Posted by
Darrell Mordecai
This month’s episode of the SEO Trends for 2021 roundup covers some big topics. All of which could make a fundamental shift in how you do SEO.
Yes, times are changing. SEO is maturing and as SEOs, we must ****** with it.
In this post, you’ll learn:
- Why covering all aspects of a topic will help your site deal with competitive and volatile SERPs
- What topical relevance is and why it’s one of the most important ranking factors today
- How semantic SEO will change the way we do SEO (forever!)
Now, before you dive into the content, here is a little challenge.
There is a hidden theme running through all of the content in this post, tying it all together. See if you can spot it.
I’ll tie it all together in the conclusion of this post. See you there.
Steve Toth

Steve is an SEO Consultant based in Toronto, Canada. He works with enterprise brands to construct SEO strategies that get results. He is also the founder of SEO Notebook which is a weekly SEO strategy email with over 8,000 subscribers.
Moving forward, competition will continue relentlessly. There is so much content on every topic now, that when Google tweaks relevancy signals, there’s still a glut of high-quality content to occupy the SERPs. The new makeup of the SERP satisfies users nearly identically, thus the quality of the search results doesn’t change between updates, Google still serves users the results they expect, and the wins from SEO are spread out amongst a larger number of sites. This creates a lot of uncertainty and it means that rankings become more precious and volatile when there is a long line of quality content to take its place. In the end, it deters people from investing in SEO when winner take all scenarios become less common.
A good way to mitigate SERP volatility is to provide full topical coverage and to concern yourself with ranking large sets of pages that all benefit from each other’s traffic. This diversifies you and helps you make sure that you’re present in the buyer’s journey even if one of your pages drops out temporarily or for good (hopefully not).
The other thing I’m having success with is not letting your supporting and money page content go stale. I like to iterate and incorporate Google Search Console keywords on a regular basis. It helps me rank for more related keywords and strengthens my pages as a whole making individual keyword ranking drops less of a burden.
Overall, SEO continues to have a bright future and in the end, you have to be able to make many decisions on a daily basis and hope that you’re right 80% of the time.
Matt Diggity

Matt Diggity is a search engine optimization expert and the founder and CEO of Diggity Marketing, The Search Initiative, Authority Builders, and LeadSpring LLC. He is also the host of the Chiang Mai SEO Conference.
Content generation still determines your website’s success in generating traffic and conversions. However, you can’t just publish several articles on many different topics and expect to get good rankings for all of those topics. Google now considers topical authority – that is, how relevant a piece of content is to the search topic – as a ranking factor.
Topical authority as a concept has been around for the past six or seven years. However, it had gained a lot of traction since 2019, when Google announced its BERT model as part of its push towards what I call a “semantic web”. BERT, in particular, seeks a deeper understanding of the relationships between words and concepts in human language – two essential elements in semantics.
Under the semantic web, each website or page has a different depth of coverage for specific topics. These entities share attributes with other entities – what we call topic ontology. Furthermore, an entity has relationships with other things, whether on the same level or if one entity is a sub-topic of another – in other words, its taxonomy.
Here’s a real-world illustration of ontology and taxonomy. Pigeons and fruit bats have a few things in common: both are warm-blooded animals with wings and the power of flight. However, when we look at their genetic relationships, we realize that pigeons are more related to dinosaurs than fruit bats, which are more closely related to wolves and zebras.
These relationships lie at the heart of semantic SEO, which is gradually taking over the space currently occupied by rule-based ranking systems. With the growing usage of natural language processing in search engines, the need for semantic SEO is greater than ever.
To maximize your site’s semantic SEO, you need to establish its topical authority. To do this, you first need to look at your site and analyze its content. Are your articles related to each other? Does each article complement what you say in other related pieces of content? Are you trying to cover too many unrelated topics? Running a quick inventory of your site content will tell you a lot about your content strategy (or lack of one).
Once you’ve looked at your site content, you need to look at your audience and possible search intents. These will depend heavily on your site’s niche. For example, if your site sells doggie treats, your content will have to cover different types of goodies such as doggie biscuits, soft treats, jerkies, dental chews, and rawhide. In addition, you can publish content about using treats as an obedience tool, making jerky at home, treat ingredients, or types of treats to avoid.
Thinking of different types of content to cover an entire topic can be a tedious process, which is why you will need visual tools such as topical maps. These are similar to mind maps but with additional layers of insight. A topical map revolves around a central topic, which you then surround with either topic categories or question words. You then create content related to those sub-categories.
Here is a topic map I created on Answer The Public for the “ treats” example above:
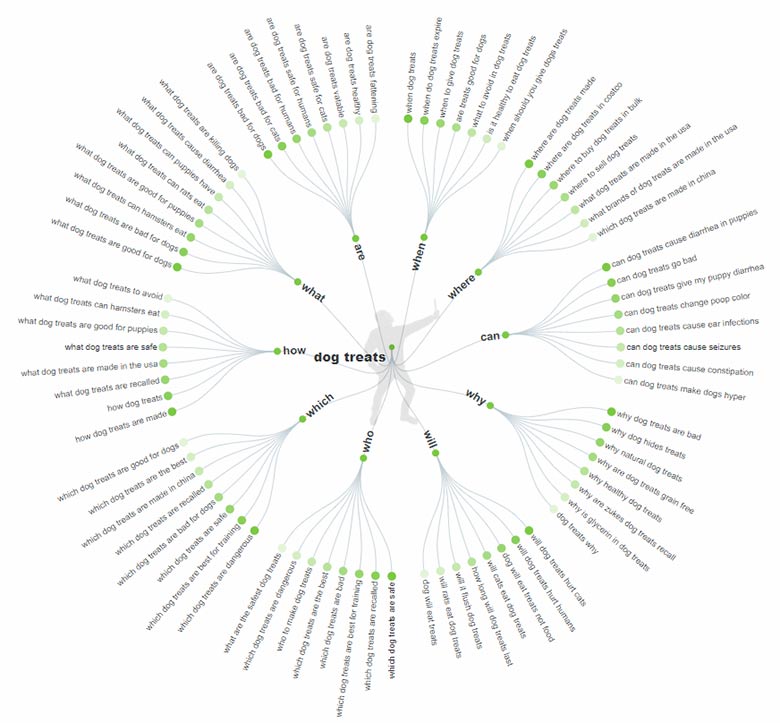
Each of the suggested topics is an opportunity to increase your topical authority. People who are searching for “why hides treats” are just as likely to ask “can treats go bad” or “will rats eat treats”. You want your site to answer all those questions and position itself as the go-to resource for all things related to treats.
In a nutshell, topical authority and semantic SEO go beyond keywords and user intent. They try to cover any possible questions a user may have about a specific topic through relevant content even before the user thinks about asking those questions. To achieve this goal, you need to do extensive research on your topic and build an entire ecosystem of content around it.
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR

Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR is the founder and owner of the Holistic SEO & Digital. He publishes SEO Case Studies, Researches, and Detailed A/B Tests along with their results and regularly attends webinars, conferences, and SEO-related events.
I define an SEO Trend as an intense interest in a new technique, perspective, or understanding that starts a change for SEO as a whole. An SEO Trend might be about an SEOs’ perspective or techniques, or it might be related to the Search Engine’s official announcements such as Page Experience Algorithm, or Spam Update Announcements.
In the coming years, there is one SEO Trend that will change our understanding and perspective on SEO. What’s more, it’ll change the very way we do SEO.
That trend is Semantic SEO.
Entity-oriented Search and Structured Search Engines along with the Semantic Web are continually changing the organization of information on the web. Since Google is a hybrid Search Engine, it uses Hypertextual Connections, Phrase-based Indexing, Social Proof along with Semantic Connections between Concepts, and the intents around them.
Semantic SEO is closely related to Natural Language Processing, its understanding, and generation.
In the future, SEOs will have to understand:
- Named Entity Recognition
- Semantic Role Labeling
- Relation Detection
- Entity Extraction and Resolution
- Entity-Cause Pairing
- Entity-Emotion Pairing
- Question Generation
- Question-Answer Pairing
- Part of Speech Tag
- Onomastics
- and more
All of these terms are closely related to Semantic SEO via Natural Language Processing. Understanding Entities, Dominant, and Minor Search Intent, Possible and Related Search Activities, Entity Type, Attributes, Attribute Relatedness and Popularity, or Semantic Dependency Tree, Query Parsing and Processing for Entities and Phrases are necessary to create a Topical Map and be able to have a Topical Authority within a group of contextual-knowledge domain.
Due to the terms, concepts, and deep understanding of Semantic SEO, Natural Text Generators will be more and more popular. The majority of SEOs don’t know which entity, question, answer, or term should be on which page, and which page it should be connected from which term with the help of Semantic Annotations.
Thus, Natural Language Generation and Optimization for SEO will be popular.
Content producing agencies, writers, and authors will try to use AI to write faster, deeper, and better. Google and other Search Engines will try to find which author and source (website) have the real expertise, usefulness, and function as a real-world entity.
The rising content supply can increase the quality threshold, and crawling costs for the search engines to protect their indexes and their quality. Thus, AI and Content Generation might be a topic for Google Search and Quality Teams in the future with the possibility of coming updates.
Besides Semantic SEO, coding, data science, machine learning, and deep learning will be more normalized terms and skills for SEOs in the light of coming years via Headless CMS, Design, or User Behavior Analysis and Quality Controls for factual writing, and useful serving. From coding to design, from data science to machine learning, natural language processing, or generation, SEO will continue to rise as a complex art and science.
To learn and implement Semantic SEO, you can try to use the methods below.
- Learn the difference between keywords and entities.
- Understand the entity types and type-dependent entity attributes.
- Know how to generate questions, and pair the related answers to those questions.
- Understand how context can shift with even a single word.
- Learn the terms WordNet, N-Grams, and Topical Distance
- Use Google Auto-suggest to find the variable parts of queries.
- Understand the related search activities and possible search intents.
- Learn how to create contextual bridges between two different entities based on a query.
- Get used to reading Google Patents, Microsoft, and IBM Patents (Also, Apple is coming).
- Crawl the competitors’ sitemaps. Filter the pages for certain topics.
- Crawl and extract the headings, questions, and statistics from your competitors’ content.
- List all the entities from your competitors’ content. Understand how they connect things to each other.
- Use the Google Knowledge Graph API to understand entities.
- Use Programmable Search Engine to understand Search Engines’ perspective to the entities.
Piecing it Back Together
If you’ve read through all the content from the top, you’ll notice that the points all seamlessly flowed from one idea to the next.
We started with how as an SEO, you must cover a topic in its entirety with multiple assets that benefit from each other’s traffic. This will help diversify your content which will help your site deal with unstable and competitive SERPs.
But, there is a hidden point here. If you do a good job of covering an entire topic, you will attain topical relevance for that topic. This is because Google now understands topics as entities and part of Google’s entity understanding is the link between topics and subtopics.
Although this might seem a little complex, there is no question that grasping this will pay off in the long run.
In this post, I’ve tried to organize the information in a way that it’s like peeling an onion. Hopefully, with each new section, you were introduced to a deeper layer in the Google entity onion.

