Do you want to rank for competitive terms without worrying about potential Google penalties? Then go white hat.
In this post, you’ll learn what white hat SEO is, how it compares to black hat SEO, and how to implement a few white hat SEO tactics.
White hat SEO refers to the use of SEO strategies, techniques, and tactics that are within Google’s guidelines.
The focus is the user. White hat SEOs prioritize users by providing relevant, high-quality content rather than content designed to “trick” search engines.
The flip side of white hat SEO is black hat SEO.
Black hat SEO refers to the use of strategies, techniques, and tactics that do not necessarily follow Google’s guidelines. Its focus is on finding and exploiting algorithmic loopholes.
Sometimes, these black hat tactics can be plain unethical—we’re talking about SEOs spamming competitors with malicious links, injecting other websites with malicious code, and more.
Sidenote.
The terms “white hat” and “black hat” came about because old films in the Western genre used those hats to symbolize the contrast between good vs. evil. (White hats were worn by heroes and black hats by villains.) This then gave rise to the terms in computer *******, which followed into SEO. They’re not necessary the best terms. But we’re using it here for now because there is no alternative in popular use.
Here are three reasons:
1. Black hat SEO is risky
Following the law confers no reward. But there are downsides in not following them, such as fines and imprisonment.
The same goes for white hat SEO. Just because you’re following Google’s guidelines doesn’t mean you’re automatically guaranteed higher rankings. And unfortunately, in some niches (for example, payday loans), black hat SEO is the name of the game.
But just like in the real world, not following the “rules” always runs the risk of getting caught. In this case, it’s not law enforcement, but Google.
If Google discovers you’re using black hat tactics, it could penalize you. When that happens, you’ll see traffic like this:
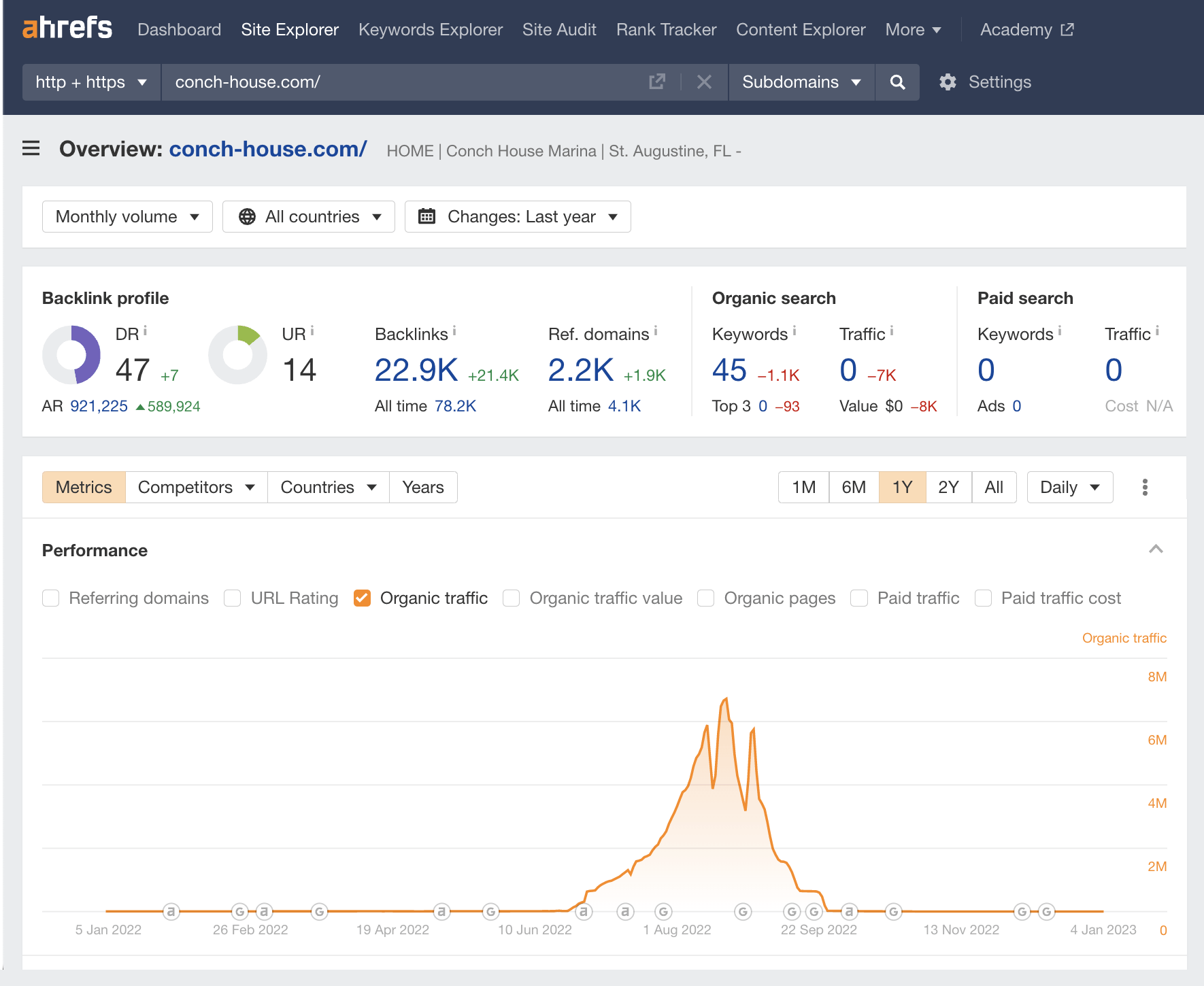
So if your goal is to build a brand for the long term and generate consistent traffic, you’ll have to use white hat SEO tactics.
2. Black hat SEO is difficult to implement
With frequent Google algorithm updates, low-cost spammy tactics, like keyword stuffing, no longer work.
So if you want to go ahead with black hat SEO, you might opt for tactics like building a private blog network (PBN). But building a PBN correctly is expensive (i.e., buying expired domains, dedicated hosting, private Whois, etc.), is technical, has no guarantees of working, and can even cause you to be penalized.
In that case, you may as well invest that money, time, and effort into white hat SEO, which can actually bring long-term traffic and brand value, like our company:
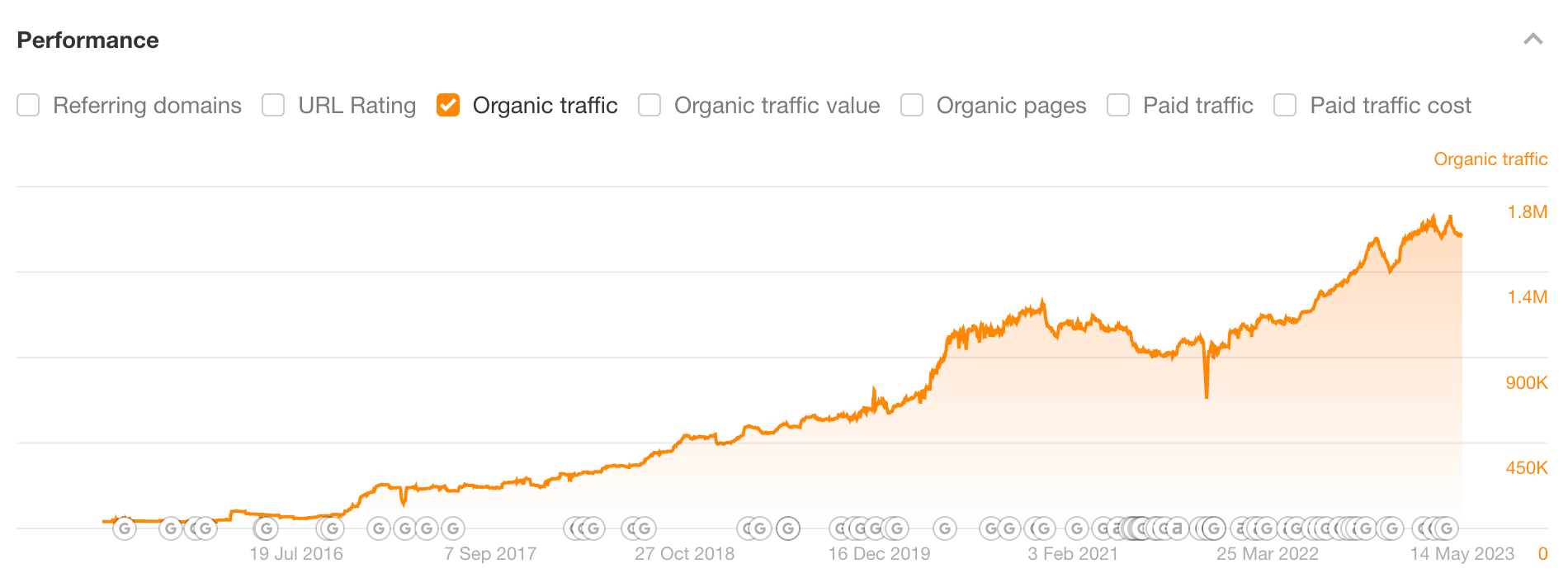
3. Black hat SEO makes everyone’s life worse
Though you’re an SEO, you’re first and foremost a search engine user. You’re probably Googling for things on a daily basis.
So you may win as a black hat SEO if you successfully spammed Google SERPs, but you’ll lose as a user if everything you search for only contains poor and irrelevant results.
So how do you get started with white hat SEO? Here are a few tactics you can use.
1. Do keyword research
One of the key best practices in Google’s Search Essentials is to “use words that people would use to look for your content.”
You can find out what these words are by doing keyword research.
Here’s how to get started:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter one or a few relevant words or phrases
- Go to the Matching terms report
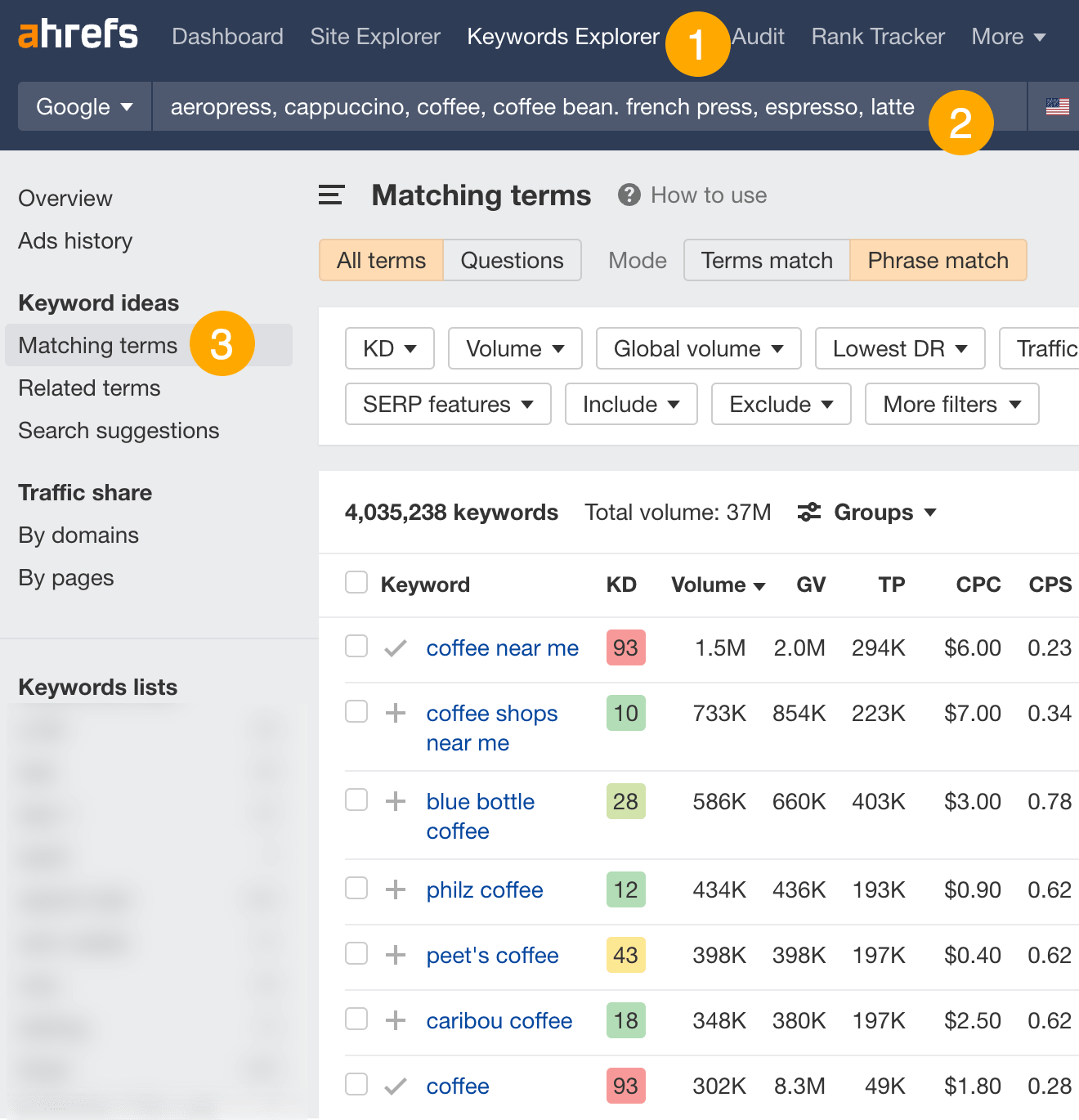
Here, you can see over 4 million potential keywords you could target. If they’re relevant, you want to rank for all of them. But you also likely have limited resources, so you should prioritize.
We can narrow the list down by focusing on two metrics:
- Traffic Potential (TP) – Pages no longer just rank for one keyword. It can rank for many and get traffic from all of them. TP is the sum of organic traffic that the #1 ranking page for your target keyword receives from all the keywords that it ranks for. You’d want this to be high.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD) – There are only so many spaces you can rank for on the first page of Google. As a result, SERPs can be competitive. KD gives an estimation of how hard it is to rank in the top 10 organic search results for a keyword on a 100-point scale. You’d want this to be low.
How high TP and how low KD should be depends on your website. But for this example, let’s set them like so:
You’ll also want to set the Target filter to check if your website is already ranking for any of these keywords.
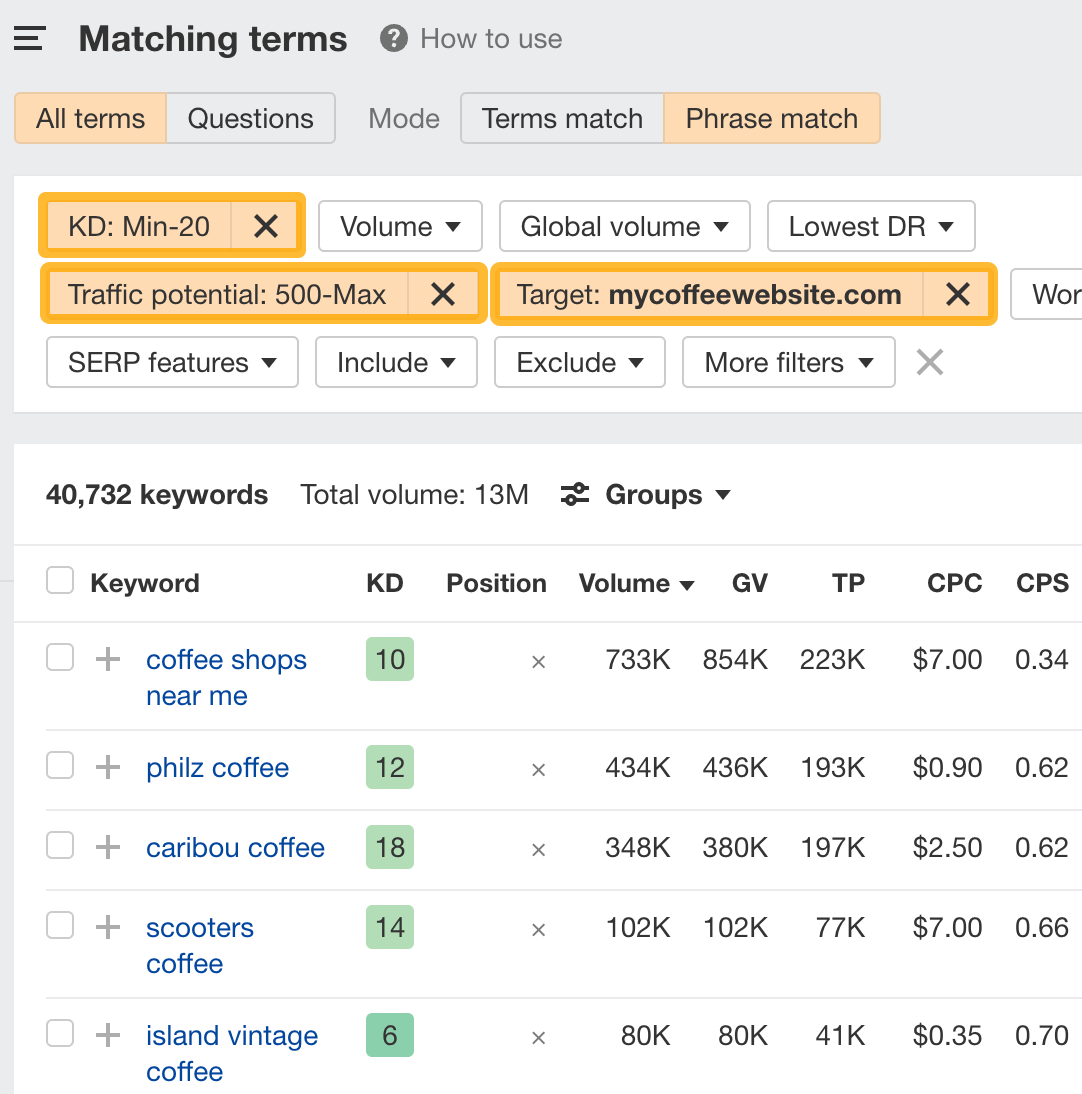
Look through the list and pick out relevant keywords.
2. Create helpful, reliable, people-first content
Google’s Search Essentials states that we should create helpful, reliable, and people-first content.
But what does that mean in reality? Here are the steps you should take:
Align your content with search intent
Google wants to serve relevant content to its users. And a key aspect of relevance is whether searchers find the search results useful.
In order for search results to be useful, Google needs to figure out why searchers are looking for that query, so it can serve the right results.
This is known as search intent.
If you want to rank high on Google, you need to figure out search intent. We can do this by analyzing the SERPs for the three Cs:
- Content type – Are they blog posts, product pages, landing pages, or something else?
- Content format – Are they tutorials, listicles, how-to guides, recipes, free tools, or something else?
- Content angle – Is there a dominant selling point, like low prices or how easy it is?
For example, let’s say we’re targeting the keyword “how to save money.”
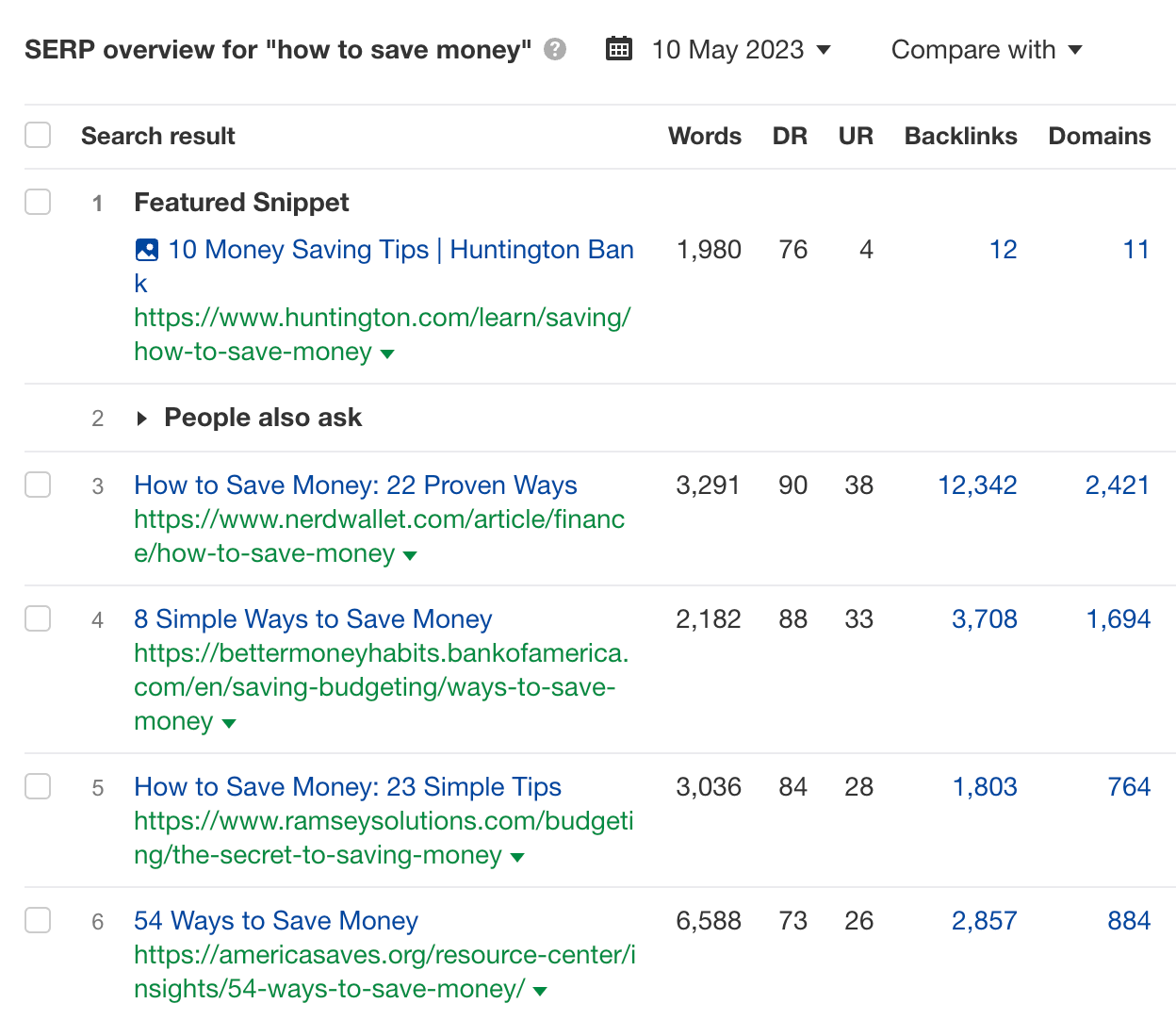
If we analyze the SERPs for the three Cs, here’s what we see:
- Content type – They’re all blog posts.
- Content format – Despite the “how to” modifier, people are actually looking for a list of ways to save money.
- Content angle – There are a few angles here: “proven,” “simple,” “easy,” and more.
If we want to rank for this keyword, we likely have to create a listicle of money-saving tips.
Cover the topic in full
The best result for a query covers everything searchers want to know. So if there are subtopics that the top-ranking pages cover, you’ll want to include them in your content too.
Here’s how to find these subtopics:
- Enter your keyword into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Scroll down to the SERP overview
- Select three to five top-ranking articles (make sure they’re similar)
- Click Open in and choose Content gap
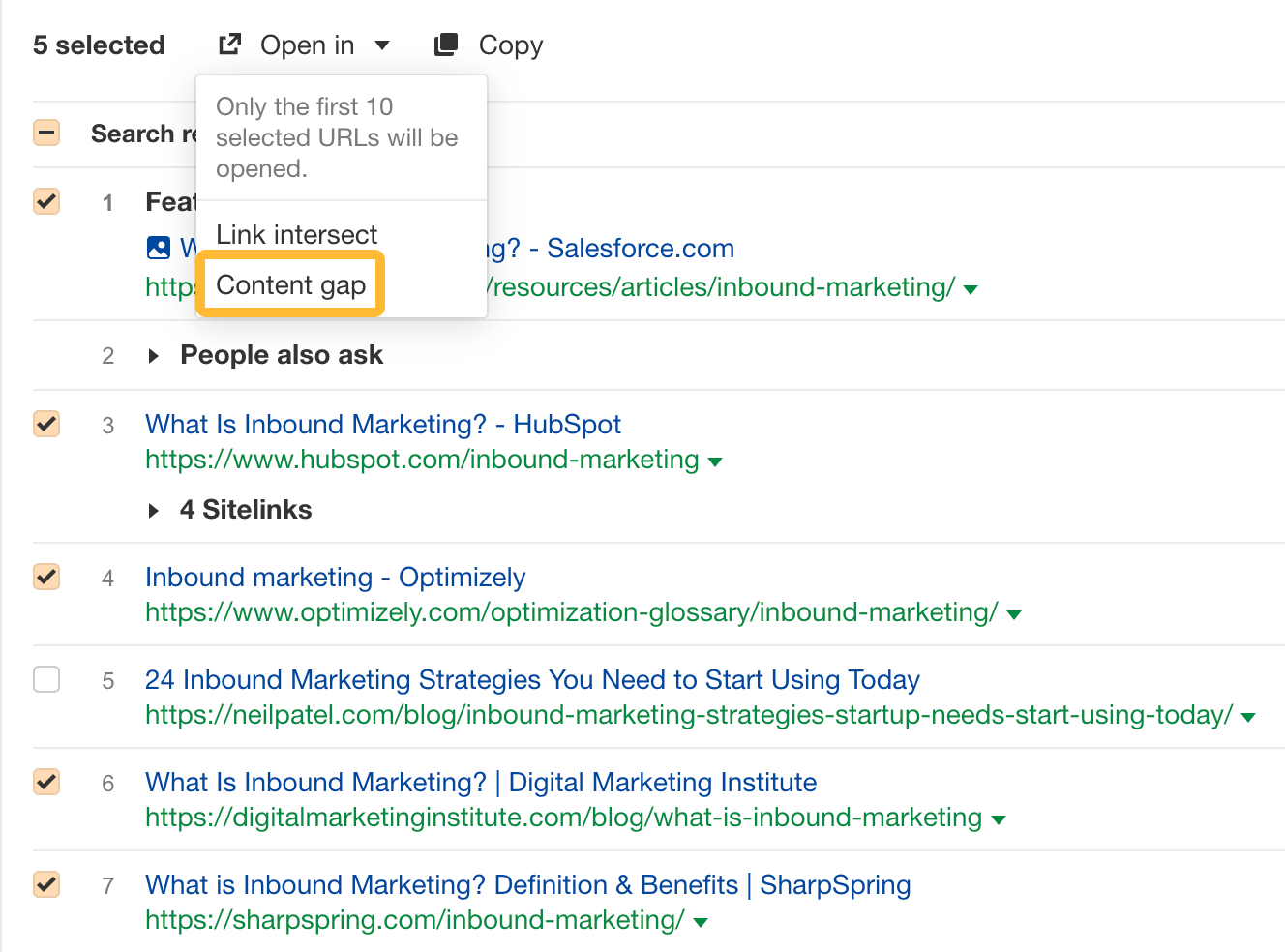
In the Content gap report, click the Intersection dropdown and choose “4, 5” to see only the most relevant subtopics:
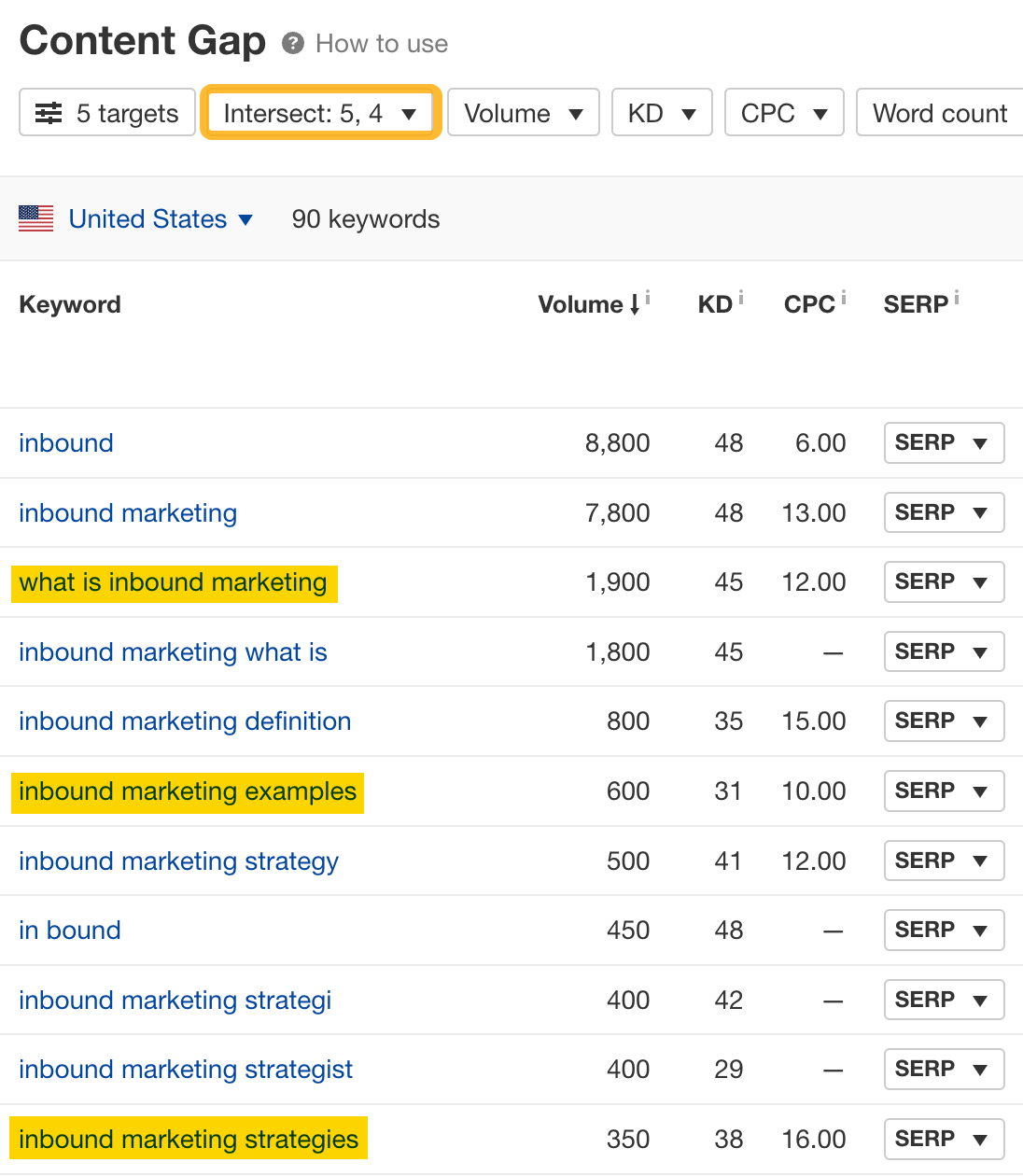
If we’re targeting the keyword “inbound marketing,” these subtopics can make great H2s:
- What is inbound marketing
- Inbound marketing strategies
- Inbound marketing examples
Create something unique and original
Google’s guide on creating helpful content suggests asking these questions:

Simply put: Google wants you to create content that’s unique and original.
How do you do that? Here are a few ways you can stand out from the rest:
- Provide original research – Consider running studies, surveys, polls, experiments, or crowdsource/interview experts.
- Give a unique perspective or opinion – This can be from you, industry experts, or someone in your organization.
- Build on what’s already out there – Imagine you’re a scientist contributing to a corpus of knowledge. Help investigate claims, expand on key ideas, or challenge existing consensus.
Ensure content is created or reviewed by someone with expertise and experience
Google also aims to reward content that demonstrates E-E-A-T:
- Experience – Firsthand or life experience in the topic.
- Expertise – High level of knowledge or skill in a particular field.
- Authoritativeness – Reputation, particularly among other experts and influencers in the industry.
- Trustworthiness – Legitimacy, transparency, and accuracy of the website and its content.
It sounds complex, but it’s what you expect good content to be. If you’re reading something, you’ll likely want it to come from someone with firsthand experience or expert knowledge. You don’t want it to be from a writer who has regurgitated what’s ranking.
Demonstrating this can be as simple as actually using a product you’re reviewing. Or having been to Milan if you’re recommending the best places to visit.
For example, most of our content is created by our marketing team, which consists of people with years of experience in the SEO industry. Like my colleague, Chris Haines, who has worked in SEO agencies for 10 years.
If you do not have the required experience or expertise, hire someone who has to create or review your content.
Make sure content is easy to read
Nobody wants to read a chunk of text. Your content should be readable for your users.
I recommend following the ASMR formula:
- Annotations – Use elements like sidenotes and blockquotes to break up the post.
- Short sentences and paragraphs – Split long sentences into shorter ones.
- Multimedia – Include videos, images, and GIFs to eliminate extra words.
- Read your copy out loud – Highlight areas where the content doesn’t flow smoothly.
3. Pay attention to on-page SEO
In Google’s own words:
Use words that people would use to look for your content, and place those words in prominent locations on the page, such as the title and main heading of a page, and other descriptive locations such as alt text and link text.
You’ve done the first part via keyword research. Now, it’s time to make doubly sure that Google can understand your content. To do this, you should:
- Include your target keyword in the title and H1 tag.
- Add concise and accurate alt text to your images.
4. Provide a good user experience
Google wants to reward pages with a good user experience. It explicitly states this in its guide on creating helpful content:
To provide a good user experience, you’ll want to:
- Use HTTPS – Encrypt your site with SSL/TLS and protect your readers’ data.
- Make sure your website is mobile-friendly – Most people search on mobile these days. Your website should work on all devices.
- Ensure your pages load fast – Slow pages are a pain. Use a tool like PageSpeed Insights to check your pages’ performance.
- Avoid intrusive interstitials – Interstitials are full-screen ads that appear before a webpage’s content is loaded. Nobody, including Google, likes them.
- Improve your Core Web Vitals (CWV) – These are speed metrics that are part of Google’s Page Experience signals used to measure user experience. They’re not make-or-break for SEO, but improving them can help with better user experience.
5. Utilize structured data
A major part of SEO is really about helping Google understand the content of your pages. You can provide explicit clues about the meaning of a page for Google by using structured data.
Structured data is a standardized way to provide information about a webpage. It conforms to a particular format, and the universally recognized format is schema markup.
For example, if I wanted to tell search engines my given name is “Si Quan,” I would have to use the givenName property and use it in its exact form in our code.

Learn more about how to implement schema markup in our guides below.
6. Build high-quality links
Links are an important Google ranking factor. But buying backlinks is against Google’s guidelines:

What should you do instead? Here are some ideas on how you can acquire backlinks the white hat way:
Guest blogging
Guest blogging is when you create content for other websites. In the process, you’ll usually be allowed to link back to your website.
Here’s how you can find potential guest blogging opportunities:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Content Explorer
- Set the dropdown to “In title”
- Enter a relevant keyword
- Set these filters:
- Language filter to English (or your target language)
- Live/broken filter to Only live
- Filter explicit results to On
- Domain Rating filter to 30–90
- Website traffic filter to >500
- Check One page per domain
- Check Exclude homepages
- Check Exclude subdomains
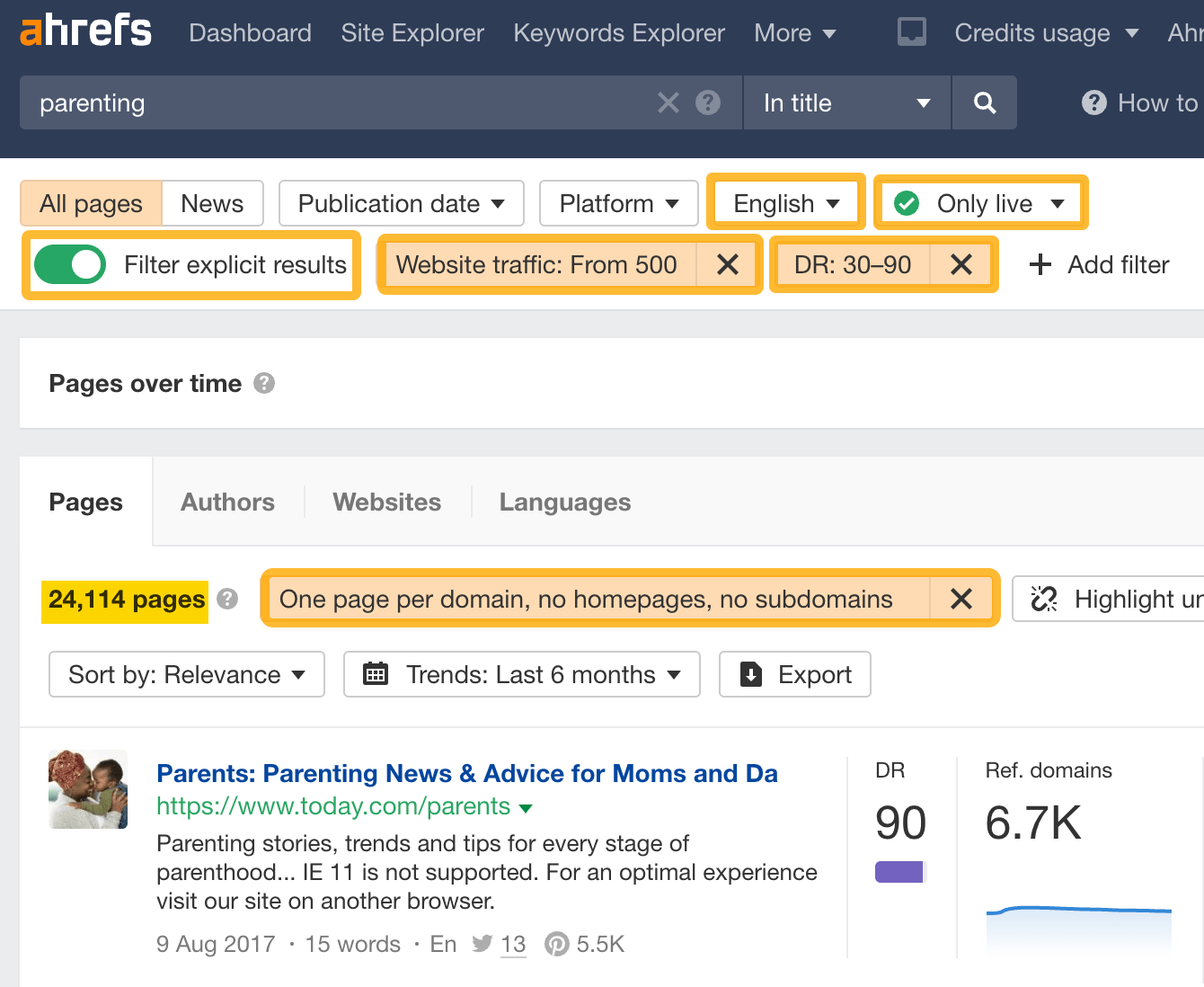
Look through the results and pick out relevant sites you could guest write for. Find the right person’s email and pitch them.
Create link bait
There are many pages you’d like links to. These are likely your “money pages,” e.g., product pages and landing pages. But nobody wants to link to them because they barely provide any value (unless they’re recommending your product).
So one way to build links to such pages is to use the Middleman Method:
- Build links to a page that attracts backlinks, i.e., link bait
- Add internal links from the link bait to your important pages
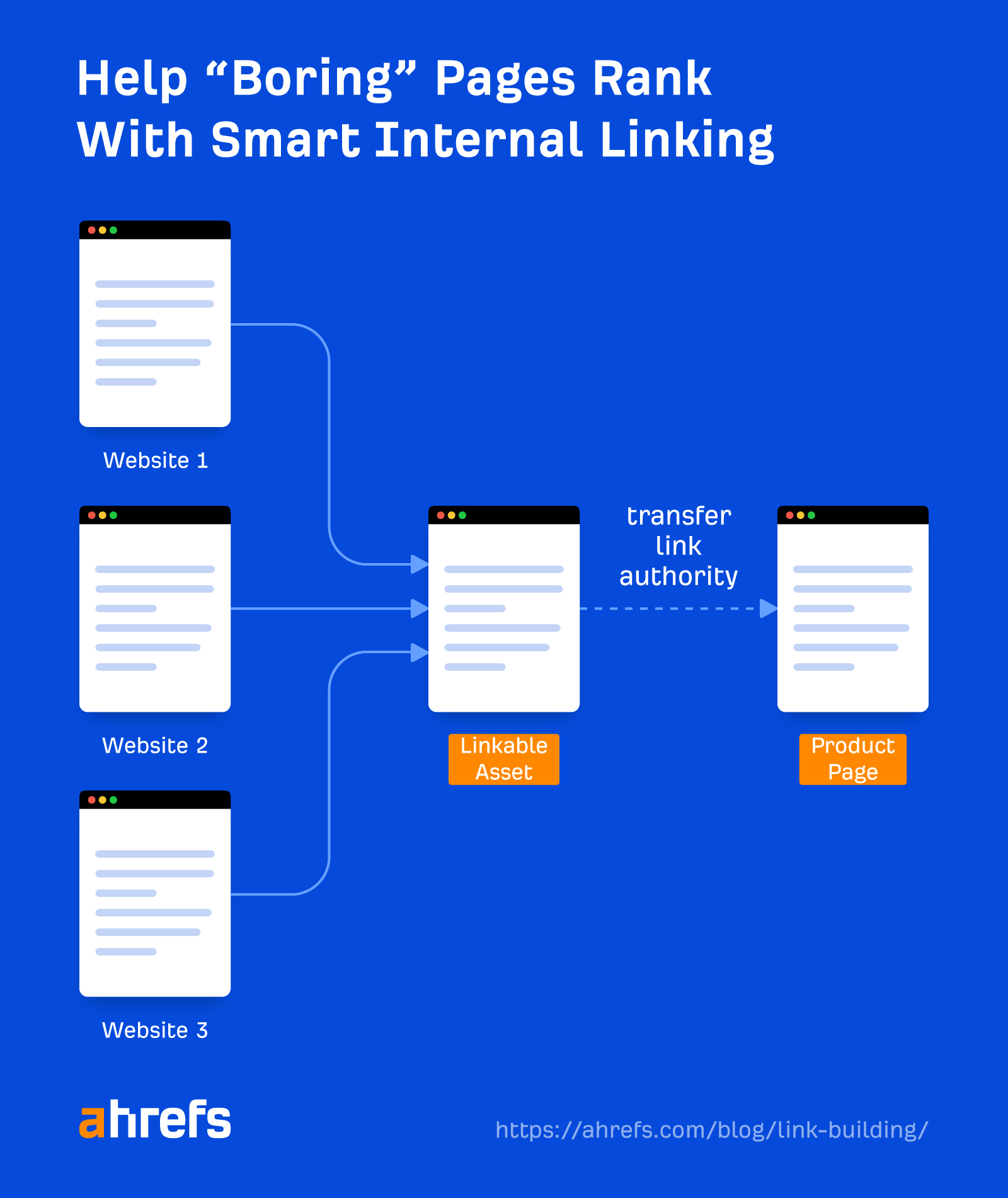
How do you find good link bait ideas? The best way is to piggyback off what’s working for your competitors:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Best by links report
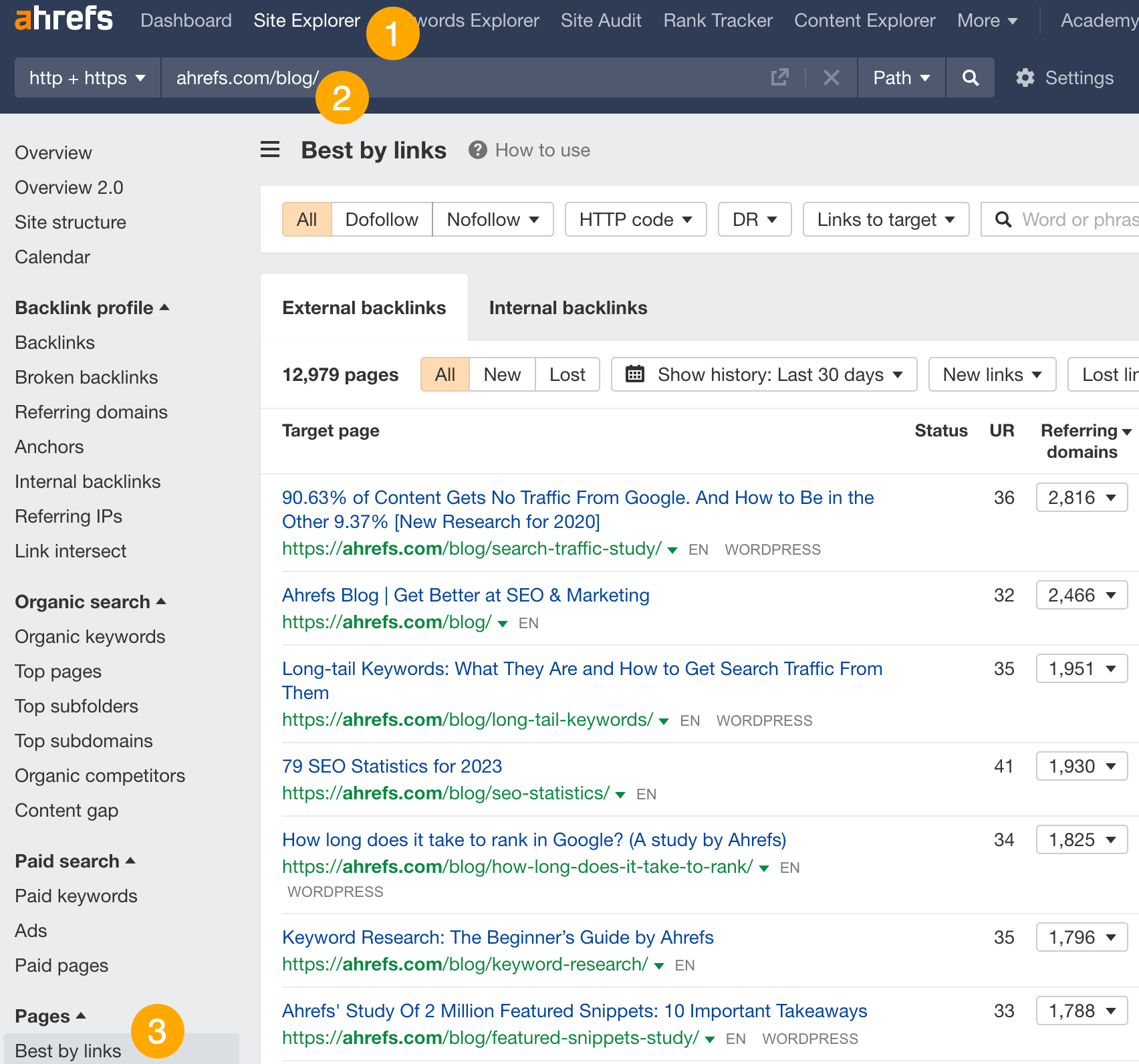
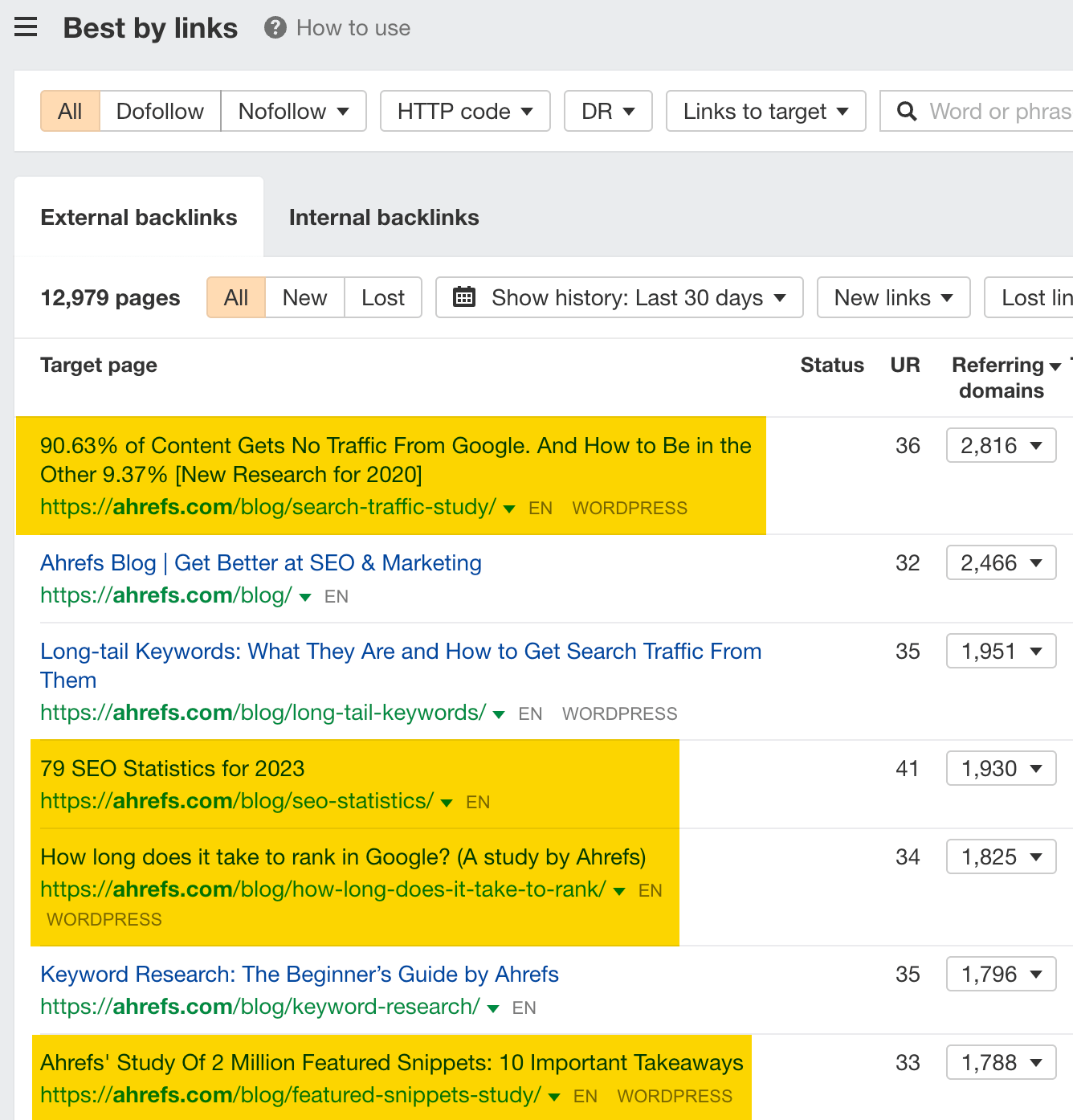
Look through the list to see what kinds of formats and topics resonate with people in your niche. For example, we can clearly see that studies and statistics are popular in the SEO space:
Use HARO
Help a Reporter Out (HARO) is a free service connecting journalists to sources and sources to journalists. Once you sign up, you’ll receive daily emails with queries from journalists of different publications.

If your response is selected, the publication might link to you.
Learn how to build links using HARO in the guide below.
Final thoughts
White hat SEO is about the right mindset: putting users first, creating useful content, and not spamming people.
Some black hat SEOs may be able to get results in the short term, but white hat SEO is essential for long-term success.
Remember, white hat SEO is a marathon, not a sprint.
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter.
Source link : Ahrefs.com
