Website optimization is an intricate and multifaceted process that requires significant investment. Understanding where your budget goes helps you save money on effective strategies. So if you want to see how SEO impacts your business, it’s important to calculate the ROI of SEO.
This article will delve into the intricacies of SEO ROI, including what it is, why it’s essential, and how to measure it effectively. We will explore how an SEO professional, whether you’re from an agency or in-house team, can leverage ROI measurement to showcase the value of your work and make informed decisions to optimize your strategies.
Key takeaways
SEO ROI involves comparing the financial gains from conversions powered by organic traffic to the resources you invested in optimizing your website. It helps you know where your budget is going while saving you money, simply by focusing on effective strategies.
Here is your three-step approach to measuring SEO ROI:
- Calculate your SEO investments, including staff, freelancers, tools, and more.
- Estimate the value of your organic traffic conversions by tracking ecommerce and lead data.
- Use this SEO ROI formula:
(Value of organic conversions – Cost of SEO investments) / Cost of SEO investments
Measuring the ROI of SEO can be complicated for various reasons. Here are the main challenges and some possible solutions to them:
- Choosing attribution ******: Figuring out which marketing attribution ****** can best help you measure SEO’s impact can be daunting. ****** like first-touch, last-touch, linear, and others distribute credit differently among touchpoints. Choose attribution ****** wisely according to your business specifics.
- Accounting for brand impact: While it’s challenging to pinpoint SEO’s impact on brand awareness, focus on measurable factors like non-branded organic conversions. Monitor your brand’s organic traffic surges and the effects of SEO campaigns on them.
- Measuring SEO’s impact on retention: Existing customers are highly valuable. Monitoring the journey of your website’s returning users could help you get to know the interests of your customers and result in a higher retention rate per your SEO efforts.
- Time to get ROI: SEO takes time to bear fruit. Positive ROI typically appears in 6-12 months, with peak results happening in the second or third year. Make sure your team and the client knows that SEO is a long-term game.
- SEO’s unpredictability: Unlike paid advertising, you can’t turn off SEO at the drop of a hat. SEO’s impact is ongoing, making it difficult to control. Despite this, SEO is still a powerful marketing channel for building a strong online presence over time.
What is SEO ROI?
SEO ROI (Return on Investment) is a metric that quantifies the profitability of your SEO efforts. It involves calculating the financial gains generated from organic traffic and conversions relative to the resources invested in website optimization for search engines. By measuring SEO ROI, businesses can assess strategy effectiveness, make data-driven decisions, and better allocate resources.
Why measure SEO ROI?
SEO ROI is a valuable metric for business owners who need to decide if their marketing investments are paying off. Still, other parties like agencies and in-house SEO teams also stand to gain from measuring the ROI of SEO. Here’s why:
- Optimizing SEO strategies for maximum efficiency
ROI insights help you decide where to allocate your SEO resources for maximum impact. Campaigns with higher ROI are usually more feasible and may warrant increased investment, while those with lower or negative ROI might require reevaluation.
This can also help you understand the feasibility of future SEO campaigns and establish more realistic expectations and goals.
- Proving the success of SEO work
ROI helps SEO specialists demonstrate clearly how their efforts impact the business’s goals as far as its performance and the successes that resulted from their SEO initiatives. For agencies, demonstrating ROI to clients strengthens their relationships with clients and justifies the services rendered. In-house SEOs, on the other hand, can use ROI data to secure budget approvals and showcase the impact of their work to higher-ups.
In essence, ROI acts as a compass, guiding SEO efforts towards campaigns that positively contribute to the business’s financial well-being.
How to measure SEO ROI: a three-step approach
To calculate ROI for SEO, follow these steps:
- Calculate your investments.
- Estimate the value of your organic traffic conversions.
- Calculate your ROI.
Now, let’s break down each step.
Step 1: Calculate your SEO investments
First, you need to calculate how much you’re spending on SEO. As for in-house SEOs, your investments should include the following:
- Cost of in-house staff work: This includes various departments: the SEO, content, design, and development teams. Break down the cost of their work to an hourly or daily rate and track all time spent on SEO tasks.
- Payments to freelancers or external agencies: This may be services such as PR or link building activities.
- Cost of SEO tools: Subscription prices depend on your needs. For example, SE Ranking users who have large teams and manage multiple projects opt for subscription plans that include multiple user seats, with pricing starting at $109 per month. Singular users with modest data needs can get started with the Essential subscription, which only costs $55 per month.
- Other SEO related expenses: Any other costs related to your SEO efforts
For agencies who need to calculate the ROI of SEO for their clients, their SEO investments would essentially be the amount billed to their clients for their services.
Get precise data for each of the factors listed above. The accuracy of the calculations depends on it.
Step 2: Estimate the value of your organic traffic conversions
Measuring the complete impact of SEO is complicated for a number of reasons. For instance, there’s a time delay in seeing the optimization results in search rankings and traffic. User behavior also adds complexity, as visitors often interact with the site multiple times before converting. SEO also affects metrics like brand visibility, user trust, and customer lifetime value, each of which are harder to measure.
We’ll further discuss the challenges of measuring SEO ROI in a later section.
For now, let’s focus on what can be directly measured. For example, we’ll begin by looking at the value of each conversion or lead.
Measuring the value of ecommerce transactions
The best way to start collecting ecommerce conversion data is to set up ecommerce tracking events for your website in Google Tag Manager. In brief, you need to create a tag with an event and its parameters. For more details on this, follow Google’s instructions.
Once you start tracking these events, you can access an ecommerce report with all the information related to your online sales.
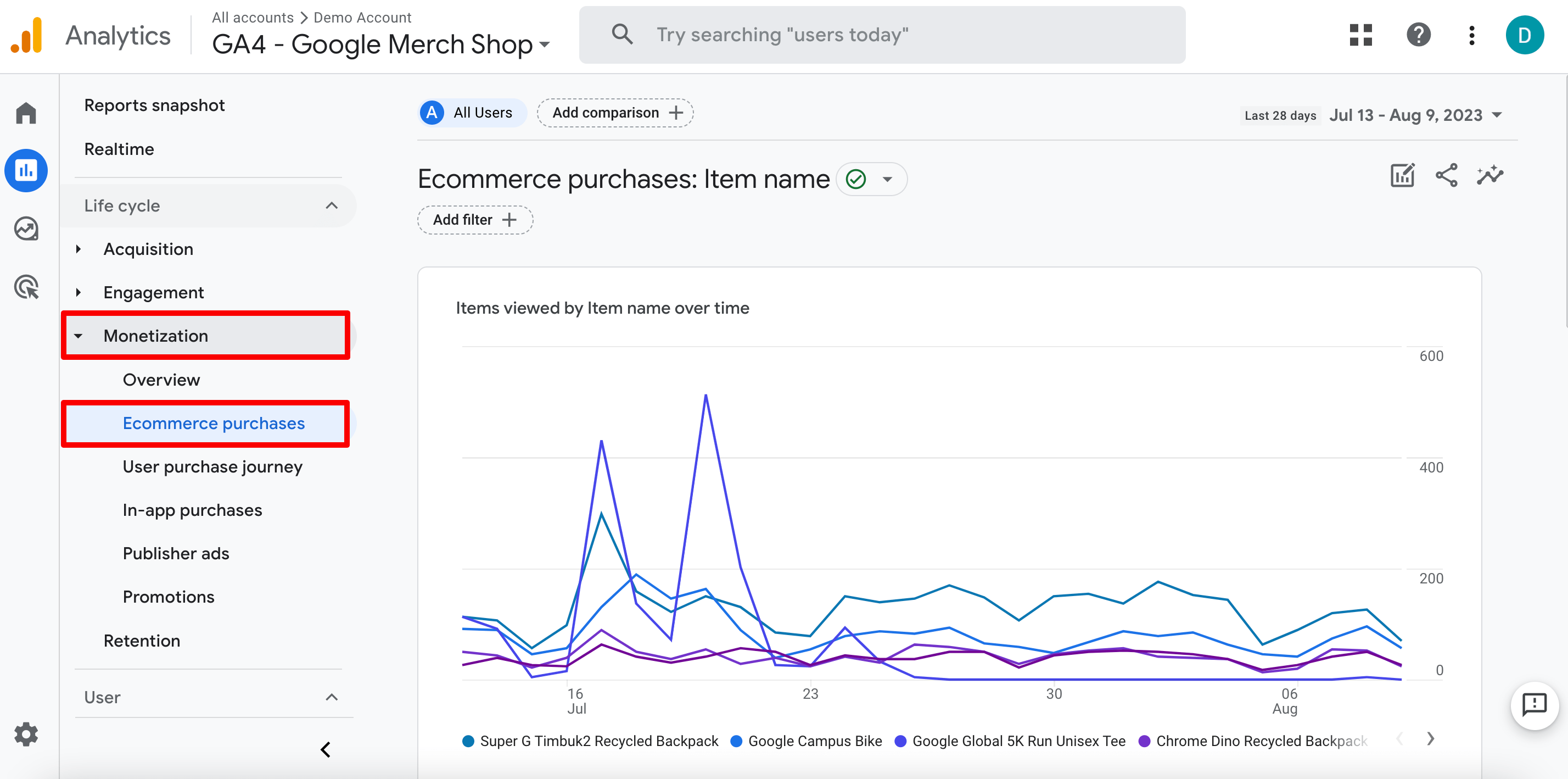
- Go to Reports ▶️ Monetization ▶️ Ecommerce purchases.
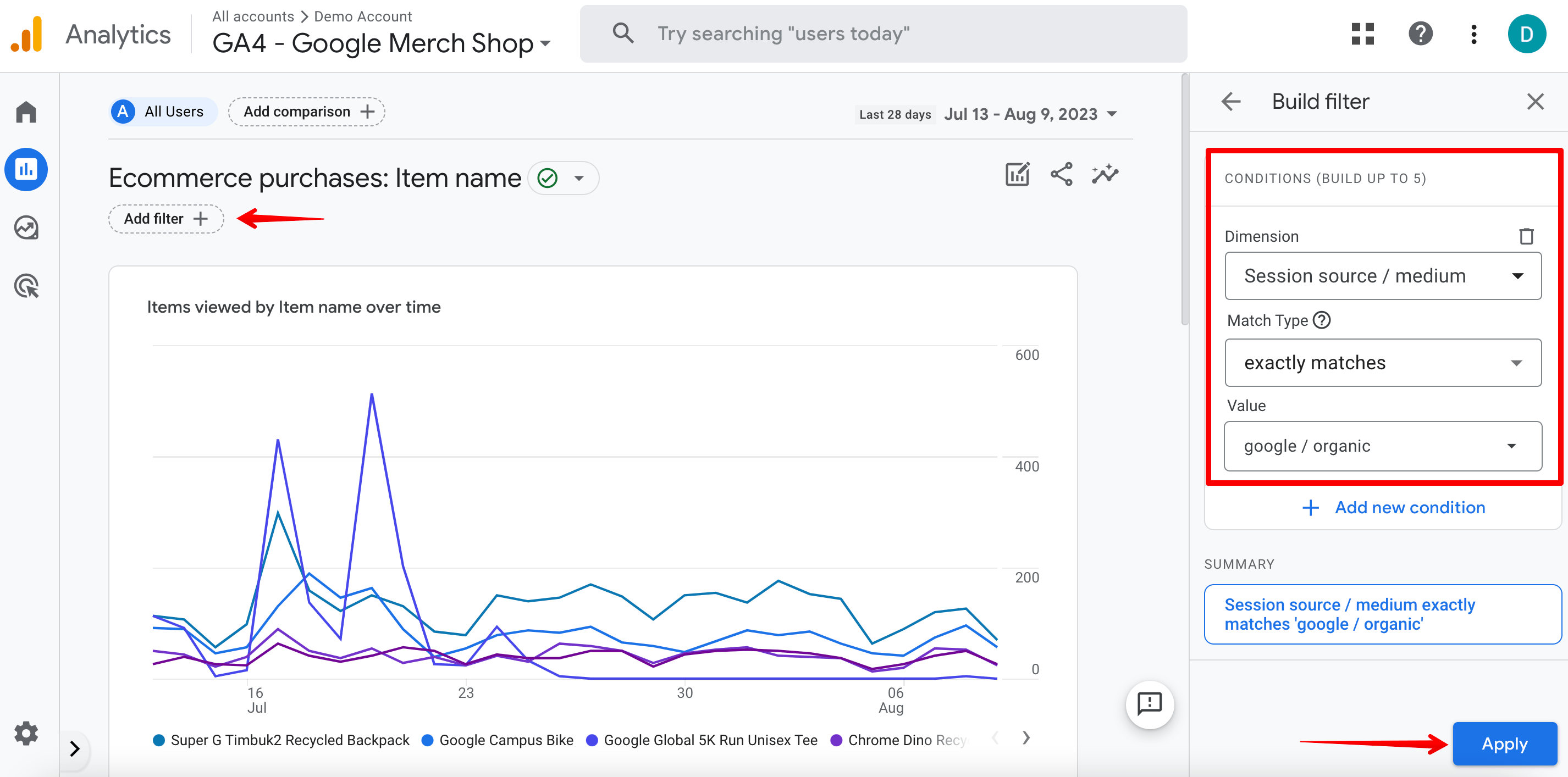
- Add a filter for organic traffic: choose the Session source / medium option and the google / organic value.
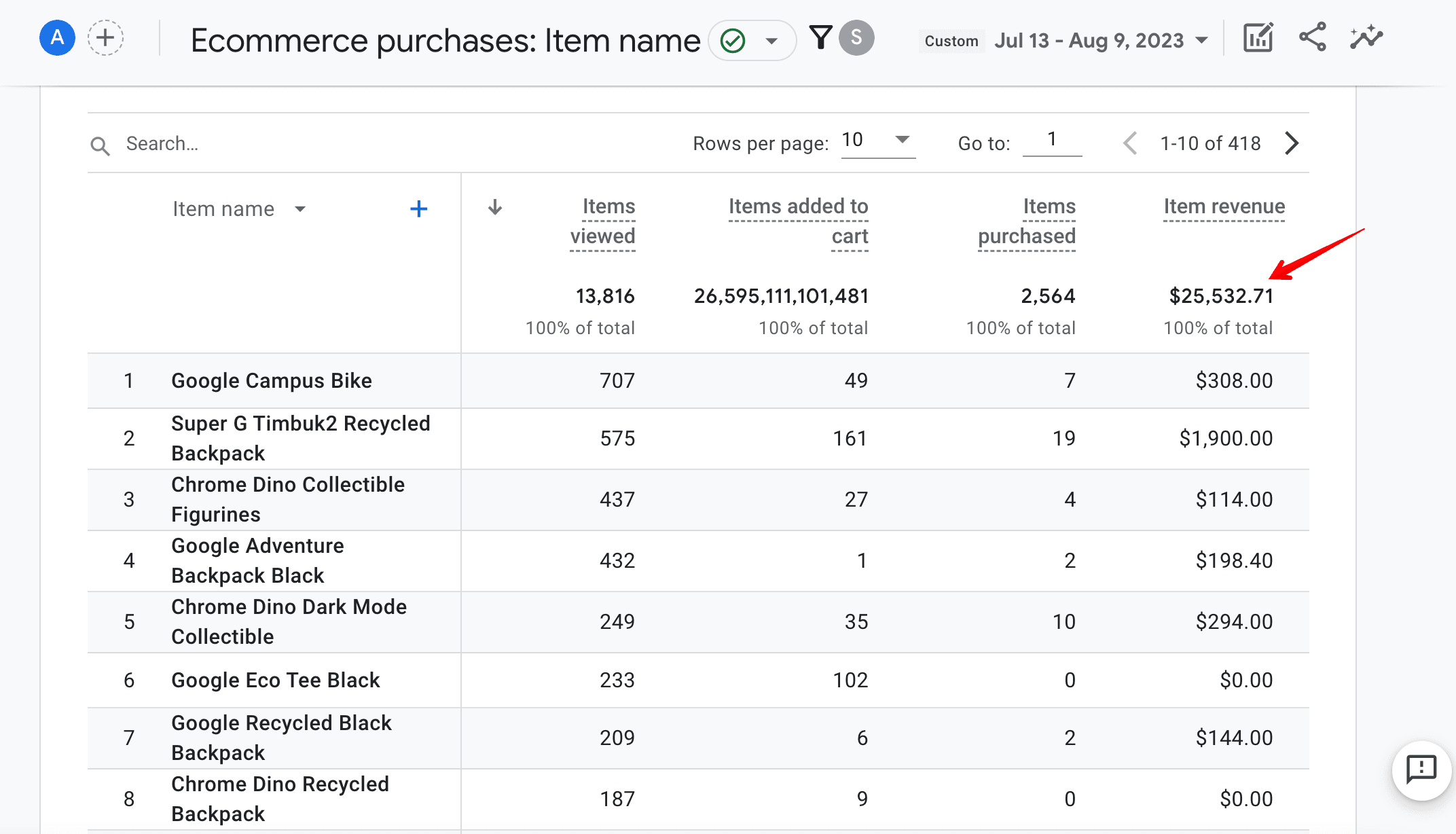
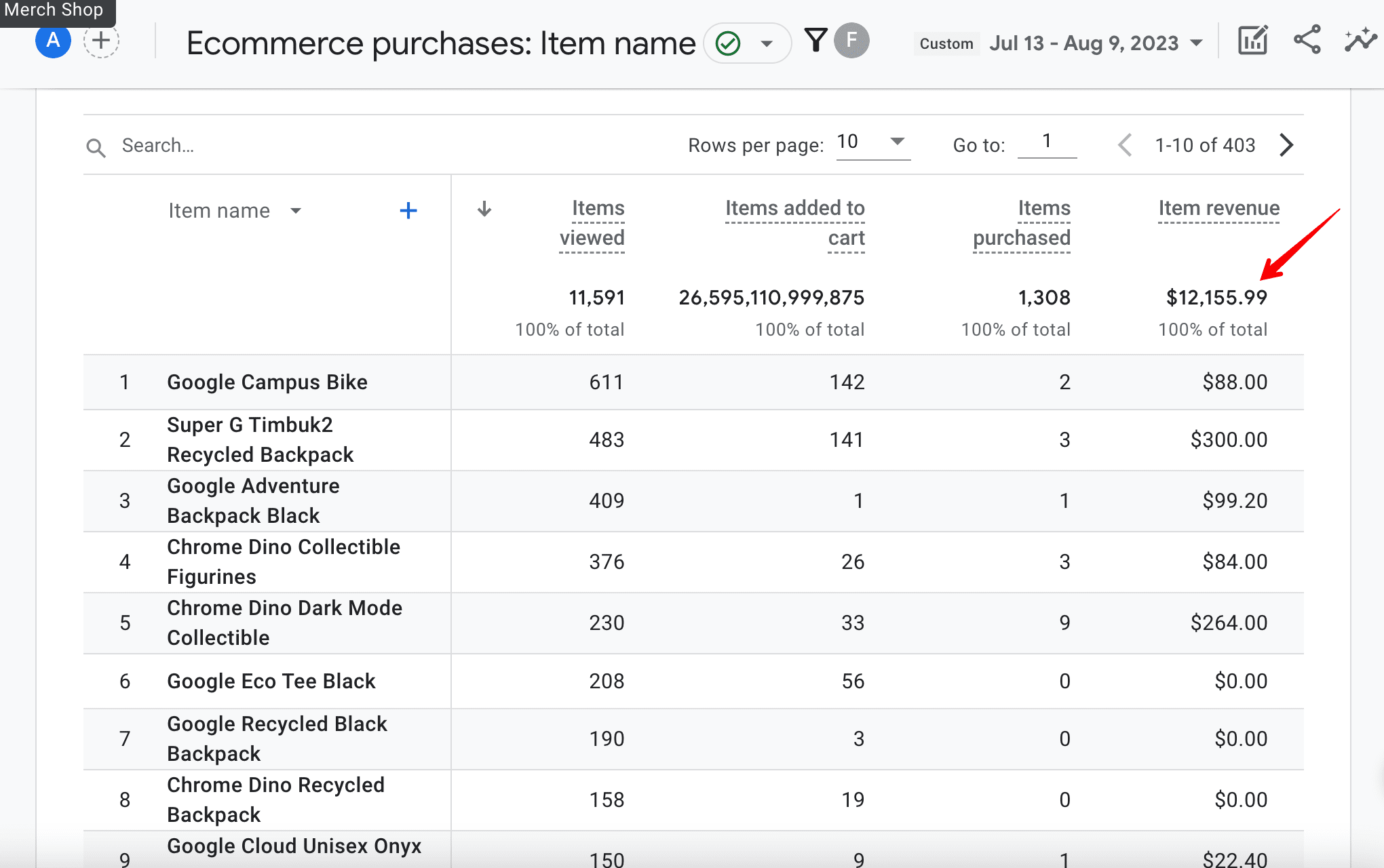
In the table below, you’ll see the item revenue from all users (new and returning) who visited the website from organic search and at some point made a purchase.
To determine the exact profit attributed exclusively to SEO, you can use the First user source filter. This filter only shows the revenue from users who visited the site from an organic search for the first time and then made a purchase.
Choose the First user source / medium option and google / organic value.
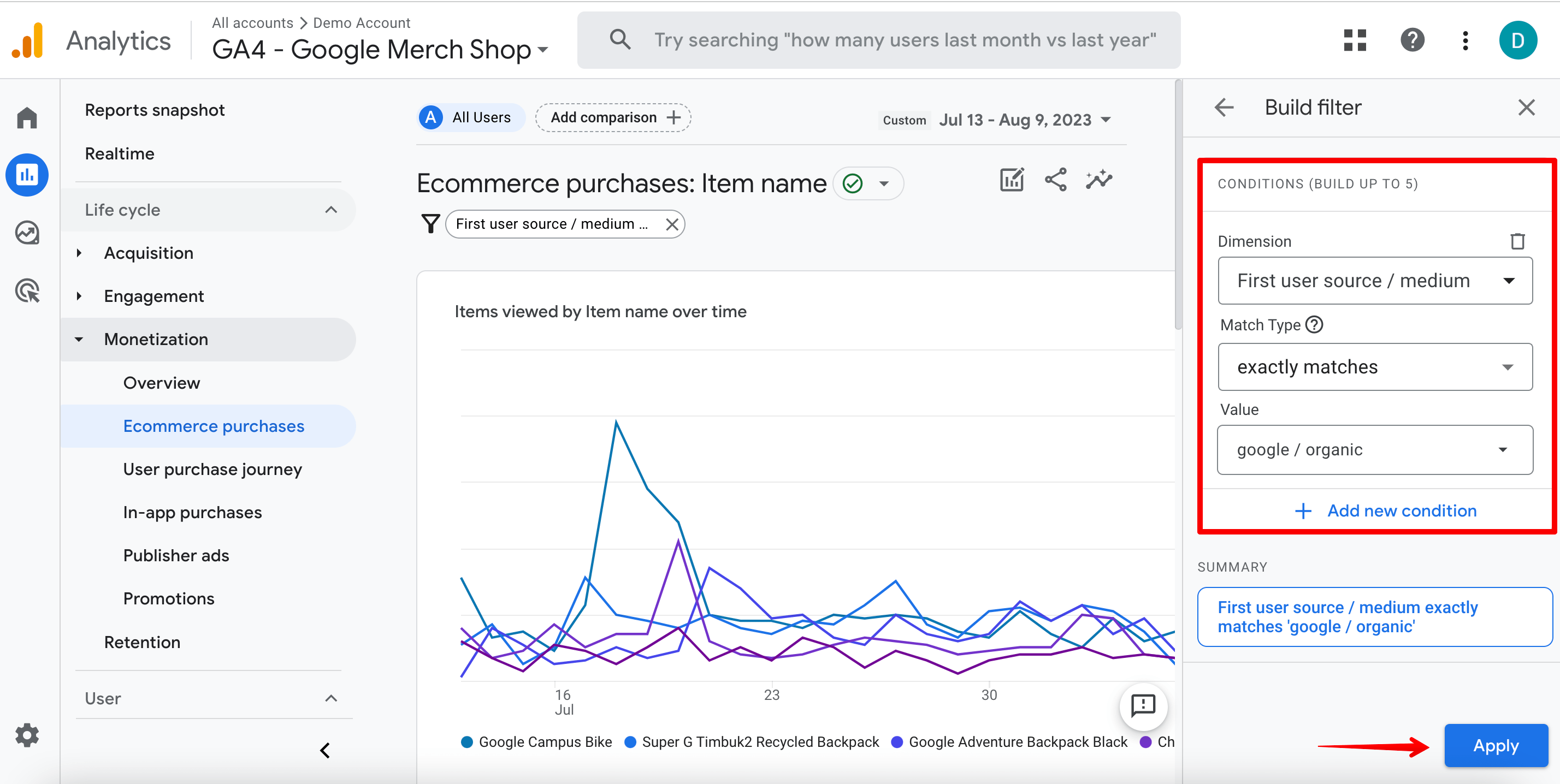
This method is widely used by marketers and SEOs because it attributes to your SEO efforts the initial interaction of users to your brand or product.
You can find this data even faster with the Insights option. Type item revenue from organic search [period] in the search bar. The tool will display the organic search revenue for the first user medium within the selected time frame.
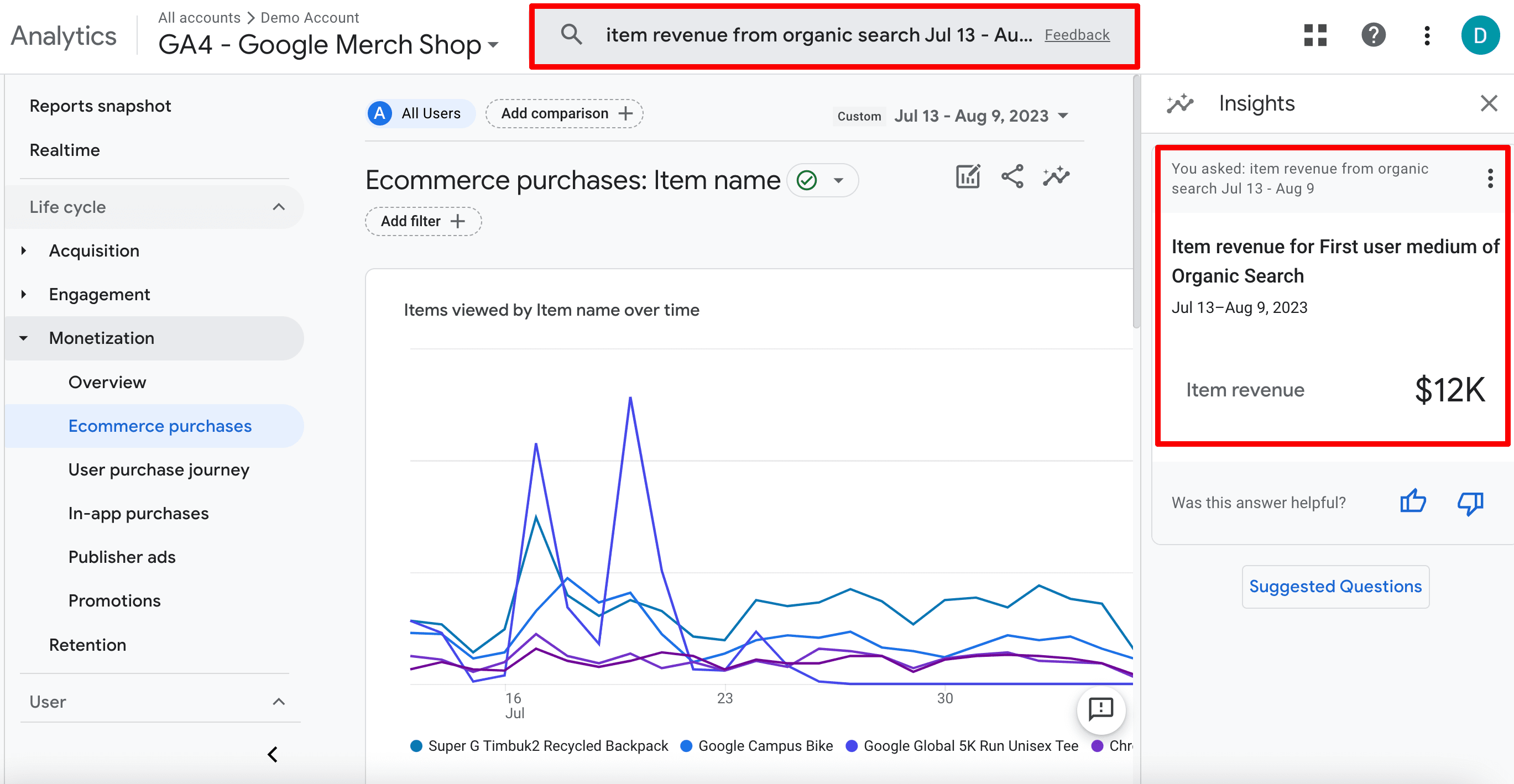
As you can see in the screenshot above, the revenue for the period spanning from July 13 to August 9 exceeds $12k. Keep these figures in mind for future calculations.
Measuring SEO leads values
If your website doesn’t directly generate sales, getting the exact data on how much revenue you generate is more challenging. The most accurate possible estimate involves assigning dollar values to new SEO leads based on past sales data.
Now, let’s break down the process of tracking these conversions step by step using GA4.
- Navigate to Admin ▶️ Events.
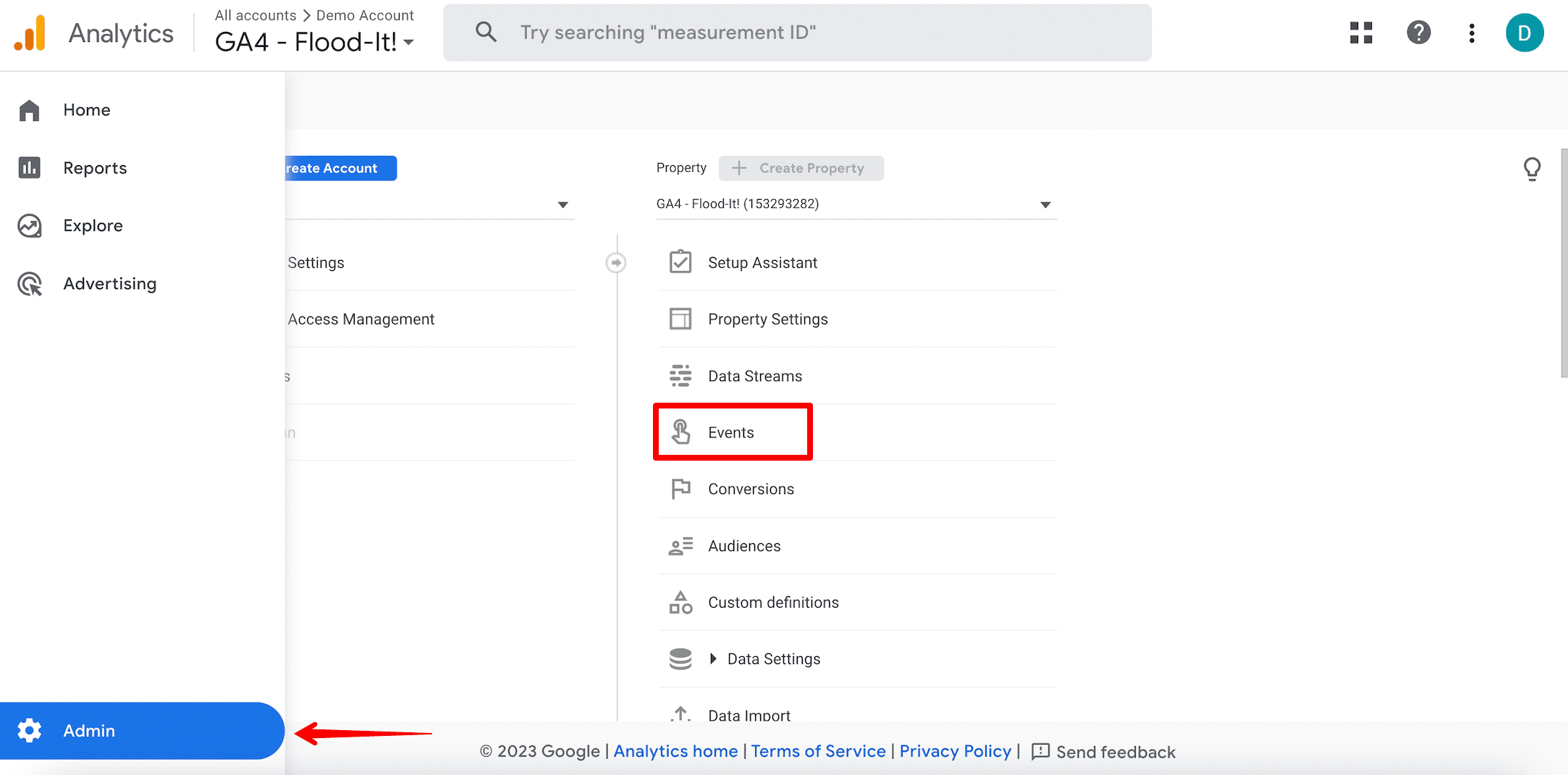
- Set up an event for every conversion. These goals can range from contact form submissions to free quote requests, and even to phone calls.
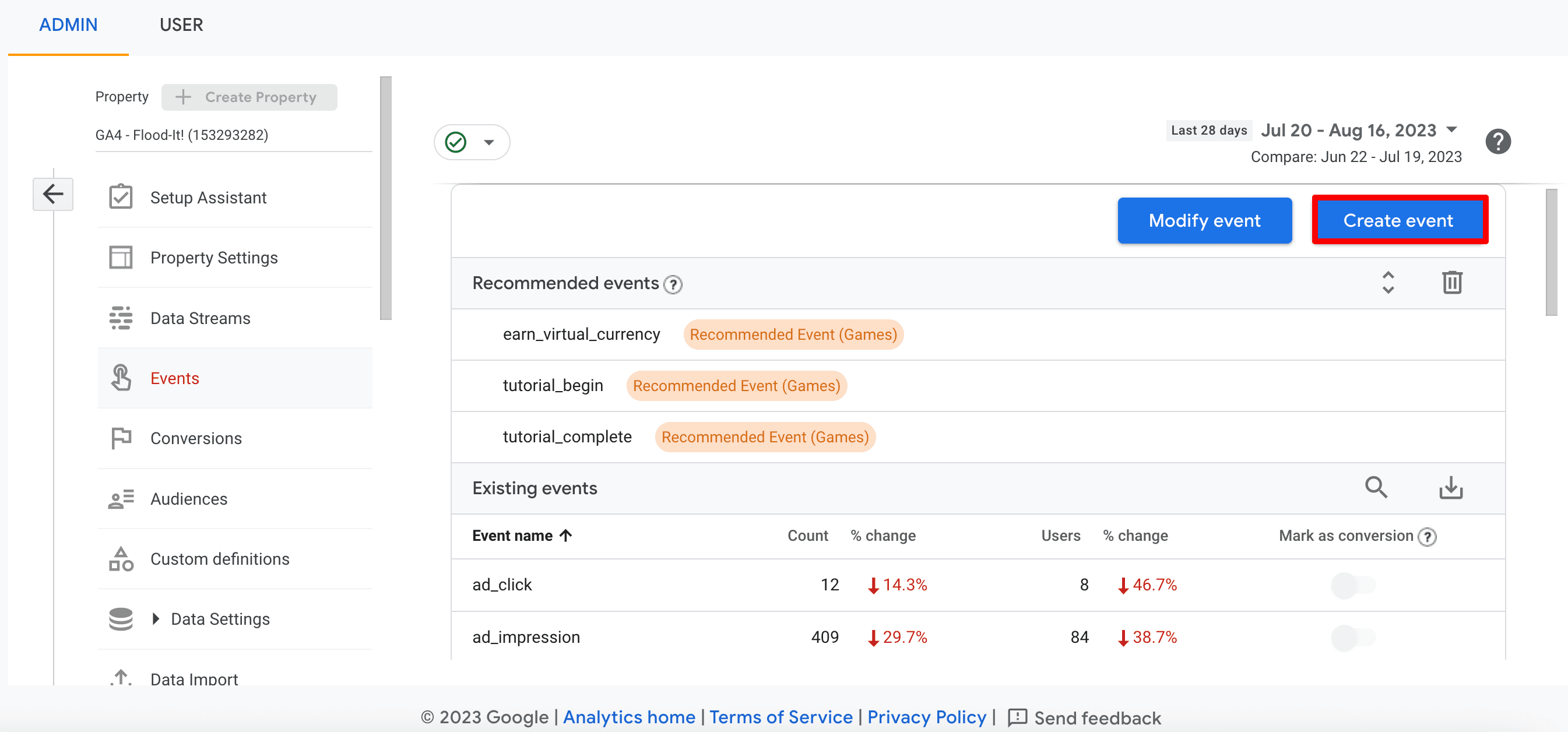
- Give your event a name. Then select your matching conditions.
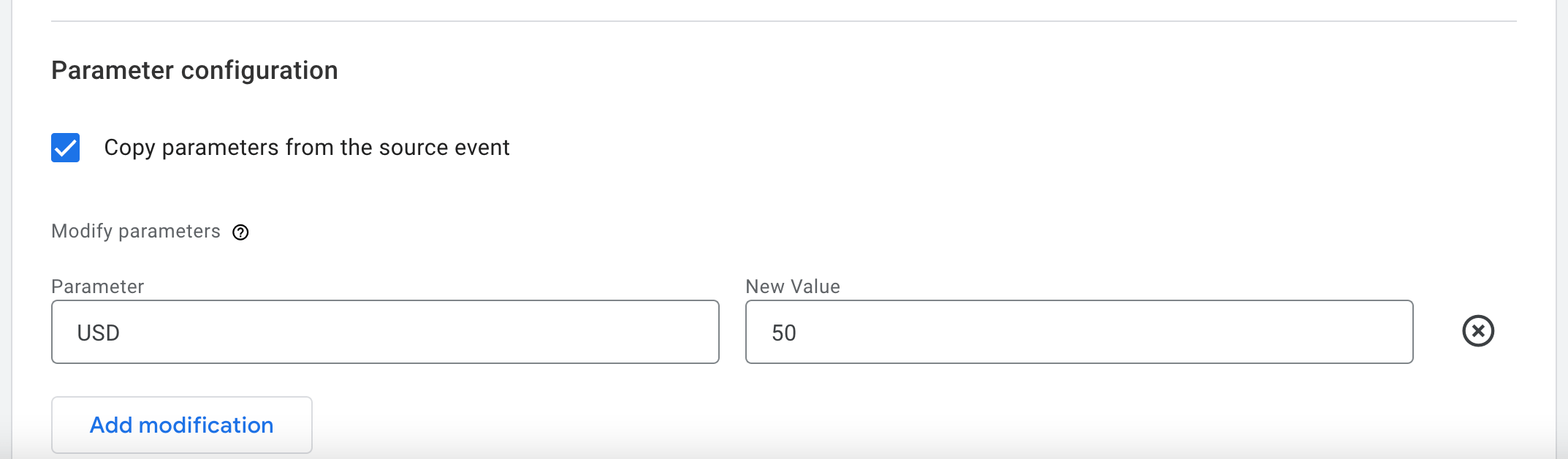
- Assign a monetary value to your conversion. In the Parameter field, enter a currency type (e.g., USD) and enter the value (e.g., “50” for 50 dollars).
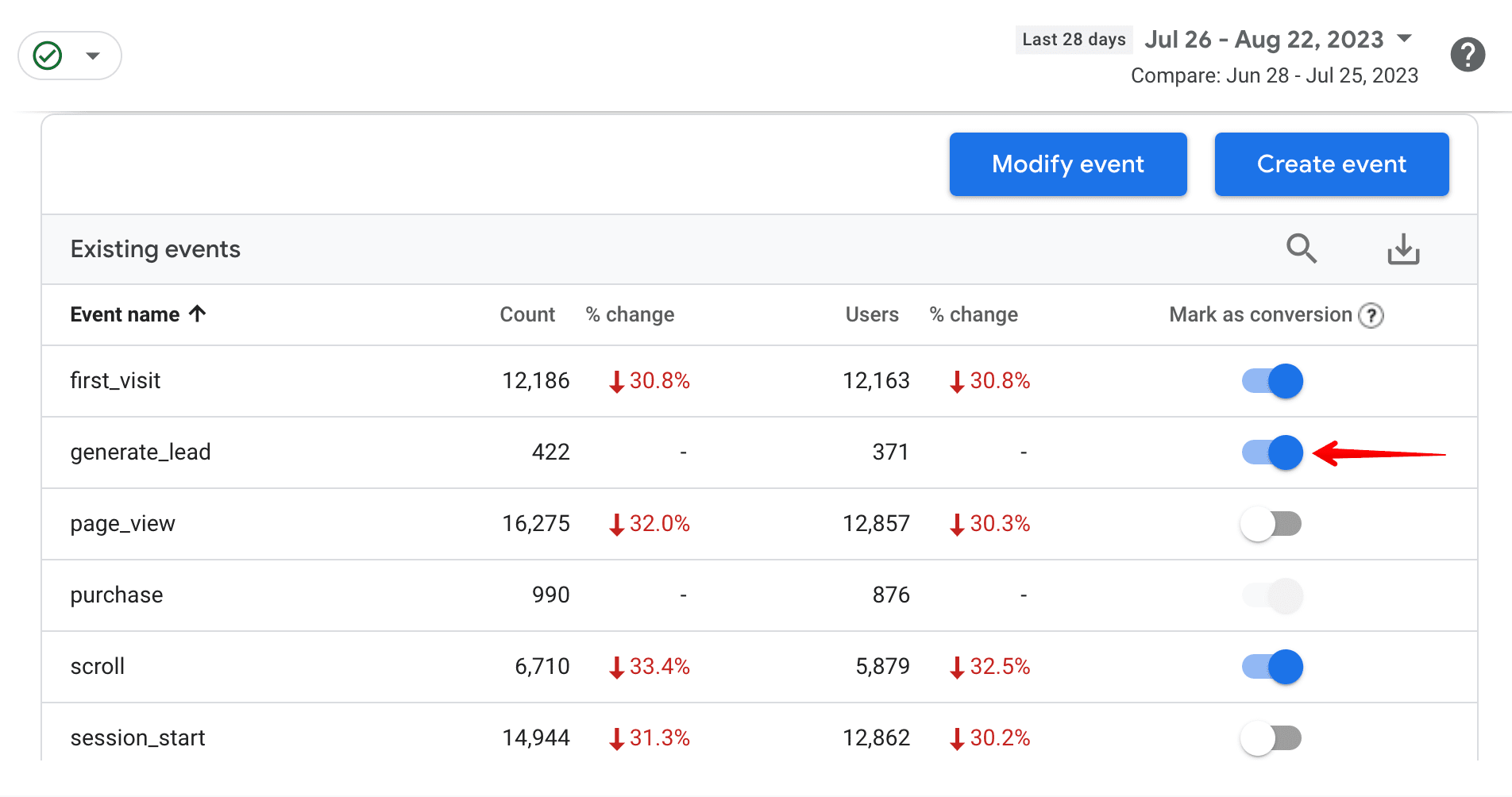
- You should see your event under Existing events. Toggle the switch under Mark as conversion.
- You’ll see your event as a conversion in the Conversions tab under the Engagement section.
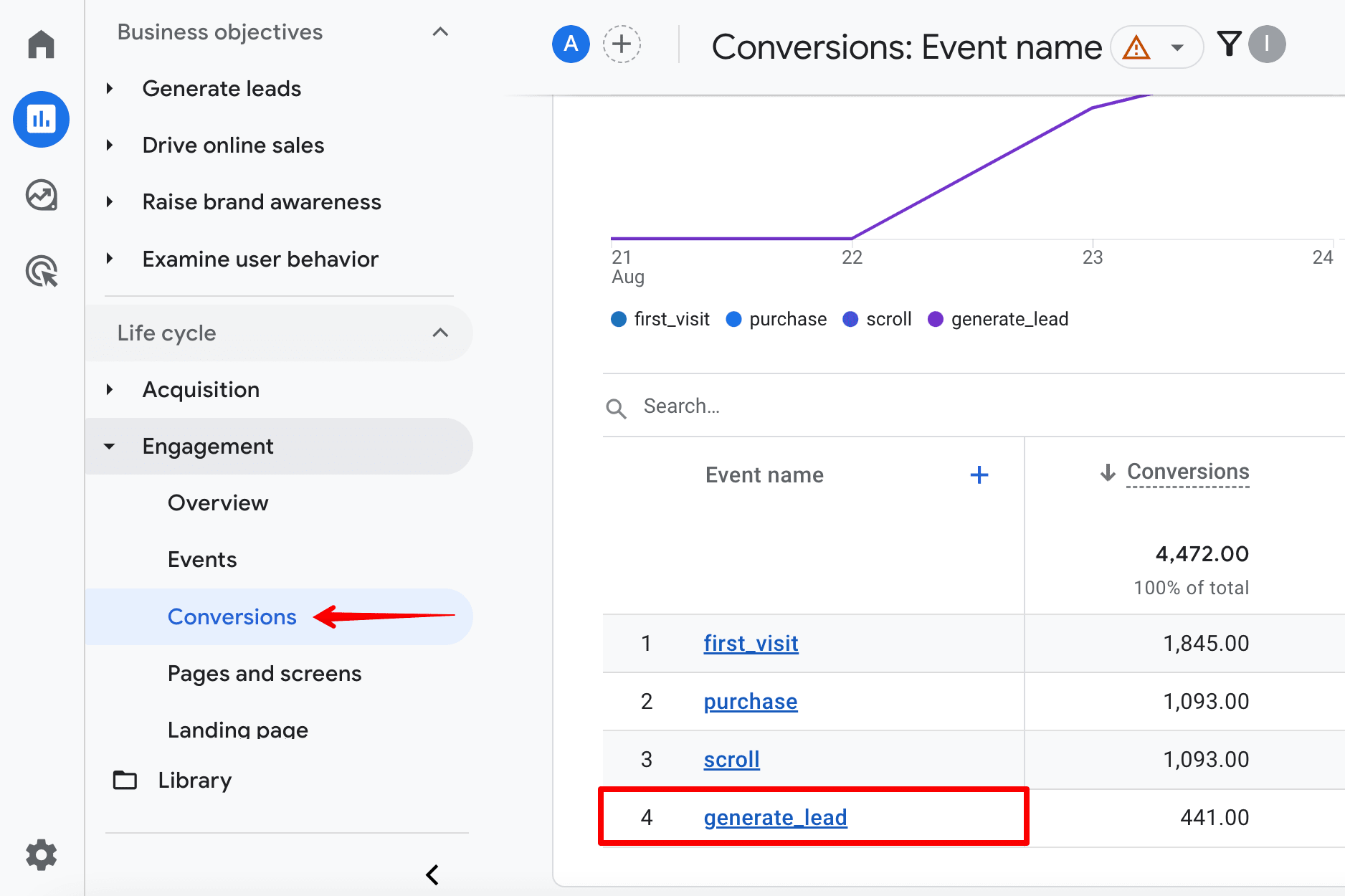
Each time an event is triggered, it is assigned a monetary value. This gives you the opportunity to measure your approximate revenue.
How do you know how much value to assign to each event?
The simplest way is by calculating:
Customer lifetime value x lead conversion rate
- Customer lifetime value refers to the total amount a customer is expected to spend with your business during the average lifetime of your relationship.
- Lead conversion rate is the percentage of leads you generate that turn into sales.
Let’s say that encouraging visitors to complete a contact form is one of your key website goals. You can assess the value of every lead. If your data reveals that about half of the leads (50%) that come in are accepted, and these leads have an average lifetime value of $1000, it makes sense to assign a value of $500 to this specific goal (1,000 x 0.5 = 500).
Step 3: Calculate your ROI of SEO
Once you’ve settled on the amount of money generated through your SEO strategy and within a specific period (e.g., a month), you can compare that sum with your SEO investment to calculate your ROI.
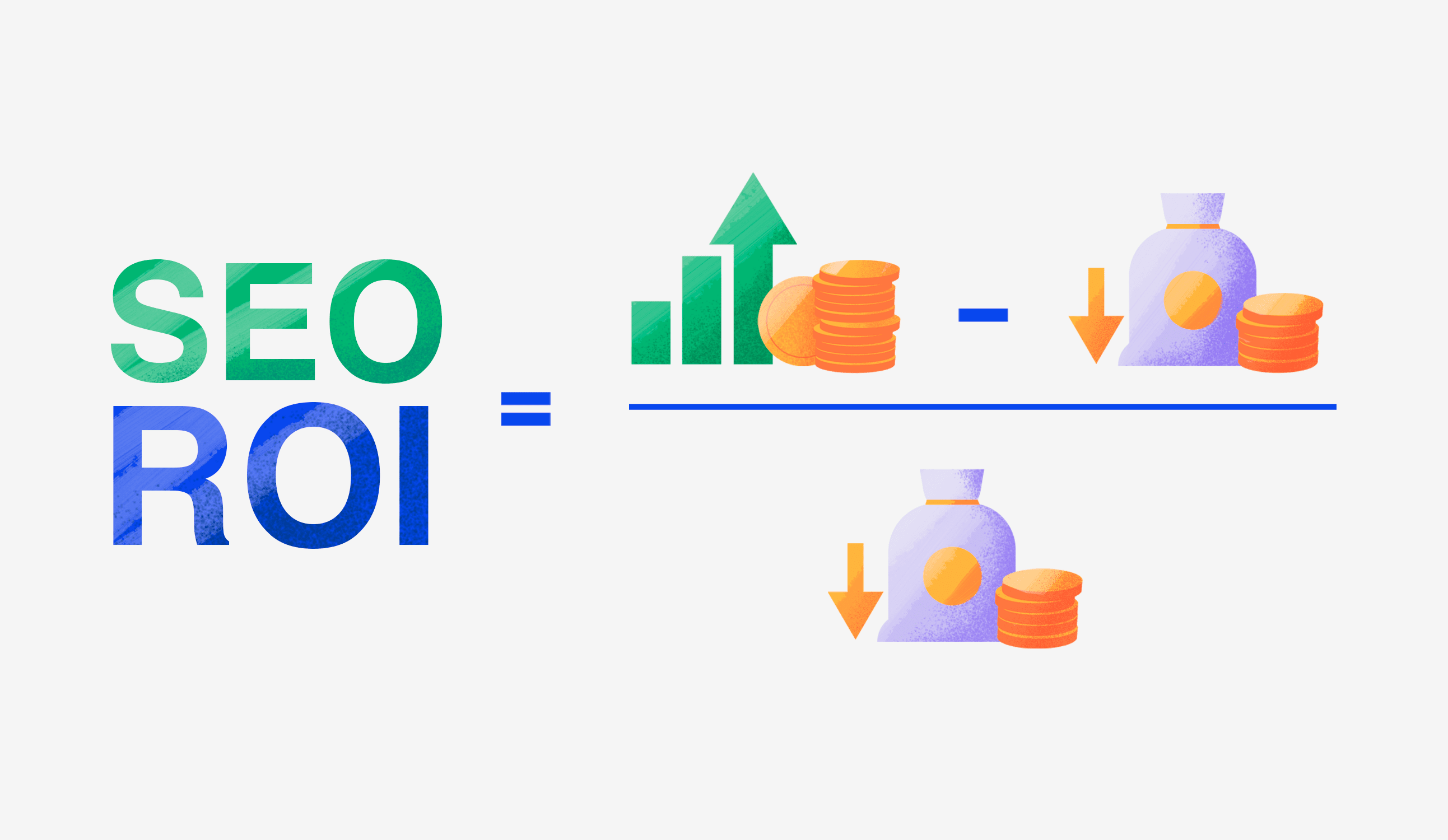
Here is the formula for calculating your SEO ROI:
Value of organic conversions – Cost of SEO investments
SEO ROI = ——————————————————————————
Cost of SEO investments
Let’s walk through an example. Suppose your organic channel raised $100,000 in one month. And the total cost of investment was $30,000.
Insert these figures into your formula:
($100,000 – $30,000)
——————————— = $2.30
$30,000
This means: for every $1 you spent on SEO, you saw a return of $2.30.
Next, multiply the resulting number by 100 to get your ROI as a percentage. Your ROI is 230% per month.
How to overcome the challenges of measuring SEO ROI
Measuring the ROI of your SEO efforts can be challenging. SEO is a long-term and complex strategy with many factors and variables that affect your website’s performance. Let’s look at a few different ways to overcome these challenges.
Choosing the best possible marketing attribution model
Selecting the right marketing attribution model is crucial for accurately measuring the impact of your SEO effortst.
A marketing attribution model is a strategy used in digital marketing to analyze and discern how different marketing activities contribute to sales or other desired outcomes.
Here is a list of the most commonly used ones:
- First-touch attribution: This model assigns all credit for a conversion to the first user interaction with your marketing, often the first click.
- Last-touch attribution: Here, all credit goes to the last interaction that led to a conversion, typically the final click before the user converted.
- Linear attribution: This model distributes credit equally among all touchpoints or interactions a user had before converting.
- Time decay attribution: In this model, more recent touchpoints receive a larger share of the credit, while earlier interactions receive progressively less credit.
- Position-based (U-shaped) attribution: This model assigns higher credit to the first and last interactions, with the remaining credit evenly divided among the interactions in between.
You can see this data in Google Analytics by going to the Advertising ▶️ Attribution ▶️ Conversion paths report.
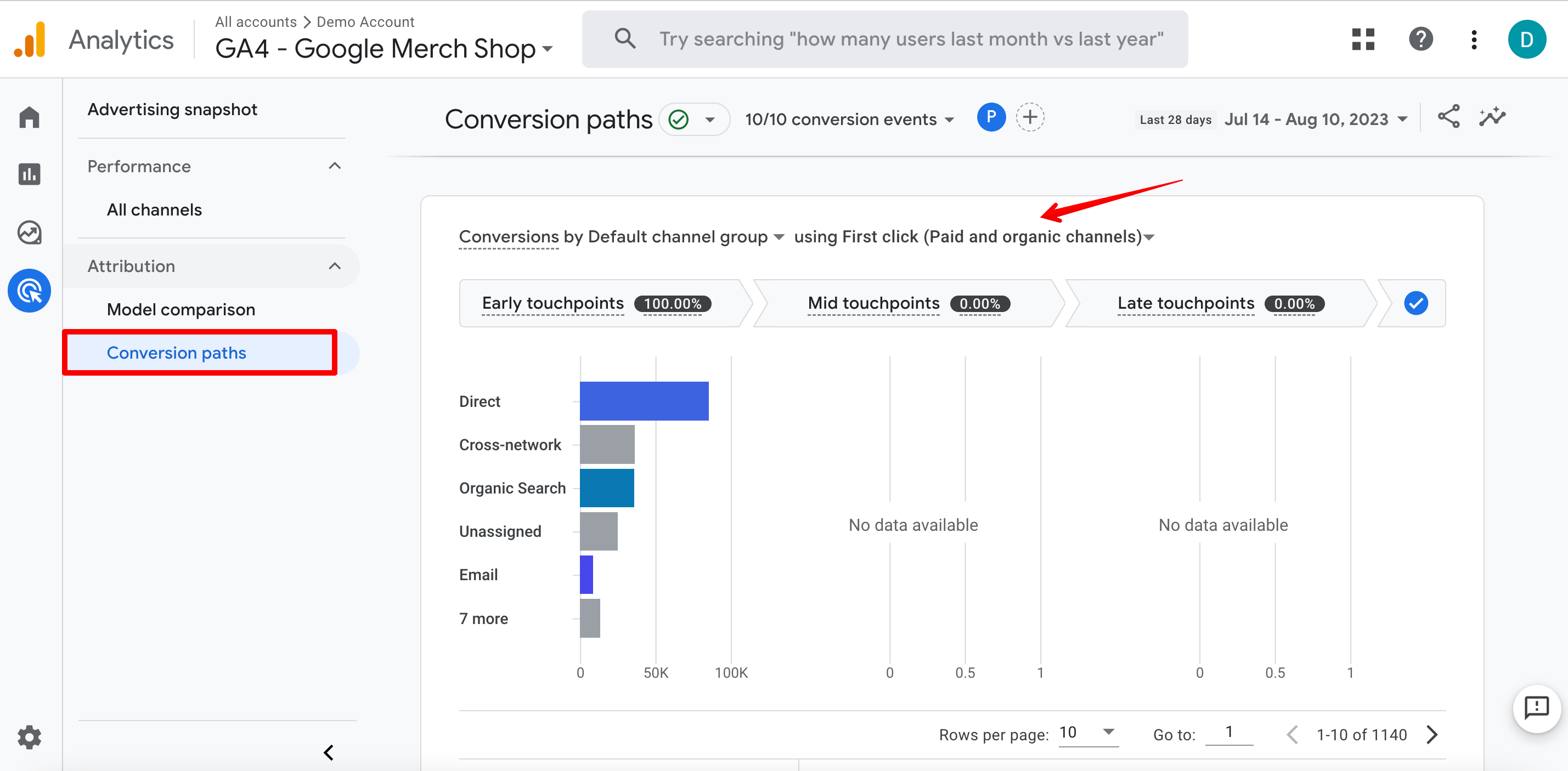
Let’s look at an example to see how these ****** work in practice.
Imagine a visitor who initially discovers your landing page through SEO, reads a post on your LinkedIn page, and eventually converts after clicking a PPC ad. First-touch attribution would assign 100% credit to SEO for this conversion because it was the first channel to interact with the lead.
Last-touch attribution would give all credit to the PPC ad.
Linear attribution evenly distributes the credit across all touchpoints. This means that SEO, LinkedIn, and PPC would each receive roughly 33% of the credit.
The main disadvantage of the First-Touch Attribution and Last-Touch Attribution ****** is that they disregard the contributions of other channels to conversions. This is why specialists recommend using the Linear attribution model or others like Time-Decay and U-Shaped. Unfortunately, these ****** have their drawbacks too—they require an experienced marketer to define accurate credit percentages and ongoing adjustments.
Different teams may assess touchpoints along the user journey differently based on their observations and experience with user behavior and marketing channels. SE Ranking, for one, uses different attribution ****** for different goals.

Vadym Onyshchenko
Senior Marketing Analyst at SE Ranking
When we need to grasp the type of audience brought in by different traffic sources, we employ a first-touch attribution model. We’ve opted for a 90-day conversion window since our users tend to take lengthy journeys on our site before committing to a purchase. For instance, a user might have initially reached our site through Facebook two months before signing up. Then, they could have interacted with our content through organic search and advertisements. Following their registration, they might have engaged with email newsletters, resulting in a final purchase.
****** rooted in the last interaction and other non-first-click ****** like the linear attribution model help us discern which sources are more effective at converting users into customers.
To enhance accuracy, work directly with your analytics team to develop a custom model that aligns with your business goals.
Measuring the impact of SEO on organic brand traffic
Every marketing method aims to raise brand awareness and attract potential customers through related searches. But it’s not always easy to measure the precise impact of top-of-the-funnel content, like guest posts or site articles, on brand awareness driven by SEO.
To tackle this, focus on measurable aspects, particularly non-branded organic conversions. This means looking at data about users who find and engage with your offerings naturally, not by searching for your brand name.
Also, pay attention to any sudden increases in organic brand traffic and the effects of specific marketing campaigns on it. These could stem from viral videos or well-timed PR releases.
For instance, let’s say you’ve been working on a series of posts about your brand and products on other websites. During this period, you observe spikes in brand-related searches, clicks to your website, and conversions. This strongly suggests that your SEO efforts are making a big impact.
Keep tabs on brand search query increases by using Google Trends.
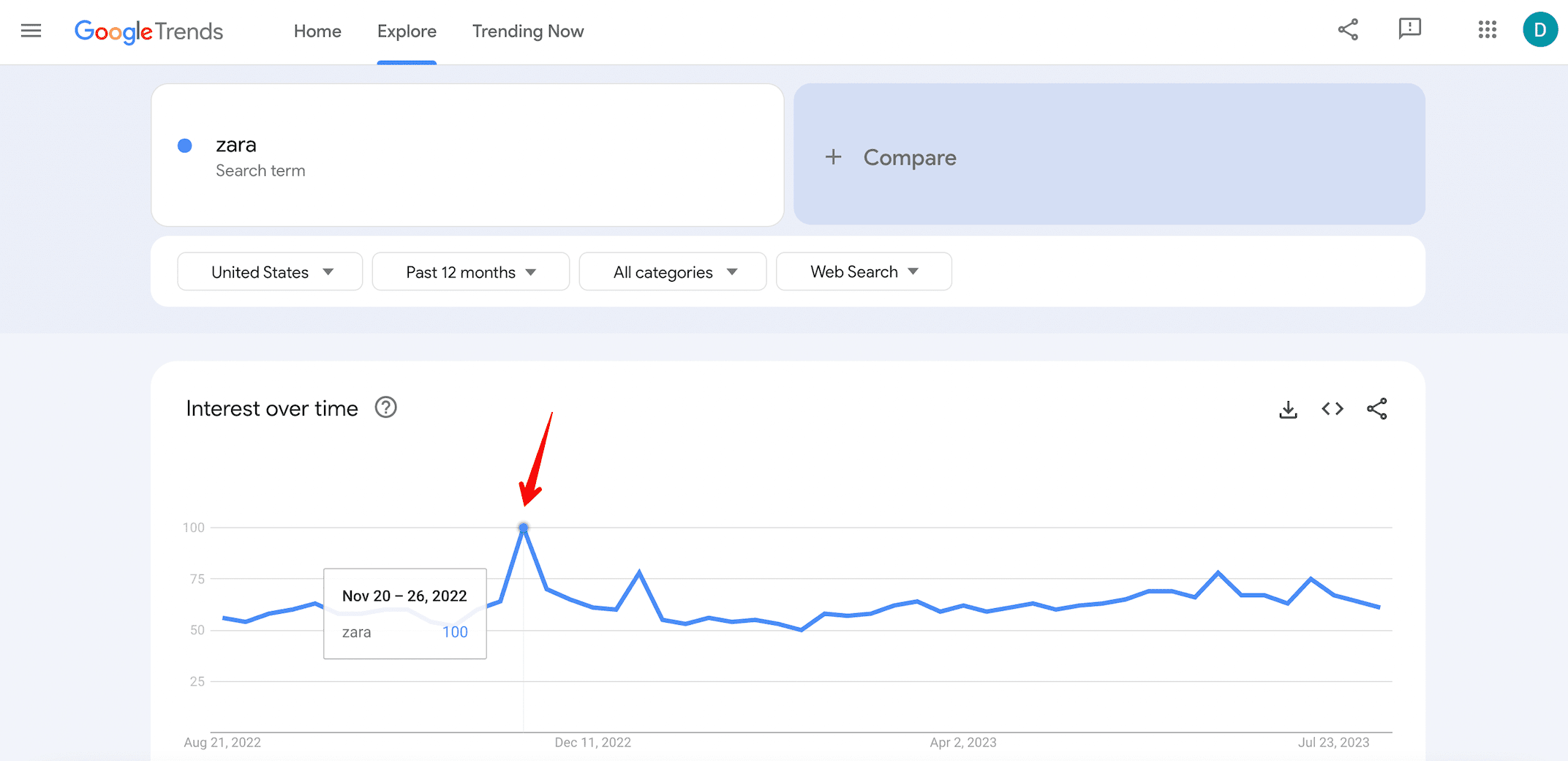
Then monitor the number of conversions through Google Analytics. The point is to compile data and track any surges of branded traffic that are resulting in conversions.
Measuring how SEO impacts customer retention
You might know that keeping existing customers is super important. They already trust your brand, it’s cheaper to keep them around, they have higher conversion rates, and they bring in stable, long-term revenue. This is why SEOs should pay special attention to retention.
In the realm of SEO, where you create lots of content as part of your strategy, specific components can have a big impact on customer engagement. This can potentially reduce the churn rate.
For instance, at SE Ranking, we make sure to create insightful, product-led content that shows our clients how to use our tools to solve their SEO and marketing challenges.

Svitlana Shchehel
Head of Content at SE Ranking
Out of all the content we publish on the SE Ranking blog, articles that explain the inner workings behind our tools and algorithms get the most attention from SE Ranking customers. For example, the blog post on our organic traffic estimation update gets up to 90% of pageviews from SE Ranking users. For educational articles on SEO topics that are targeted primarily at organic search, the share of SE Ranking clients among the readers is not that high—just around 16%. At the same time, SE Ranking’s customers demonstrate positive behavioral patterns: they scroll deeper and stay on the page for a longer time than first-time visitors. Also, out of all users who visit SE Ranking’s blog main page to check out our new content, 46% of readers are our customers.
These stats suggest that our existing customers find our content useful and insightful.
But it can still be tricky to accurately pinpoint SEO as the sole cause of improved customer retention. Many factors come into play, like ads, seasonal patterns, and social media activity. It’s wise to invest resources in understanding how your current website visitors are using your site.
One effective approach involves segregating and differentiating between two distinct user categories:
- Cold users: These visitors are encountering your site for the first time.
- Loyal client users: These users have engaged with your brand before.
By doing this, you can understand what content your customers are interested in and how to keep them interested.
To identify the pages your customers visit most frequently, navigate to the Explore section and select the Paths Explorations report. This report will show you the paths that users take on your sight.
Here, you only need to filter the data to focus on returning users. Then select the Page title and screen name option to see exactly which pages clients visited.
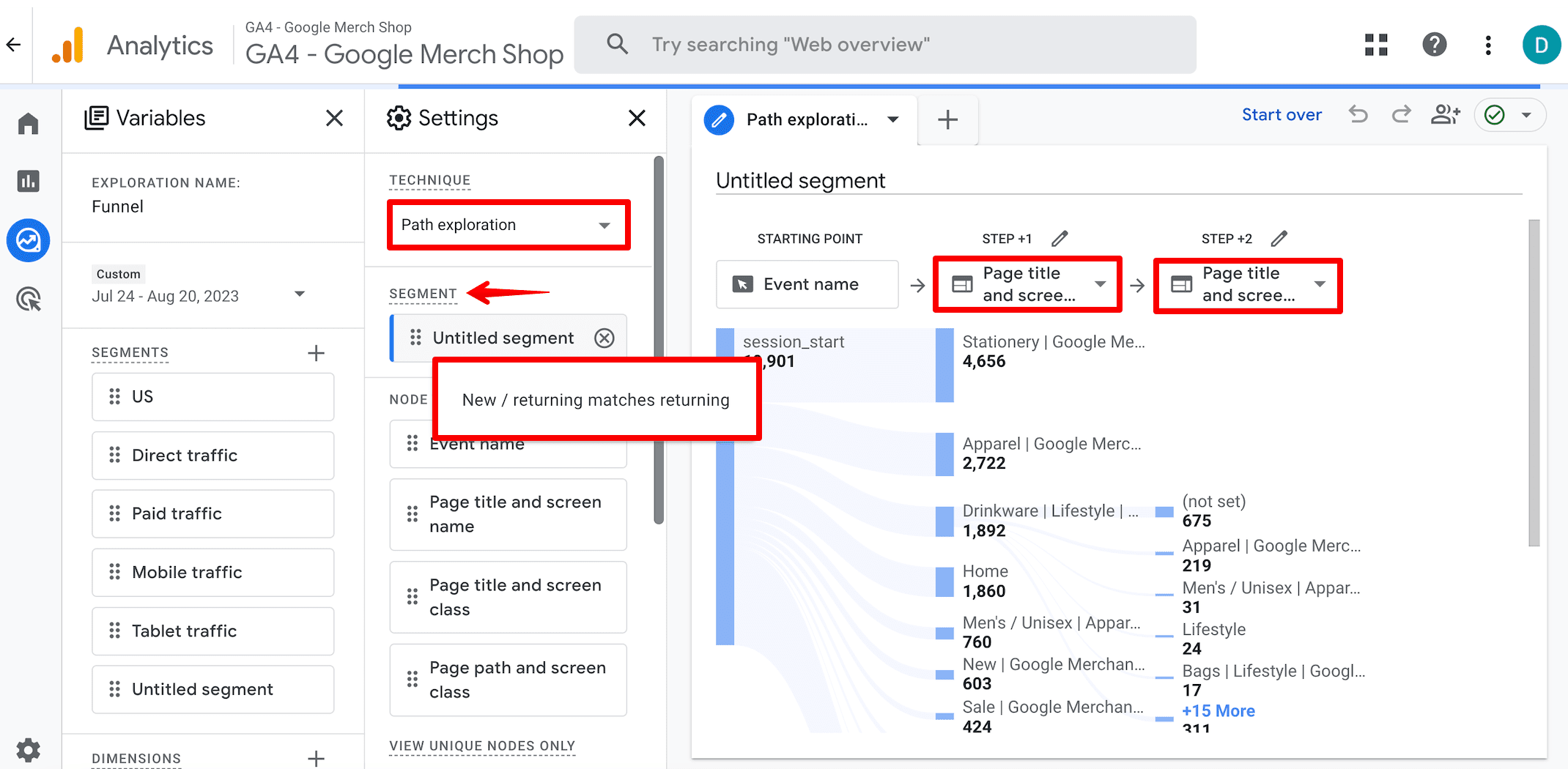
This data gives you the power to make your content and optimization better for these users.
Gauging how long it takes to get a return on SEO investments
Patience is key when measuring the ROI of SEO, especially since results don’t happen overnight. According to studies, it usually takes 6-12 months to see a positive ROI from an SEO campaign, and peak results typically occur in the second or third year of the campaign. The time it takes to wait for campaign results also varies based on the industry. For instance, it takes approximately 10 months to break even in the IT Staffing niche, whereas the B2B SaaS niche might take around seven months.
So, SEO is a long-term game. Well-optimized content and strategic backlinking continue to attract traffic and generate conversions, leading to a steady revenue stream. But in addition to these long-term strategies, you can also work on some strategies to get quicker wins. It’s important to clearly explain to clients or colleagues that SEO takes time, and you can use industry-specific data to backyour explanations.
Moreover, instead of just choosing random time periods, a better way is to focus on smaller details and calculate ROI for individual categories, pages, or keywords. This can give you an idea of how much you stand to gain from improving the rankings of specific pages. It will also help you understand the impact of your efforts.
Measuring SEO’s impact on your bottom line
Unlike paid advertising, SEO cannot be easily turned off. SEO keeps working, even when you’re not actively running SEO campaigns focused on immediate purchases. You can never fully control the impact of SEO on your business success.
While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution to address this, SEO is undeniably one of the most powerful marketing methods out there. Even though it’s hard to figure out exactly how much SEO is helping, you shouldn’t underestimate how powerful SEO can be. It’s like planting seeds that grow into strong trees: you nurture them, and with time, they become tall and sturdy. By working on your SEO and improving your website, you’re building a stronger online presence, and this can help your business succeed in the long run.
Wrapping up
In the world of digital marketing, understanding and measuring the results of your SEO efforts are crucial for steady growth. Taking a close look at the money and time you put into SEO helps you calculate the value generated by the people who visit your website, which helps you understand how well your efforts are paying off.
Sometimes, it’s not easy to figure out exactly how much you’re getting back from SEO. But remember that SEO is a powerful method for bringing in people to your website without having to pay for ads. It also helps your brand get noticed and is a valuable asset for keeping people interested.
