Posted by
Liraz Postan
On-page SEO is one of the pillars of a sound SEO strategy to get your pages ranking on the Google SERP. While over time some of the elements that fall under on-page SEO may no longer be as vital as they once were… there’s no way around making sure the content on your page, its URL, etc. are properly optimized.
Here’s a list of 31 essential elements to check in order to get your on-page SEO right!
What is On-Page SEO
Before we get to some practical tips, let’s first understand what is on-page SEO, and why you need it.
Firstly, SEO or search engine optimization refers to the process of improving your site’s visibility on search engine results pages. On-page optimization or on-page SEO is the process of optimizing the actual pages on your site so that they gain search visibility and gain relevant traffic.
On-page SEO is used to help search engines understand that your content is relevant to people’s search queries, giving you the opportunity to optimize your web pages and blog posts.
This on-page SEO guide is easy to understand and comprehensive. It offers no-frills, just easy-to-follow guidelines to achieve your internet marketing goals – the driving of more traffic and more customers to your website.
Your Checklist for Optimal On-Page Optimization
Here are 31 on-page optimizations designed to boost your relevance so that search engines place it at the top of search results.
But, before I get into the list, if you **** checklists, you might find these useful:
1. Make sure your site is secure
Switching to HTTPS will not only protect your site visitors’ data, but it also boosts your search engine ranking. Many studies have found a significant relationship between higher rankings and using HTTPS. Also, keep in mind that when migrating from HTTP to HTTPS, you need to be careful not to forget about any mixed content or loose ends. Generally speaking, site migration can also produce a lot of complexity, so just make sure to crawl your site to identify any errors. (You can also check out Aleyda Solis’s site migration checklist!)
2. Set up Google Analytics
Google Analytics will allow you to track your SEO efforts, such as how much traffic you’re getting from search engines, which pages are getting a lot of traffic, and how much profit you’re earning from organic traffic. Note, you can explore and spend days with all this data, so I advise you stay focused on landing pages and analyze user behaviors such as bounce rate (as high bounce rates can indicate the content isn’t good enough for query satisfaction), what pages users move to after arriving at your site (or maybe even convert from), exit pages, etc.
3. Ensure that your site is mobile-friendly
Since an increasing amount of web traffic now comes from mobile searches you need to ensure that your site is mobile-friendly. It pays to be certain that you’re serving the same content as your desktop version and that the page is ready for the mobile-first indexation that Google announced a while ago.
You can test your pages by using Google’s mobile-friendly test tool, Yandex’s mobile-friendly test, and Bing’s mobile test. See if it passes the test, and if not, learn how to fix your elements and design your site to serve mobile users.
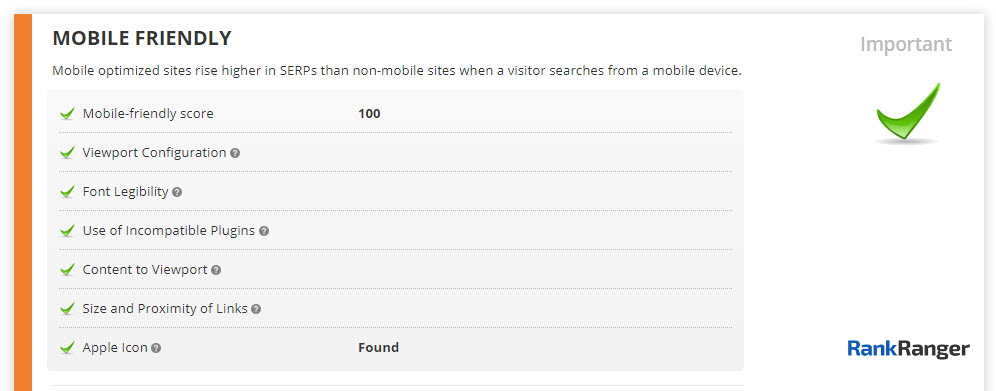
Rank Ranger’s On-Page Optimization Tool showing a breakdown of a page’s mobile-friendly status
4. Perform keyword research
Years back, we would do keyword research differently: we would probably look for pure search volume stats in order to decide on the best strategy, not to mention keyword stuffing.
Today, since Google can understand super-synonyms and search intent, we can focus more on relevancy and bring high value/ROI with less search volume.
As such, the most important on-page SEO strategy is finding the best keyword for a specific content page. The best keyword is relevant to the theme of the content and is regularly searched by your target audience.
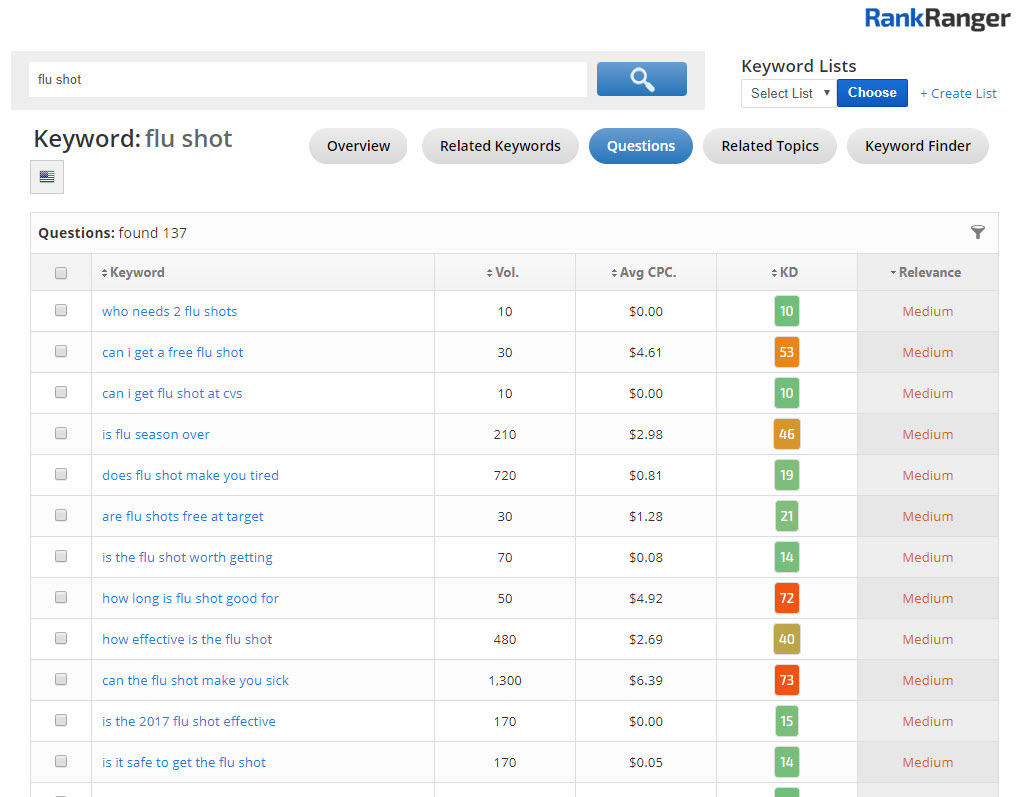
Knowing which questions are relevant to your user and content is an important part of doing keyword research
[For more on how to do keyword research that is topically focused see Rank Ranger’s post on what good keyword research should look like.]
5. Find long-tail keyword variations
Long-tail keyword variations are terms and phrases that are related or synonymous to your primary keyword. Sometimes, long-tail keywords can be a real diamond for your business strategy and generate a nice amount of conversions for a very focused search intent. Also, due to the voice search trends as well as the overall importance of Featured Snippets, you can now rely more on a long-tail strategy than ever before. Just know, Featured Snippets can increase your CTR 15-25%, simply by answering some valuable questions with the proper formatting.
6. Choose a primary keyword for your content
In order to ensure that you choose the perfect primary keyword for your content, you need to go through extensive keyword qualification analysis. Pro tip, avoid keyword cannibalization and focus on the right content for the right search term.
7. Create a content plan for your keyword
Once you have chosen your primary keyword, you need to develop a content strategy in order to support your marketing and sales funnel. You can tie each content pillar to its KPI and measure your content by its unique target: engagement, conversions, backlinks, social sharing, PR, brand awareness, etc. Creating a good piece of content can take time and resources. This is why it is important to remember to track your progress so that you can replicate success in the future!
8. Include the target keyword in the URL
Your URL is the first thing that search engines see, so including your keyword in the URL tells them what your page is all about. Of course, there’s an ongoing debate as to whether there is a real benefit to including a target keyword within the URL. I personally always try to include it – What do you have to lose?
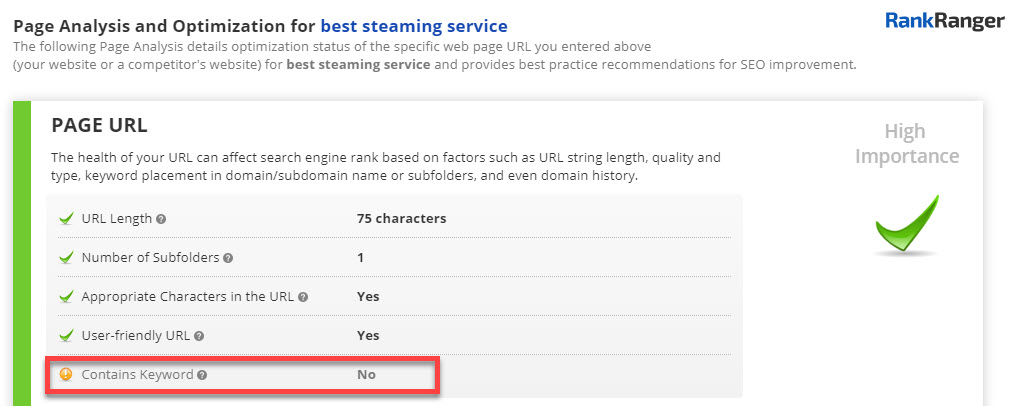
The On-Page Optimization Tool showing a URL that does not contain the targeted keyword
9. Use short, descriptive URLs
A lot of research proves that shorter URLs rank higher than long ones. Your URL should contain your main keyword and what the page is all about. Try to keep your URL short and to the point. As Google’s John Mueller said, less than 1000 characters will be fine. I personally believe that shorter URLs are a UX and social sharing signal benefit!
10. Add keywords to your title tag
When people search on Google or other search engines, the title tag is the first thing they will see. This is the reason why you should include your keyword in your title tag. Be sure to check that your title tag is descriptive, concise, and doesn’t exceed ~52 characters.
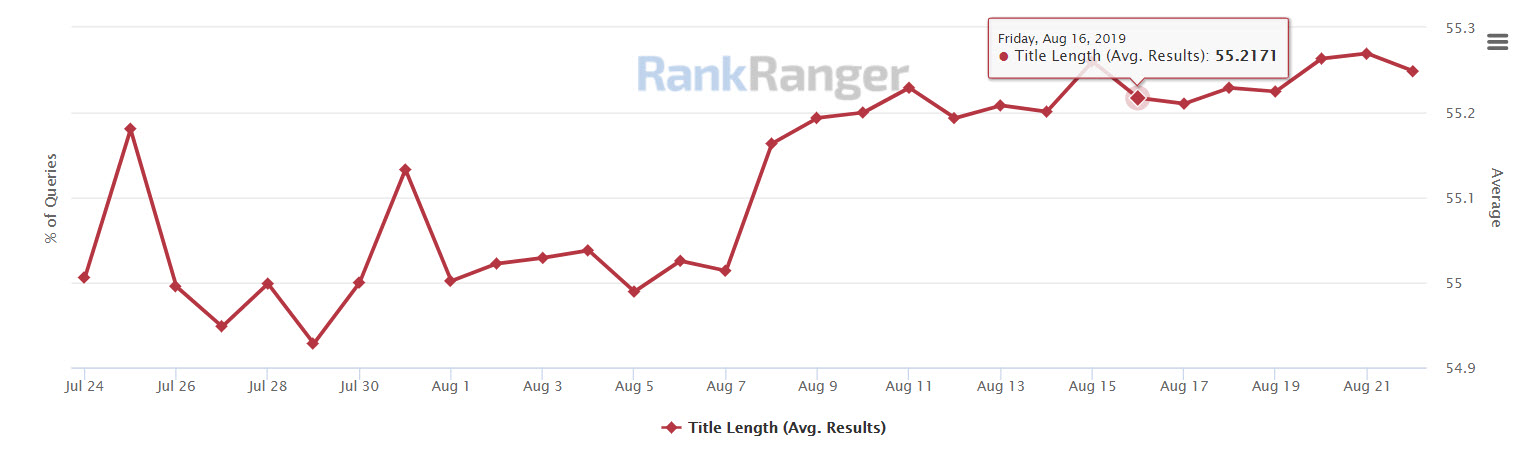
The SERP Feature Tracker showing the average amount of characters contained in the titles found on the Google SERP
Remember, the title is different from the H1. The title tag is what users see on the SERP whereas the H1 is the title users see on the actual page once they click on a result. (For the H1, you may want to go with what creates the best literary flow.) Write catchy titles using your target keywords to help the user click on your content over your competitors.
Once you’ve done that, it’s important to track how your title tags appear in Google search. The reason this is important is Google sometimes rewrites them.
11. Add modifiers to your title
Adding relevant modifiers to your title such as the current year, a number, or the words “best” or “checklist” will allow long-tail versions of your primary keyword to rank higher. When you add modifiers, your page will appear in more relevant searches which may increase your traffic. Plus, modifiers can indicate intent. For example, adding the year/month will help Google and the user identify the content is fresh and relevant to a specific timestamp.
12. Optimize the title for organic click-through rate
Organic click-through rate (CTR) is the percentage of people who click your page. A high CTR indicates that your page provides a better answer to people’s queries compared to other sites. Query satisfaction can be a ranking factor so track down your CTR in Google Search Console and if you find a place for organic CTR optimization, do it. Sometimes, it can be a quick win for you and an easy fix.
13. Add the keyword to the meta-description
A persuasive meta-description that includes your keyword can help raise your CTR.
You can also test your meta by using our search rank insights tool. Also, don’t be alarmed if you notice Google “deciding” on the best meta description and presenting completely different content on the SERP. Google, sometimes, can swap content to match the metadata to the query the user was searching for. To do this, Google usually pulls content that appears towards the top of a page. Either way, creating a solid meta-description is not terribly time-consuming, so go for it!
14. Add the keyword in the H1 tag
An H1 title tag is an important description of the content. As such, your primary keyword should be a part of it. The H1 is not a ranking factor, but it does help your users easily scan your content and understand what your page is all about.

A breakdown of the targeted keyword’s usage within the elements of a specific page
15. Don’t include the keyword in all H2 subheadings
Using H2 tags makes your content more reader-friendly. Although you can use multiple H2 tags per page, remember that you should include H2 tags only where they’re natural and relevant.
Do not overstuff keywords in your headings, think user-first in these cases.
Know, the H2 can also help you rank for Featured Snippets, with the proper formatting… which can seriously increase your traffic. So be strategic when creating those H2s!
16. Link to relevant internal resources
Whenever it’s relevant, it is ideal to add links to other pages on your site. This is useful because it helps establish an information hierarchy for your website and helps spread ranking power within your website. You can build a whole strategy along with internal linking and see great results. Context is very important to Google and it helps Google understand the anchor text and the text around the links you’re referring to on your site.
17. Add external links
Links that lead to other relevant and high-quality sites add context and aid search crawlers to understand your content. If you have a research or a study you’re referring to in your content, link to it so your users can read more and explore this amazing data. Don’t be afraid to link out. Just check that you link to the right resources so that they bring value to your users.
18. Be certain all external links open in a new window
Since your goal is to keep users on your site as long as possible, you should make sure that your external links open in a new window. This way, when a user clicks on the great external resources you’ve included they don’t leave your site without ever returning.
19. Add the keyword to the body of the page
Many SEO experts recommend that the keyword should appear in the first 100 words of the copy. Years ago, we had ‘SEO content writers’ since it was crucial to use the actual keywords inside the text a certain number of times. Today, you can write naturally, use your target keywords, use synonyms, and just make sure the content is focused on your main subject.
20. Write original and high-quality content
Write content that is relevant, engaging, valuable, and original. Don’t forget to add long-tail variations throughout your content. Also, always check that the content you post on your site is original and not duplicated. You can check duplicate content via a Site Audit or Copyscape, for example.
21. Add synonyms of the primary keyword to your copy
Google is very concerned about usability, so there is no need to over-saturate the content with your primary keyword. Instead, you can use keyword synonyms and Google will still acknowledge them. This way, you can use more natural language and still stay relevant to the primary keyword that you’re aiming to rank for.
22. Use engaging multimedia content
Visual content is more likely to get shared on social media compared to other content types. Embedding a YouTube video inside your article may help it rank better on YouTube as well. Readers will stay on your page longer if they have something interesting to read or watch. Make sure that you add videos, infographics, and engaging images to your page, and add the proper alt-tags to help it rank in Google images, as well as, appear in a Featured Snippet.
23. Optimize images with alt-tags
Add the primary keyword of the page to the image alt-tag. Alt-tags are used to describe images. They are important because it increases the overall accessibility of your website (think users who are vision impaired and rely on a reader to engage with your content). Also, alt-tags can be used for TTS readers, who might read the alt-tag to understand your images. Google definitely likes this accessibility.
24. Align content types with SERP intent
Google is now putting more weight on user intent when they rank websites. To get a higher ranking, your content should satisfy user intent. Therefore, you should know when to publish videos, blog posts, product pages, or resource pages. User intent is usually grouped based on two categories: informational intent or commercial intent. There isn’t a magic formula here: Google your query to find out which search intent you’ll need to focus on. For example, queries that include the term “vs” (as in DVDs vs Blu-ray) typically bring up a lot of informative content (reviews and the like), in addition to straight-up commerce sites.
25. Optimize for Featured Snippets
Many searchers want answers to specific questions in the fastest time possible. In order to answer questions more directly, Google uses Featured Snippets. Google believes this serves the best user experience by bringing real value to those who are looking for a quick-and-easy answer to their query. Also, voice search results are taken from SERP, as we usually ask questions from our home-devices.
If you manage to land a Featured Snippet, you can exponentially increase your organic traffic.
Once you do win a Featured Snippet, be sure to track its performance and consistency via the Featured Snippets tool.
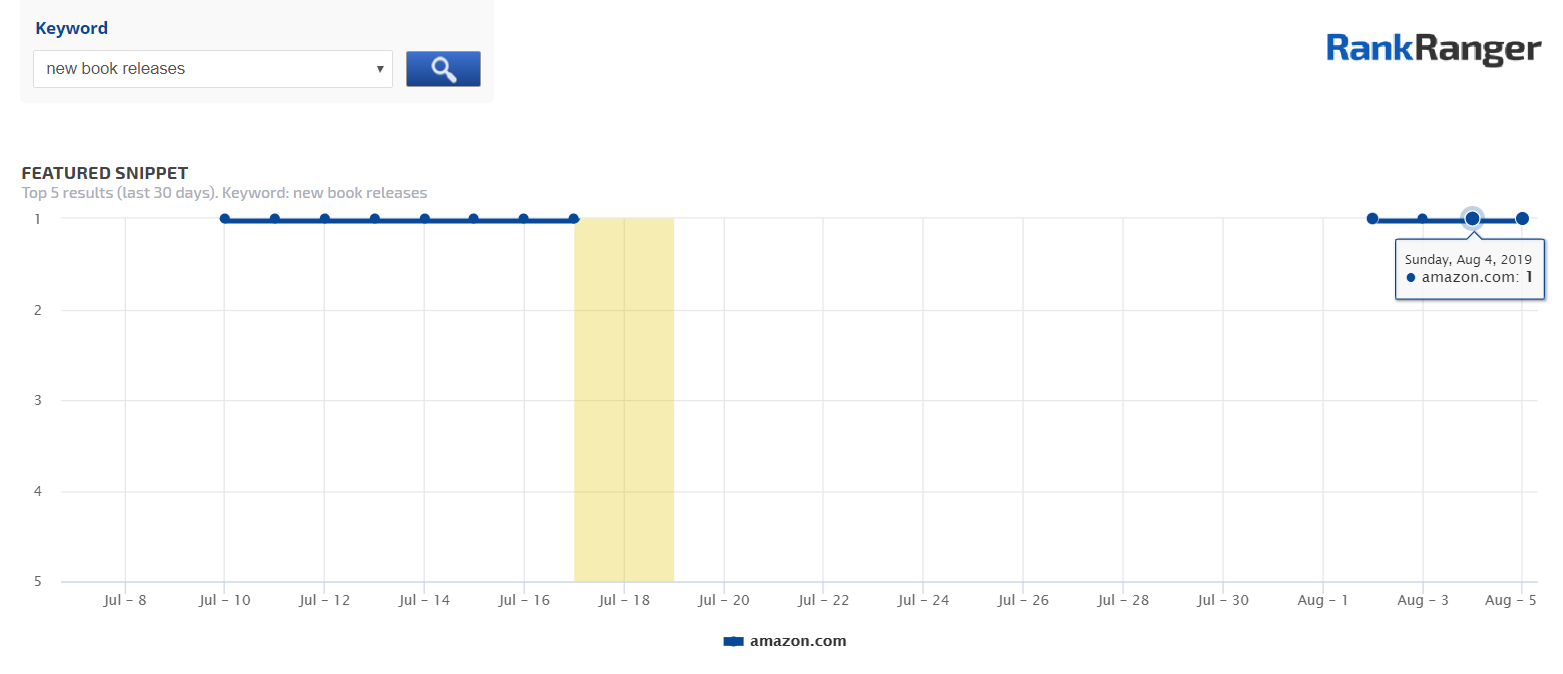
Tracking a SERP feature’s display trends has become a vital part of your overall SEO strategy
26. Proofread your content
Always proofread your content for spelling and grammatical errors. You don’t want to lose a reader just because of one mistake! Poor quality content can lead to increased bounce rates and your brand being seen as a less reliable source of information. It only takes one poorly-written article to ruin a site’s entire reputation. Also, make sure your content has the right messaging to its brand. If you have doubts, consult your PR or brand marketing manager.
27. Boost site speed
You need to make sure that your site loads fast. According to Google, page loading speed is a ranking signal and is part of Google’s user experience algorithms. As a rule, you need to make sure that your site doesn’t take more than 3 seconds to load. Also, if you’re competing against really fast websites, you’ll need to optimize even further to reach their level.
Optimize your images, code structure, and DOM size to make sure you serve the best user experience on mobile and desktop.
You can check your site speed with Google page speed insights and tools like Pingdom, GTmetrix, and more.
28. Boost dwell time
“Dwell time” is the amount of time that a visitor stays on your site. You can boost dwell time and user engagement by adding videos, providing longer and more valuable content, encouraging blog comments, and other strategies.
29. Check for broken links
When updating landing pages with a new URL, you might end up with a bunch of broken links. Often, those links can be really valuable to your site.
If you have broken links on your site, you need to fix them by redirecting the broken URL to a working URL and updating the missing content (unless, of course, you want the page removed from Google’s index altogether). Crawl your site to identify errors as these errors prevent search engines from viewing your content. You need to fix all crawl errors, which can be viewed on the Coverage report of Google Search Console and in your crawl audit results.
Use 301 redirects for a permanent redirect, use 302 for a temporary one, and 410 for a nonexistent URL.
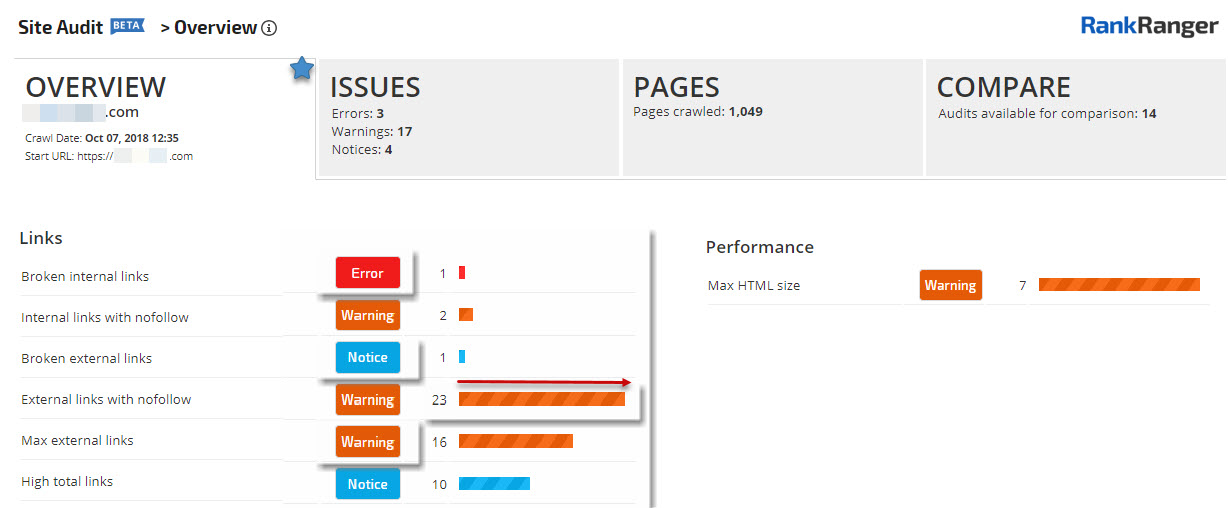
A site audit report showing the link issues found on a site’s pages
30. Use social sharing buttons
When content is optimized for social media, it is more likely to be found in search engines. Thus, you’ll want to prominently add social sharing call-to-actions to the page.
31. Optimize for E-A-T
Since August 2018 the conversation around a site’s authority and E-A-T has reached epic proportions.
E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Does your content serve all of these? More than ever before, Google is able to fight possibly misleading content. The content authority battle is all the more pertinent if your site discusses sensitive topics (medical issues, laws, safety, etc.). It’s vital to consider how authoritative and trustworthy your content is!
Check: Is the author of a page’s content listed? If not, it should be! Also, make sure to include a short bio to show-off your author’s expertise on the topic! It pays to build your E-A-T profile carefully and creatively!
Go Forth and Spread On-Page Goodness!
Without exaggeration, on-page SEO is one of the most important optimization tasks you’ll ever undertake. It is an ongoing task, and you should always be one step ahead of your competitors. It’s an ongoing process that may demand you revisit a page multiple times with a fresh pair of eyes! It might seem overwhelming, but by following these 31 points (and by building trustworthy content) you’ll get there!

