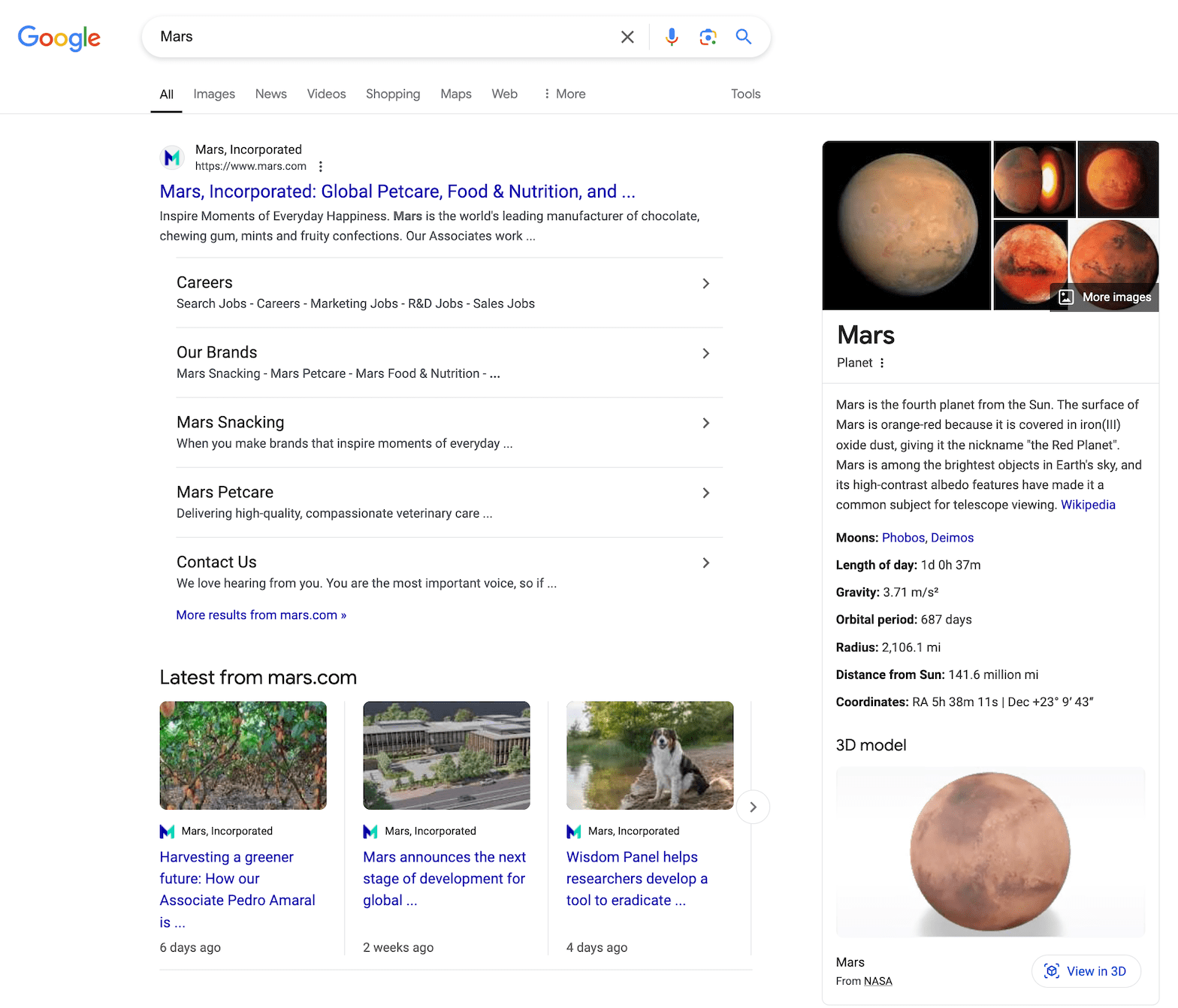
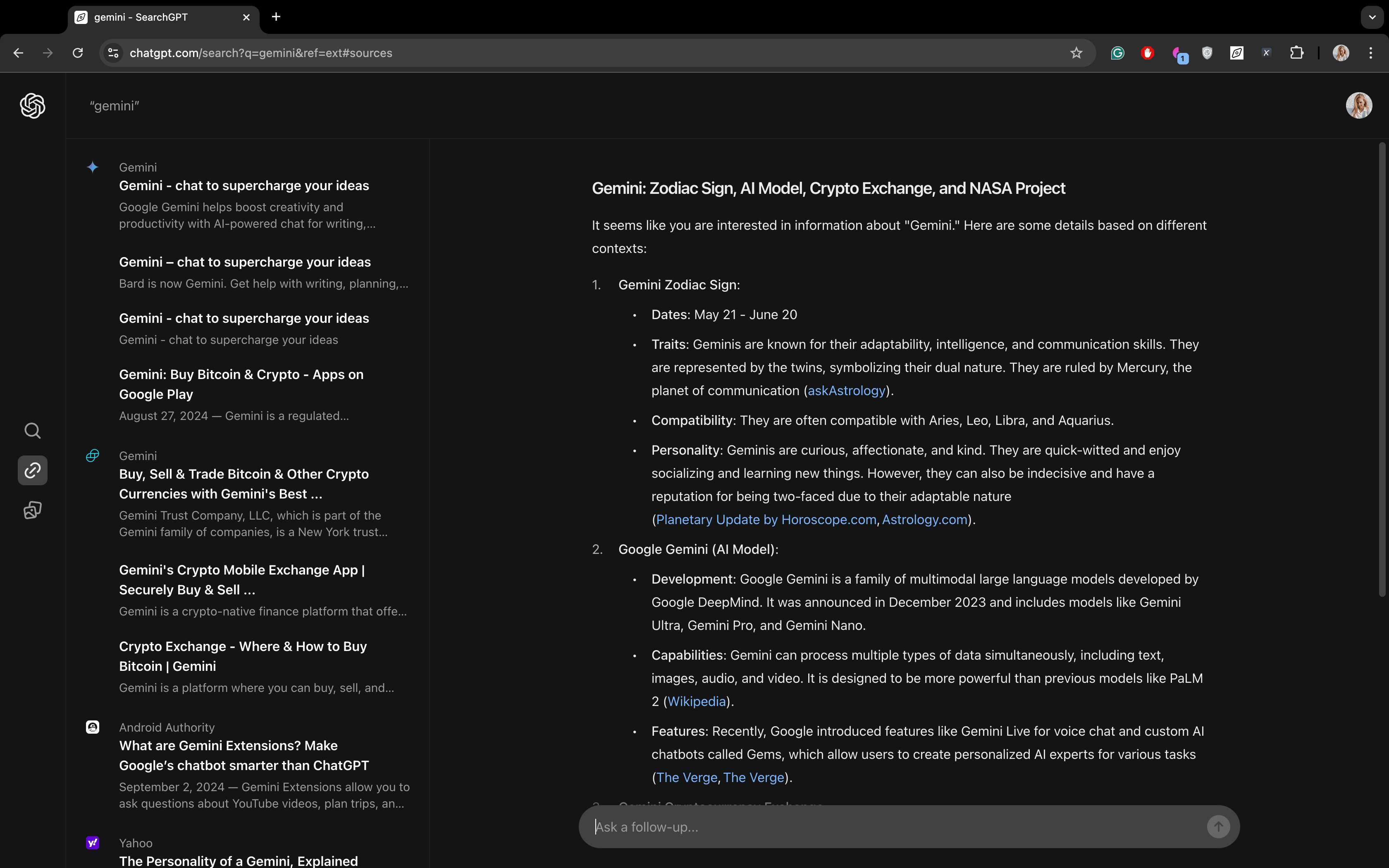
For the query “Gemini,” SearchGPT understands different meanings and provides definitions for all of them, with the search results being as diverse as possible. This suggests that the new search engine can interpret multiple meanings for some queries. However, Google is still more effective at handling this.
Long-tail keywords
For long-tail queries, the results look like this:
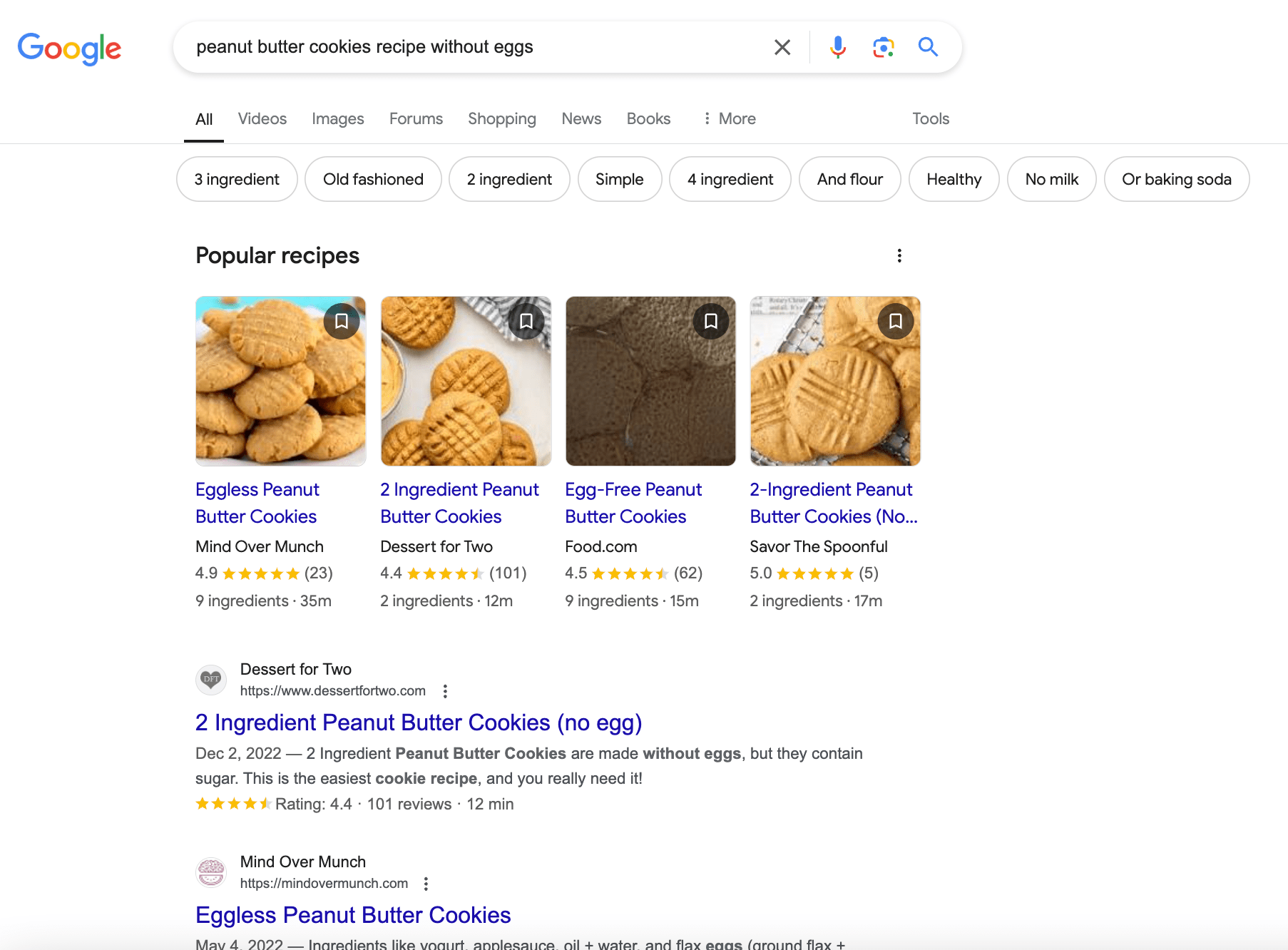
For a detailed query like “peanut butter cookies recipe without eggs,” SearchGPT generates a step-by-step recipe while offering links to websites with similar recipes.
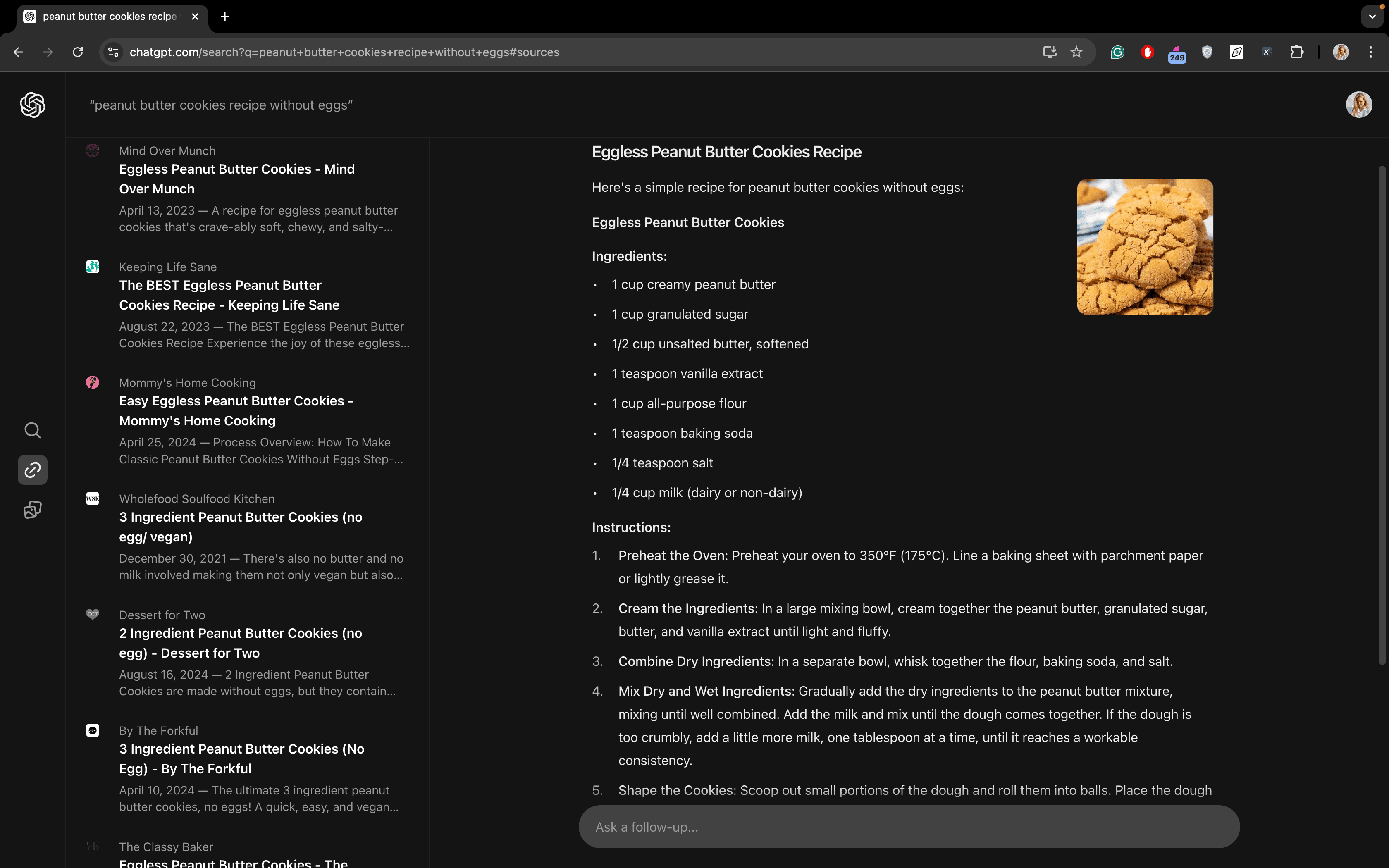
Note that Google doesn’t generate a recipe with its AIO for this query in New York. Instead, you’ll need to visit one of the websites it lists to find a recipe. However, it presents a list of recipes in a convenient format, highlighting key details like cooking time.
For the other two detailed queries, SearchGPT shows similar lists as it does for short-tail keywords.
- “winter sweaters to add to your closet for women over 50”:
- “history of Google’s algorithm updates”:
Conclusion: There’s no distinction between short and long queries in SearchGPT; it provides similar lists for both. In contrast, Google tends to show more AI-generated summaries (AI Overviews) for long-tail queries, while displaying traditional search results for short-tail queries. According to SE Ranking’s research, single-word queries triggered AIOs only 0.8% of the time, while ten-word queries showed an upward trend with a 19.1% rate.
Now, let’s move on to queries by search intent.
Informational queries
As expected, SearchGPT performs well with informational queries. It either offers relevant articles or generates accurate and comprehensive responses. This isn’t surprising considering that its strength lies in summarizing.
When generating an answer, SearchGPT pulls data from various sources, citing them so you can see where the information comes from. Here are a few examples:
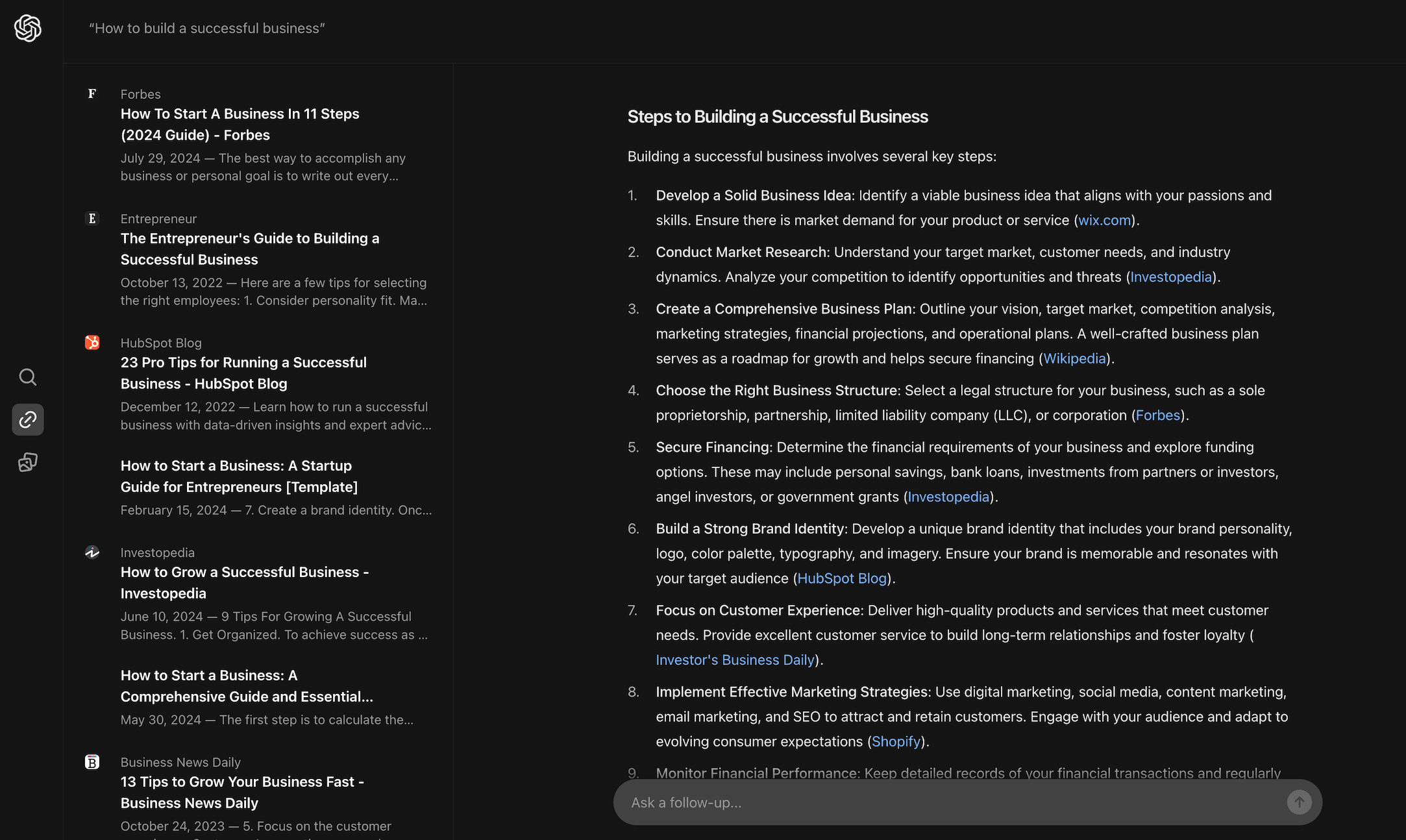
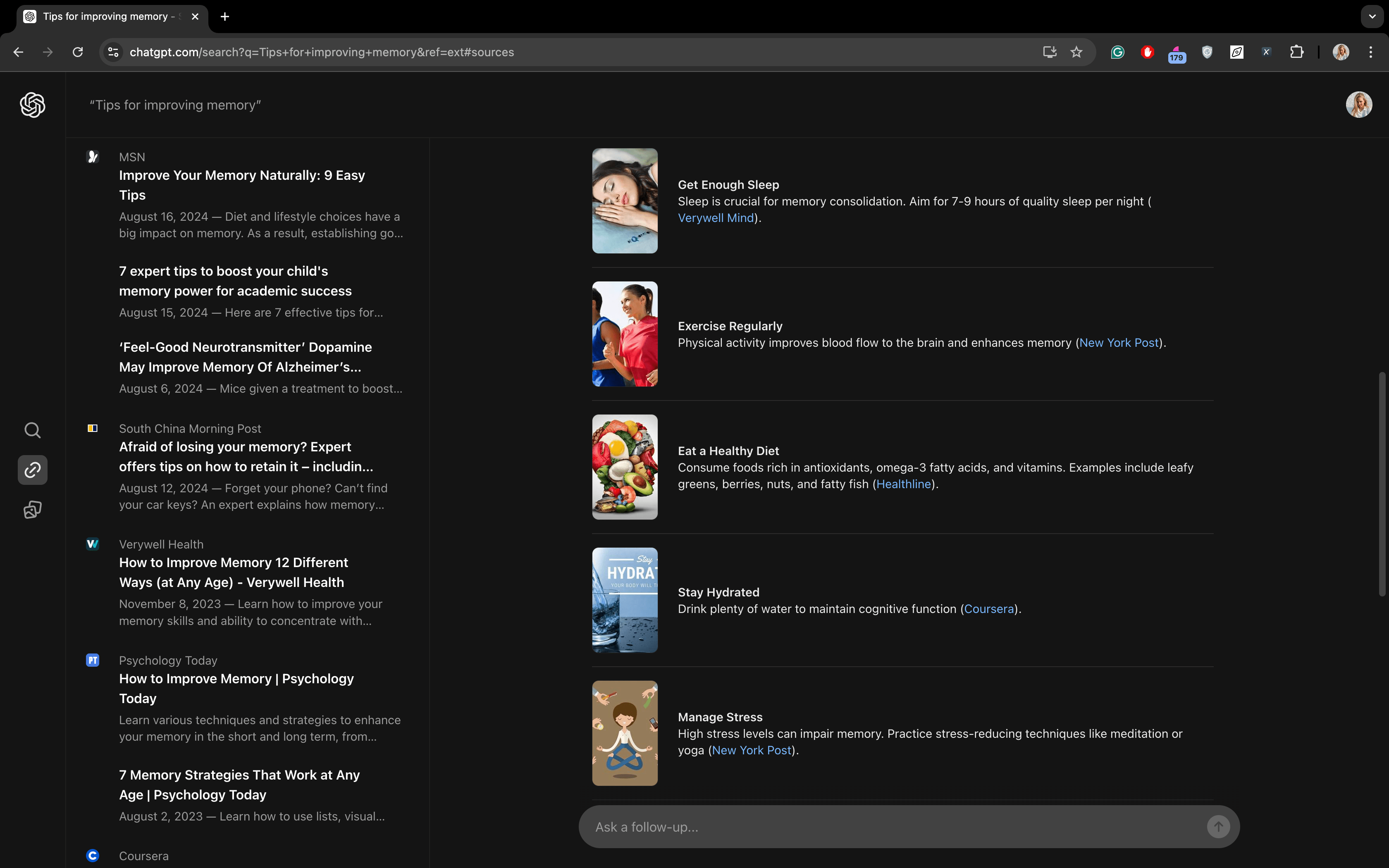
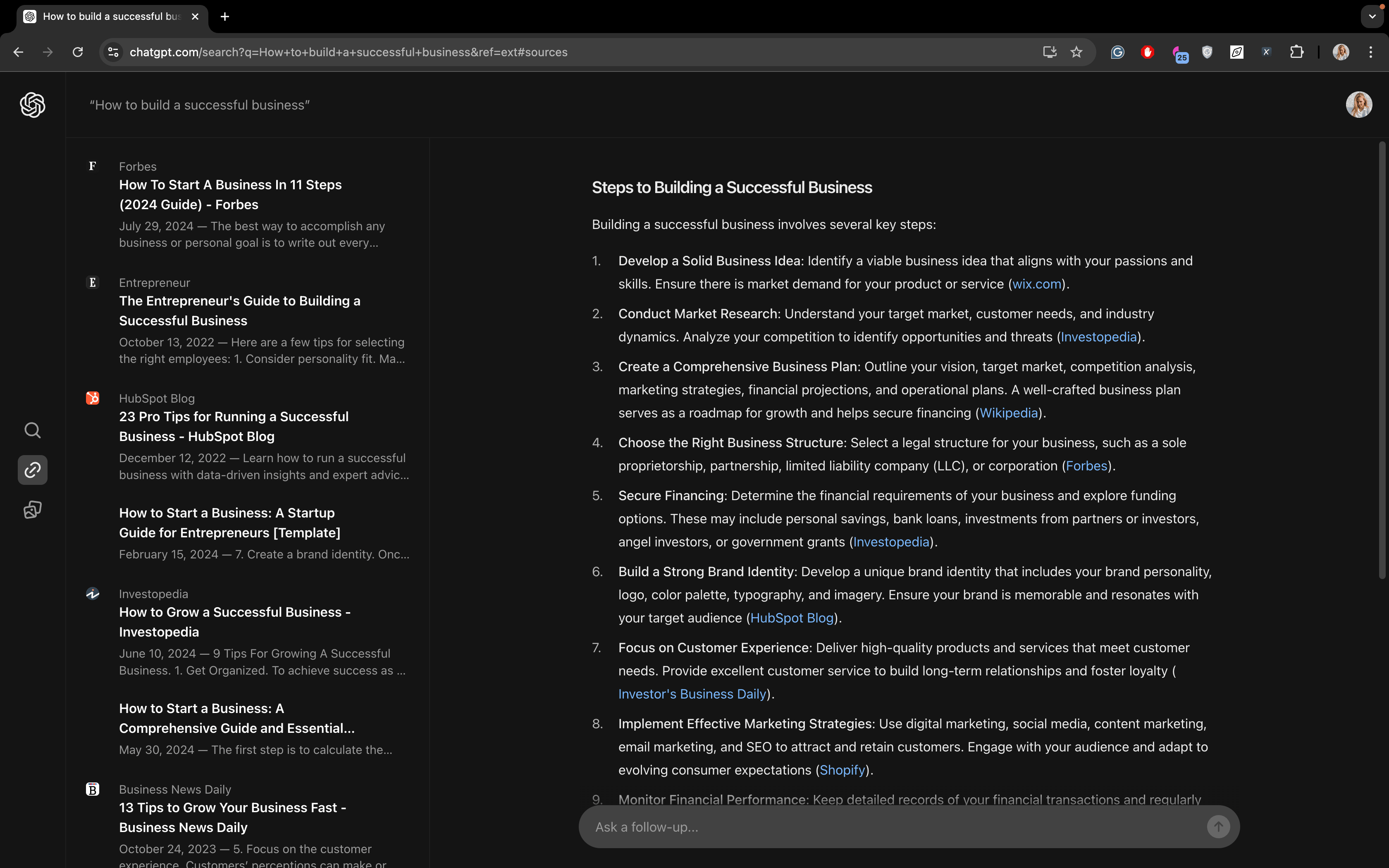
- “How to build a successful business”:
- “What is psychoanalysis”:
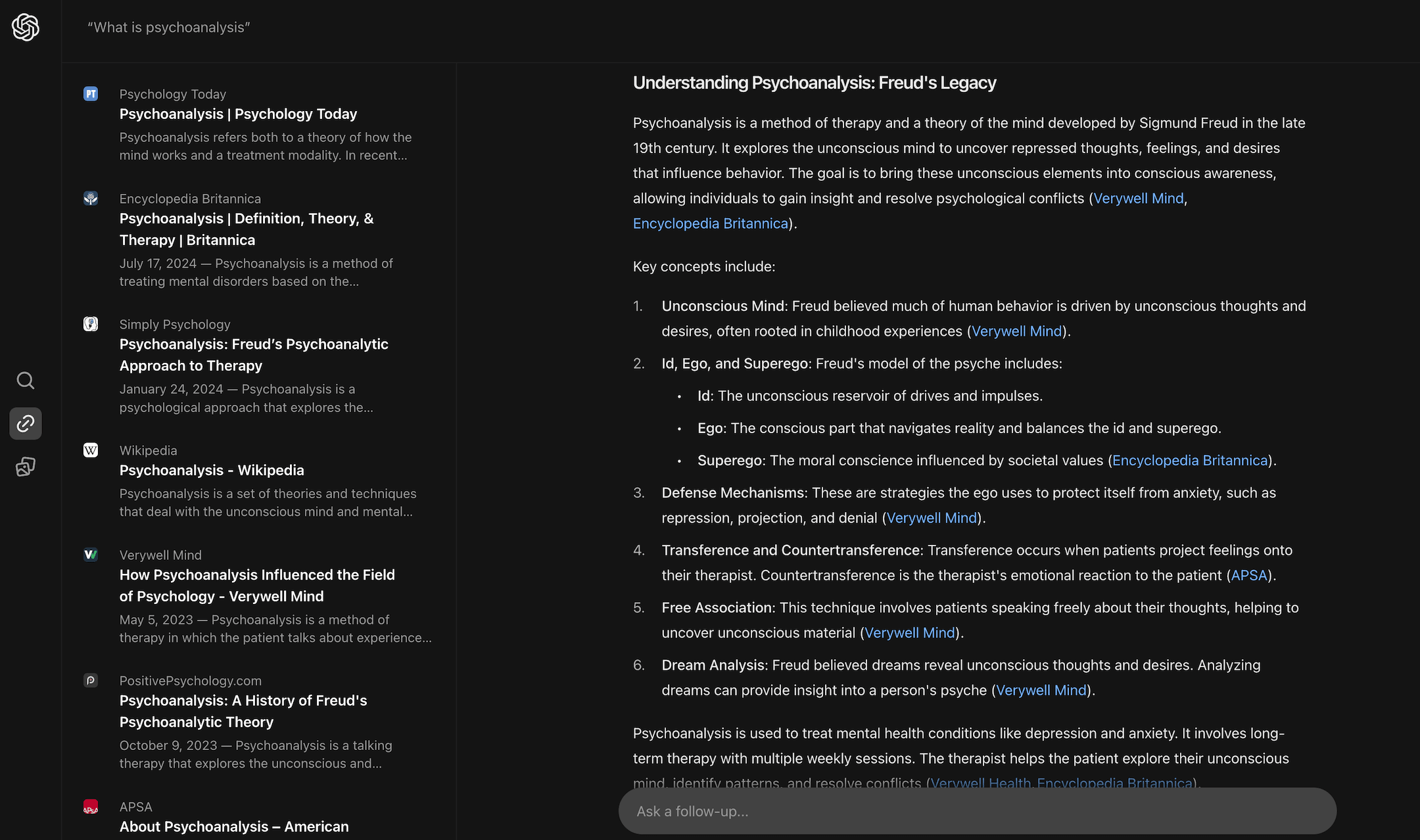
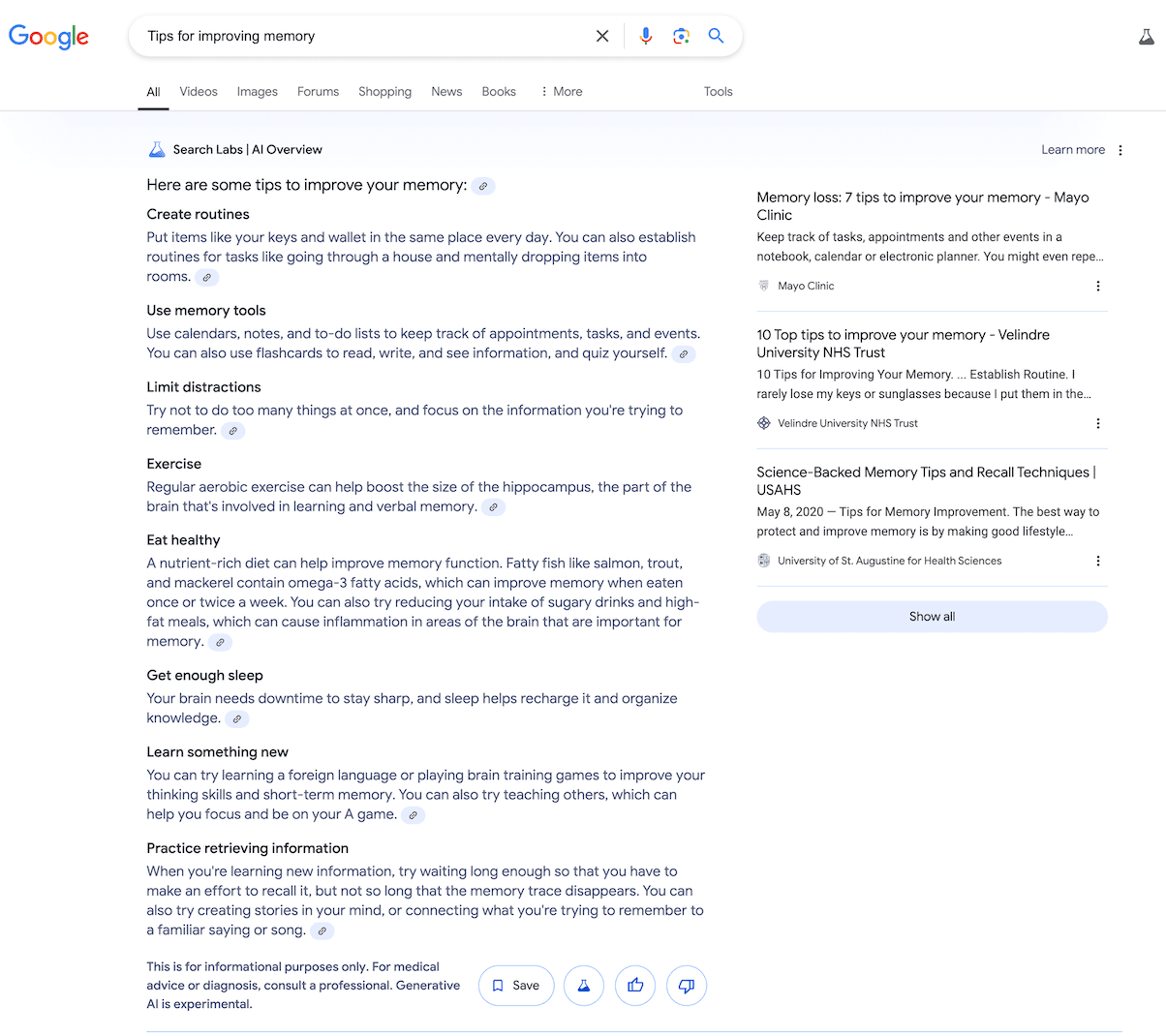
For the query, “Tips for improving memory,” SearchGPT tends to provide a list of sources rather than a detailed response with actionable advice.
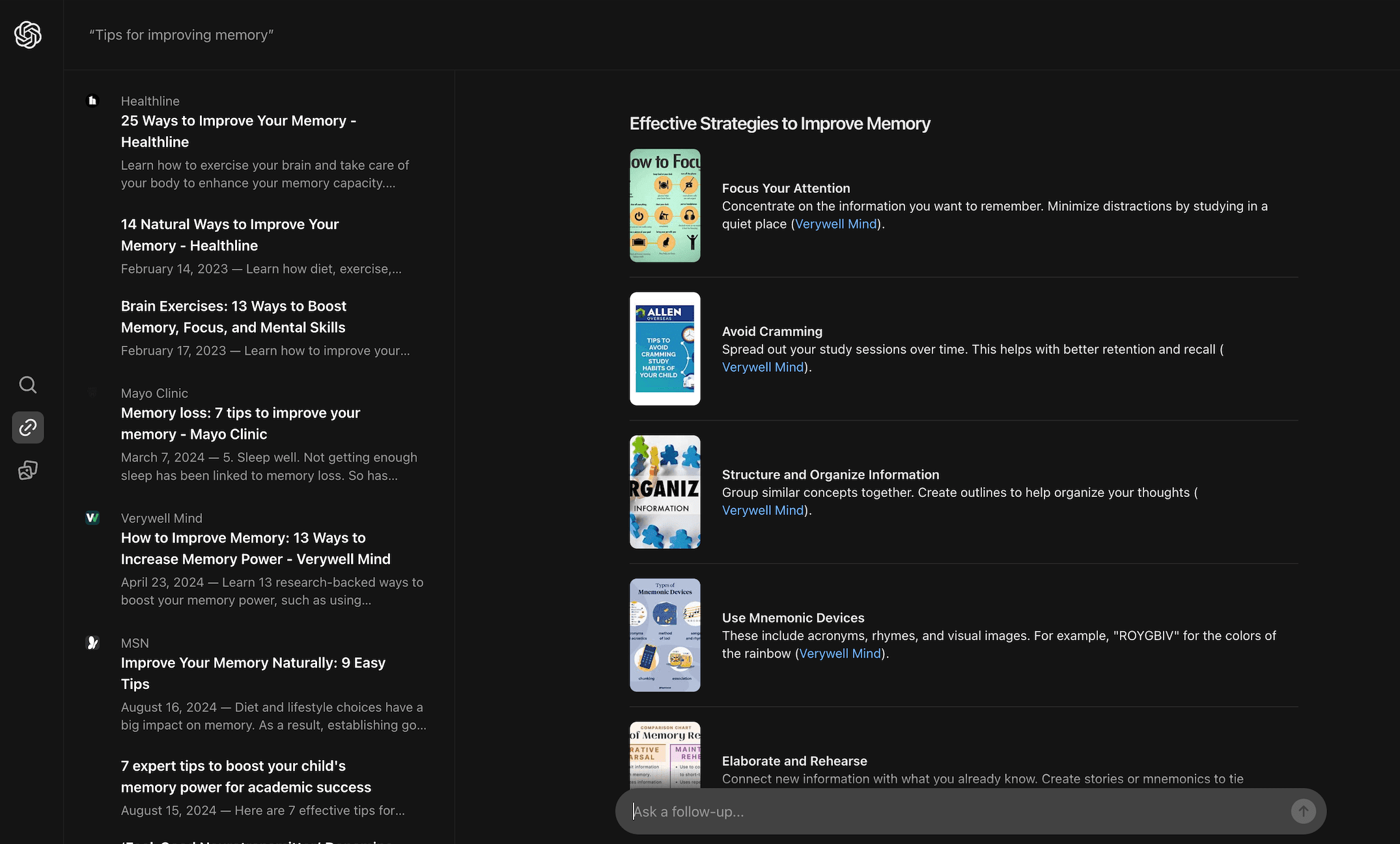
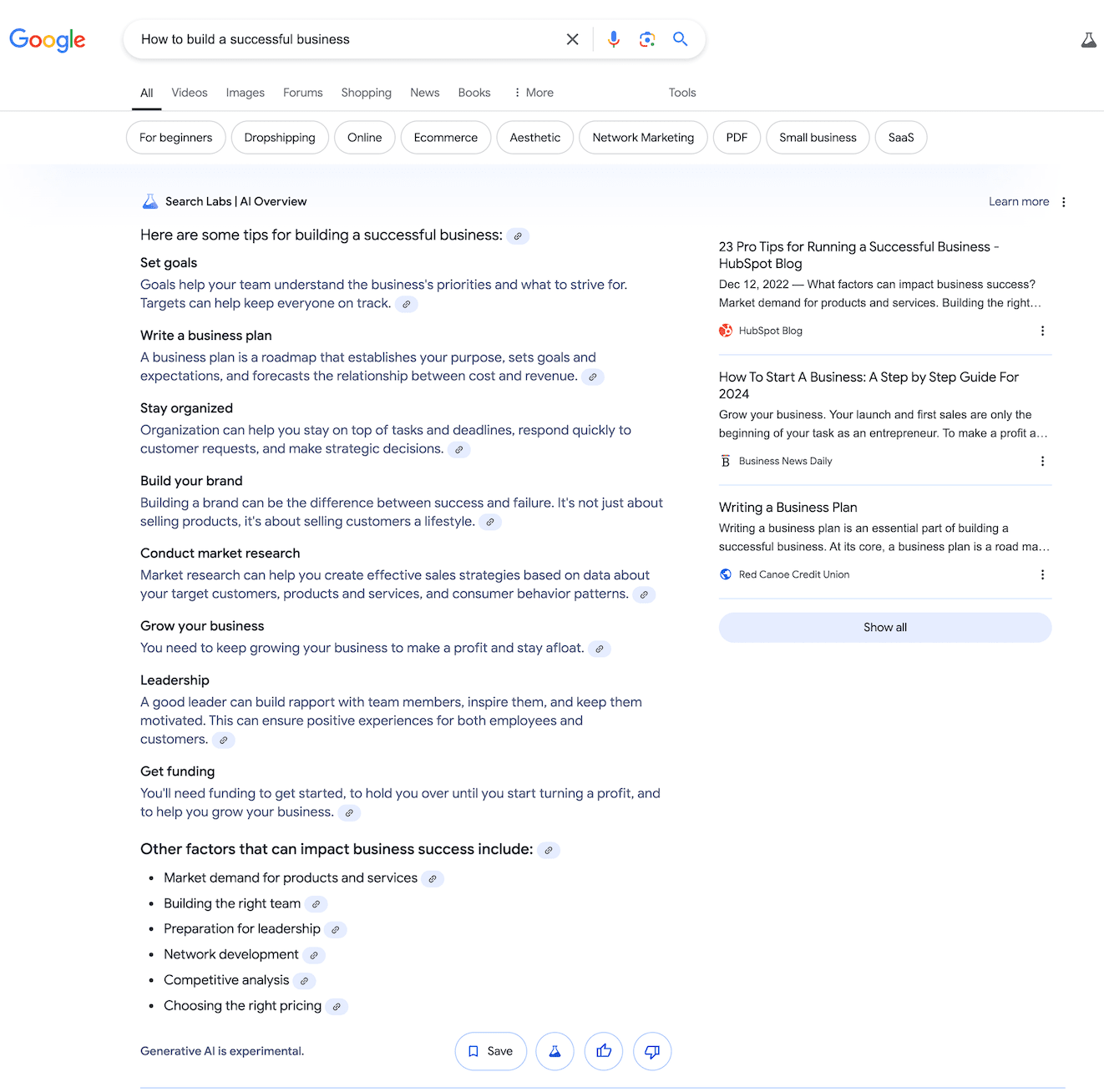
For queries like “Tips for improving memory” and “How to build a successful business,” Google also offers a comprehensive AI-generated response based on multiple sources, followed by links to relevant articles.
Conclusion: SearchGPT tends to be useful for informational queries. With its extensively generated answers that cite different sources, it can fully replace the need for users to open sites. The downside of SearchGPT is that it doesn’t offer much source variety yet. For example, in the last query (“Tips for improving memory”), the top three links were all from Healthline.
Navigational queries
For navigational queries, SearchGPT aims to display websites owned by the brands you’re looking for. Here’s how well it handles that:
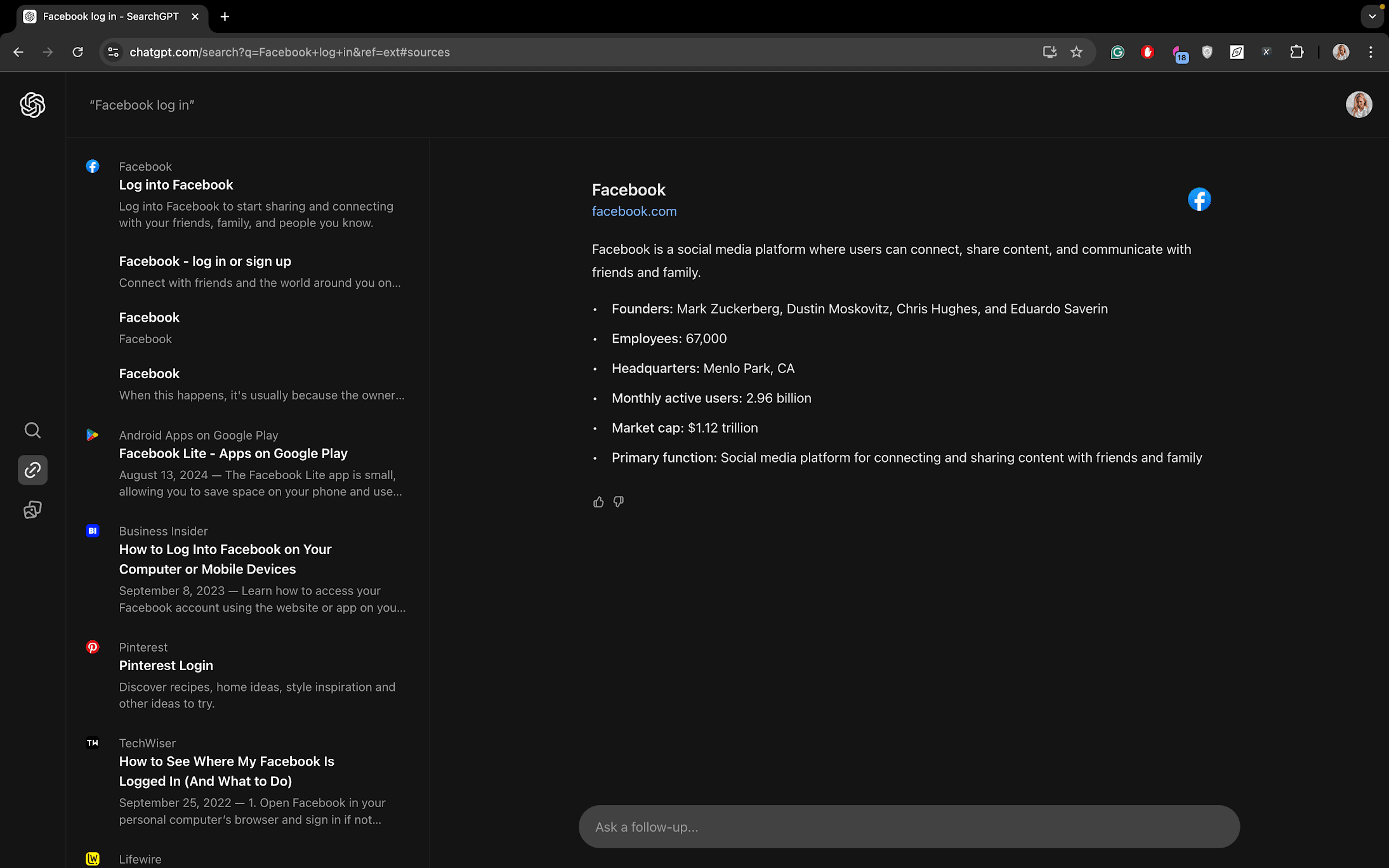
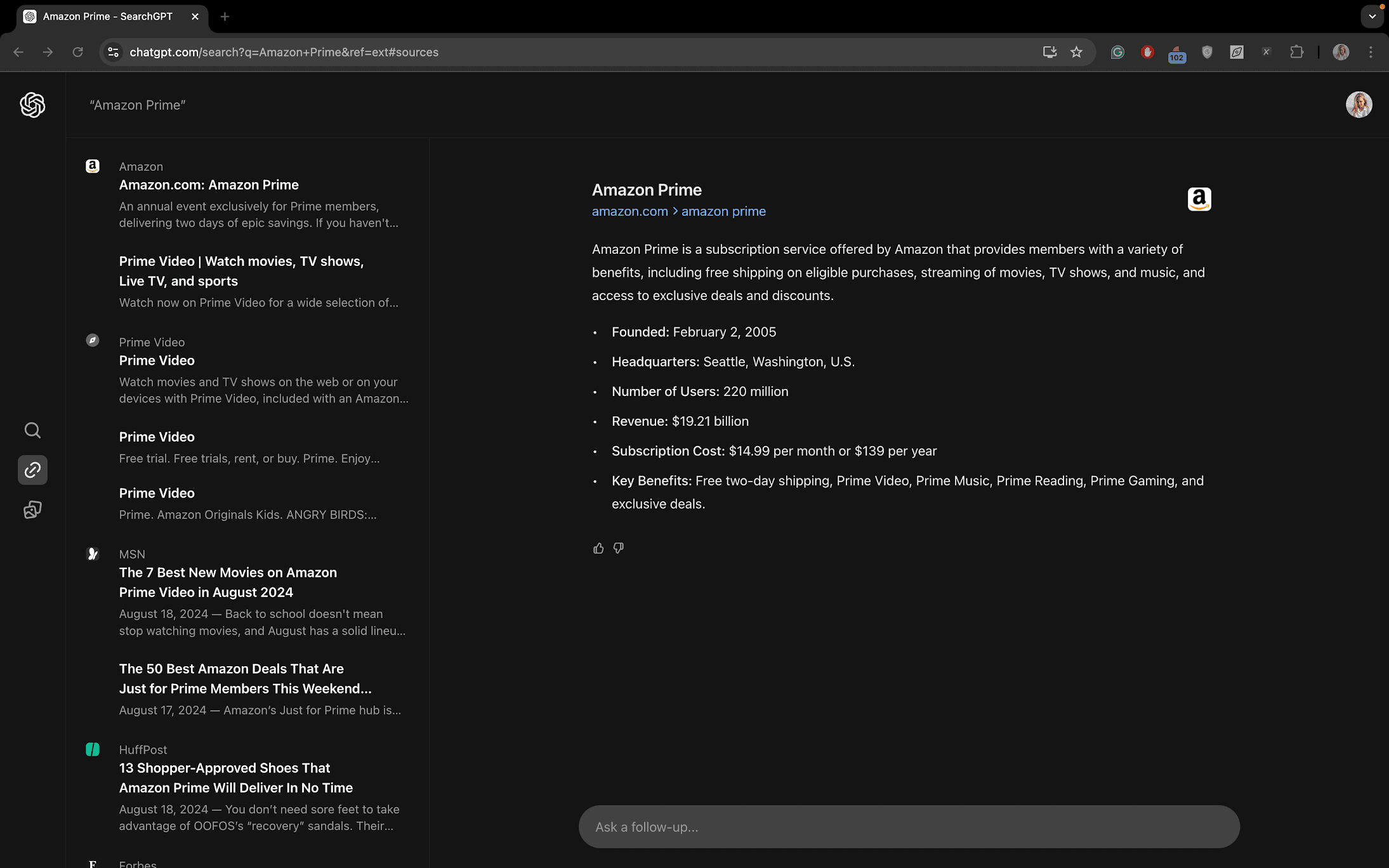
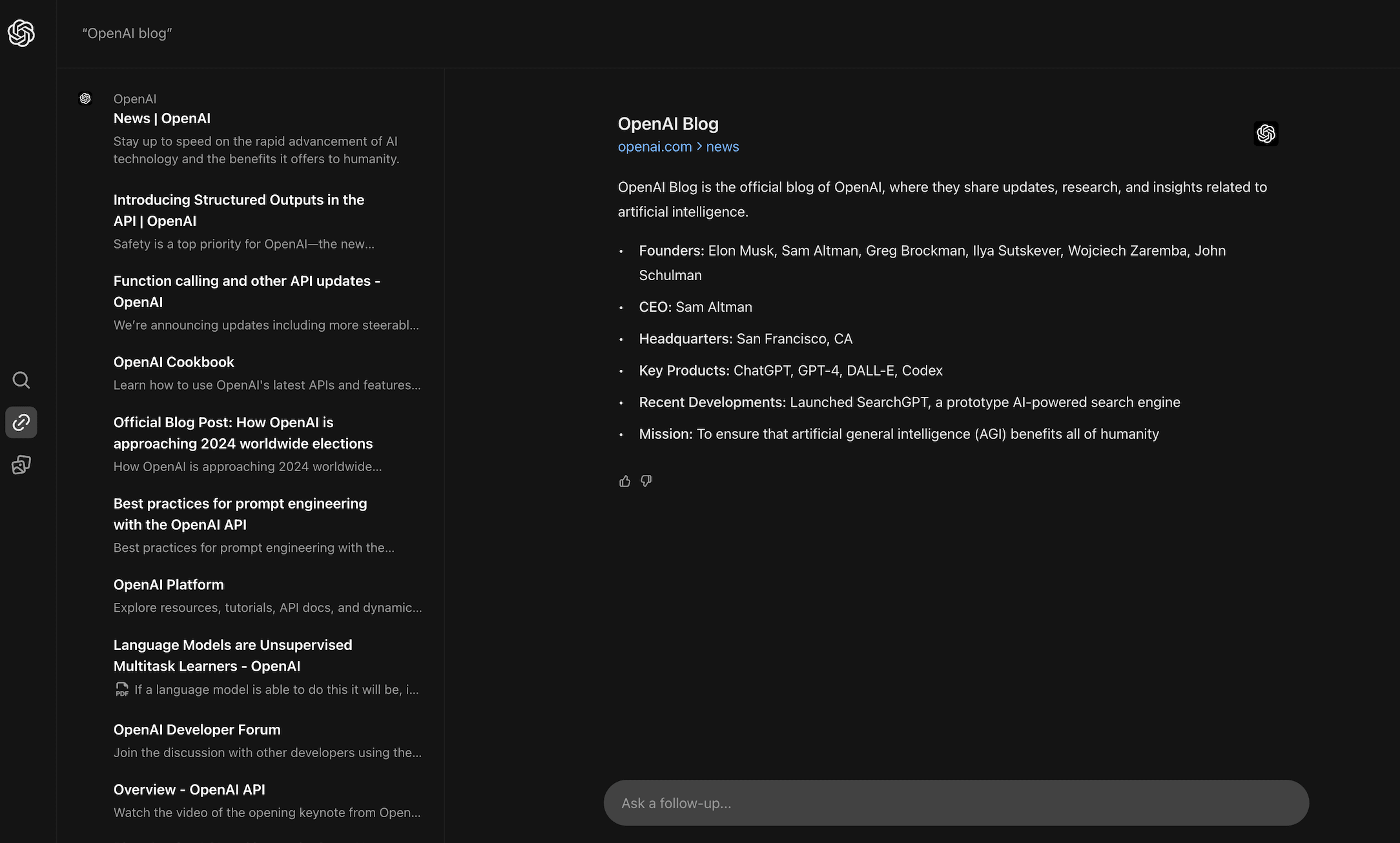
This is where you can find links to the brands you’re looking for, plus the descriptions of the brands themselves. For the query, “Facebook log in,” SearchGPT also includes numerous informational resources in the SERP about how to access the social network. Google is different in that it focuses solely on delivering the specific websites you’re searching for.
Conclusion: SearchGPT addresses search intent in its SERP panel by providing links to the brands you’re looking for. However, its main screen, which shows the generated answers, doesn’t quite focus on this intent as much. It’s a bit like Google’s knowledge panel for brands that often appears on the right-hand side, except it doesn’t highlight the brand’s website as clearly.
Commercial queries
Let’s look at the search results for commercial queries, where users typically expect to find product comparisons, top product lists, reviews, and similar information.
For our analysis, we selected three different queries: “best web hosting for small business,” “top-rated car seats for infants,” and “Spotify vs. Apple Music.” For the first two queries, SearchGPT presents well-curated lists of top products, complete with descriptions, pros and cons, and pricing. This makes it easier to make informed choices.
For the query “Spotify vs. Apple Music,” SearchGPT provides an in-depth comparison of the two platforms. It covers key aspects like pricing, quality, libraries, features, interface, and more.
For all queries, you can find links to various comparisons and listicles on the left side of the SERP. This is the same for Google. It doesn’t generate its own answers but instead links to various websites and forums like Reddit. It may also provide its own answers using the combined knowledge of sources from across the web. It achieves this via a SERP feature that automatically pulls top brands from the content.
Conclusion: SearchGPT excels at summarizing information, making its generated answers useful for quick decision-making. For these queries, you get a list of top products along with their pros and cons, prices, and sources. The SERP provides relevant content similar to what you’d find on Google.
Transactional queries
For this type of query, SearchGPT isn’t as useful as Google. SearchGPT’s e-commerce options are currently limited, and it takes more clicks to complete a purchase.
For example, when you search for “winter men boots,” “sunglasses under $50,” “kindle book,” or “cheap Barcelona tickets,” Google shows specific products with prices and descriptions that you can buy with a single click. In contrast, SearchGPT creates its own lists of items as it does for commercial queries. It even provides how-to guides, which are not what the user was looking for.
Conclusion: In the e-commerce sector, Google is the dominant player, with many experts suggesting that Google’s strategy is to build an ecosystem where users can shop without leaving the SERP. Right now, SearchGPT falls behind Google in this area. It is much more useful for handling informational queries.
Local queries
As Google users, we’re used to seeing maps for local searches. SearchGPT does things a bit differently. It gives you lists of places with details like hours of operation (for queries like “london apple store” or “dentist near Phinney Ridge”), features (like “pet-friendly restaurants in London”), and addresses (for all three queries). You can also find links to various locations on the SERP.
For the query “pet-friendly restaurants in London,” SearchGPT gives you a handy list with images and links, but it’s missing a map, which would be useful. For “london apple store” and “dentist near Phinney Ridge,” there’s a link to Google Maps at the top. It looks like they’re working on improving local searches and map integration.
For event queries, like “Barcelona live music events,” SearchGPT generates a list with links. This is similar to Google’s Events SERP feature.
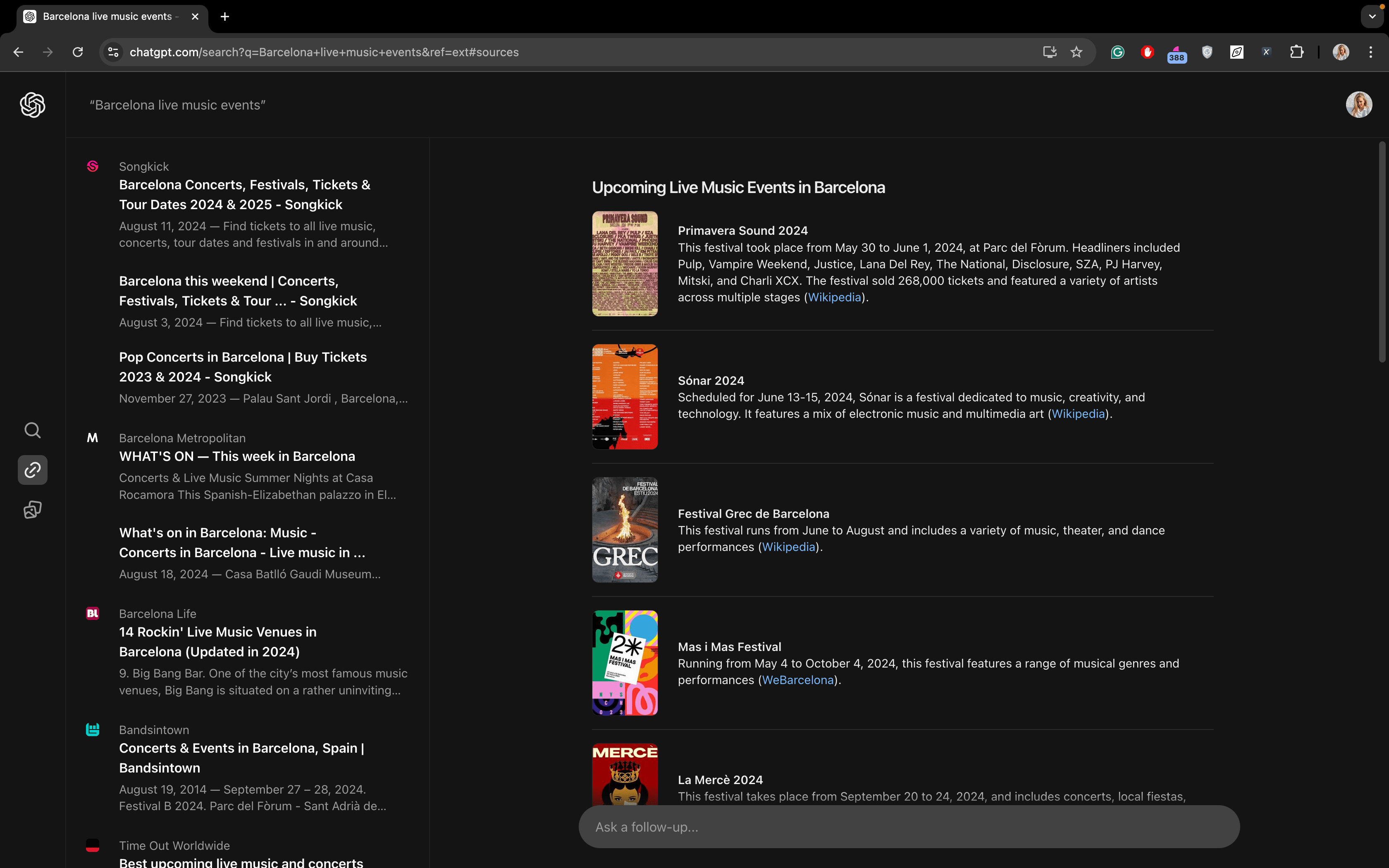
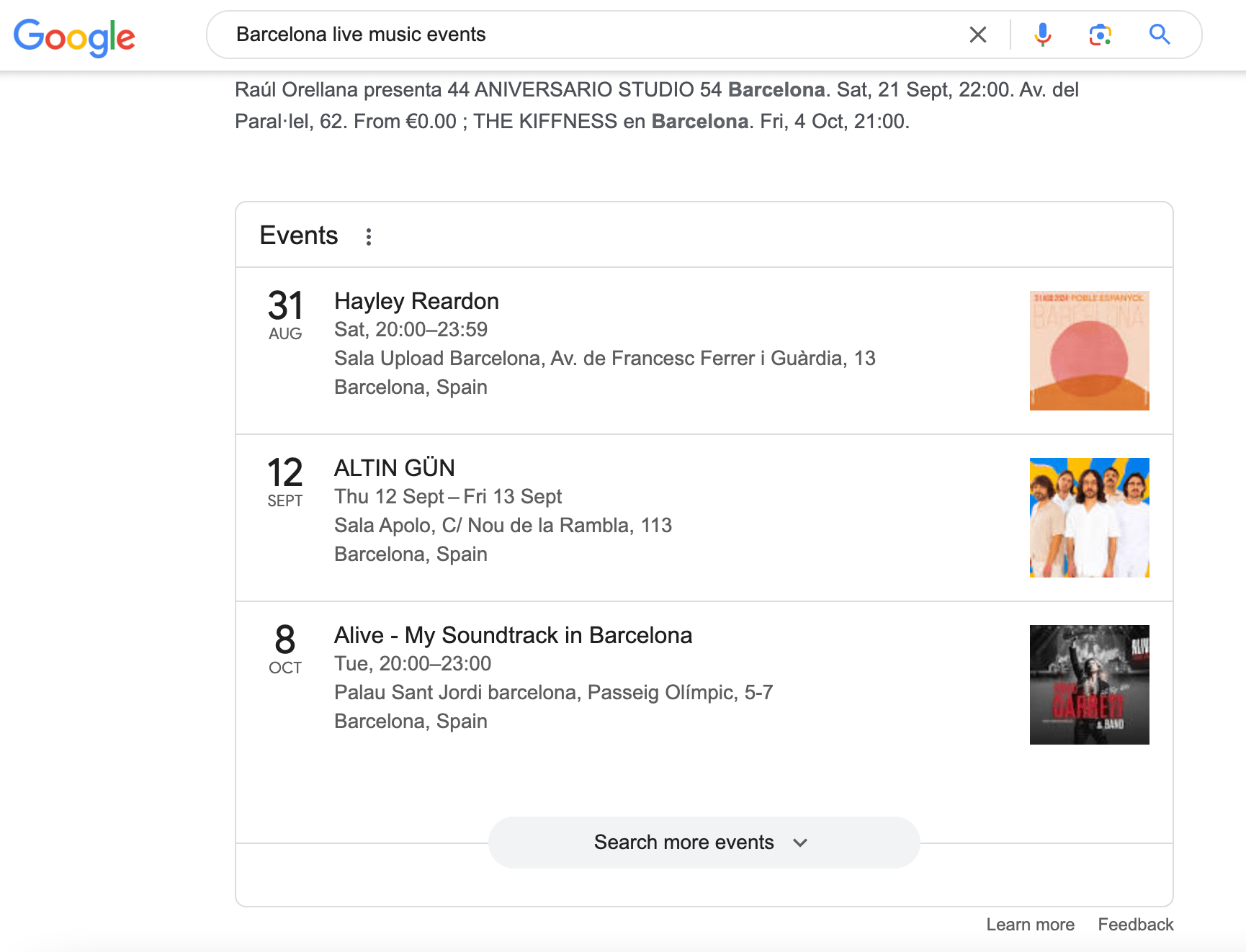
Conclusion: Overall, while the results are relevant, SearchGPT still lacks maps and an alternative to Google Business Profile. However, there’s potential, as just a week ago, the local results for queries like “london apple store” were much weaker. This shows that SearchGPT’s results are improving almost daily.
How similar are SearchGPT’s search results to Google’s and Bing’s?
We didn’t stop there with our SearchGPT research; we also analyzed patterns in its results by comparing the similarities between SearchGPT’s search results and those of Google and Bing. We analyzed the domains from the top 10 results for the same list of keywords across three search engines in the US.
This is crucial because it determines how different the sources will be in the new search engine (compared to current leaders) and how to optimize your site to rank at the top of SearchGPT’s SERP.
Here are our findings:
- According to our research, the similarity in search results (referring domain intersection) with Bing is 73%, while with Google, it is 46%. It’s no surprise that there is more overlap with Bing, as Microsoft owns roughly 49% of OpenAI’s equity.
- Domains that rank in SearchGPT usually get traffic from Google as well. For the domains that appeared in SearchGPT across all analyzed keywords, the average traffic from Google amounted to 57 million. Additionally, considering the number of referral domains (689K vs. 851K in Google) that the top 10 sites have on average, it seems likely that backlinks (referral domains) are also a ranking factor in SearchGPT.
- About 26% of the URLs ranking in SearchGPT for our queries receive no traffic from Google at all. This means that sites can reliably attract visitors through this new search engine, even if they’re not ranking high on Google. Especially considering that as Google rolls out its AIOs more extensively, covering most queries, it will become even harder to get traffic from Google.
- Among the top 10 domains most frequently appearing in SearchGPT’s results for our queries, many are just as popular in Google and Bing. For example, the overlap with Bing is 50%. Sites like openai.com, amazon.com, and forbes.com appear most frequently across all three search engines for our keywords. The Amazon website appears at the top of SearchGPT’s SERP for almost all e-commerce-related queries (which is also typical for Google).
This means that, similar to Google, SearchGPT favors well-established, authoritative sites in its rankings. Newer or less trusted sites face similar challenges in reaching the top here.
This first batch of data shows that SearchGPT’s ranking factors might be identical to other search engines. To rank well here, the basics of website optimization won’t be very different.
Analysis of media presence in SearchGPT’s results
We also couldn’t overlook the presence of media platforms in our SearchGPT research, as their current dominance in Google search results makes it more difficult for other sites to compete. At the same time, media outlets fear losing traffic by being used solely as informational sources for AI-generated answers.
For the analysis, we included both non-media queries (which we examined above) and media-related queries (where we expected to see media), such as “Google AI Overviews news,” “SearchGPT news,” “Latest AI news,” “Latest cybersecurity news,” and “Latest tech news.”
Our research found that about 32% of the results for all the queries were from media sources. The most frequent domains were:
- forbes.com
- searchenginejournal.com
- psychologytoday.com
- businessinsider.com
- cnet.com
By the way, they are quite similar to the top five most frequently mentioned media outlets in AI Overviews: forbes.com, businessinsider.com, entrepreneur.com, inc.com, and theguardian.com. AI Overviews link to these news media sources less than 2.23% of the time, which is over 14 times less frequent than SearchGPT.
For the commercial query, “Spotify vs. Apple Music”, SearchGPT shows the highest number of media for non-media queries (15 sources out of 18).
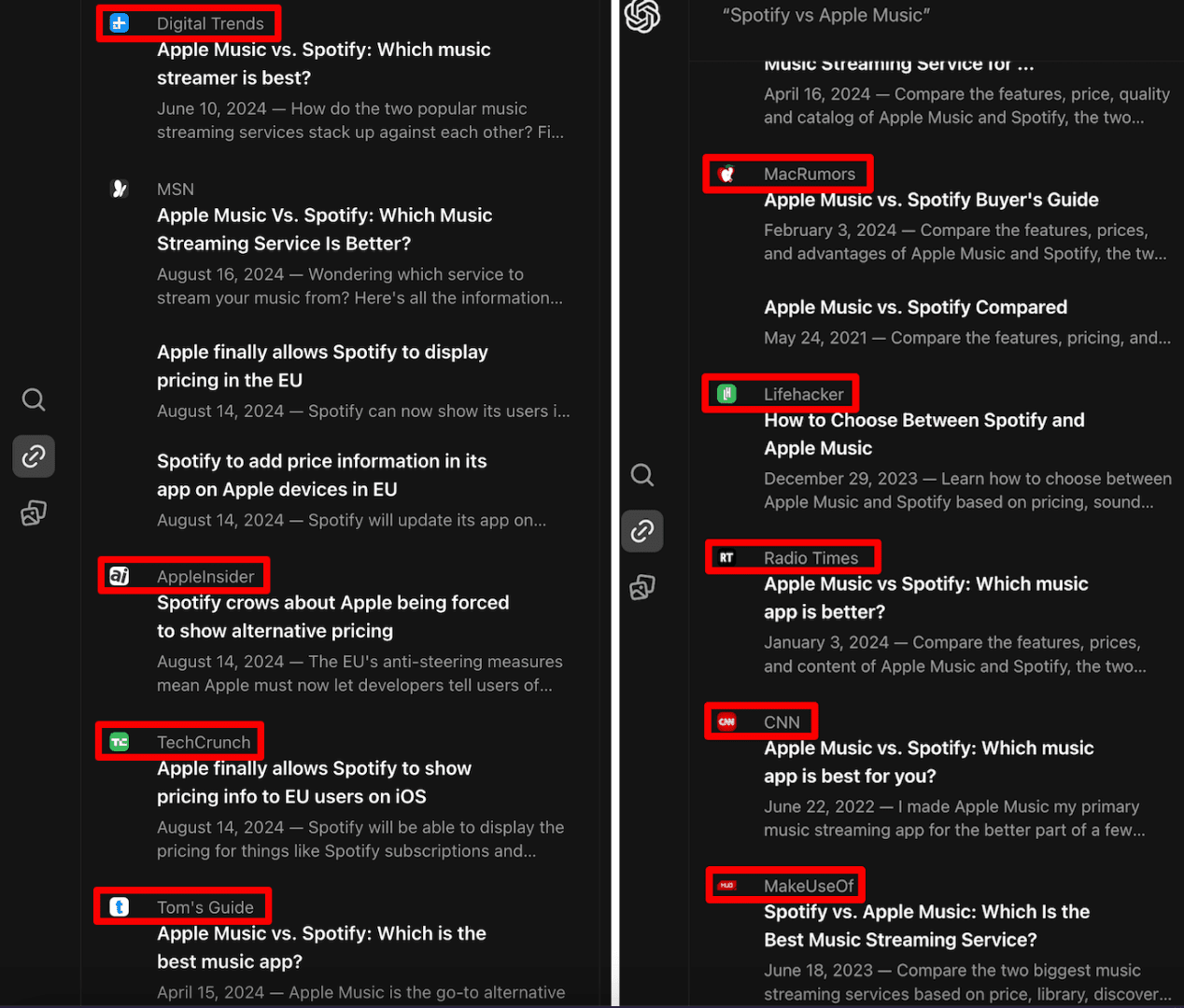
Big media outlets like Forbes often dominate search results and get a lot of traffic in SearchGPT (which is pretty common for Google nowadays as well). This makes it tough for smaller, less influential sites, including small businesses or affiliates, to compete. Unfortunately, this can lead to the rise of parasite SEO practices. Google has faced and continues to deal with this today.
For media-related queries, news media presence in the SearchGPT SERPs exceeded 75%, with the most frequent domains being:
- theverge.com
- techcrunch.com
- reuters.com
- ft.com
- apnews.com
This data shows that the new search engine could be a big win for media outlets, as they can generate traffic from Google, Bing, and even SearchGPT.
Oddly enough, we didn’t find media results with a paywall.
Let’s now observe how SearchGPT’s search results perform for media-related queries.
SearchGPT provides quick news summaries. It includes links to sources that take you to the full articles. Its headlines typically offer a quick overview of trending topics.
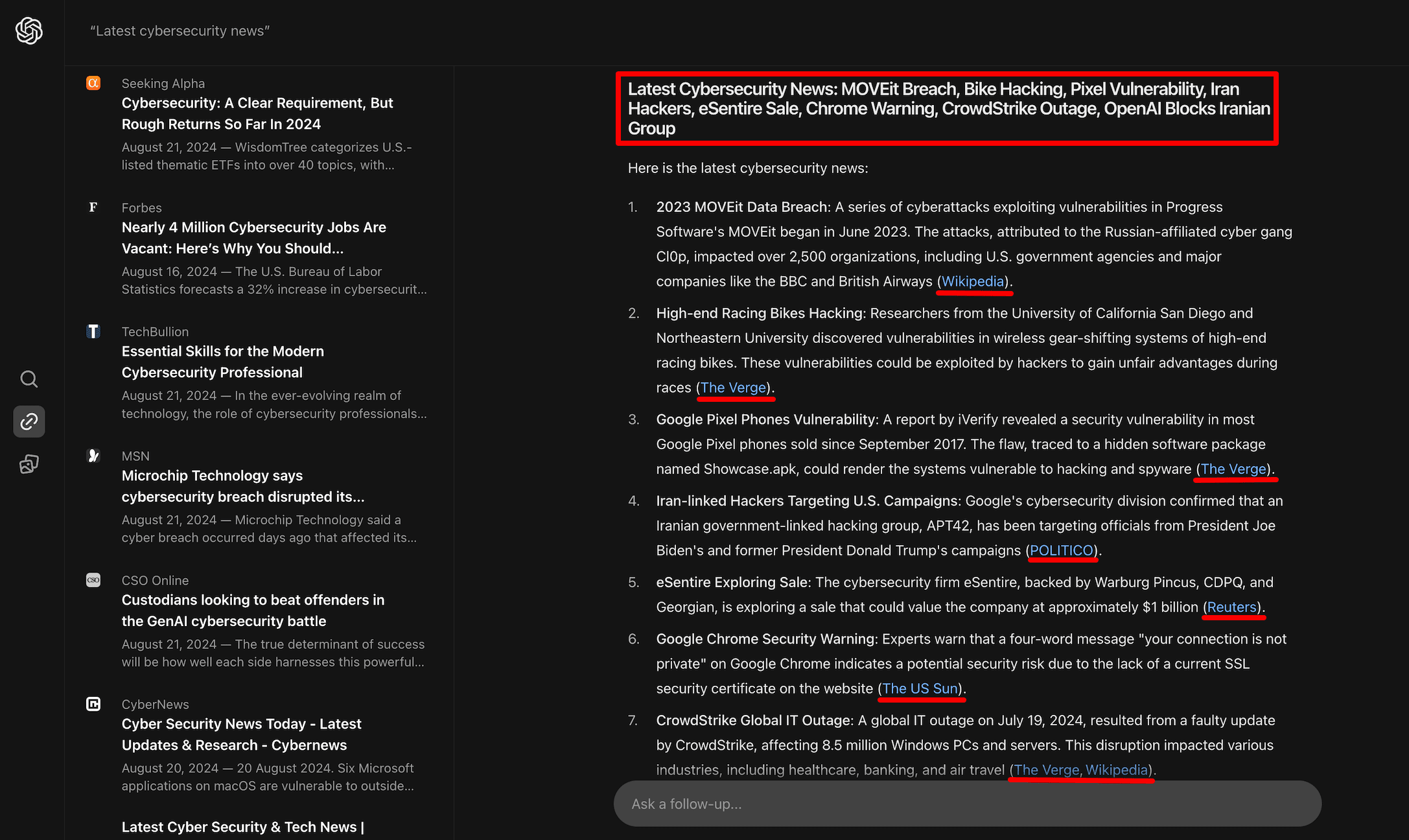
Many of the links in SearchGPT’s summaries don’t appear in the SERP on the left side, and sometimes the difference can be as much as 39%.
SearchGPT’s primary disadvantage is that it still needs improvement in providing the latest news. We found a good portion of old news, including content from a month ago and even from 2023. For instance, in the screenshot above, the generated response for the “Latest cybersecurity news” query starts with news about the MOVEit breach, which began in 2023. Plus, it references Wikipedia—a source that isn’t usually focused on the latest news.
Although for queries “SearchGPT news” and “Latest AI news”, it pulls news from today (note: our analysis was conducted on August 21), for the query “Google AI Overviews news,” SearchGPT did not provide 24-hour news. For the latest query, the top 3 news items are more than a week old.
It is not competitive with Google here. The search giant, on the other hand, provides the latest news daily in its SERP feature and even has a dedicated tab for news.
Aside from this, SearchGPT excels at providing accurate and detailed news summaries. For example, let’s check out the news items it gave for the query “Google AI Overviews news.”
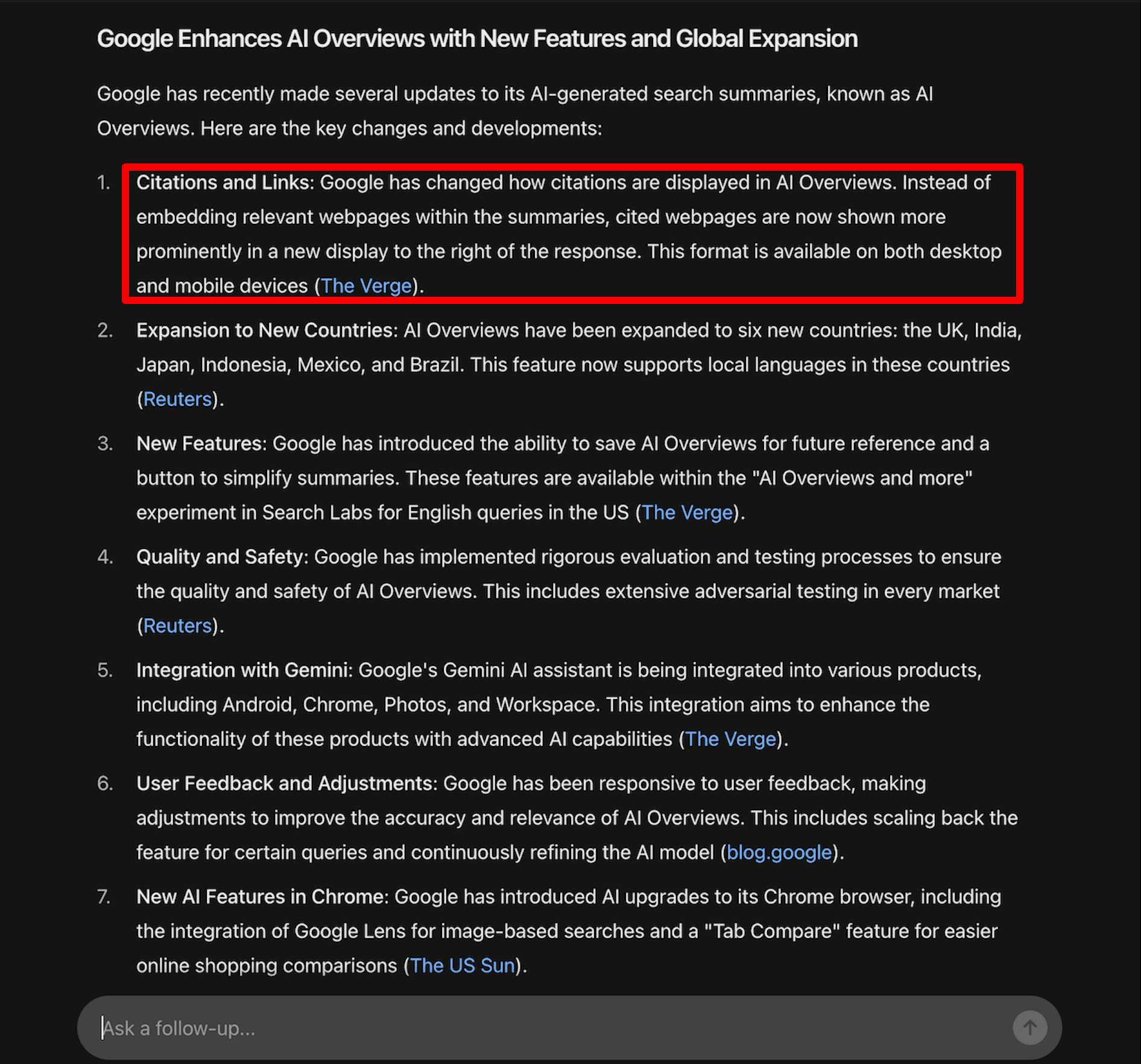
The first item briefly describes a news story from The Verge about how Google changed how it displays links in its AI Overviews. You can compare what’s written on the website with what’s provided by SearchGPT:
It shows the same clear and concise description for the second news item: Reuters’ story about the expansion of AI Overviews to new countries. SearchGPT accurately retrieved information about the countries affected by this update.
Overall, SearchGPT effectively highlights the main points, giving users an easy grasp of the key insights without the full news article. This is exactly what media outlets are concerned about—readers might be satisfied with the response from a generated summary and choose not to visit the media website. This could reduce traffic and impact advertising and subscription revenue.
Although, during the release, SearchGPT promised to provide many links to media sites and thus drive more traffic to them, it’s not certain this will actually happen, considering the above. On the bright side, because SearchGPT uses more information from media sources, its responses tend to be higher quality and less likely to give poor or risky advice, helping to avoid the kinds of issues that have happened with AIOs.
Comparison of AIOs and SearchGPT’s AI-snippet
Of course, many people compare the generated responses in SearchGPT with Google’s AIOs. In fact, to compete with OpenAI, Google rushed to release its AIOs before it was fully ready.
Both of these search engines have some things in common. Each search system generates comprehensive answers to questions and includes sources used to create the text.
Let’s now compare the two queries mentioned earlier in this article: “Tips for improving memory” and “How to build a successful business.”
- “Tips for improving memory”
- “How to build a successful business”
The length of the generated responses is roughly the same on both platforms. In each case, it’s a list of tips. The answers are generally comprehensive, but if you need to dive deeper into the topic, you must visit external sites; the tips themselves are brief (1-2 sentences).
The sources for the queries differ. For example, for “Tips for improving memory,” Google pulls most of its content from medical sites, while SearchGPT relies on media resources like the New York Post. Google also includes references to YouTube videos, something SearchGPT doesn’t offer. Google also includes a disclaimer recommending consultation with a doctor for medical advice.
For “How to build a successful business,” Google provides content from Shopify, whereas SearchGPT features a variety of sources, including Wikipedia, Wix, Forbes, and HubSpot.
Overall, SearchGPT pulls from more sources to generate a response (12 to 15), compared to Google’s 9 to 10. Both tend to repeat some domains.
Google also allows users to rate (like or dislike) the answer and save it.
Conclusion
Since Google holds over 87% of the US search engine market share, it will be tough for SearchGPT to surpass it anytime soon, but even a small shift in market share could be significant. If SearchGPT captures just 5-10% of the market, it would create a major disruption in the industry. And SearchGPT has the potential to do so. Here are its main advantages:
- It generates detailed answers instantly, so users don’t have to browse multiple sites to find what they need.
- It also lets you refine queries with follow-up questions to achieve better, more accurate results.
- It keeps search results free of ads, offering users a cleaner and more streamlined experience.
SearchGPT still has room for improvement:
- It shows much fewer URLs than Google’s extensive results. It lacks additional features like videos or maps, offering a more uniform but less dynamic SERP with fewer, lower-quality images.
- It repeats domains frequently, with only 57% unique domains. Google’s uniqueness rate is higher.
- SearchGPT recognizes multiple meanings of terms but doesn’t offer varied results as effectively as Google.
- Some SearchGPT results are outdated, with articles from 2018-2019 appearing for certain queries.
Note that this version of SearchGPT is only a prototype. OpenAI will likely refine its search engine based on user feedback. We’ll continue to monitor its development and update you whenever changes in search occur.
