Ranking troubles? Let’s solve them


Let’s face it. Most URLs don’t rank and will never get traffic from search. There’s nothing strange about that. Most URLs aren’t search-optimized. But many are and still don’t rank. So in this piece, we’re going to answer a question you may have asked yourself…
Why don’t I rank in Google?
The successful pages receive exponentially greater visibility and traffic than those ranking lower, making it a worthwhile pursuit.
We won’t delve into technical SEO concerns (load speed, mobile friendliness, duplicates of meta tags, sitemap, or HTTP issues ); my team and I have observed that most web pages do not have these issues. This article will highlight mostly content aspects.
Delaying the resolution of ranking issues can lead to substantial decreases in visibility, traffic, and conversions. So, let’s discover common SEO pitfalls and the path to Google’s first page right now!
Understanding SEO Success
SEO can be compared to rowing a boat; you can buy traffic (put gas in the tank) or earn it through email and social media (rolling the boat).
Image source: Orbit Media
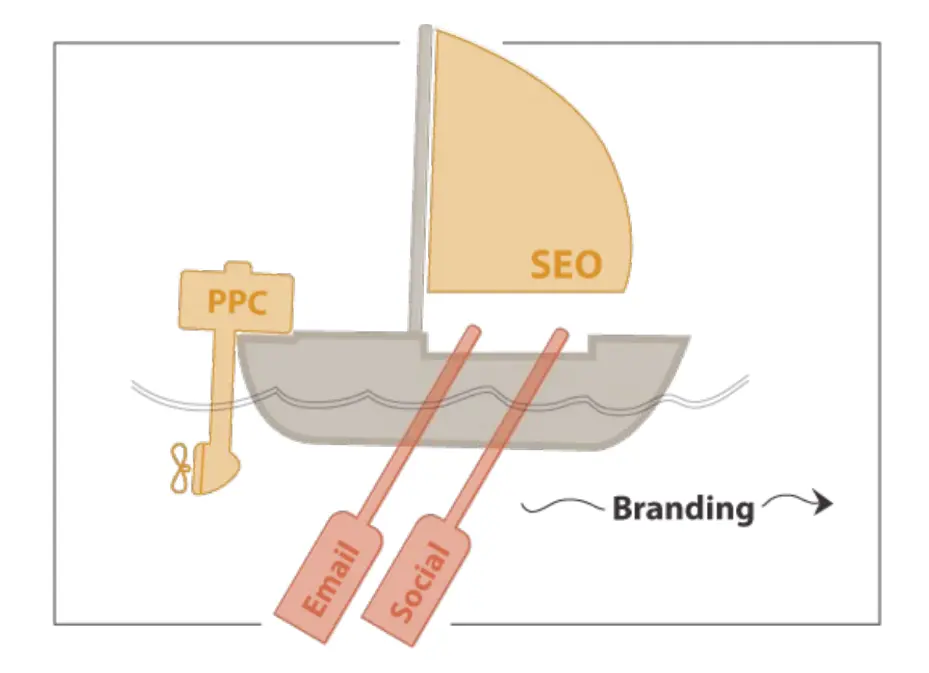
In other words, when it works, the search can become a passive source of traffic, attracting huge numbers of visitors over time without lots of ongoing, incremental effort. Every page has the chance to catch traffic, like a sail catches wind.
However, perfectly optimized SEO pages can provide a continuous stream of passive traffic, limited only by the number of phrases you can target.
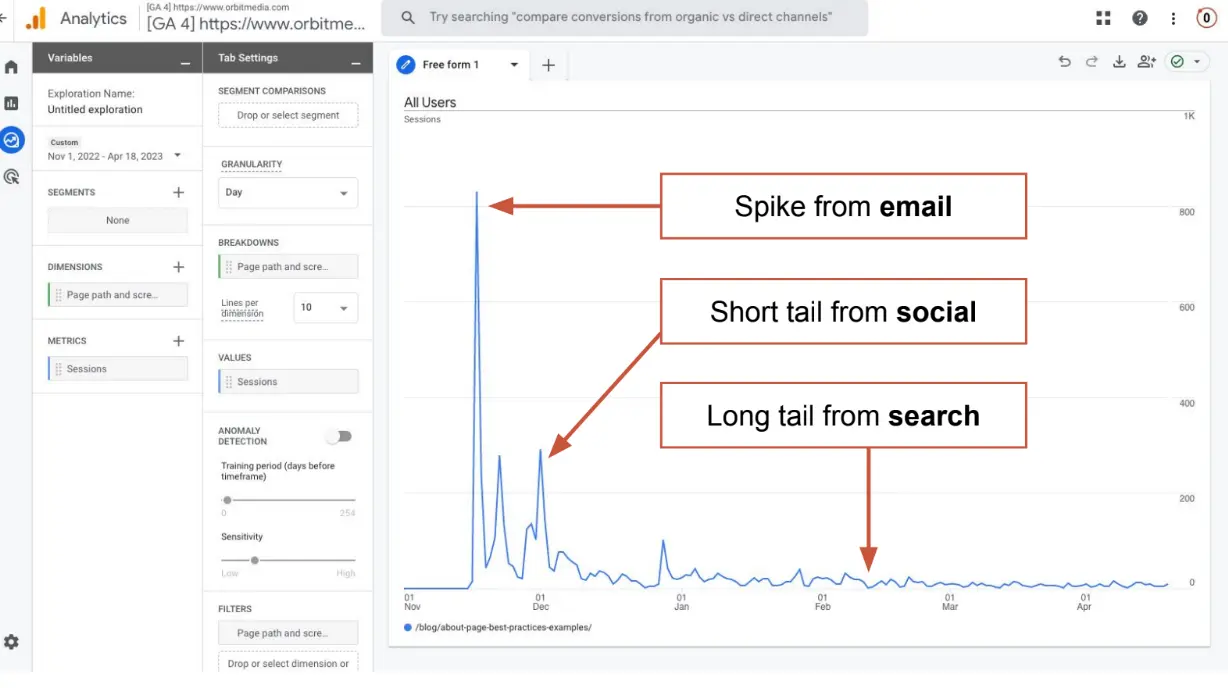
From this metaphor, we can assume that SEO success is about creating pages optimized for specific keywords (it’s because pages, not entire websites, rank on search engines). However, publishing more search-optimized pages increases overall website traffic and aligns brand awareness.
To achieve SEO success, several fundamental rules and principles must be considered. These guidelines form the cornerstone of effective strategies:
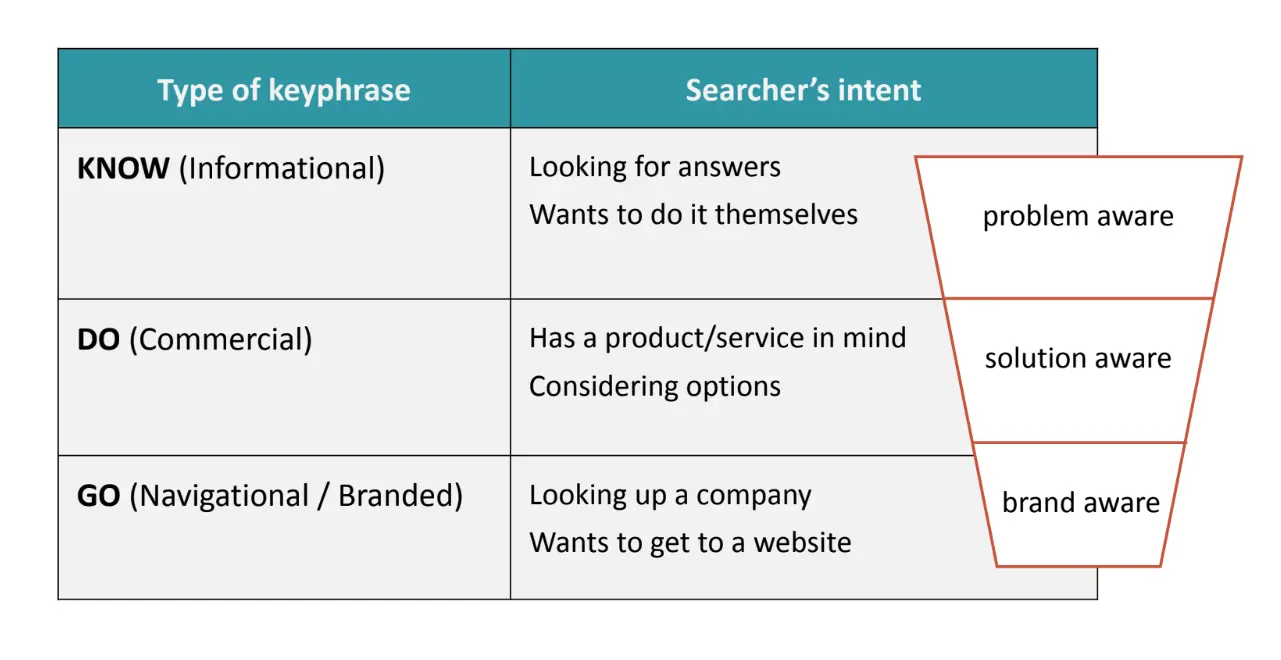
2.Site mapping and targeted page creation. The homepage often targets navigational intent queries, and it’s the page with the most authority, capable of targeting competitive commercial intent keywords. Deeper internal pages can target various phrases.
3.SEO and UX. SEO and user experience considerations are separate. Not everything you target needs to appear in the main navigation, and you can create off-nav pages for targeting more phrases without cluttering menus.
Understanding the intent behind a particular topic helps shape your content strategy and determines if it’s worth creating content about it.
5.URL’s merits evaluation. Page-level search ranking factors are more important and heavily weighted than site-level ranking metrics.
6.Authority and relevance. Links represent authority, and the quality of links matters more than quantity. A link from an authoritative site is exponentially more valuable.
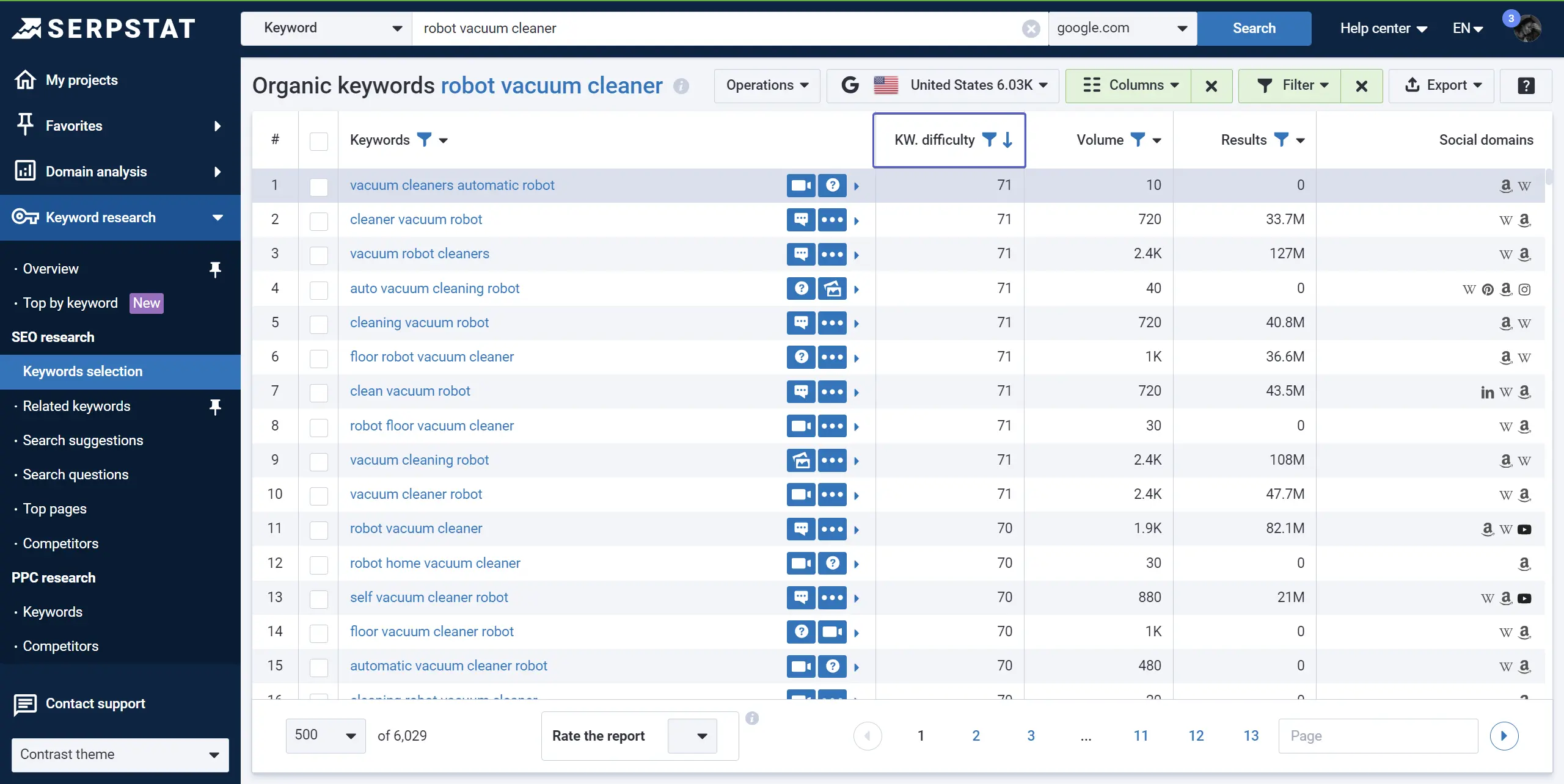
7.Keyword difficulty (KD). Evaluating keyword difficulty compared to a website’s ranking helps determine if a phrase is too competitive.
Serpstat, KD in the Keyword selection report
By keeping these basic rules in mind and adapting them to the specific needs of your site, you can navigate the complex world of SEO with a clearer understanding of how to join best ranked websites.
The 5 Reasons Why Your Page Won’t Rank Top 10
Without understanding the reasons, you’ll be uncertain about the suitable course of action, potentially leading to unhelpful steps. Let’s cover the most common causes.
1. You’re not targeting the keyphrase
A keyword-focused page is essential for SEO. Additionally, keyword-based URLs are crucial for making your webpage content understandable to search engines. If your website lacks such pages on a particular topic, it might not rank well in SERP.
Each keyword represents a competitive arena, while every page holds the potential to become a competitor; that’s why it is worth a thorough analysis.
How to fix it?
You can secure higher positions by crafting content that answers questions related to the keyword or provides information on topics relevant to your business. Ensure your search-optimized page is tailored to the target keyword, effectively conveying relevance.
A proficiently optimized website boasts an array of pages, each meticulously crafted to cater to various keywords. The site’s structure and navigation should be designed, focusing on these keywords.
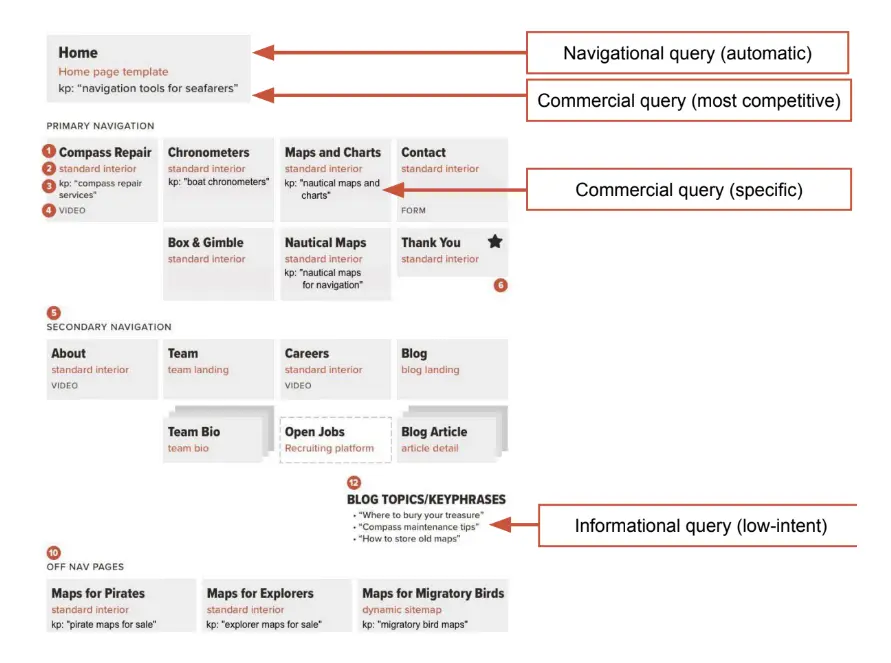
To check the keywords of ranking site with a tree-view structure, you can try the self-titled Serpstat domain analysis report:
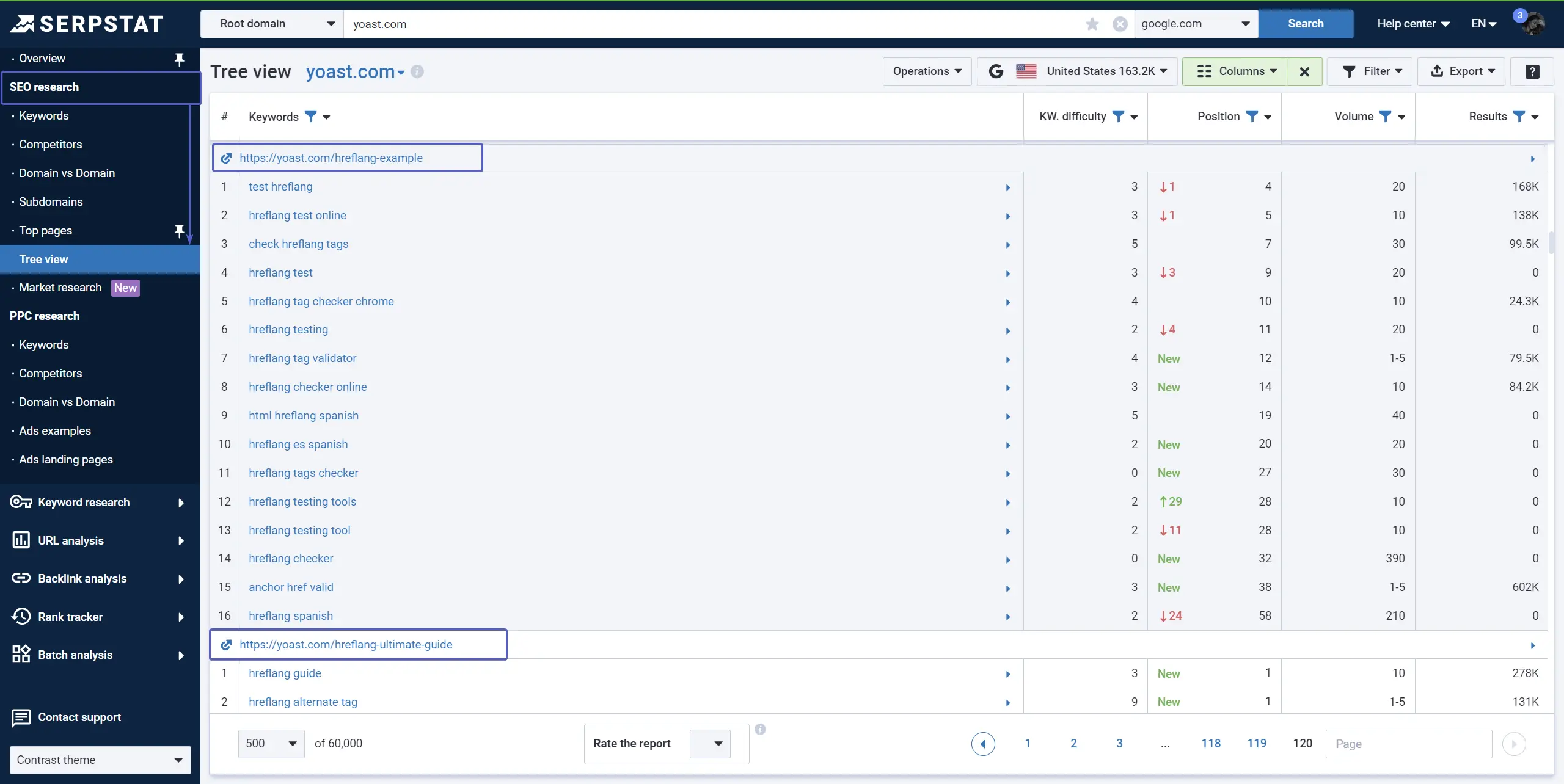
Unlock the power of multitasking tools and improve your chances of ranking higher in SERP.
Try Serpstat for free with a 7-day trial and ensure its credibility!
Start Exploring
2. The keyword is too competitive
You’re not alone in optimizing your website to secure a spot on Google’s first page. Every one of your competitors is actively engaged in similar efforts. When a keyword is highly competitive, it means many websites are trying to rank for it. This competition makes it harder for your webpage to rank well, especially if those competing websites have higher authority or have been established longer.
Use the Keyword Difficulty (KD) indicator to assess the risks during your keyword research. Please note that most services calculate the KD based on how many backlinks the Google top 10 ranking websites have. Keyword difficulty relies on the number of referring domains and the authority rating of competitor backlinks.
The Serpstat KD algorithm relies on a formula encompassing three key indicators:
- The number of backlinks
- Frequency of a specific URL appearing at the top of SERPs for various keywords
- The classification of keywords as “commercial” or “non-commercial.”
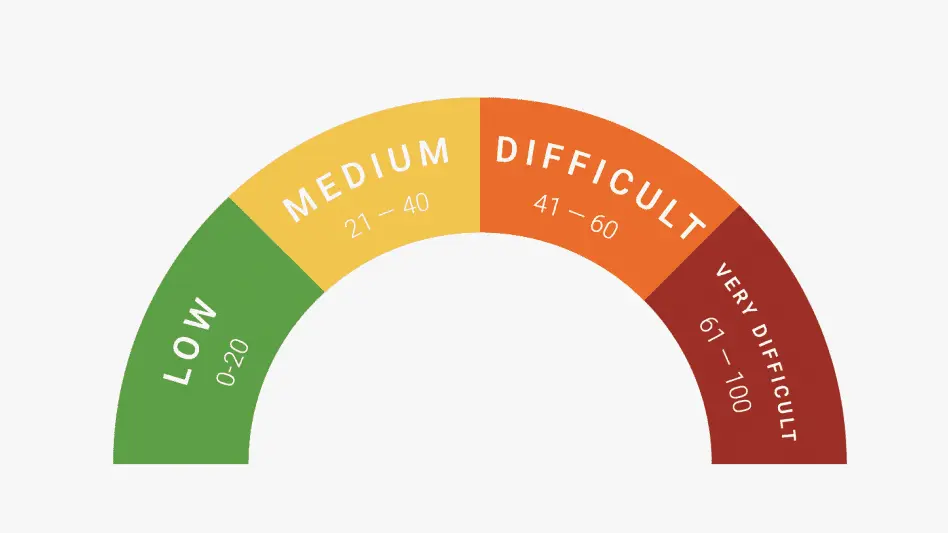
The KD score ranges from 0 to 100, where:
0–20 indicates that the keyword is easy to rank for
21–40 shows medium difficulty
41–60 means that the keyword is challenging to rank for
61–100 indicates that the keyword is tough to rank for.
How to fix it?
Go back to keyword research and opt for realistic queries. Consider targeting less competitive or long-tail keywords that are more specific and relevant to your content. Instead of wasting time tracking down highly competitive keywords that are difficult to rank for, you can focus on keywords guaranteed to bring a lot of traffic.
SEOs consistently assess the competition before honing in on a specific keyword. They evaluate the keyword’s difficulty against the authority of their page or, if the page doesn’t exist yet, the domain’s authority.
In the long run, always seize opportunities to acquire backlinks to improve your authoritativeness. Authority is determined by the quality of your content and the number and quality of backlinks pointing to your website.
3. The page isn’t that relevant
Relevance is a critical factor in search engine rankings. If a page isn’t relevant to the keywords it’s targeting, compared to competing pages, it may rank poorly for several reasons:
1.User experience. Search engines aim to provide users with the most relevant results for their queries. If a page isn’t relevant to a user’s search, it may lead to a poor user experience, causing users to quickly leave the site (a high bounce rate), which search engines can interpret as a signal of low relevance.

3.Content quality. The dedicated SEO professional doesn’t expect a first-page ranking on Google search without creating exceptional content. If a page’s content is thin or lacks depth, it may be seen as less relevant. Besides, failing to address user queries with comprehensive content on your website can lead to the risk of a Google thin content penalty. In essence, if the content you’re creating barely covers the topic, you could be dealing with an issue of thin content.
How to fix it?
Improving relevance could involve:
- Refining your keyword strategy.
- Enhancing your content quality.
- Working on getting high-quality backlinks.
- Ensuring that your page aligns with user intent.
Incorporate the primary keyword into the title, headers, URL, and body text. Include semantically related phrases in the body text, addressing relevant subtopics and questions to cover the subject matter comprehensively. This is the key to semantic SEO, which aligns with how Google understands quality.
While word count doesn’t directly affect site ranking on Google, longer, more comprehensive content often better satisfies users’ information needs.Try to assist Google in understanding the central focus of your page, improving its chances of being discovered by users.
4. Visitors don’t like your page
Your website rankings are being negatively impacted by unfavorable “user interaction signals”:
- Dwell time — the duration visitors spend on your page after arriving from search results. A high dwell time, often called “the long click,” suggests that the page offers valuable content. Conversely, a low dwell time, known as “the short click,” signals Google that the page doesn’t meet users’ expectations.
- Pogosticking — Closely related to dwell time, this is the phenomenon of users quickly returning to the search results after clicking on a page.
- User engagement — interaction with your page, such scrolling, watching videos or clicking into deeper content. Engaged visitors are less likely to jump back to the SERP quickly and, therefore, less likely to suggest to Google that the page was unsatisfying.
How to fix it?
To enhance user satisfaction, focus on improving the user experience. This involves optimizing site speed, creating an intuitive navigation structure, delivering pertinent, structured content, etc.
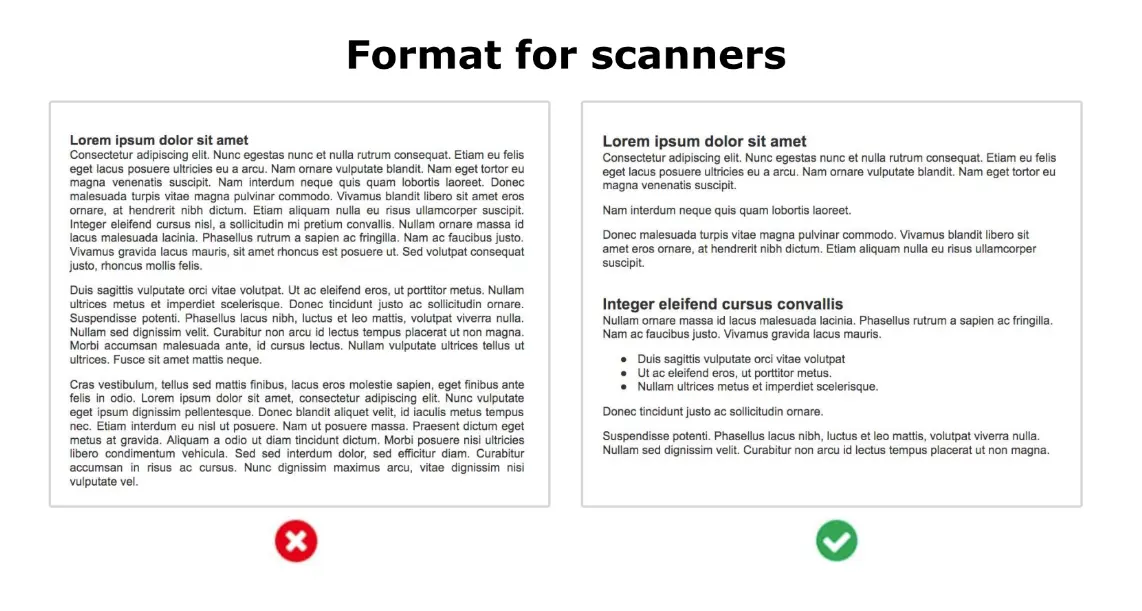
Applying these formatting and visual elements to your content can significantly improve dwell time, keeping your readers engaged and indirectly benefiting your search rankings.
5. You only wrote it once
Search engines aim to provide users with the most accurate and up-to-**** information. If your content remains static, it may be outranked by newer content that covers the same topic. So, in case you’re targeting competitive keywords, your content needs to be regularly updated to rank well.
How to fix it?
Regularly update your content with new information, insights, or resources to improve your rankings. Revamping an existing page that was close to achieving high rankings is among the most reliable strategies in the field of search marketing. The concept is straightforward: target not just a keyword you prefer but one that’s already gaining traction in search results. In other words, let Google Search Console guide your keyword research. However, it’s vital to maintain the existing URL.
The Mindset of an SEO for High-Ranking Websites
The SEO professional’s mindset is strategically enhancing search engine visibility for the highest-ranking sites. It encompasses using keywords effectively, optimizing user engagement, maintaining content freshness, earning quality backlinks, and consistently analyzing and adapting strategies. This long-term approach demands patience, persistence, and adaptability to achieve improved rankings over time.
If you don’t see yourself in search results, ask yourself a few key questions:
- Do I have a page that is totally focused on that topic?
- Is that a phrase that I have a chance of ranking for based on the Keyword Difficulty?
- Is the page detailed, comprehensive, visual, supported with evidence, and otherwise one of the 10 best pages on the internet for the topic?
- Has the page been updated to better indicate its relevance based on its search performance?
If you haven’t answered yes to each of those questions, you have no right to rank.
While achieving a top ranking for every industry-specific search term may not be feasible, securing high rankings for crucial search terms on key pages can significantly contribute to the organic growth of your business from within.
But ranking isn’t traffic… Your perspective should extend beyond rankings, which, in isolation, do not directly influence the tangible bottom-line business results. Revenue generation occurs only when these rankings result in clicks, engaged visitors, and leads.
The opinion of the guest post authors may not coincide with the opinion of the Serpstat editorial staff and specialists.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter to tell us
Discover More SEO Tools
Backlink Cheсker
Backlinks checking for any site. Increase the power of your backlink profile
API for SEO
Search big data and get results using SEO API
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community 🙂
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.
