Voice search is a technology that allows users to search by simply using their voices instead of typing. It works through the automatic speech recognition (ASR) system that transforms voice signal into text. Then search engines like Google match the search query with the right results.
In 2022, around 142M people in the US used voice assistants. The forecast is that this number will grow to 157.1M voice search users in 2026. That’s why optimizing for voice search should be a part of your strategy.
If you are new to the topic, don’t worry. This post is all about voice search SEO. We’ll dive into what it is and how to optimize your site to get found when people run a search using their voice.
-
Voice commands tend to be more conversational and natural compared to traditional typed searches.
-
Voice searches frequently pull information from featured snippets and quick answers at the top of the search results.
-
Voice search is often used for local queries such as finding nearby services or businesses.
-
Voice search optimization requires additional strategies like using long-tail keywords, structuring content around questions, and implementing structured data to help search engines better understand the content.
-
As voice search technology evolves, businesses, SEO specialists, and search marketers need to stay informed about new developments like AI Overviews, video search integration, and changes in consumer behavior.
How voice search differs from traditional search
There’s a huge difference between speaking and typing your question or search query into a device. Besides the obvious advantage for users in terms of how they input their query, there are other consequences to using voice search.
- Longer and more conversational queries
When we ask our smart devices something using our voice, we typically phrase the queries very naturally as if we’re speaking to someone we know. Unlike traditional search, we don’t just mash together and throw in several keywords that indicate our search intent.
However, this line between voice and traditional search is now blurring. With the rollout of Google’s AI Overviews, traditional search is becoming more conversational. Google’s Gemini model has multi-step reasoning capabilities, which allow users to input more complex, longer queries. Our recent research indicates that AIOs are frequently triggered by longer, prompt-like queries. As users adapt to these changes, voice and traditional search are likely to share more similarities in terms of query length and conversational nature.
Another thing that impacts the future of search in general and the future of voice search in particular is video search. Google is experimenting with allowing users to ask questions through videos in Google Lens. If combined with voice search, this will create a whole new experience for users. Queries for voice search may become shorter and more precise because Google will be able to detect all the search details in the video. So we need to keep a finger on the pulse as these changes go live.
- Local listing searches include voice queries
The vast majority of verbal searches include the keywords “near me” in addition to questions about time and things like ‘What are Best Buy open hours?’ or ‘Where is the closest Pizza Hut?’
Ultimately, these results are displayed in local listings.
Unless you live under a rock, you’ve probably used voice search devices to find somewhere to shop, eat, relax, visit, and more. So, if you want your business to be found for such searches, you must have an up-to-**** Google Business Profile, which we’ll get to later on.
- Clear and concise search results
When we submit a search using our voice to search engines, the results we get are typically taken from the featured snippets we see at the top of the page when we type in a search.
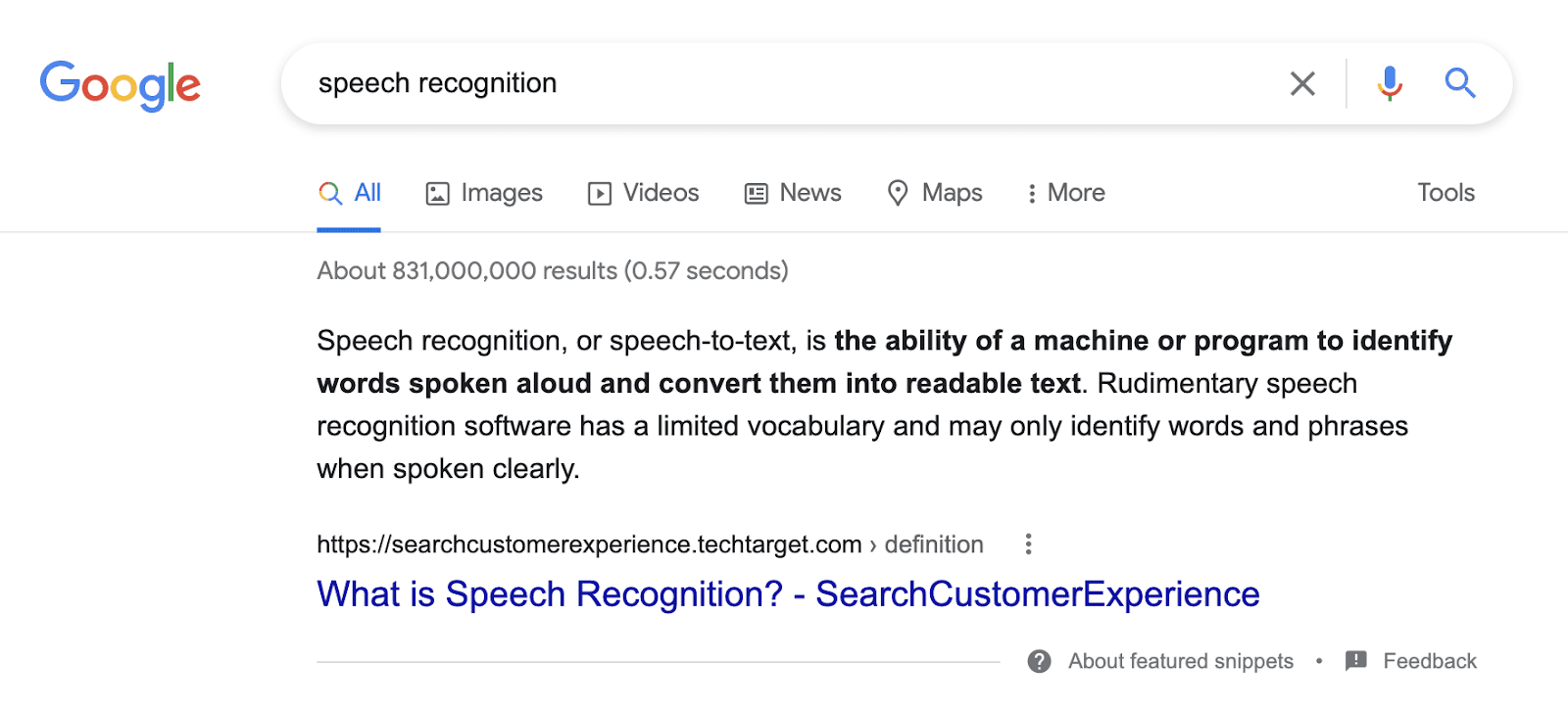
Google takes the information from featured snippets and knowledge graphs and speaks the answer to the searcher to provide a quick answer. We don’t know whether Google will read answers from AI Overviews which appear above featured snippets in search, but this could one of the scenarios since these AIOs accompany featured snippets in 63.67% cases.
Giving searchers instant answers boosts customer service and their overall satisfaction rate, but this also means that your website will get fewer visits because people will convert to phone calls or buying directly from the SERP.
What is voice search SEO?
Voice SEO is the process of optimizing your website for searchers who use different voice search assistants (Google Assistant, Alexa, Siri, and other digital voice assistants). Some believe that it is no different from traditional SEO as all voice text is transformed into written text in the process.
Apart from increased visibility, voice search SEO will help you:
- Provide better user experience
- Increase foot traffic and local customers to your business
- Make your content more reachable for users with disabilities
- Increase your branch authority and user trust.
Although voice search does help create better customer experiences, it does take traffic away from your website. As a result, you have to do some fine-tuning to get people to convert from voice searches.
How to optimize your website for voice search
If you decide that your business should take a shot at voice search traffic and rankings, you don’t need to reinvent the wheel (general SEO principles). You just need to make sure your voice search optimization strategy includes specific tactics described below.
Research keywords for voice search SEO
Traditionally, optimizing for voice search has involved focusing on conversational keywords, reflecting the natural, question-based way people speak when using voice assistants. For example:
- Typed query: veggie burger best recipe
- Voiced query: what is the best recipe for a veggie burger
However, not all users adhere strictly to this pattern. Moreover, different generations use search differently:
- Baby Boomers (born 1946-1964) prefer detailed, specific queries containing 5-7 words using traditional search engines to find information.
- Gen X (born 1965-1980) uses a mix of specific and general queries, searching for information through search engines and social media.
- Millennials (born 1981-1996) search with short, conversational queries, mostly through mobile and voice search and social media.
- Gen Z (born 1997-2012) prefers short and fragmented queries on social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram.
- Gen Alpha (born 2013-present) makes voice-activated searches with very short queries.
So the best advice here would be to analyze your target audience and the way they search for information and build your strategy around this data.
Consider user intent
You should understand what users seek behind the queries they pronounce aka their search intent. They could be looking for directions, answers to their questions, products to buy, etc.
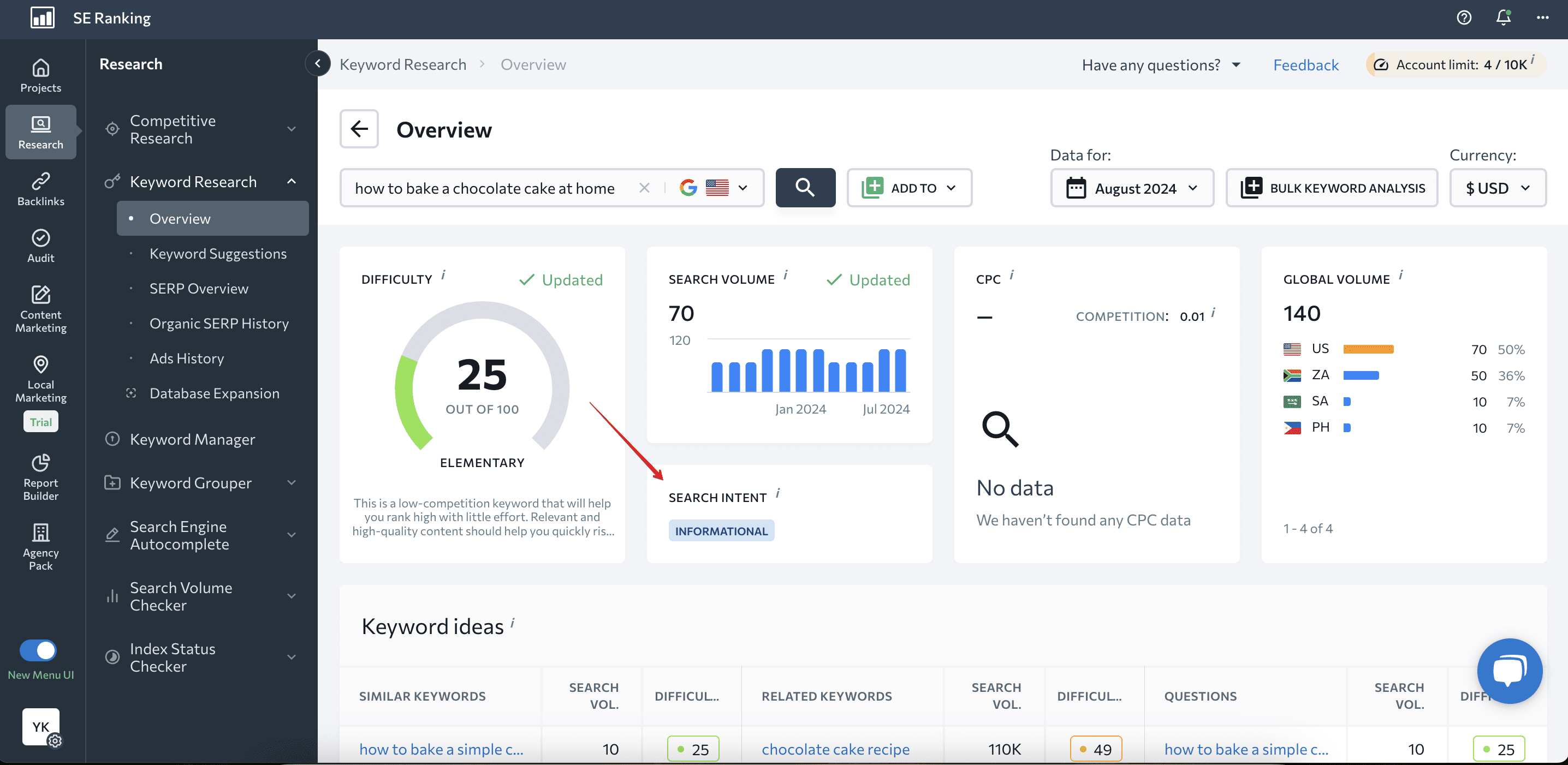
SE Ranking’s Keyword Research Tool analyzes any keyword you want to target and determines its search intent. If the keyword addresses several search intents, you’ll see all of them specified.
Focus on long-tail keywords
To collect long-tail queries with a low search volume for your seed keyword, go to Keyword Research, open Keyword Suggestions and proceed to Low Search Volume tab.
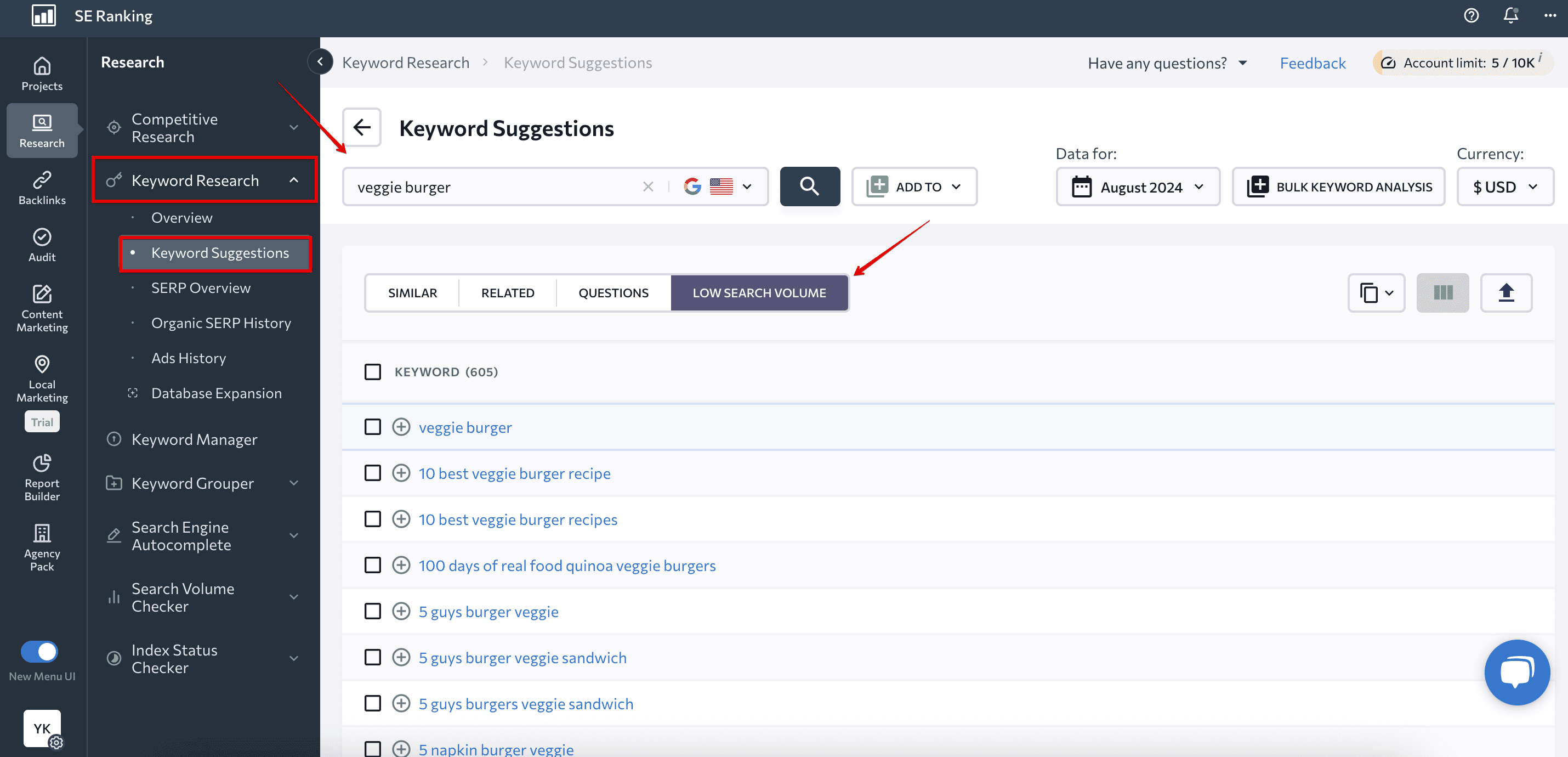
And just keep scrolling down the list to find more ideas for conversational voice search keywords related to your business.
When you have your long-tail search queries on hand, you don’t need to think about optimizing a separate page for each one of them. Just sprinkle your content with them. And remember that Google doesn’t need to see them in H-tags in order to use them for voice search answers—they can be picked up from any part of your content.
Use question keywords
A large share of voice search queries accounts for questions. So one should target question phrases while building up your site’s keyword list.
You can collect questions for a given keyword with Answer the Public. Go to the main page, enter the seed keyword and get the results broken down into question groups (where, what, why, how to, etc.).
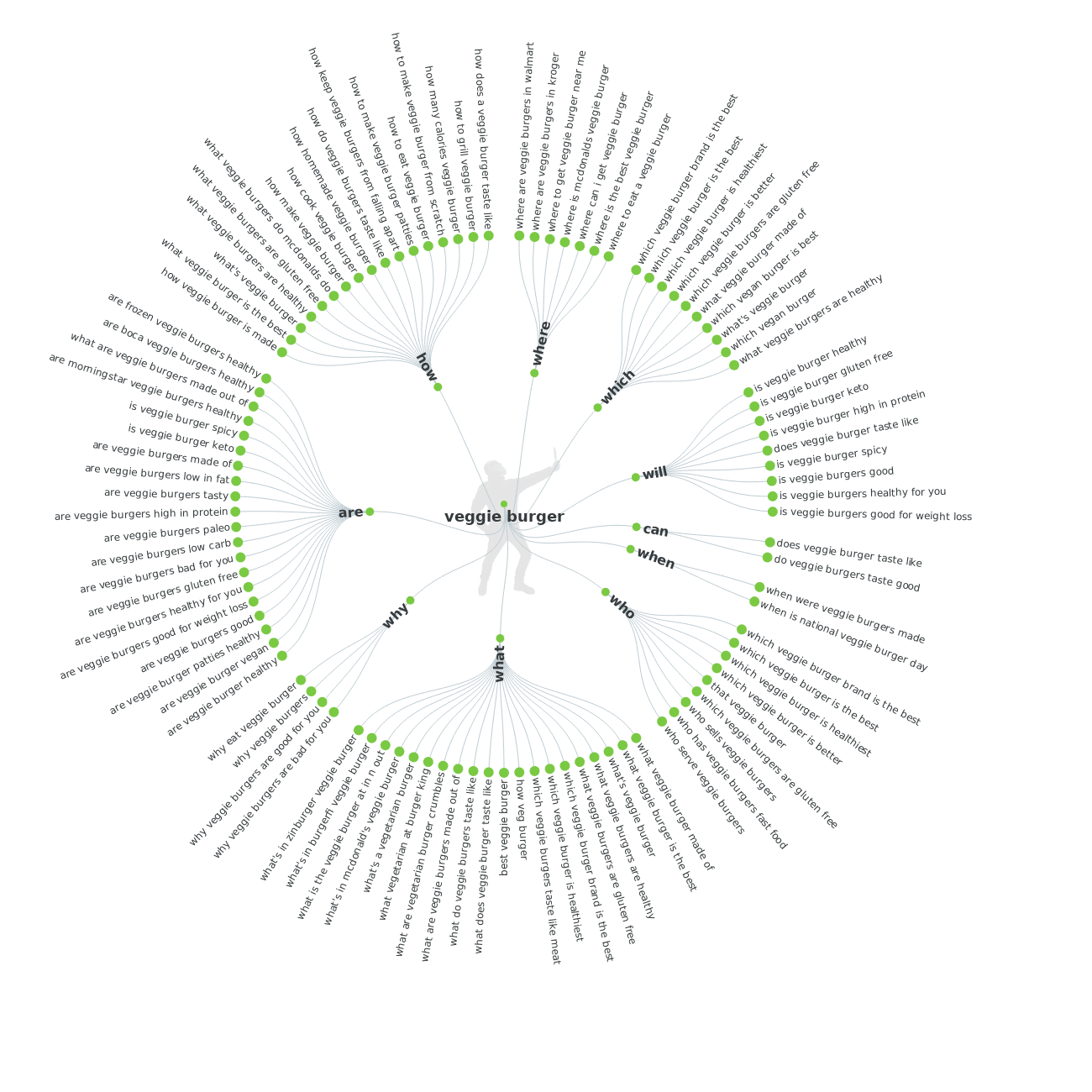
You can export the results in a CSV file or see them in a radial graph. It’s not a super user-friendly image, but does the job (and looks pretty cool too). You can then provide answers to their questions in written form on your site. Focus on a single search intent on a page and match search intent keywords with content.
Keep in mind the context
Your website content should take semantic search into account that includes context, user search intent as well as the relationship between the words you use on the page. Aim to write content that honestly answers your customers’ questions, and Google will reward you for it.
Ideally, you can incorporate the phrases your customers use to run searches and use that text in your content.
Avoid using technicalese where you can afford to on your site or blog. For best results, use simple and concise single-line answers so that Google has the opportunity to use them when answering voice queries. Try to make texts that are no longer than 1 paragraph and at a 9th grade reading level.
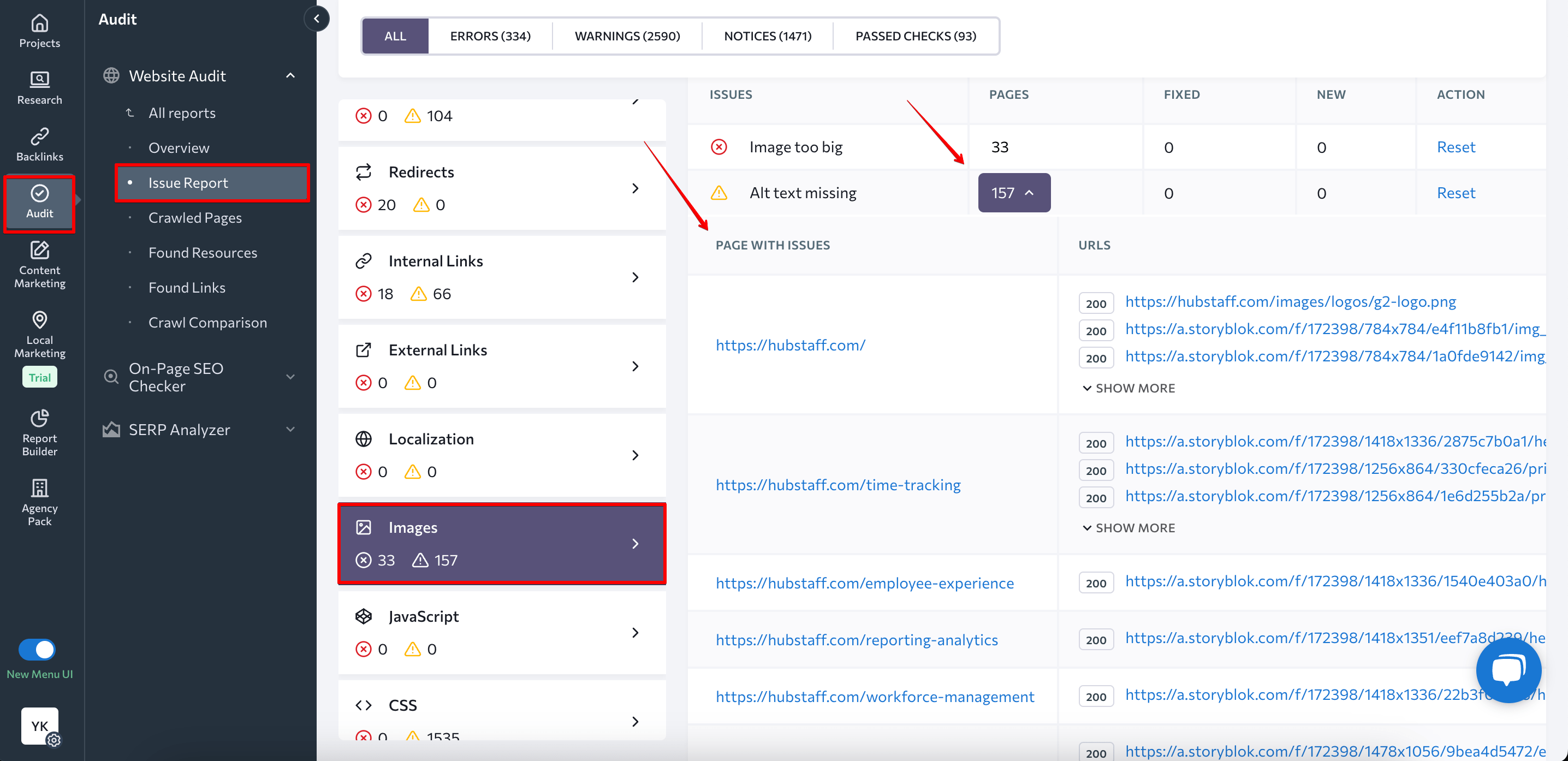
Optimize images
Besides working on optimizing the written content on your website, make sure to optimize visual content as well because Google looks at alt tags and file names to understand how to rank such content.
Run website audits regularly to detect images that miss all tags and make sure to add descriptive texts for each image on your website.
Use structured data for voice search
When you ask a smart device a question like “What is the capital of the United Kingdom?” and it answers with “London,” it’s likely using structured data to pull that information from a web page. Structured data, embedded in your site’s code, helps search engines understand and retrieve specific details from your content. While it requires some effort to implement, it’s crucial for voice search optimization.
Whenever people look for a business in their area, they often look for specific information relating to that business, such as where it’s located, when it’s open, what number to call, and so on. Structured data helps Google and other search engines identify this exact information and classify it accordingly. That way, you will enable your content to be found as an answer to a verbal search query.
Set up FAQ pages and apply FAQ markup
FAQ is believed to be the optimal form of content to match a voice search result. So the best way to shape your FAQ page is to form a list of the most relevant questions people ask about your service or product. Give a clear and concise answer to each question. It should be written in 8-9 grade-level English and jump right to the point.

While adding structured data to your site’s code, it’s worth also focusing on marking up your FAQ pages. Frequently Asked Question (FAQ) pages are structured as a list of questions and answers that are related to a particular topic.
Here’s the sweet part that makes it all worth your while: FAQ pages that are marked up correctly satisfying the appropriate conditions can be used by Google Assistant when answering user queries.
There are content guidelines that you should follow and properties that are required if you want to provide a better experience for your site’s users. These properties include:
- The FAQPage type. This property indicates that the web page is an FAQ that contains answered questions. Make sure to have only a single FAQPage type definition on a page.
- The Question type. This property defines a single answered question that can be found on the FAQ page. Every use of the Question instance must be put into the mainEntity property array of the schema.org/FAQPage.
- The Answer type. This property defines the acceptedAnswer to each of the Question instances on the FAQ page.
Set up your Google Business Profile
The vast majority of voice searches are specific to a certain location, plus local mobile searches result in a same-day store visit most of the time. That’s why you need to verify that the name, address, and phone number (NAP) data of your business is consistent and accurate on your Google Business Profile. You can use SE Ranking’s Local Marketing tool as it detects errors in your business listings, including GBP. Apart from other helpful features, the tool analyzes how your NAP is written and informs you if it’s incorrect.
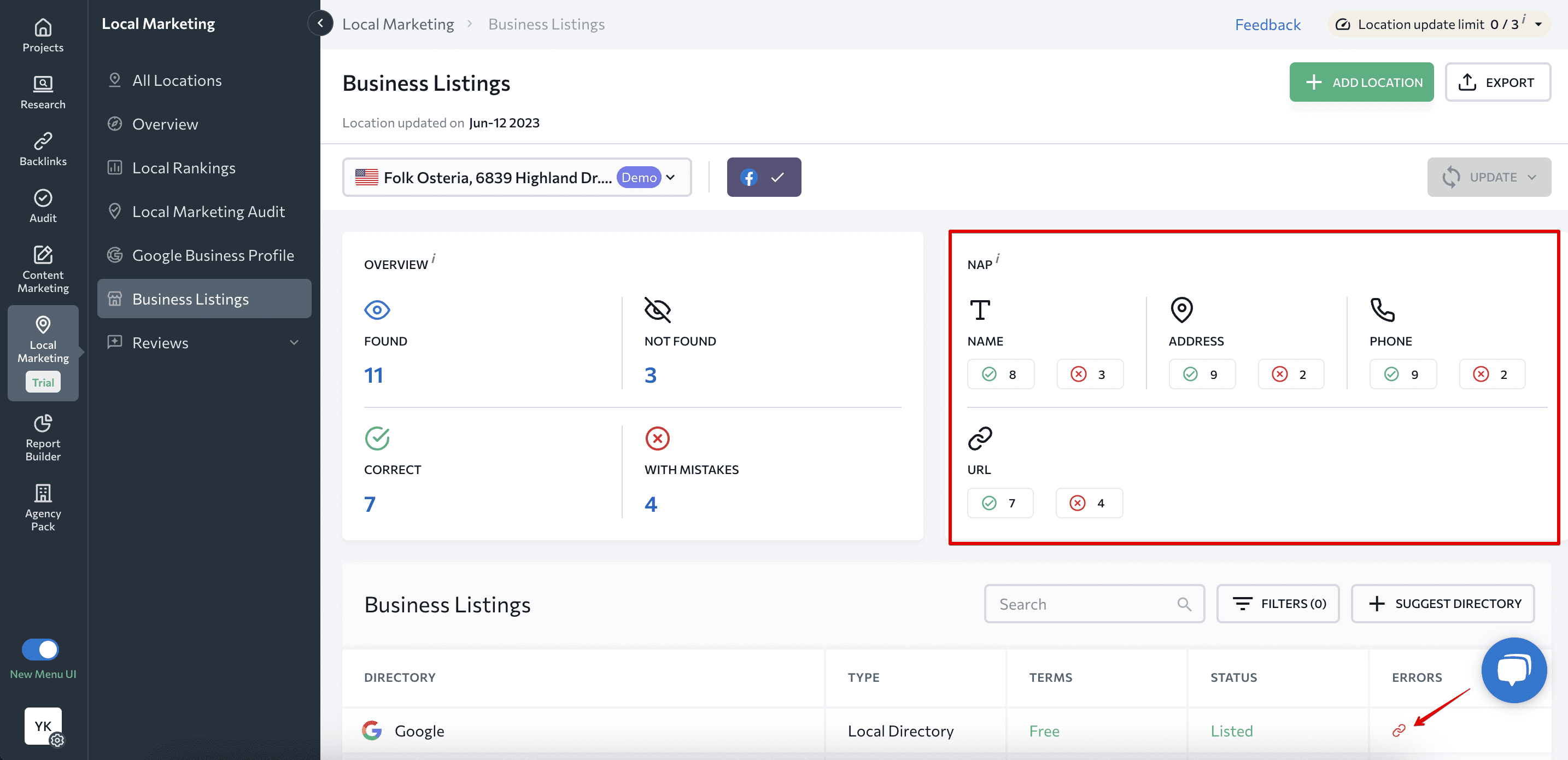
Add quality photos and images to your profile and reach out to happy customers for positive reviews. You can also monitor reviews in the Local Marketing tool and even respond to them from the platform.
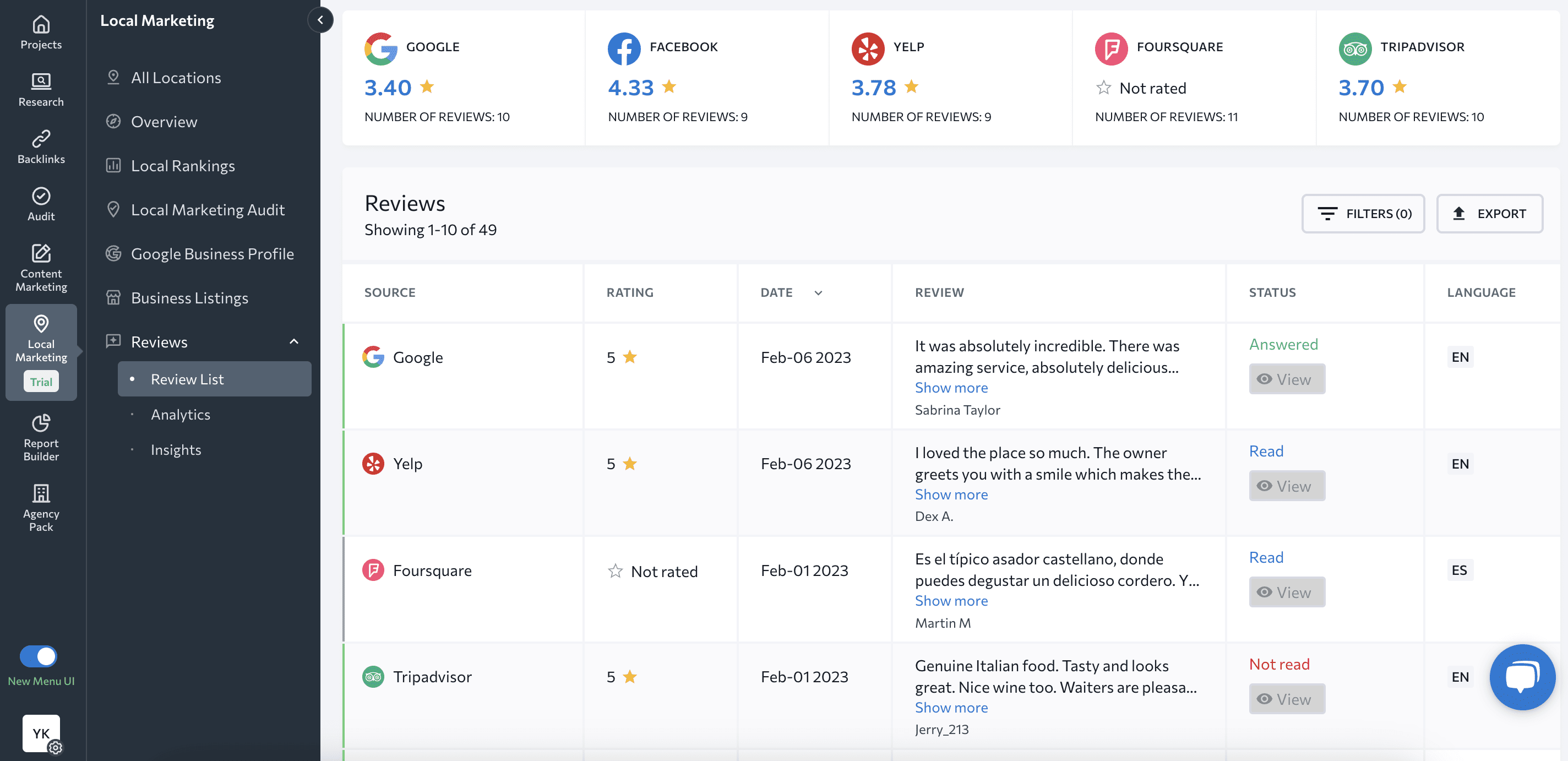
Similar to FAQs, be sure to take advantage of the Q&A section in your Google Business Profile.
Then, to make sure everything is set up properly, use your phone or voice assistant device to run verbal searches for your business. If you see any inconsistencies or if your business is misrepresented, go back and polish off your GBP as well as your NAP data.
Follow general SEO recommendations for voice search
For voice search optimization, you need a full package of the basic SEO setups. The higher a page is ranked (the best is to get into Google’s top 3), the better its chances of becoming a voice search answer. Pay particular attention to:
- Moving to HTTPS
- Building up a domain authority
- Indexability and crawlability of your website’s pages
- Loading speed of your pages
- Mobile-friendliness
Do Multilingual SEO for Voice Search
People use voice search in their own language, which makes multilingual SEO especially relevant. Failing to do so will result in people who search in the native language not being able to find your website. Simple as that.
Let’s focus on what you can do to cater to your multilingual customers.
- Do keyword research in each supported language. For multilingual SEO, it’s crucial to do keyword research for each language that you offer your content in. Simply translating texts won’t do the trick at all. Get a professional translator to translate the original language, then brainstorm different keyword variations, and finally, use an SEO tool like Keyword Research to research each keyword and keyword phrase that is not in the original language of your website. Pay attention to the keyword search volume and level of competition.
- Hreflang annotations are a must for websites that support multiple languages. This annotation helps Google and other search engines understand which visitor needs to see which page. Hreflang makes it possible for English-speaking people to see the English version of a website and Spanish speakers to see its Spanish version. Furthermore, make sure to use the alternate attribute. This attribute helps avoid having issues with duplicate content by letting Google know that the page is a translation of a pre-existing web page, not its copy.
- Pay attention to the URL structure. Multilingual SEO often results in you creating different versions of a page under a single domain. To avoid issues, create a URL structure for each language version. Here’s what Google has to say on the topic.
- Another vital aspect is the content writing style. As was already touched on, create content in a conversational form and do not make it difficult to absorb. Voice search SEO isn’t about using a specific number of keywords in all the necessary places. It’s about being natural and using questions. So, stick to short, concise answers and you should be better prepared to answer verbal queries.
Wrapping it up
Voice search is expected to grow more in the coming years. There are things we need to be ready for, including SERP-less search, a rise of simple content forms, a spread of conversational but AI-friendly tone of voice across the web, and many many others.
Think of voice search as an additional cool feature of the devices that we already use and have been using for some time. If you focus on creating valuable content for your customers and take care of the above tips, you will boost your chances of becoming an answer to a verbal query.
